SLVUBV4A December 2020 – December 2021 TPS272C45
7 Current Limit Configuration
The TPS272C45EVM has the ability to configure both the ILIM1 and ILIM2 pins of the TPS272C45 to set a wide range of current limits that are custom tailored to the end design. Additionally the user is able to custom tailor the duration of time taken before the output current shuts off through the resistor connected to the ILIMD pin. The external current limits of the TPS272C45EVM are controlled by external resistors R13 and R14 (ILIM1), R2 (ILIM2), and R3 (ILIMD). Note that these resistors are populated in the 0805 package size allowing for easy soldering and desoldering.
The ILIM1 pin is configured in such a way that multiplexed current limits can be selected from an external microcontroller through the BoosterPack headers. This feature can seen below in Figure 7-1:
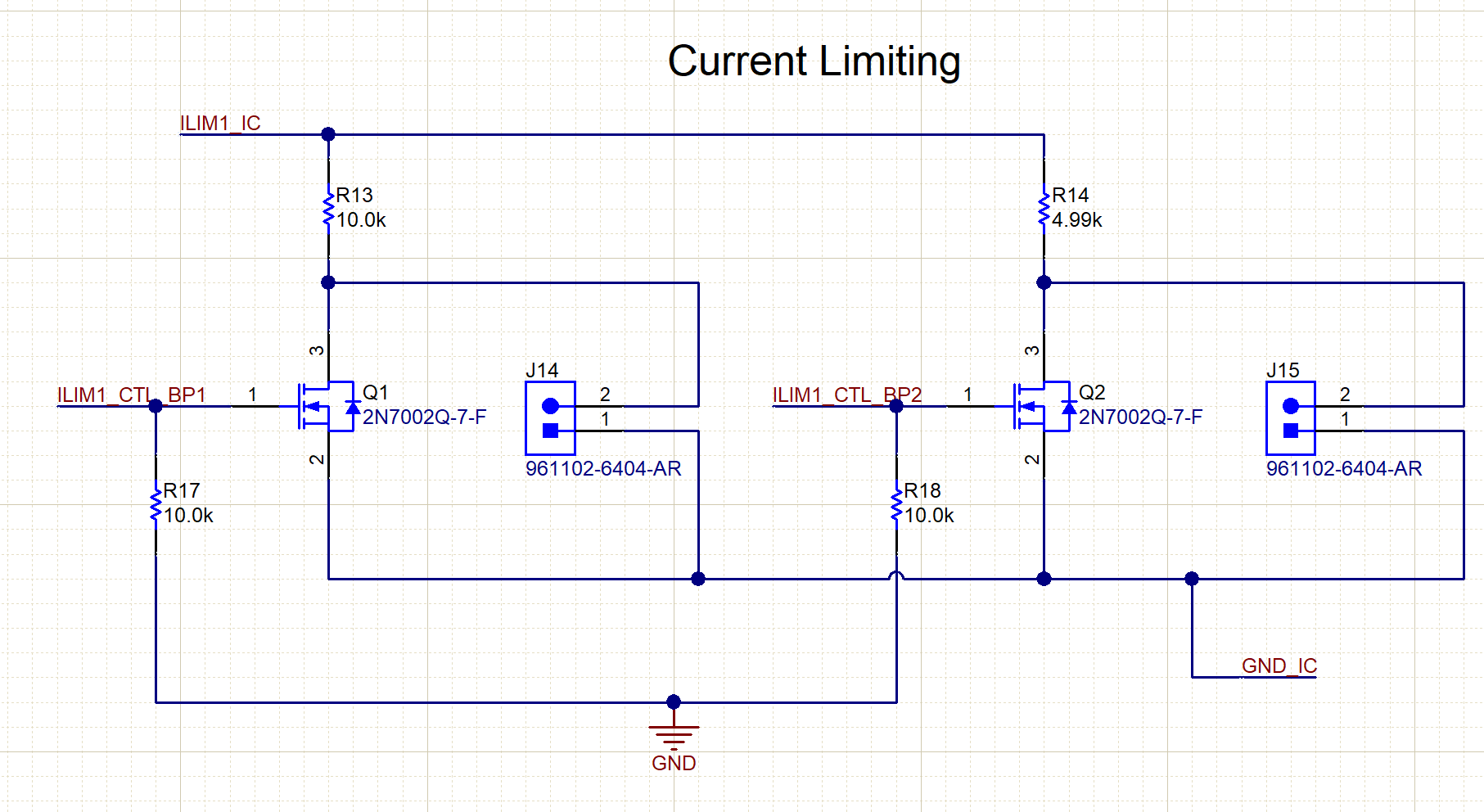 Figure 7-1 Multiplexed Current Limit
Figure 7-1 Multiplexed Current LimitWith this configuration, the user can choose to enable the MOSFET Q1 if the 10.0-kΩ resistor is desired or enable the MOSFET Q2 if the 4.99-kΩ resistor is desired. TI does not recommend to enable both channels simultaneously as this would parallel both of the resistors and add an undesired capacitance to the line. If multiplexing is not needed, the user can manually populate either the J14 or J15 jumpers. Please refer to the TPS272C45 data sheet for information on how to calculate delays from relevant resistor values.