JAJU817 May 2021
- 概要
- リソース
- 特長
- アプリケーション
- 5
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2 Highlighted Products
- 2.3 Design Considerations
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5About the Author
3.4.2 Battery Life Calculations
The following parameters affect the battery-life and power consumption for the entire system:
- Capacity rating of battery (mAH)
- Average off-state current consumption (mA)
- Off-state duration (s)
- Average on-state current consumption (mA)
- On-state duration (s)
Equation 1 describes the estimated battery life for this design:
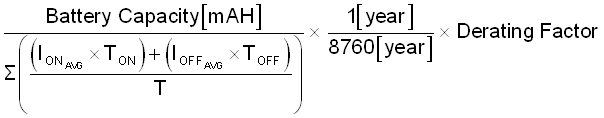
Where:
- IONAVG is the average on-state current consumption in mA
- TON is the on-state duration in seconds
- IOFFAVG is the average off-state current consumption in mA
- TOFF is the off-state duration in seconds
- Derating factor accounts for self aging of the battery - typically 80%
Substituting available battery capacity = 2100 mAH, TON = 5 s, number of activations per day = 5, IONAVG measured = 200 mA, IOFFAVG measured = 2 mA, TOFF per day = (24 × 60 × 60) - TON = 86375 s from Equation 1, the estimate for one month of battery life is shown in Equation 2.
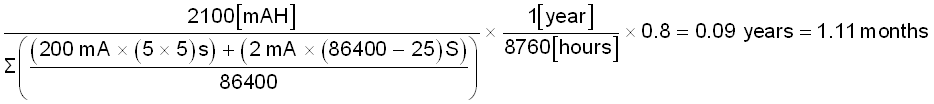
Software can be further optimized to achieve the standby current consumption of < 0.3 mA (CC3235MODS standby current of 120 μA for MCU in LPDS mode and NWP in idle mode), CC1352R standby current of 3 μA, 5 μA shutdown current for other peripherals and up to 100 μA current due to passives). This results in battery life of higher than 6 months as shown in Equation 3. Battery life of 1.5 years is achieved with 6000 mAH battery capacity for similar conditions. Table 3-2 and Table 3-3 show battery lifetime versus the number of activations for different battery capacities.
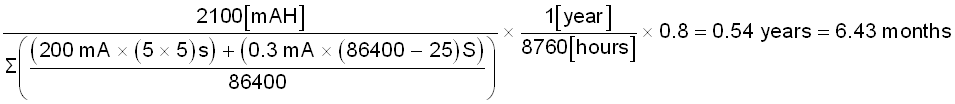
| BATTERY CAPACITY (mAH) | ACTIVE DURATION (s) | NUMBER OF ACTIVATIONS PER DAY | BATTERY LIFE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6000 | 5 | 5 | 1.5 years (18 months) |
| 6000 | 5 | 10 | 1.3 years (16 months) |
| 6000 | 5 | 15 | 1.1 years (14 months) |
| 6000 | 5 | 20 | 1 year (12 months) |
| 6000 | 5 | 25 | 0.9 year (11 months) |
| 6000 | 5 | 30 | 0.8 year (10 months) |
| 6000 | 5 | 35 | 0.7 year (9 months) |
| BATTERY CAPACITY (mAH) | ACTIVE DURATION (s) | NUMBER OF ACTIVATIONS PER DAY | BATTERY LIFE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2100 | 5 | 5 | 6.4 months |
| 2100 | 5 | 10 | 5.5 months |
| 2100 | 5 | 15 | 5 months |
| 2100 | 5 | 20 | 4.3 months |
| 2100 | 5 | 25 | 4 months |
| 2100 | 5 | 30 | 3.5 months |
| 2100 | 5 | 35 | 3.2 months |
To optimize the system for even longer battery life, optimize the following factors:
- Longer TOFF for each device
- Shorter TON for each device
- Lower ION and IOFF for each device
- Lessen the number-of-activations per day