SLVU356A January 2010 – October 2021 TPS54290 , TPS54291
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2TPS54291EVM-431 Electrical Performance Specifications
-
3Schematic
- 3.1 Enable Jumpers (JP1 and JP2)
- 3.2 Error Amplifier Outputs
- 3.3
Test Point Descriptions
- 3.3.1 Input Voltage Monitoring (TP1 and TP2)
- 3.3.2 Channel 1 Output Voltage Monitoring (TP3 and TP4)
- 3.3.3 Channel 1 Loop Analysis (TP5, TP6, TP7, and TP8)
- 3.3.4 Channel 1 Switching Waveforms (TP9 and TP10)
- 3.3.5 TPS54291 IC Ground (TP11)
- 3.3.6 Channel 2 Switching Waveforms (TP12 and TP13)
- 3.3.7 Channel 2 Loop Analysis (TP14, TP15, TP16, and TP17)
- 3.3.8 Output Voltage Monitoring (TP18 and TP19)
- 4Test Setup
- 5TPS54291EVM-431 Typical Performance Data and Characteristic Curves
- 6EVM Assembly Drawings and Layout
- 7List of Materials
- 8Revision History
4.5 Control Loop Gain and Phase Measurement Procedure
- Connect a 1-kHz to 1-MHz isolation transformer to TP6 and TP8 as shown in Figure 4-3
- Connect the input signal amplitude measurement probe (Channel A) to TP8 as shown in Figure 4-3.
- Connect output signal amplitude measurement probe (Channel B) to TP6 as shown in Figure 4-3.
- Connect ground lead of Channel A and Channel B to TP5 and TP7 as shown in Figure 4-3.
- Inject 30-mV or less signal across R1 through an isolation transformer.
- Sweep frequency from 1 kHz to 1 MHz with 1-0Hz or lower post filter.
- Control loop gain can be measured by
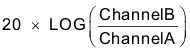 .
. - The control loop phase is measured by the phase difference between Channel A and Channel B.
- The control loop for Channel 2 can be measured by
making the following substitutions:
- Change TP6 to TP16.
- Change TP8 to TP14.
- Change TP5 to TP17.
- Change TP7 to TP15.
- Disconnect the isolation transformer before making any other measurements (signal injection into feedback can interfere with the accuracy of other measurements).