SLAU903 October 2023
- 1
- Description
- Get Started
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1Evaluation Module Overview
- 2Hardware
-
3Software
- 3.1 Software Description
- 3.2 PurePath Console 3 Installation
- 3.3 TAx5x1x-Q1 EVM GUI
- 3.4 Configuration Examples
- 3.5 System Overview
- 4Hardware Design Files
- 5Additional Information
- 6References
2.3.1.1 Line Inputs
For the line input configuration shown in Figure 3-10, the TAx5x1x-Q1 captures the audio signal provided through RCA terminals J2 (IN1), J3 (IN2) or header J47 or J48. The RCA white connector is connected to the INxP and RCA red connector is connected to the INxM. Depending on differential or single-ended configuration, populate J6 or J7 jumper as described in Table 2-1 accordingly. The input accepted in this mode is a differential 10-VRMS full-scale audio signal. If a single-ended source is used, the 5-VRMS signal is supported. The gang potentiometer R43 and R44 provide the input bias resistors for this AC-Coupled input mode depending on the desired input swing and impedance.
Using the TAx5x1x-Q1 AC-Coupled external resistor calculator, enter the maximum input level and the desired MICBIAS voltage to determine the resistance required to achieve full input swing as shown in Figure 2-10.
From the calculator example below, the maximum resistance allowed is 2399.4 Ohm and the closest standard resistance is 2375 Ohm. Based on this standard value resistance, the effective impedance looking into the device is about 2184 Ohm. This effective input impedance forms a high pass filter with the external capacitor. The Vcm is the common voltage for the respective MICBIAS and Input Swing. One can adjust the R50 and R51 potentiometer to get the common mode voltage (Vcm). By default, the EVM Vcm is set to 7.3V with 8 V MICBIAS.
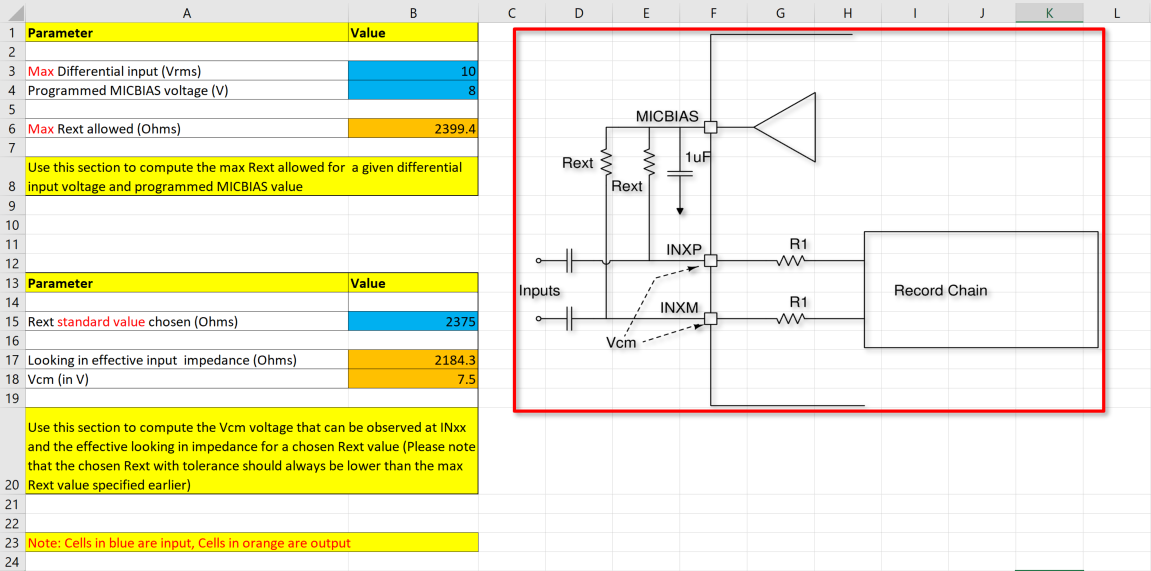 Figure 2-10 AC-Coupled External Resistor Calculator
Figure 2-10 AC-Coupled External Resistor Calculator