SLAAEG7 April 2024 TAC5111 , TAC5111-Q1 , TAC5112 , TAC5112-Q1 , TAC5211 , TAC5212 , TAC5212-Q1 , TAD5112 , TAD5112-Q1 , TAD5212 , TAD5212-Q1
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Headset Plugs and Connection Diagrams
- 2Example for a Pseudo-Differential (Capacitor-less) Output Configuration
- 3Example for an AC-Coupled (Capacitor) Output Configuration
- 4Flowchart for Pseudo-Differential (Capacitor-less) Output Configuration
- 5Flowchart for AC-Coupled (Capacitor) Output Configuration
- 6Summary
- 7References
1.2.2 How to Determine the Comparator Threshold V1 and V2 – Capacitor Interface
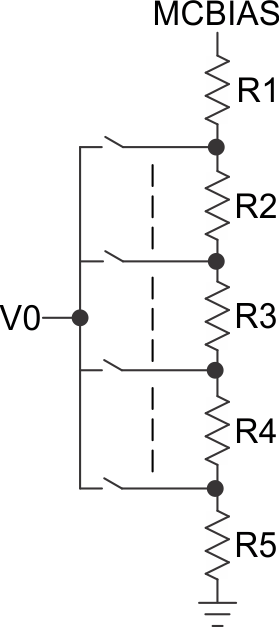
Note that for V1 and V2 there will be a lot more threshold possible than the ones shown previously which can be based on eternal resistor and ADC loading.