SLUSAP5A December 2011 – November 2016 TPS53316
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
Good layout is essential for stable power supply operation. Follow these guidelines for an efficient PCB layout:
- Separate the power ground and analog ground. Connect analog ground to GND plane with single via or a 0-Ω resistor at a quiet place.
- Use 4 vias to connect the thermal pad to power ground.
- Place VIN and VREG3 decoupling capacitors as close to the device as possible.
- Use wide traces for VIN, VOUT, PGND and SW. These nodes carry high-current and also serve as heat sinks.
- Place feedback and compensation components as close to the device as possible.
- Keep analog signals (FB, COMP) away from noisy signals (SW, VBST).
- See 5-A Step-Down Regulator with Integrated Switcher (SLUU671) for a layout example.
10.2 Layout Example
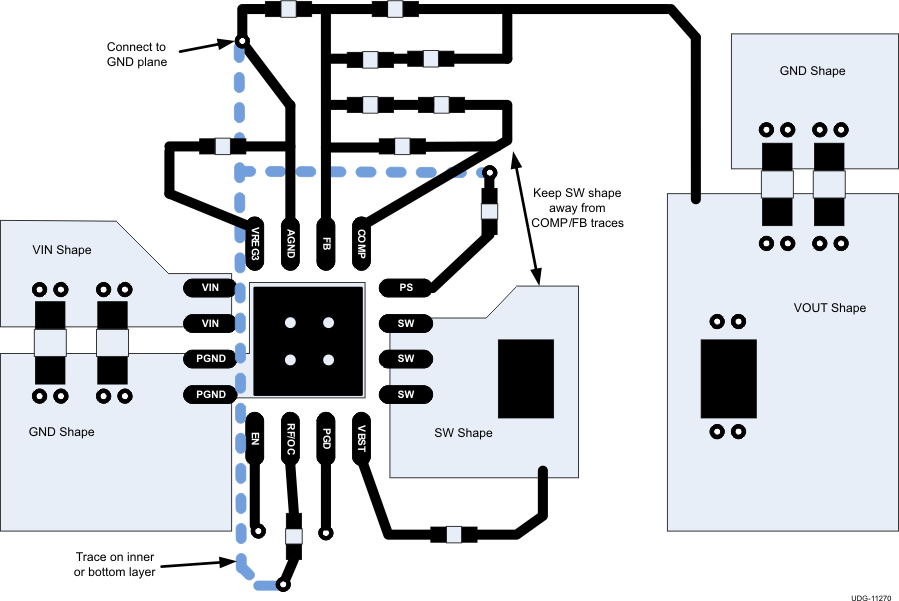 Figure 54. Layout Recommendation
Figure 54. Layout Recommendation