SLAAEO3 September 2024 MSPM0L2227 , MSPM0L2228
5.1.1 Hardware-Driven Layout
In a hardware-driven layout approach, one option is for pins to be connected to the closest LCD-capable pins on the MSPM0 to minimize crossings and layout the board in a single layer. However, the hardware-driven approach in layouts where the pins mapped to the MSPM0 LCD memory are scattered through memory, meaning more software work and overhead when writing the code.
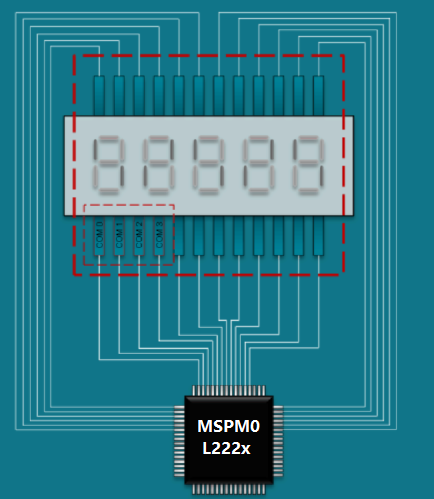 Figure 5-2 Example Layout Grouping LCD
Lines Bus-Style in a Single Layer
Figure 5-2 Example Layout Grouping LCD
Lines Bus-Style in a Single Layer