at TA = 25°C, VDD = 3.3V, FSR =
±2.048V, DR = 8SPS (unless otherwise noted)
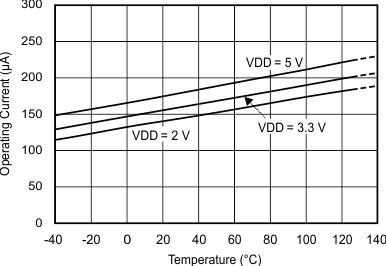 Figure 5-2 Operating Current vs Temperature
Figure 5-2 Operating Current vs Temperature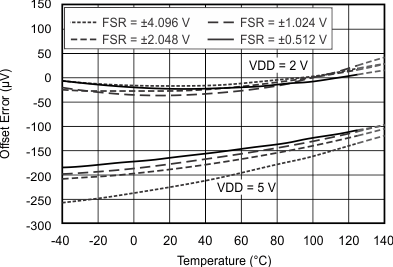 Figure 5-4 Single-Ended Offset Error vs Temperature
Figure 5-4 Single-Ended Offset Error vs Temperature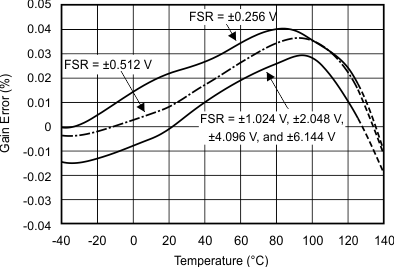 Figure 5-6 Gain Error vs Temperature
Figure 5-6 Gain Error vs Temperature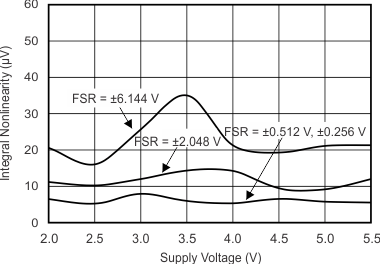 Figure 5-8 INL vs Supply Voltage
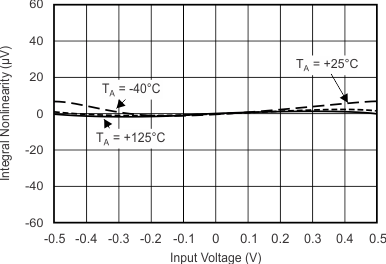
Figure 5-8 INL vs Supply Voltage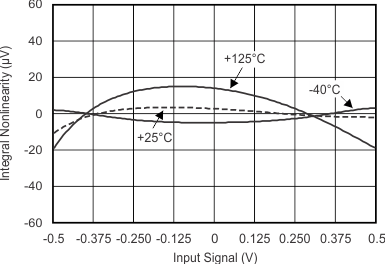
| VDD = 3.3V, FSR = ±0.512V, DR = 8SPS, best
fit |
| VDD = 5V, FSR = ±0.512V, DR = 8SPS, best
fit |
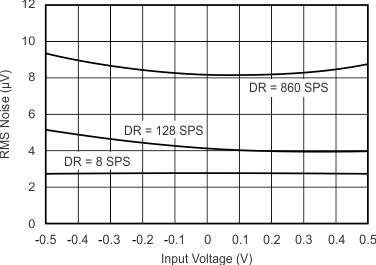 Figure 5-14 Noise vs Input Signal
Figure 5-14 Noise vs Input Signal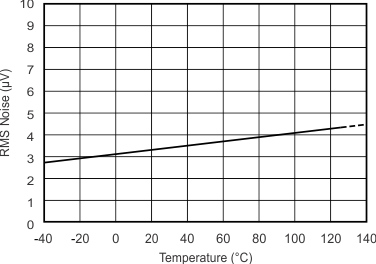 Figure 5-16 Noise vs Temperature
Figure 5-16 Noise vs Temperature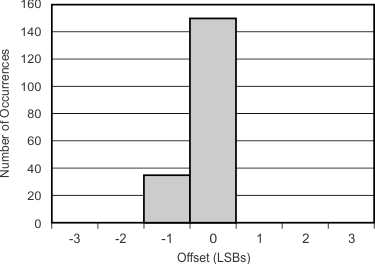 Figure 5-18 Offset Histogram
Figure 5-18 Offset Histogram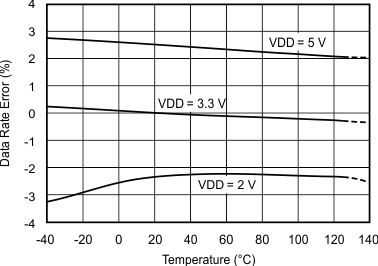 Figure 5-20 Data Rate vs Temperature
Figure 5-20 Data Rate vs Temperature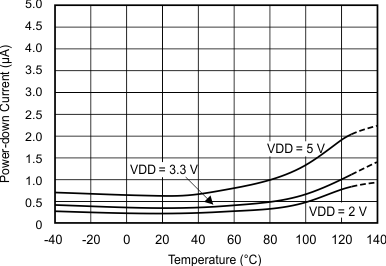 Figure 5-3 Power-Down Current vs Temperature
Figure 5-3 Power-Down Current vs Temperature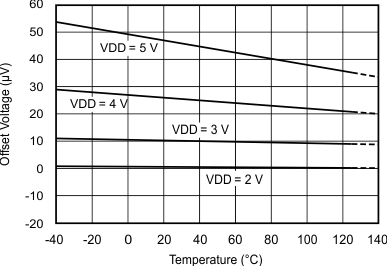 Figure 5-5 Differential Offset Error vs Temperature
Figure 5-5 Differential Offset Error vs Temperature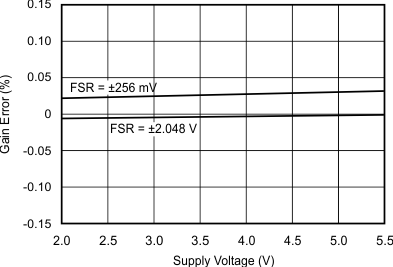 Figure 5-7 Gain Error vs Supply Voltage
Figure 5-7 Gain Error vs Supply Voltage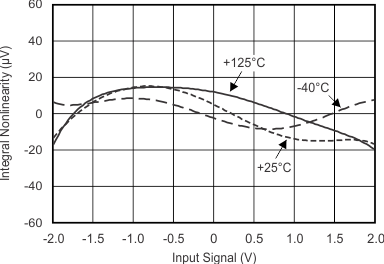
| VDD = 3.3V, FSR = ±2.048V, DR = 8SPS, best
fit |
| VDD = 5V, FSR = ±2.048V, DR = 8SPS, best
fit |
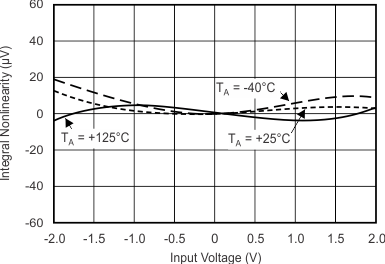
 Figure 5-13 INL vs Temperature
Figure 5-13 INL vs Temperature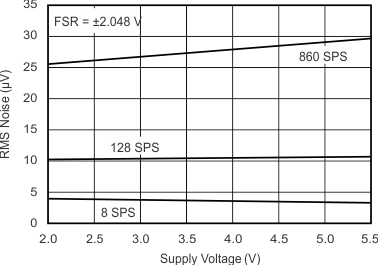 Figure 5-15 Noise vs Supply Voltage
Figure 5-15 Noise vs Supply Voltage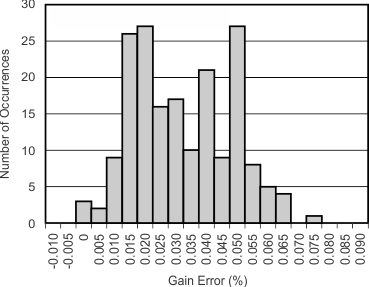 Figure 5-17 Gain Error Histogram
Figure 5-17 Gain Error Histogram
| Differential inputs; includes noise, offset and gain
error |
Figure 5-19 Total
Error vs Input Signal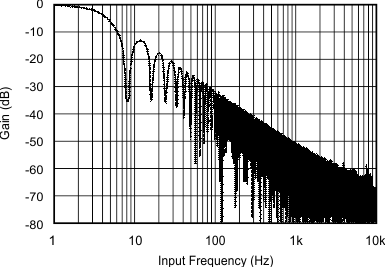 Figure 5-21 Digital Filter Frequency Response
Figure 5-21 Digital Filter Frequency Response


















