JAJU510H March 2018 – December 2022
- 概要
- リソース
- 特長
- アプリケーション
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 3.1 Required Hardware and Software
- 3.2 Testing and Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Trademarks
- 6About the Authors
- 7Revision History
2.3.1.3 Inductor Design
With the filter being one of the major contributors to the size and weight of a solar inverter, ensure that the individual components are correctly sized. As seen in Section 2.3.1.2, the increase in the system switching speed provided by the SiC MOSFETs has already resulted in an inverter inductor that is of much smaller value than normal.
In Equation 49, the switching frequency is in the denominator. Any increase in switch frequency, all else being the same, results in an inverse relationship. Looking at the simplified equation for the inductance of a given inductor, there is a positive relationship between inductance and inductor cross sectional area by a number of turns. Both have a direct effect on the size of the component.
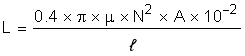
where
- µ is core permeability
- N is the number of turns
- A is the cross sectional area
- l is the mean magnetic path length
The starting point for evaluating a solution to the variables in Equation 13 is to determine a valid core material and subsequent permeability. The core manufacturer typically has a range of suitable materials with selection criteria based on the design inductance and the inductor current. For this design, the nominal inductor current (with an overload factor of 105%) is defined as:


Using a selection guide for a toroidal inductor core manufacturer, at 347 µH, the core permeability comes to 26 µH. The core also provides a value for the inductance factor, AL, which enables a quick path to selecting the number of turns.
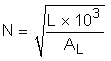

One last piece of information required for the inductor design is the winding wire size. This size is easily computed using the nominal inductor current rating. Using copper, with a current carrying density of 4 A/mm, this inductor requires a cross sectional area of:
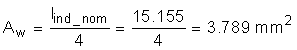
This area is an equivalent to American Wire Gauge #12, which has a cross sectional area of 3.309 mm2. This slight derating is acceptable because the switching current allows a smaller gauge to be used when compared to a static DC bias current. For this inductor, flat winding is used to increase surface area for cooling and decrease potential skin depth effects.
Using the overall design of the core, with the flat 12 AWG winding, the total length of each winding is determined to be 64.87 mm. At this point, the DC resistance of the inductor can be calculated using Pouillet's Law:
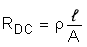

To determine the AC resistance, first calculate the skin depth at the inverter switching frequency:


RAC is then determined by RDC, Sd, and Ss, which is the equivalent square conductor width.
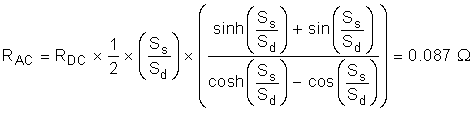
This determination of RAC helps determine total system losses.