SLVUCF6 july 2023
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Requirements
- 3TPS65219 Resources Overview
- 4EVM Configuration
- 5NVM Programming
- 6Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- 7Schematics, PCB Layouts, and Bill of Materials
6.6 NVM Configuration Page
The NVM Configuration page (shown in Figure 6-9) is the main feature of the GUI and highlights the configurability of the PMIC. On this page, register fields are grouped according to their use case and are labeled to indicate which part of the PMIC is controlled by each block. The NVM configuration page also provides the interface to save a custom configuration or load an existing configuration into the NVM of the target device. A full register read can be done using the READ ALL REGISTERS button in the top left of the page.
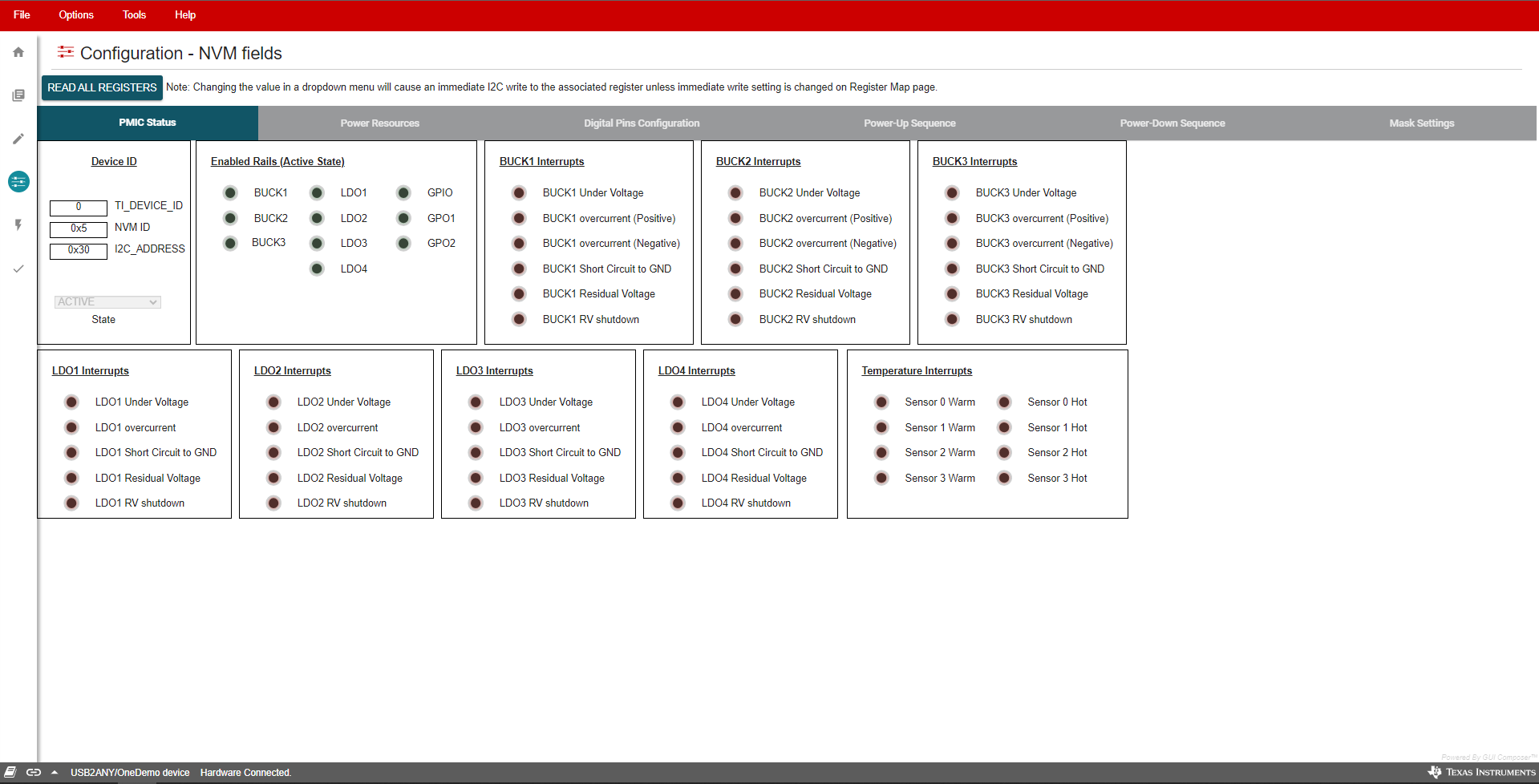 Figure 6-9 NVM Configuration Page
Figure 6-9 NVM Configuration Page