-
Headset Detection for TAx52xx Family SLAAEG7 April 2024 TAC5111 , TAC5111-Q1 , TAC5112 , TAC5112-Q1 , TAC5211 , TAC5212 , TAC5212-Q1 , TAD5112 , TAD5112-Q1 , TAD5212 , TAD5212-Q1
-
Headset Detection for TAx52xx Family
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Headset Plugs and Connection Diagrams
- 2Example for a Pseudo-Differential (Capacitor-less) Output Configuration
- 3Example for an AC-Coupled (Capacitor) Output Configuration
- 4Flowchart for Pseudo-Differential (Capacitor-less) Output Configuration
- 5Flowchart for AC-Coupled (Capacitor) Output Configuration
- 6Summary
- 7References
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
Headset Detection for TAx52xx Family
Abstract
A common feature in most of today's electronic devices – including cell phone, PDAs, notebooks, handheld media players, game systems, and so on, is the provision for connecting to external accessories. The devices therefore include dedicated logic circuitry that can detect not only the presence of an accessory, but also the type.
The TAx5x1x includes extensive capability to monitor a headphone, microphone (mic), or headset jack, determine if an audio plug has been inserted, and then detect what type of headset is wired to the plug. This application note mainly discusses the headset detection scheme for two different headset output configurations: pseudo-differential (capacitor-less) output, and ac-coupled output. The content of this document applies to the TAD5212, TAD5112, TAC5212, TAC5112, TAC5211, TAC5111, TAD5212-Q1, TAD5112-Q1, TAC5212-Q1, TAC5112-Q1, and TAC5111-Q1
Trademarks
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1 Headset Plugs and Connection Diagrams
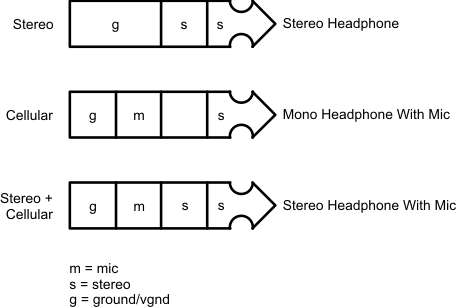 Figure 1-1 Different Configurations of 4-Conductor Headset Plug
Figure 1-1 Different Configurations of 4-Conductor Headset Plug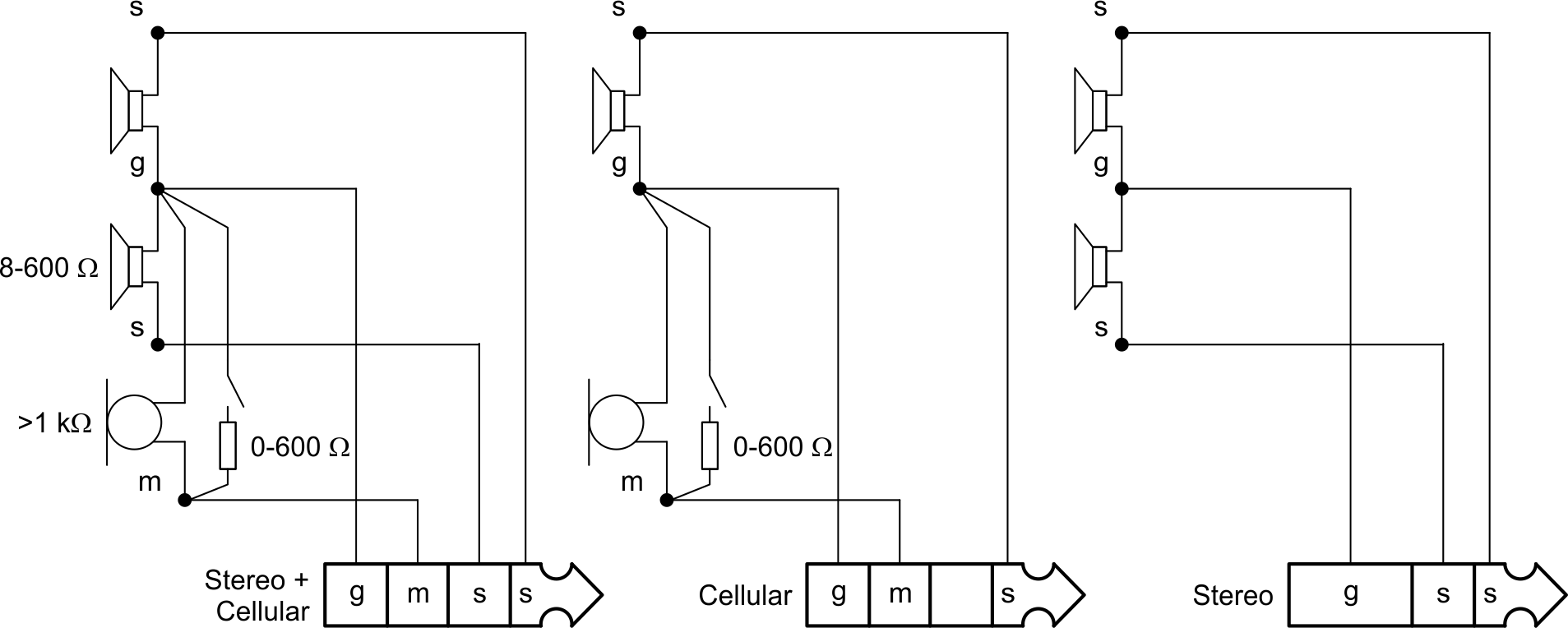 Figure 1-2 Connection Diagrams for Various Headsets
Figure 1-2 Connection Diagrams for Various Headsets1.1 Part I: Pseudo-Differential (Capacitor-less) Headset Output Configuration
Figure 1-3 shows one configuration of the device that enables detection and determination of headset type when a pseudo-differential (capacitor-less) stereo headphone output connection is used. Note that for best results, it is recommended to select a MICBIAS value as high as possible, and to program the output driver common-mode level at a 1.6-V or 1.5-V level.
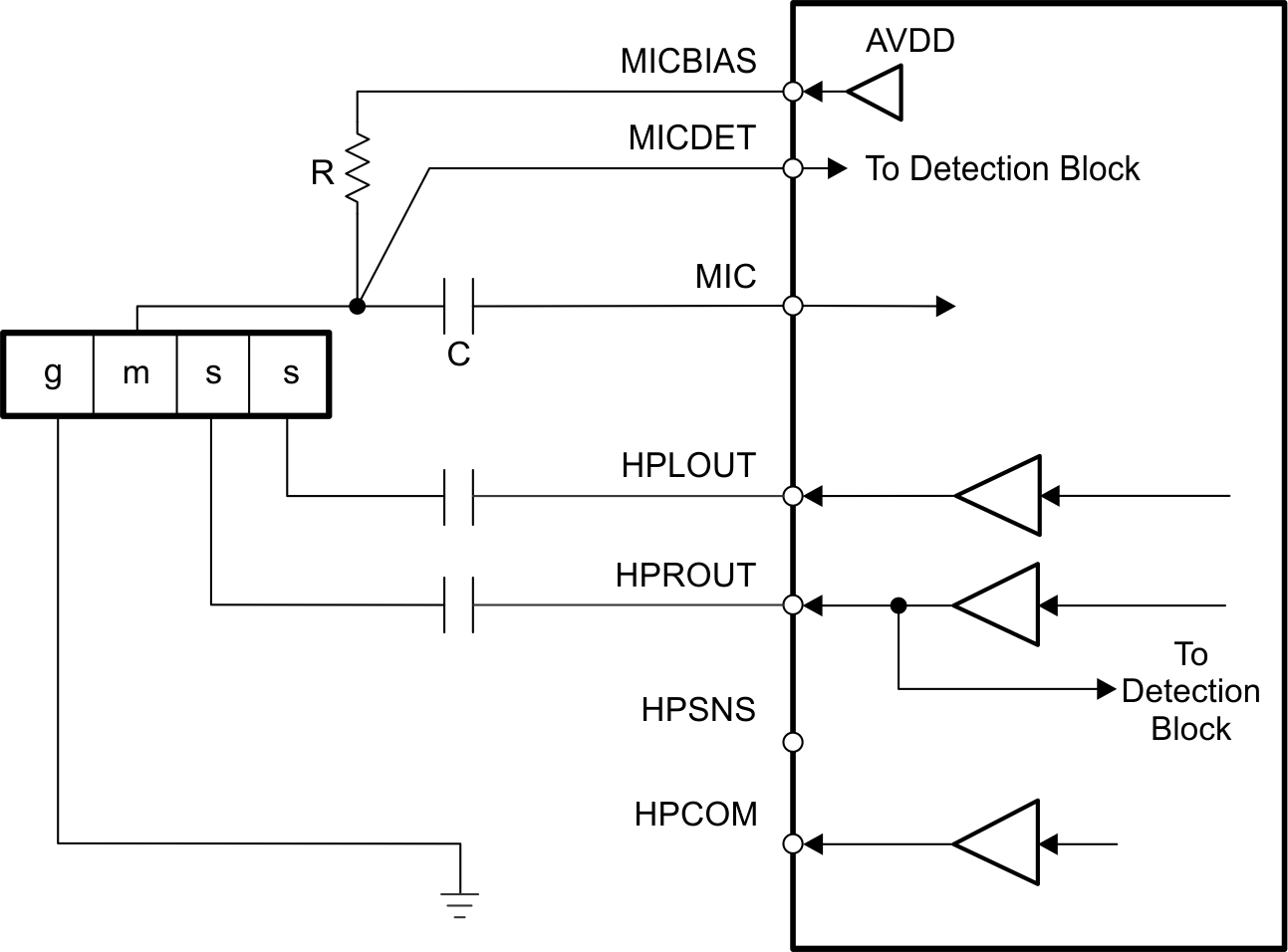 Figure 1-3 Device With a
Pseudo-Differential (Capacitor-less) Headset Output Connection
Figure 1-3 Device With a
Pseudo-Differential (Capacitor-less) Headset Output ConnectionFigure 1-4 demonstrates the internal circuitry that implements the detection logic. The two comparators in this figure is used for headphone and jack detection.
 Figure 1-4 Circuit Diagram of Detection Scheme for Capacitor-less Interface
Figure 1-4 Circuit Diagram of Detection Scheme for Capacitor-less Interface