SNAA333 April 2020 CDCE6214-Q1
- eAVB Media Clock Synchronization Using CDCE6214-Q1 Clock Generator
2 AVB Protocols and Network Structure
AVB is a family of protocols that include:
- IEEE 802.1AS for time synchronization. IEEE 802.1AS defines generalized Precision Time Protocol (gPTP) profile based on IEEE 1588.
- IEEE 802.1Qav for traffic shaping.
- IEEE 802.1Qat for stream reservation.
- IEEE 802.1BA that specifies defaults and profiles of AVB components. IEEE 802.1BA is an umbrella standard for IEEE 802.1AS, IEEE 802.1Qav and IEEE 802.1Qat.
- IEEE 802.1Q that specifies Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks. IEEE 802.1Qav and IEEE 802.1Qat have been incorporated to IEEE 802.1Q.
- IEEE 1722 Layer 2 A/V transport protocol.
An example AVB system is shown in Figure 2:
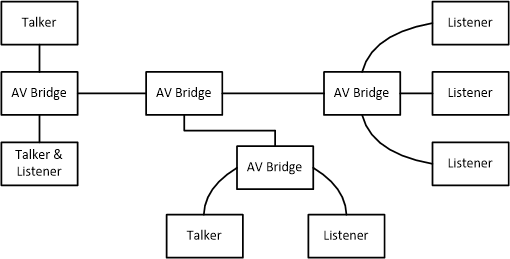 Figure 2. Example High Level AVB Network
Figure 2. Example High Level AVB Network An AVB network consists of three types of components:
- AV Bridges. An AV Bridge is a relay device that conforms to IEEE 802.1BA. It acts as a switch that receives and forwards IEEE 802.1BA compliant data to the destination device.
- End stations. An end station can be a Talker, Listener, or both. A Talker is an end station that is the source, transmitter or producer of a stream. A Listener is an end station that is the destination, receiver or consumer of a stream.
- Ethernet LANs (Local Area Network). Individual LANs interconnect the Bridges, Talkers and Listeners.
To understand more about the AVB end stations see Section 3.