JAJSVM2 November 2024 TDP142-Q1
ADVANCE INFORMATION
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- Parameter Measurement Information
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
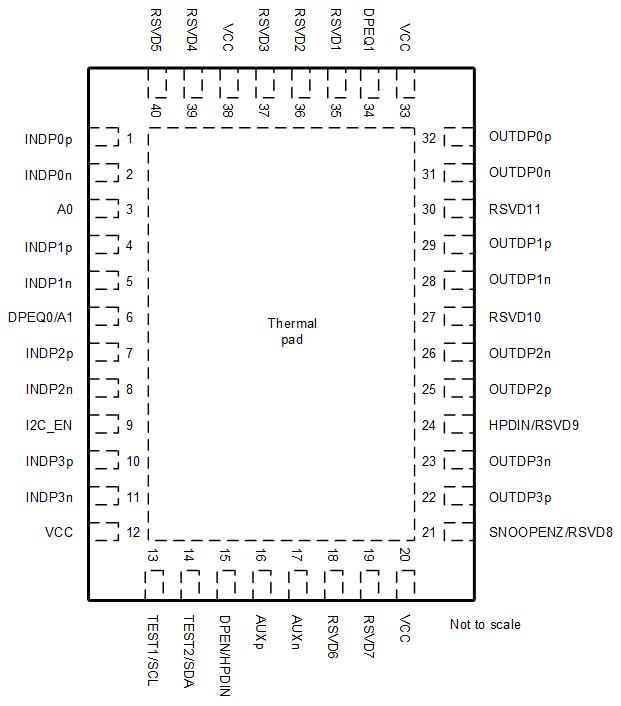 Figure 4-1 RGF Package40-Pin (VQFN)Top View
Figure 4-1 RGF Package40-Pin (VQFN)Top ViewTable 4-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| INDP0p | 1 | I | DP Differential positive input for DisplayPort Lane 0. |
| INDP0n | 2 | I | DP Differential negative input for DisplayPort Lane 0. |
| A0 | 3 | 4 Level I | When I2C_EN = 0, leave the pin unconnected. When I2C_EN is not ‘0’, this pin also sets the TDP142-Q1 I2C address. See Table 6-4. If I2C_EN = “F”, then this pin must be set to “F” or “0”. |
| INDP1p | 4 | Diff I | DP Differential positive input for DisplayPort Lane 1. |
| INDP1n | 5 | Diff I | DP Differential negative input for DisplayPort Lane 1. |
| DPEQ0/A1 | 6 | 4 Level I | DisplayPort Receiver EQ control. This along with DPEQ1 selects the DisplayPort receiver equalization gain. Refer to Table 6-2 for equalization settings. When I2C_EN is not ‘0’, this pin also sets the TDP142-Q1 I2C address. See Table 6-4. |
| INDP2p | 7 | Diff I | DP Differential positive input for DisplayPort Lane 2. |
| INDP2n | 8 | Diff I | DP Differential negative input for DisplayPort Lane 2. |
| I2C_EN | 9 | 4 Level I | I2C Programming Mode or GPIO Programming Select. I2C is only disabled when this pin is ‘0". 0 = GPIO mode (I2C disabled). R = TI Test Mode (I2C enabled at 3.3V). F = I2C enabled at 1.8V when RSVD11 = "0" and RSVD10 = "0". Otherwise, GPIO mode (I2C disabled) 1 = I2C enabled at 3.3 V. |
| INDP3p | 10 | Diff I | DP Differential positive input for DisplayPort Lane 3. |
| INDP3n | 11 | Diff I | DP Differential negative input for DisplayPort Lane 3. |
| VCC | 12, 20, 33, 38 | P | 3.3V Power Supply. |
| TEST1/SCL | 13 | 2 Level I | When I2C_EN=’0’, pull down with 10k or directly connect to ground. Otherwise this pin is I2C clock. When used for I2C clock, pull up this pin to the VCC I2C supply of the I2C controller. |
| TEST2/SDA | 14 | 2 Level I | When I2C_EN=’0’ , pull down with 10k or directly connect to ground. Otherwise this pin is I2C data. When used for I2C data, pull up this pin to the VCC I2C supply of the I2C controller. |
| DPEN/HPDIN | 15 | 2 Level I (Failsafe) (PD) | DP Enable Pin. When I2C_EN = ‘0’, this pin enables or disables the DisplayPort functionality. Otherwise, when I2C_EN is not "0", DisplayPort functionality is enabled and disabled through I2C registers. L = DisplayPort Disabled. (Pull down with 10k resistor) H = DisplayPort Enabled. (Pull up with 10k resistor) When I2C_EN is not "0" this pin is an input for Hot Plug Detect (HPD) received from DisplayPort sink. When this HPDIN is low for greater than 2ms, all DisplayPort lanes are disabled. |
| AUXp | 16 | I/O, CMOS | This pin along with AUXN is used by the TDP142-Q1 for AUX snooping. See the Application and Implementation section for more detail. |
| AUXn | 17 | I/O, CMOS | This pin along with AUXP is used by the TDP142-Q1 for AUX snooping. See the Application and Implementation section for more detail. |
| RSVD6 | 18 | I/O, CMOS | Reserved.(1) |
| RSVD7 | 19 | I/O, CMOS | Reserved.(1) |
| SNOOPENZ/RSVD8 | 21(2) | I/O (PD) | When I2C_EN ! = 0, this pin is reserved. When I2C_EN = 0 , this pin is SNOOPENZ (L = AUX snoop enabled and H = AUX snoop disabled with all lanes active). |
| OUTDP3p | 22 | Diff O | DP Differential positive output for DisplayPort Lane 3. |
| OUTDP3n | 23 | Diff O | DP Differential negative output for DisplayPort Lane 3. |
| HPDIN/RSVD9 | 24(2) | I/O (PD) | When I2C_EN ! = 0, this pin is reserved. When I2C_EN = 0, this pin is an input for Hot Plug Detect received from DisplayPort sink. When HPDIN is low for greater than 2ms, all DisplayPort lanes are disabled. |
| OUTDP2p | 25 | Diff O | DP Differential positive output for DisplayPort Lane 2. |
| OUTDP2n | 26 | Diff O | DP Differential negative output for DisplayPort Lane 2. |
| RSVD10 | 27 | I | Reserved. Connect to GND when 1.8V I2C is used, otherwise leave pin floating. |
| OUTDP1n | 28 | Diff O | DP Differential negative output for DisplayPort Lane 1. |
| OUTDP1p | 29 | Diff O | DP Differential positive output for DisplayPort Lane 1. |
| RSVD11 | 30 | I | Reserved. Connect to GND when 1.8V I2C is used, otherwise leave pin floating. |
| OUTDP0n | 31 | Diff O | DP Differential negative output for DisplayPort Lane 0. |
| OUTDP0p | 32 | Diff O | DP Differential positive output for DisplayPort Lane 0. |
| DPEQ1 | 34 | 4 Level I | DisplayPort Receiver EQ control. This along with DPEQ0 selects the DisplayPort receiver equalization gain. Refer to Table 6-2 for equalization settings. |
| RSVD1 | 35 | I | Reserved.(1) |
| RSVD2 | 36 | O | Reserved.(1) |
| RSVD3 | 37 | O | Reserved.(1) |
| RSVD4 | 39 | I | Reserved.(1) |
| RSVD5 | 40 | I | Reserved.(1) |
(1) Leave unconnected on PCB.
(2) Not a fail-safe I/O. Actively driving pin high while VCC is removed results in leakage voltage on VCC pins.