SNLA437 December 2023 DP83822H , DP83822HF , DP83822I , DP83822IF , DP83826I
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1DP83822 Application Overview
-
2Troubleshooting the PHY Application
- 2.1 Schematic and Layout Checklist
- 2.2 Verify Successful Power-up of PHY
- 2.3 Read and Check Register Values
- 2.4 Peripheral Pin Checks
- 2.5 Verifying Strap Configurations During Initialization
- 2.6 Debugging Link Quality
- 2.7 Built-In Self Test With Various Loopback Modes
- 2.8 Debug the Fiber Connection
- 2.9 Debug the MAC Interface
- 2.10 Debug the Start of Frame Detect
- 2.11 Tools and References
- 3References
1 DP83822 Application Overview
Designed for harsh industrial environments, the DP83822 is an ultra-robust, low-power single-port 10/100 Mbps Ethernet PHY. The DP83822 provides all physical layer functions needed to transmit and receive data over standard twisted-pair cables, or connect to an external fiber optic transceiver. Additionally, the DP83822 provides flexibility to connect to a MAC through a standard MII, RMII, or RGMII interface.
Figure 1-1 is a high-level system block diagram of a typical DP83822 application.
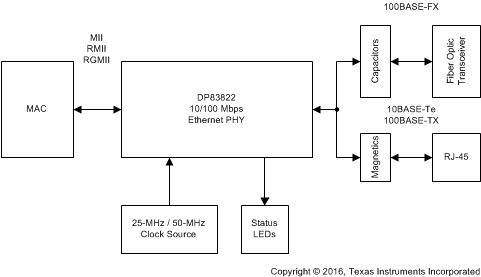 Figure 1-1 DP83822
Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 DP83822
Block DiagramThe DP83822 connects to an Ethernet MAC and to the MDI. The connection to the MDI is via a transformer and a connector (for copper applications) or capacitors and a transceiver (for fiber applications).