SLAU472C February 2013 – November 2023 TAS2505 , TAS2505-Q1
- 1
- Trademarks
- 1 TAS2505 Device Overview
- 2Description
-
3
TAS2505 Application
- 3.1 Terminal Descriptions
- 3.2 Audio Analog I/O
- 3.3 Analog Signals
- 3.4
Audio DAC and Audio Analog Outputs
- 3.4.1 DAC
- 3.4.2 DAC Gain Setting
- 3.4.3 Interrupts
- 3.4.4 Programming DAC Digital Filter Coefficients
- 3.4.5 Updating DAC Digital Filter Coefficients During PLAY
- 3.4.6 Digital Mixing and Routing
- 3.4.7 Analog Audio Routing
- 3.4.8 Analog Outputs
- 3.4.9 Audio Output-Stage Power Configurations
- 3.4.10 5V LDO
- 3.4.11 POR
- 3.4.12 DAC Setup
- 3.5
PowerTune
- 3.5.1 PowerTune Modes
- 3.5.2 DAC Power Consumption
- 3.5.3
Speaker output Power Consumption
- 3.5.3.1 Speaker output, Mono, 48 kHz, Highest Performance, DVDD = IOVDD = 1.8 V, AVDD = 1.8 V, SPKVDD = 3.6V
- 3.5.3.2 Speaker output, Mono, Lowest Power Consumption
- 3.5.3.3 Speaker output, Mono, 8 kHz, Highest Performance, DVDD = IOVDD = 1.8 V, AVDD = 1.8 V, SPKVDD = 3.6V
- 3.5.3.4 Speaker output, Mono, Lowest Power Consumption
- 3.5.4
Headphone output Power Consumption
- 3.5.4.1 Headphone output, Mono, 48 kHz, Highest Performance, DVDD = IOVDD = 1.8 V, AVDD = 1.8 V, SPKVDD = 3.6V
- 3.5.4.2 Headphone output, Mono, Lowest Power Consumption, DVDD = IOVDD = 1.8 V, AVDD = 1.5 V, SPKVDD = 3.6V
- 3.5.4.3 Headphone output, Mono, 8 kHz, Highest Performance, DVDD = IOVDD = 1.8 V, AVDD = 1.8 V, SPKVDD = 3.6V
- 3.5.4.4 Headphone output, Mono, Lowest Power Consumption, DVDD = IOVDD = 1.8 V, AVDD = 1.8 V, SPKVDD = 3.6V
- 3.6 CLOCK Generation and PLL
- 3.7 Digital Audio and Control Interface
- 3.8 Power Supply
- 3.9 Device Special Functions
- 4Device Initialization
-
5Example Setups
- 5.1 Example Register Setup to Play Digital Data Through DAC and Headphone/Speaker Outputs
- 5.2 Example Register Setup to Play Digital Data Through DAC and Headphone Output
- 5.3 Example Register Setup to Play AINL and AINR Through Headphone/Speaker Outputs
- 5.4 Example Register Setup to Play AINL and AINR Through Headphone Output
- 5.5 Example Register Setup to Play Digital Data Through DAC and Headphone/Speaker Outputs With 3 Programmable Biquads
- 5.6 Example Register Setup to Play Digital Data Through DAC and Headphone/Speaker Outputs With 6 Programmable Biquads
-
6Register Map
- 6.1
TAS2505 Register Map
- 6.1.1 Control Registers, Page 0 (Default Page): Clock Multipliers, Dividers, Serial Interfaces, Flags, Interrupts, and GPIOs
- 6.1.2 Control Registers, Page 1: DAC Routing, Power-Controls and MISC Logic Related Programmabilities
- 6.1.3 Page 2 - 43: Reserved Register
- 6.1.4 Page 44: DAC Programmable Coefficients RAM
- 6.1.5 Page 45 - 52: DAC Programmable Coefficients RAM
- 6.1.6 Page 53 - 61: Reserved Register
- 6.1.7 Page 62 - 70: DAC Programmable Coefficients RAM
- 6.1.8 Pages 71 – 255: Reserved Register
- 6.1.9 DAC Coefficients A+B
- 6.1.10 DAC Defaults
- 6.1
TAS2505 Register Map
- 7Revision History
3.7.2.2 SPI Digital Interface
In the SPI control mode,the TAS2505 uses the pins SCL/SSZ=SSZ, SCLK=SCLK, MISO=MISO, SDA/MOSI=MOSI as a standard SPI port with clock polarity setting of 0 (typical microprocessor SPI control bit CPOL = 0). The SPI port allows full-duplex, synchronous, serial communication between a host processor (the master) and peripheral devices (slaves). The SPI master (in this case, the host processor) generates the synchronizing clock (driven onto SCLK) and initiates transmissions. The SPI slave devices (such as the TAS2505) depend on a master to start and synchronize transmissions. A transmission begins when initiated by an SPI master. The byte from the SPI master begins shifting in on the slave MOSI pin under the control of the master serial clock(driven onto SCLK). As the byte shifts in on the MOSI pin, a byte shifts out on the MISO pin to the master shift register.
The TAS2505 interface is designed so that with a clock-phase bit setting of 1 (typical microprocessor SPI control bit CPHA = 1), the master begins driving its MOSI pin and the slave begins driving its MISO pin on the first serial clock edge. The SSZ pin can remain low between transmissions; however, the TAS2505 only interprets the first 8 bits transmitted after the falling edge of SSZ as a command byte, and the next 8 bits as a data byte only if writing to a register. Reserved register bits should be written to their default values. The TAS2505 is entirely controlled by registers. Reading and writing these registers is accomplished by an 8-bit command sent to the MOSI pin of the part prior to the data for that register. The command is structured as shown in Table 3-17. The first 7 bits specify the register address which is being written or read, from 0 to 127 (decimal). The command word ends with an R/W bit, which specifies the direction of data flow on the serial bus. In the case of a register write, the R/W bit should be set to 0. A second byte of data is sent to the MOSI pin and contains the data to be written to the register. Reading of registers is accomplished in similar fashion. The 8-bit command word sends the 7-bit register address, followed by R/W bit = 1 to signify a register read is occurring. The 8-bit register data is then clocked out of the part on the MISO pin during the second 8 SCLK clocks in the frame.
| Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit1 | Bit0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADDR(6) | ADDR(5) | ADDR(4) | ADDR(3) | ADDR(2) | ADDR(1) | ADDR(0) | R/WZ |
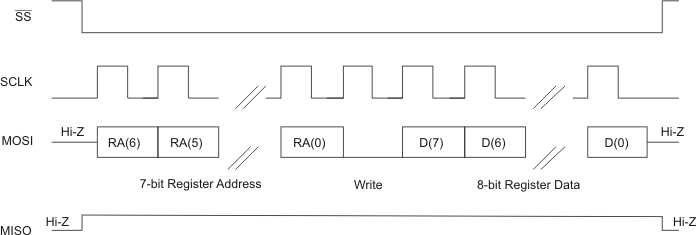 Figure 3-24 SPI Timing Diagram for Register Write
Figure 3-24 SPI Timing Diagram for Register Write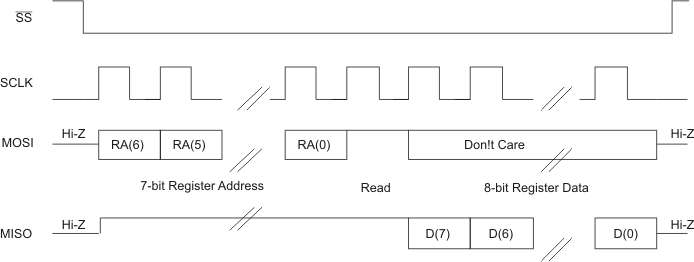 Figure 3-25 SPI Timing Diagram for Register Read
Figure 3-25 SPI Timing Diagram for Register Read