SNAU298A October 2023 – October 2024
5.1 Typical Phase Noise Characteristic
The typical phase noise performance for 156.25MHz reference clock input using a SMA100B is shown in Figure 5-1.
LMKDB1120EVM was configured in cascaded mode to get these measurements:
- SMA100B → LMKDB1120EVM input. Then, LMKDB1120EVM to secondary LMKDB1120 EVM. This was done to get good slew rate at the input. Other methods like a clipping circuit can be used to get a desired slew rate and square wave form from the SMA100B.
- Outputs phase noise is measured
through a Balun to convert the differential waveform from the LMKDB1120 into a
single-ended waveform for a phase noise analyzer.
As shown below in Figure 5-1, reference input jitter is 36.7 fs. The measured jitter on the output of LMKDB1120 is 43.7 fs is shown in Figure 5-2. Calculated typical additive jitter is about 24 fs for the LMKDB1120.
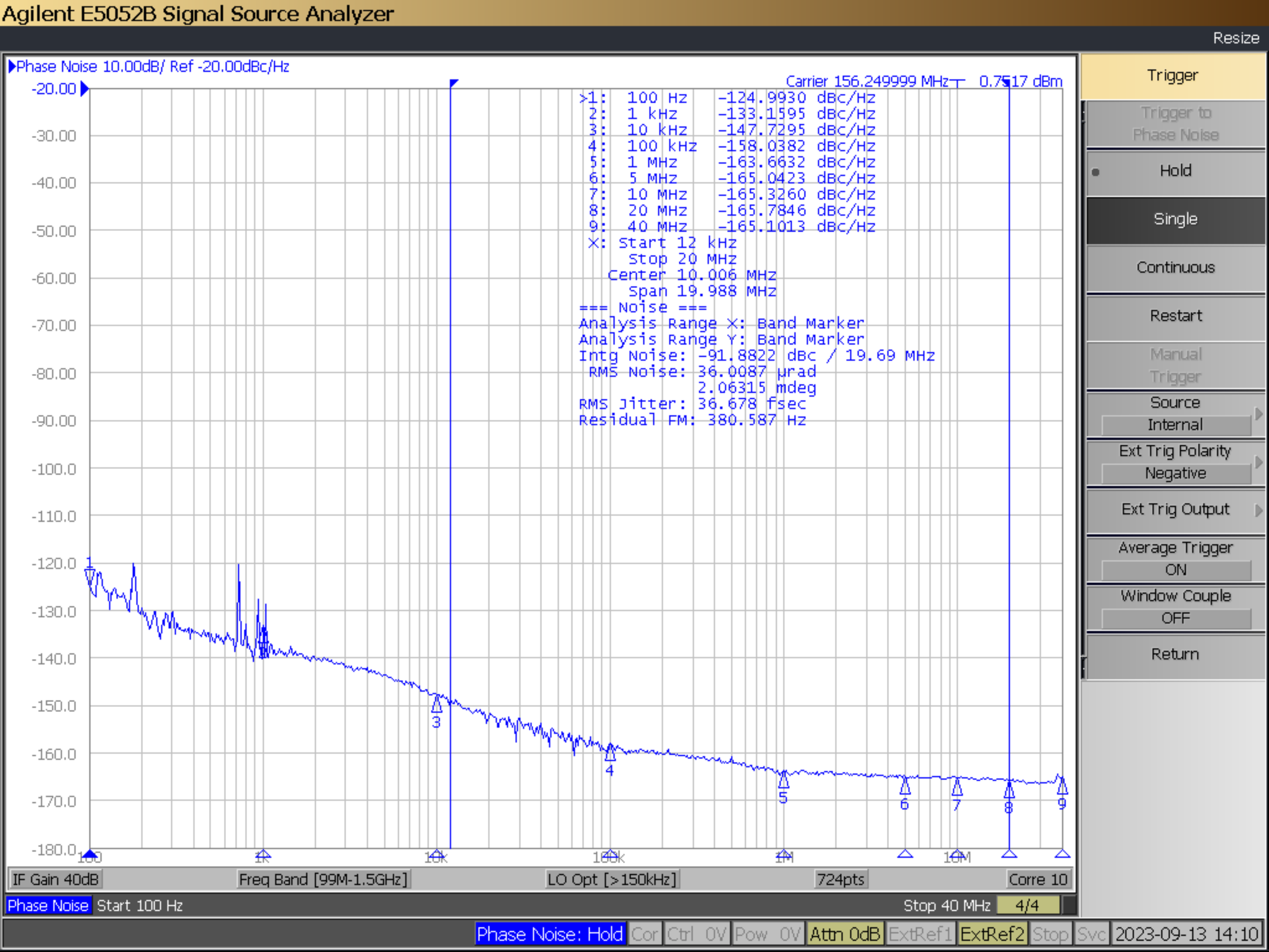 Figure 5-1 Reference Clock Input Phase
Noise
Figure 5-1 Reference Clock Input Phase
Noise
Figure 5-2 LMKDB1120 Output Clock Phase Noise