SLVS810C June 2009 – September 2015 TPS65000 , TPS650001 , TPS650003 , TPS650006 , TPS65001 , TPS650061
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Device Options
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
12 Layout
12.1 Layout Guidelines
- The VINDCDC and VINLDOx pins must be bypassed to ground with a low-ESR ceramic bypass capacitor. TI recommends the typical bypass capacitance is 10 μF and 2.2 μF with a X5R dielectric.
- The optimum placement is closest to the VINDCDCx and VINLDOx pins of the device. Minimize the loop area formed by the bypass capacitor connection, the VINDCDC and VINLDO pins, and the thermal pad of the device.
- The thermal pad must be tied to the PCB ground plane with multiple vias.
- The VLDOx and VDCDCx pins (feedback pins) traces must be routed away from any potential noise source to avoid coupling.
- VODC output capacitance must be placed immediately at the VODC pin. Excessive distance between the capacitance and DCDCx pin may cause poor converter performance.
- AGND star back to PGND as close to IC as possible.
- DGND connect to thermal pad.
12.2 Layout Example
 Figure 34. Layout Recommendation
Figure 34. Layout Recommendation
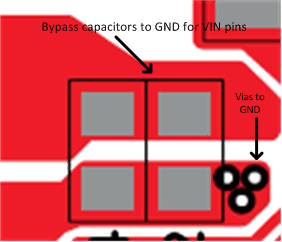 Figure 35. Bypass Capacitor and Via Placement Recommendation
Figure 35. Bypass Capacitor and Via Placement Recommendation