SLAAEO8 October 2024 MSPM0C1103 , MSPM0C1103-Q1 , MSPM0C1104 , MSPM0C1104-Q1 , MSPM0G1105 , MSPM0G1106 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G1519 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3105-Q1 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3106-Q1 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3107-Q1 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3505-Q1 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3506-Q1 , MSPM0G3507 , MSPM0G3507-Q1 , MSPM0G3519 , MSPM0L1105
2.1.1 ADC Noise
ADC internal noise includes quantization noise and thermal noise.
- Quantization noise
The quantization noise of ADC refers to the noise caused by quantization errors between the input analog signal and the output digital signal, and its magnitude is determined by the resolution of ADC. The peak to peak value of quantization noise is 1 LSB, and the higher the resolution of ADC, the smaller the quantization error.
- Thermal noise
Thermal noise is an inherent phenomenon in all electrical components, and it still exists even without ADC input. The sum of all noise inside the ADC, except for quantization noise, is usually referred to as thermal noise. Usually, thermal noise exhibits a Gaussian distribution, and since it is not related to quantization noise, the total noise within the ADC can be calculated using Root Sum Squares.
Equation 12.According to the calculation formula of the total noise inside the ADC, it can be seen that the ADC noise is determined by the larger one of quantization noise and thermal noise. For low resolution ADCs, the quantization noise is much greater than the thermal noise, in which case, the method to reduce ADC noise is to select a smaller reference voltage to reduce quantization noise. For high-resolution ADC, due to its small LSB and low quantization noise, the full-scale range can be increased by increasing the reference voltage of the ADC, thereby reducing the proportion of thermal noise in the signal and increasing the signal-to-noise ratio.
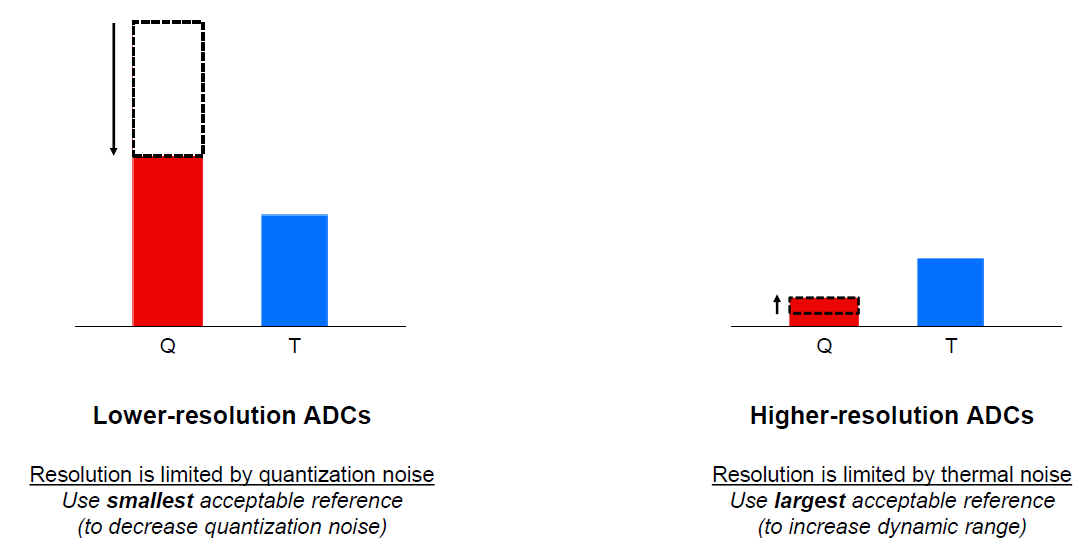 Figure 2-2 Quantization Noise and Thermal Noise of ADC With Different Resolutions
Figure 2-2 Quantization Noise and Thermal Noise of ADC With Different Resolutions