SLVS762C June 2007 – July 2015 TPS62242
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
As for all switching power supplies, the layout is an important step in the design. Proper function of the device demands careful attention to PCB layout. Care must be taken in board layout to get the specified performance. If the layout is not carefully done, the regulator could show poor line and/or load regulation, and additional stability issues as well as EMI problems. It is critical to provide a low inductance, impedance ground path. Therefore, use wide and short traces for the main current paths. The input capacitor should be placed as close as possible to the IC pins as well as the inductor and output capacitor.
Connect the GND pin of the device to the PowerPAD™ land of the PCB and use this pad as a star point. Use a common power GND node and a different node for the signal GND to minimize the effects of ground noise. Connect these ground nodes together to the PowerPAD land (star point) underneath the IC. Keep the common path to the GND pin, which returns the small signal components, and the high current of the output capacitors as short as possible to avoid ground noise. The FB line should be connected right to the output capacitor and routed away from noisy components and traces (for example, the SW line).
11.2 Layout Examples
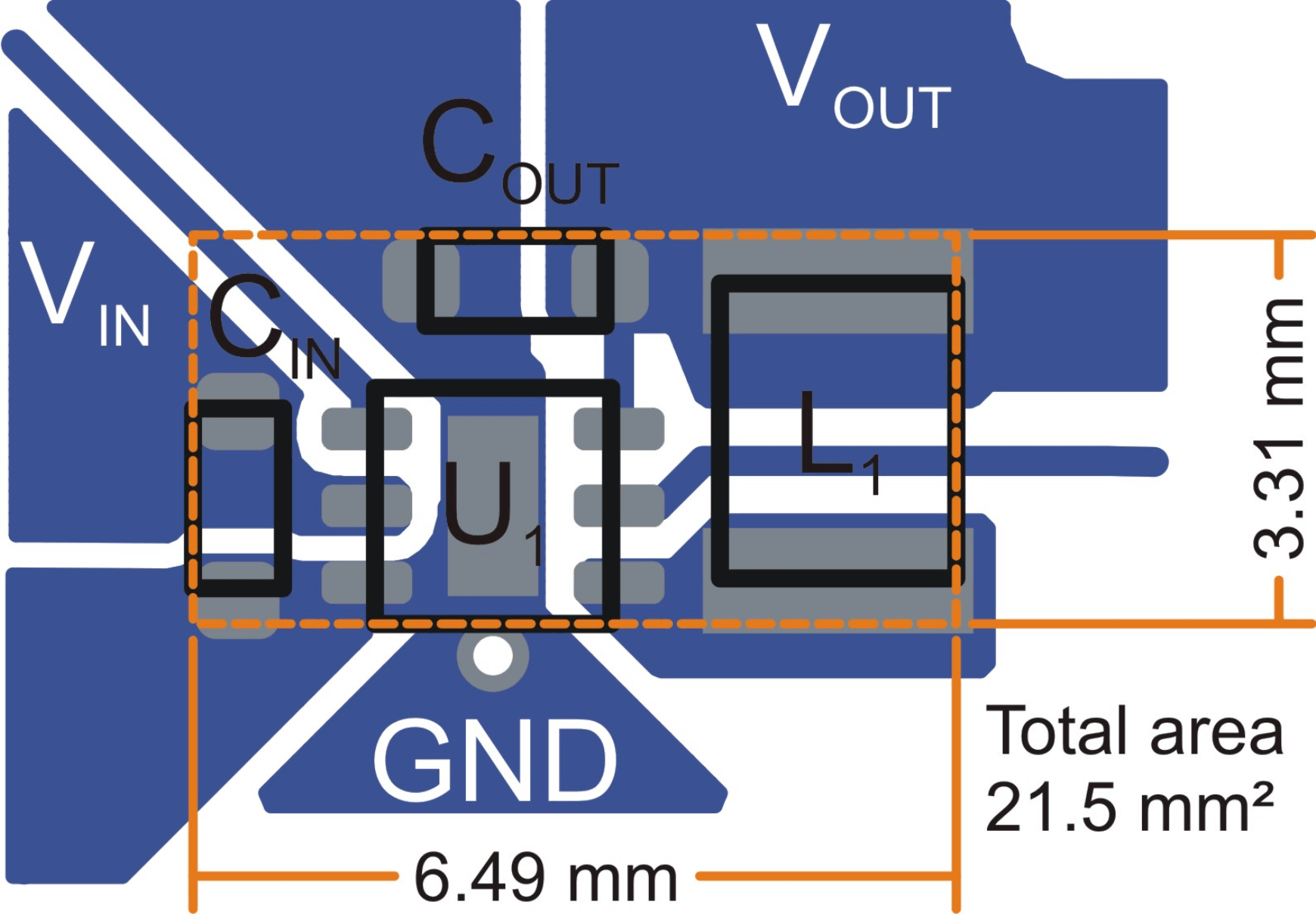 Figure 30. Suggested Layout for Fixed Output Voltage Options
Figure 30. Suggested Layout for Fixed Output Voltage Options
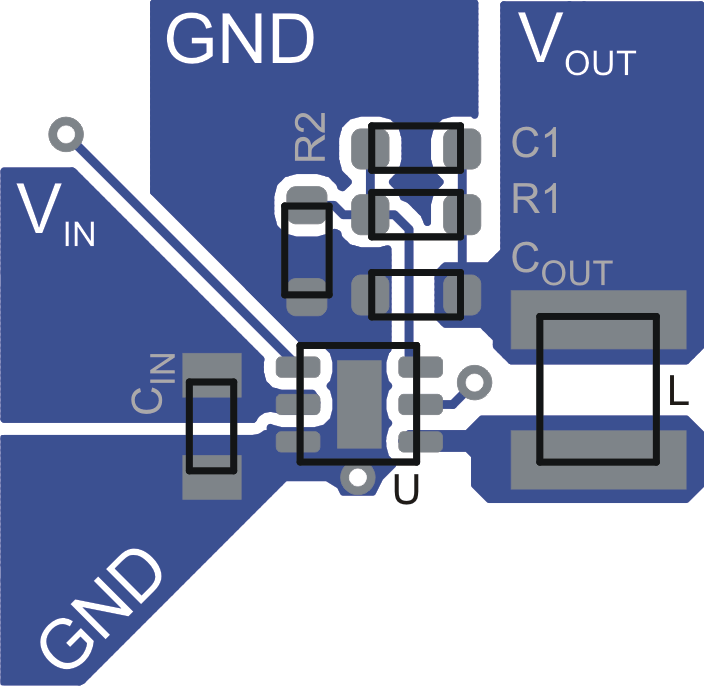 Figure 31. Suggested Layout for Adjustable Output Voltage Version
Figure 31. Suggested Layout for Adjustable Output Voltage Version