JAJU808 July 2021
- 概要
- リソース
- 特長
- アプリケーション
- 5
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2
Design Considerations
- 2.2.1 System Control and Processing
- 2.2.2 Analog Front End
- 2.2.3 Input Voltage Monitoring: 5 V, 20 V, 40 V, and ±5 V
- 2.2.4 Bidirectional Current Sense: ±2 A
- 2.2.5 Unipolar Current Sense: 0.25 A to 1 A
- 2.2.6 TMP461-SP: Local and Remote Temperature Sensing
- 2.2.7 NTC Thermistor Temperature Sensing
- 2.2.8 Adjustable Voltage Source
- 2.2.9 Fixed Output Current Source
- 2.2.10 Adjustable 4-mA Current Source
- 2.2.11 Power Tree and Power Sequencing
- 2.3 Highlighted Products
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5About the Author
3.2.1 Voltage Monitor Test Setup
Figure 3-2 illustrates the voltage monitor test setup.
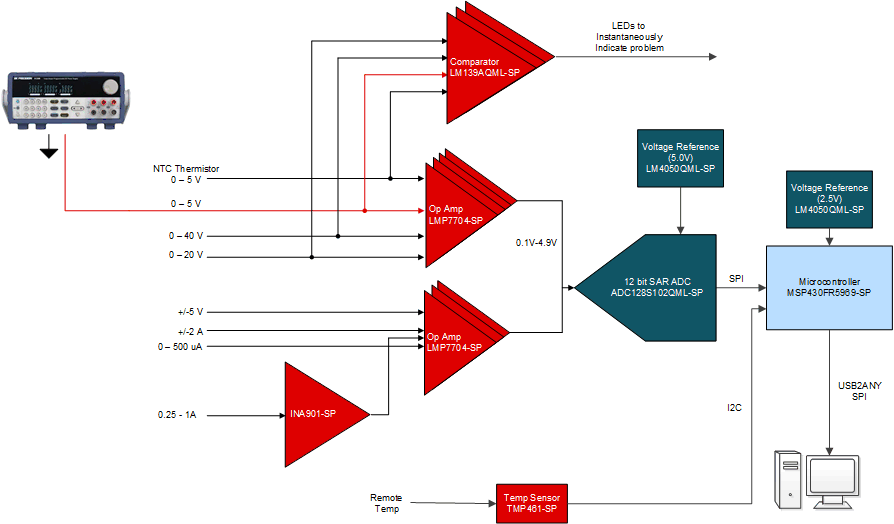 Figure 3-2 Voltage Monitor Test
Setup
Figure 3-2 Voltage Monitor Test
SetupTo test the voltage monitoring circuits, a power supply is required for the testing. For each of the voltage rails, tie the positive output rail of the power supply to the input of the terminal block for the ±5-V, 5-V, 20-V, and 40-V rails. Two tests are performed for each of the voltage rails: Noise floor and Linearity. All tests were done at an ambient temperature of 25°C.
The following list provides the test procedure for Noise floor:
- Short the voltage input on the terminal block, to ground.
- Open Code Composer Studio (CCS) to run the MSP430 software.
- Configure the MSP430 software for either internal or external ADC, and set the desired ADC channel.
- Capture and plot 1000 plots by using memory export and Microsoft Excel to convert the digital data to the ADC voltage reading using the ADC conversion equation.
- Calculate the actual voltage
reading by solving the linear equation Equation 6.
- Repeat for the rest of other the voltage inputs
The following list provides the test procedure for Linearity:
- Connect the power supply to the desired terminal block as shown in Figure 3-2.
- Open CCS to run the MSP430 software.
- Configure the MSP430 software for either internal or external ADC, and set the desired ADC channel.
- Capture and export 1000 measurements by using the memory export and Microsoft Excel to convert the digital data to the voltage reading using the ADC conversion equation.
- Calculate the actual voltage
reading by solving the linear equation Equation 7.
- Repeat over the rest of the voltage range.