-
DS110DF1610 8.5- to 11.3-Gbps 16-Channel Retimer
- 1Features
- 2Description
- 3Revision History
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Specifications
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 6.3 Feature Description
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6 Register Maps
- 7Application and Implementation
- 8Power Supply Recommendations
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
DS110DF1610 8.5- to 11.3-Gbps 16-Channel Retimer
1 Features
- Pin-Compatible Family
- DS150DF1610: 12.5 - 15G
- DS125DF1610: 9.8 to 12.5G
- DS110DF1610: 8.5 – 11.3G
- 4x4 Analog Cross Point Switch for Each Quad
- Fully-Adaptive CTLE
- Self-Tuning DFE, With Optional Continuous Adaption
- On-Chip, AC-coupling on Receive Inputs
- Adjustable Transmit VOD
- Adjustable 3-Tap Transmit FIR Filter
- Locks to Half/Quarter/Eighth Data Rates For Legacy Support
- On-Chip Eye Monitor (EOM), PRBS Checker, PRBS Pattern Generator
- Supports IEEE 1149.1 and 1149.6
- Programmable Output Polarity Inversion
- Input Signal Detection, CDR Lock Detection
- Single 2.5-V ±5% Power Supply
- SMBus-Based Register Configuration
- Optional EEPROM Configuration
- 15-mm × 15-mm, 196-Pin FCBGA Package
- Operating Temp Range : –10°C to +85°C
Typical Application Diagram
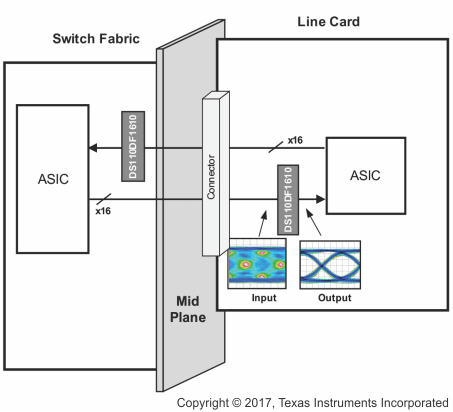
2 Description
The DS110DF1610 is a sixteen-channel multi-rate retimer with integrated signal conditioning. The device includes a full adaptive Continuous Time Linear Equalizer (CTLE), Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE), clock and data recovery (CDR), and a transmit FIR filter to enhance the reach and robustness over long, lossy, crosstalk impaired high speed serial links to achieve BER < 1×10-15.
Each channel of the DS110DF1610 independently locks to serial data at 8.5 to 11.3 Gbps and any supported sub-multiple. A simple external oscillator (±100ppm) that is synchronous or asynchronous with the incoming data stream can be used as a reference clock to speed up the lock process. Integrated 4x4 cross point switches allow for full non-blocking routing or broadcasting within each quad of the DS110DF1610.
Programmable transmit FIR filter offers control of the pre-cursor, main tap and post-cursor for transmit equalization. The fully adaptive receive equalization (CTLE and DFE) enables longer distance transmission in lossy copper interconnects and backplanes with multiple connectors.
A non-disruptive mission mode eye-monitor feature allows link monitoring internal to the receiver. The built-in PRBS generator and checker compliment the internal diagnostic features to complete standalone BERT measurements. Built-in JTAG enables manufacturing tests.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| DS110DF1610 | FCBGA (196) | 15.00 mm × 15.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
3 Revision History
Changes from * Revision (January 2014) to A Revision
- Changed device status from PRODUCT PREVIEW to PRODUCTION DATAGo
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
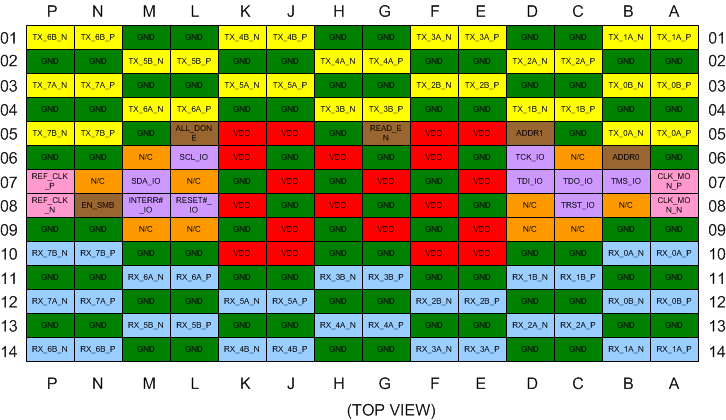
Pin Descriptions
| DS110DF1610, DS125DF1610 PIN NAME | DS150DF1610 PIN NAME | NO. | I/O TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIGH-SPEED DIFFERENTIAL I/Os | ||||
| RX_1A_P RX_1A_N |
RX_0_0P RX_0_0N |
A14 B14 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_0B_P Rx_0B_N |
RX_0_1P RX_0_1N |
A12 B12 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_0A_P RX_0A_N |
RX_0_2P RX_0_2N |
A10 B10 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_2A_P RX_2A_N |
RX_0_3P RX_0_3N |
C13 D13 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_1B_P RX_1B_N |
RX_0_4P RX_0_4N |
C11 D11 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_3A_P RX_3A_N |
RX_0_5P RX_0_5N |
E14 F14 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_2B_P RX_2B_N |
RX_0_6P RX_0_6N |
E12 F12 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_4A_P RX_4A_N |
RX_0_7P RX_0_7N |
G13 H13 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_3B_P RX_3B_N |
RX_1_0P RX_1_0N |
G11 H11 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_4B_P Rx_4B_N |
RX_1_1P RX_1_1N |
J14 K14 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_5A_P RX_5A_N |
RX_1_2P RX_1_2N |
J12 K12 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_5B_P RX_5B_N |
RX_1_3P RX_1_3N |
L13 M13 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_6A_P RX_6A_N |
RX_1_4P RX_1_4N |
L11 M11 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_6B_P RX_6B_N |
RX_1_5P RX_1_5N |
N14 P14 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_7A_P RX_7A_N |
RX_1_6P RX_1_6N |
N12 P12 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| RX_7B_P RX_7B_N |
RX_1_7P RX_1_7N |
N10 P10 |
I, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible, AC coupled differential inputs. An on-chip 100 Ohm differential termination resistor connects these inputs. |
| TX_1A_P TX_1A_N |
TX_0_0P TX_0_0N |
A1 B1 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_0B_P TX_0B_N |
TX_0_1P TX_0_1N |
A3 B3 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_0A_P TX_0A_N |
TX_0_2P TX_0_2N |
A5 B5 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_2A_P TX_2A_N |
TX_0_3P TX_0_3N |
C2 D2 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_1B_P TX_1B_N |
TX_0_4P TX_0_4N |
C4 D4 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_3A_P TX_3A_N |
TX_0_5P TX_0_5N |
E1 F1 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_2B_P TX_2B_N |
TX_0_6P TX_0_6N |
E3 F3 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_4A_P TX_4A_N |
TX_0_7P TX_0_7N |
G2 H2 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_3B_P TX_3B_N |
TX_1_0P TX_1_0N |
G4 H4 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_4B_P TX_4B_N |
TX_1_1P TX_1_1N |
J1 K1 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_5A_P TX_5A_N |
TX_1_2P TX_1_2N |
J3 K3 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_5B_P TX_5B_N |
TX_1_3P TX_1_3N |
L2 M2 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_6A_P TX_6A_N |
TX_1_4P TX_1_4N |
L4 M4 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_6B_P TX_6B_N |
TX_1_5P TX_1_5N |
N1 P1 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_7A_P TX_7A_N |
TX_1_6P TX_1_6N |
N3 P3 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| TX_7B_P TX_7B_N |
TX_1_7P TX_1_7N |
N5 P5 |
O, CML | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs. Driver presents an output impedance of 100 ohms between these outputs when switching. |
| CLOCK PINS | ||||
| REF_CLK_P REF_CLK_N |
P7 P8 |
I, LVDS/LVCMOS | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential inputs for 25 MHz, 125 MHz, or 312.5 MHz clock. When configured for single-ended input operation, apply LVCMOS ref clock to REF_CLK_P and float REF_CLK_N. Single-ended signals should be DC coupled. |
|
| CLK_MON_P CLK_MON_N |
A7 A8 |
O, LVDS | Inverting and non-inverting CML-compatible differential outputs to monitor system differential clock. When daisy chaining to another retimer the output frequency should be set to 25 MHz or 125 MHz. |
|
| SMBUS INTERFACE | ||||
| SDA_IO | M7 | I/O, Open Drain | Data Input / Open Drain Output External pull-up resistor is required. Pin is 3.3 V LVCMOS tolerant. |
|
| SCL_IO | L6 | I/O, Open Drain | Clock input/output, Pin is 3.3 V LVCMOS Tolerant EEPROM configuration (SMBus Master mode) will be available in final silicon |
|
| JTAG INTERFACE | ||||
| TMS_IO | B7 | I, LVCMOS | JTAG Test Mode Select, internal pull-up | |
| TDO_IO | C7 | O, LVCMOS | JTAG Test Data Out | |
| TRST_IO | C8 | I, LVCMOS | JTAG Test Reset, internal pull-up | |
| TCK_IO | D6 | I, LVCMOS | JTAG Test clock, internal pull-up | |
| TDI_IO | D7 | I, LVCMOS | JTAG Test Data Input, internal pull-up | |
| OTHER PINS | ||||
| RESET_IO | L8 | I, LVCMOS | Resets registers and state machines on rising edge. Expected pulse of 10µs. | |
| INTERR_IO | M8 | O, Open Drain | Active Low interrupt signal. Pin goes low when an interrupt event occurs. Interrupts must be enabled via SMBus. | |
| ADDR0 (GPIO0) | B6 | I/O, LVCMOS | 4 level input strap pin for SMBus address code LSB. Standard LVCMOS output. | |
| ADDR1(GPIO1) | D5 | I/O, LVCMOS | 4 level input strap pin for SMBus address code MSB. Standard LVCMOS output. | |
| READ_EN (GPIO2) | G5 | I/O, LVCMOS | Tie low for SMBus slave mode operation. Pin has internal pull down. | |
| ALL_DONE (GPIO3) | L5 | I/O, LVCMOS | EEPROM load status. Pin goes LOW when EEPROM load is complete. | |
| EN_SMB (SCAN_MODE) |
N8 | I, LVCMOS | Connect to GND through ≤1kΩ resistor for SMBus slave operation. Connect to VDD through ≤1kΩ resistor for EEPROM configuration |
|
| POWER | ||||
| VDD | E5, E7, E9, E10, F5, F6, F8, F10, G7, G9, H6, H8, J5, J7, J9, J10, K5, K6, K8, K10 | Power | VDD = 2.5 V +/- 5% | |
| GND | A2, A4, A6, A9, A11, A13, B2, B4, B9, B11, B13, C1, C3, C5, C10, C12, C14, D1, D3, D10, D12, D14, E2, E4, E6, E8, E11, E13, F2, F4, F7, F9, F11, F13, G1, G3, G6, G8, G10, G12, G14, H1, H3, H5, H7, H9, H10, H12, H14, J2, J4, J6, J8, J11, J13, K2, K4, K7, K9, K11, K13, L1, L3, L10, L12, L14, M1, M3, M5, M10, M12, M14, N2, N4, N6, N9, N11, N13, P2, P4, P6, P9, P11, P13 | Power | Ground reference | |
| N/C | B8, C6, C9, D8, D9, L7, L9, M6, M9, N7 | No Connect, leave floating | ||
5 Specifications
5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings (DS110DF1610)
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (VDD) | –0.5 | 2.75 | V | |
| LVCMOS input/output voltage | –0.5 | 2.75 | V | |
| Open-drain I/O supply voltage | –0.5 | 4 | V | |
| CML input voltage | –0.5 | VDD + 0.5 | V | |
| CML input current | –30 | 30 | mA | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| ESD Ratings | Human Body Model (HBM) - JESD22-A114F | >4 | kV | |
| Charged Device Model (CDM) - JESD22-A114F | >1 | kV | ||
5.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | 2.375 | 2.5 | 2.625 | V | |
| Ambient temperature | –10 | 25 | 85 | °C | |
| SMBus (SDA, SCL), INTERR_IO | 2.5 | 3.6 | V | ||
5.3 Thermal Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| BOARD | θ JA (°C / W) | Ψ JT (°C / W) | Ψ JB (°C / W) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JEDEC | 18.2 | 0.7 | 5.4 | |
| 8x6 inches 10 layer | 7.2 | 0.3 | 3.2 | |
| 8x6 inches 20 layer | 6.4 | 0.3 | 3.2 | |
| 8x6 inches 30 layer | 6.3 | 0.3 | 3.2 | |
5.4 Electrical Characteristics
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R_baud | Input Data Rate | Full Rate | 8.5 | 11.3 | Gbps | |
| Half Rate | 4.25 | 5.65 | ||||
| Quarter Rate | 2.125 | 2.825 | ||||
| Eighth Rate | 1.0625 | 1.4125 | ||||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| W | Power Consumption per Active Channel | CTLE only, 800mVp-p VOD, per channel, CDR locked |
210 | mW | ||
| CDR Locking with CTLE only, 800mVp-p VOD, per channel |
342.8 | |||||
| CTLE and DFE, 800mVp-p VOD, per channel, CDR locked |
235 | |||||
| CDR Locking with CTLE and DFE, 800mVp-p VOD | 367.8 | |||||
| PRBS Checker | 57 | |||||
| PRBS Generator | 83 | |||||
| WSTATIC | Static Power consumption | Power applied, no signals present |
300 | mW | ||
| LVCMOS | ||||||
| V IH | High level input voltage | 1.75 | VDD | V | ||
| VIL | Low level input voltage | GND | 0.7 | V | ||
| VOH | High level output voltage | IOH = 4mA | 2 | V | ||
| VOL | Low level output voltage | IOL = –4mA | 0.4 | V | ||
| IIH | Input High Leakage current | Vinput = VDD, Open Drain pins |
+30 | mA | ||
| Vinput = VDD, JTAG pins, Ref_CLK pins |
+25 | |||||
| Vinput = VDD, CLK_MON pin |
+50 | |||||
| Vinput = VDD, GPIO pins, EN_SMB pin |
+75 | |||||
| IIL | Input Low Leakage current | Vinput = 0V, Open Drain pins |
–15 | mA | ||
| Vinput = 0V, JTAG pins, Ref_CLK pins |
–45 | |||||
| Vinput = 0V, CLK_MON pin |
–50 | |||||
| Vinput = 0V, GPIO pins, EN_SMB pin |
–120 | |||||
| RX INPUTS | ||||||
| RRD | DC Input Resistance | 80 | 100 | 120 | Ω | |
| VRX-IN | Input Differential Voltage | 1600 | mVPP | |||
| Vcm-RX | Input common mode | Internal coupling cap | VRX-IN / 4 | VDD – (VRX-IN/ 4) | V | |
| TX OUTPUTS | ||||||
| VOD | Output Differential Voltage | drv_sel_vod[5:0] = 31, DEM, C0 = default | 825 | 1000 | 1200 | mVPP |
| drv_sel_vod[5:0] = 15, DEM, C0 = default | 400 | 525 | 675 | |||
| ΔVOD | Step Size for drv_sel_vod Control | Default DEM, and FIR settings | 32 | mVPP | ||
| ΔVODVT | Change in Output Differentential Voltage due to Change in Temperature and Voltage | <15 | mVPP | |||
| RRd | Output Differential Resistance | 100 | Ω | |||
| RRDZ | Output Resistance of Shutdown Termination Resistor | Resistor connects output pin to VDD | 50 | Ω | ||
| tr, tf | Output Rise/Fall Time | 20% - 80% using 8T Pattern, fir_sel_edge = default | 35 | ps | ||
| IOS | Output Short Circuit Current | Differential Driver Output pin short to GND drv_sel_vod = >4 |
–16 | mA | ||
| RETIMER JITTER SPECS | ||||||
| JTJ | Total Output Jitter | PRBS-7 pattern, measured to 1e-12 10.3125 Gbps data rate |
8.6 (89) |
ps (mUI) |
||
| PRBS-7 pattern, measured to 1e-12 8.625 Gbps data rate |
9.35 (80.6) |
|||||
| JRJ | Output Random Jitter | PRBS-7 pattern, measured to 1e-12 10.3125 Gbps data rate |
400 (4.125) |
fs-rms (mUI-rms) |
||
| PRBS-7 pattern, measured to 1e-12 8.625 Gbps data rate |
439 (3.78) |
|||||
| JDJ | Output Deterministic Jitter | PRBS-7 10.3125 Gbps data rate |
3.15 (33) |
ps (mUI) |
||
| PRBS-7 8.625 Gbps data rate |
3.35 (28.9) |
|||||
| JTRANS | Jitter Transfer | –6 | dB | |||
| JPEAK | Jitter Peaking | <0.1 | dB | |||
| BWPLL | PLL Bandwidth | Data Rate = 8.625 Gbps | 6.35 | MHz | ||
| Data Rate = 11.3 Gbps | 8.43 | |||||
| RETIMER TIMING SPECS | ||||||
| tD | Propagation Delay from Rx inputs to Tx outputs | Data Rate = 10.3125Gbps, No Cross Point |
480 | ps | ||
| Data Rate = 10.3125 Gbps, Cross Point enabled |
505 | ps | ||||
| tSK | Channel To Channel Skew | <80 | ps | |||
| RECOMMENDED REFERENCE CLOCK SPECS | ||||||
| REFf | Input Reference Clock Frequency | 25 | MHz | |||
| 125 | ||||||
| 312.5 | ||||||
| REFPPM | Reference Clock PPM Tolerance | –100 | 100 | PPM | ||
| REFTH | Reference Clock Input High Threshold | Differential mode | 100 | mV | ||
| REFTL | Reference Clock Input Low Threshold | Differential mode | –100 | mV | ||
| SMBus ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| VIH | Input High Level Voltage | SDA and SCL | 1.75 | VDDIO | V | |
| VIL | Input Low Level Voltage | SDA and SCL | GND | 0.7 | V | |
| CIN | Input Pin Capacitance | <5 | pF | |||
| VOL | Low Level Output Voltage | SDA and SCL VDDIO = 2.5V IOL = 2mA |
0.4 | V | ||
| RECOMMENDED SMBus SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| fSCL | SCL Clock Frequency | 10 | 100 | 400 | kHz | |
| tHD:DAT | Data Hold Time | 15 | ns | |||
| tSU:DAT | Data Setup Time | 170 | ns | |||
| RECOMMENDED JTAG SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| tTCK | TCK Clock Period | 100 | ns | |||
| tSU | TDI, TMI Setup Time to TCK | 50 | ns | |||
| tHD | TDI, TMS Hold Time to TCK | 50 | ns | |||
| tDLY | TCK Falling Edge to TDO | 50 | ns | |||
6 Detailed Description
6.1 Overview
The DS110DF1610 is a multi-rate, 16-channel retimer with integrated 4x4 cross point switches and receiver AC coupling capacitors. There is 1 cross point switch per 4 channels (quad). Each channel in the DS110DF1610 operates independently even if the cross point switch routing is enabled. All channels include a Continuous Time Linear Equalizer (CTLE), Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE), Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA), Clock and Data Recovery circuit (CDR) and a differential driver with a 3-tap transmit Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter. Each channel also has its own Eye Opening Monitor (EOM) and configurable Pseudo-Random Bit Sequence (PRBS) pattern checker and pattern generator that can be used for debug purposes.
The DS110DF1610 also supports IEEE 1149.1 (DC) and IEEE1149.6 (AC) JTAG. The DS110DF1610 is configurable through a single SMBus port. The DS110DF1610 can also act as an SMBus master to configure itself from an EEPROM.
The sections below describe the functionality of the various circuits and features within the DS110DF1610. For more information about how to program or operate these features please consult the DS110DF1610 Programming Guide.
6.2 Functional Block Diagrams
 Figure 1. DS110DF1610 Simplified Cross Point Diagram
Figure 1. DS110DF1610 Simplified Cross Point Diagram
 Figure 2. DS110DF1610 Simplified Data Path Diagram
Figure 2. DS110DF1610 Simplified Data Path Diagram
6.3 Feature Description
6.3.1 Device Data Path Operation
The DS110DF1610 data path consists of several key blocks as shown in Figure 2. These key circuits are:
- AC-coupled Receiver with Signal Detect
- CTLE
- Cross Point Switch
- DFE with VGA
- CDR
- Differential Driver with FIR Filter
6.3.1.1 AC-Coupled Receiver With Signal Detect
The differential receiver for each DS110DF1610 channel contains on chip AC coupling capacitors. The minimum bandwidth for this AC coupled receiver is 16kHz. The receiver also contains a signal detect circuit.
The signal detect circuit monitors the energy level on the receiver inputs and powers on or off the rest of the high speed data path if a signal is detected or not. By default, each channel allows the signal detect circuit to automatically power on or off the rest of the high speed data path depending on if a signal is present. Users can obtain manual control over the signal detect block through the SMBus channel registers. This can be useful if it is desired manually force channels to be disabled. For information on how to manually operate the signal detect circuit please see the DS110DF1610 Programming Guide and channel register 0x15 information.
6.3.1.2 CTLE
The CTLE in the DS110DF1610 is a fully adaptive equalizer with adjustable bandwidth and optional limiting stage. The CTLE is adapted to a boost setting according to a Figure of Merit (FOM) during the lock acquisition process. Once the CDR has locked, the CTLE boost level will be frozen until a manual re-adapt command is issued or until the CDR re-enters the lock acquisition state.
The CTLE consists of 4 stages, with each stage having 2-bit boost control. This allows for 256 different stage-boost combinations. The CTLE adaption algorithm allows the CTLE to adapt through 32 of these stage-boost combinations. These 32 stage-boost combinations comprise the EQ Table in the channel registers; see channel registers 0x40 through 0x5F. This EQ Table can be reprogrammed to support up to 32 of the 256 stage-boost settings. Users also have the option of limiting the EQ table length to any value between a minimum value of 1 and a maximum value of 32.
CTLE boost levels are determined by summing the boosts levels of the 4 stages. Different stage-boost combinations that sum to the same number will have approximately the same boost level, but will result in a different shape for the EQ transfer function (boost curve). The boost levels can be set between 6 dB and 38 dB.
The CTLE bandwidth can be adjusted through SMBus control to 3 different levels:
| CTLE BANDWIDTH SETTING | RESULTING BANDWIDTH (GHz) |
|---|---|
| Full Rate | 9 |
| Mid Rate | 7 |
| Half Rate | 5 |
The fourth stage in the CTLE can be programmed through the SMBus interface to become a limiting stage rather than a linear stage. This is useful in some applications, but it should not be typically used in combination with the DFE.
6.3.1.3 Cross Point Switch
Each quad has a 4x4 non-blocking analog cross point switch. This allows for full switching or broadcasting of data between any input within the quad to any output within the quad. Since the cross point switch is an analog implementation, all of the channels are allowed to operate asynchronously. The analog implementation also minimizes added latency through the device.
As shown in Figure 1, the cross point switch connections for each quad are located between CTLE and DFE in each channel.
The cross point switch consists of consists of 4 sets of MUXs and buffers. In each channel there is a local buffer and a multi-drive buffer. The local buffer transmits data from the CTLE to the DFE of the same channel. The multi drive buffer transmits data from the CTLE to the DFE(s) of other channels within the quad. Each channel has two MUXs:
- Data path mux – Selects whether to get data from the local buffer or from other channel’s multi-driver buffer
- Control bus mux – Selects where the signal detect and EQ control bus should be connected. This setting should mirror the data path mux setting. Note, when an EQ is connected to another channel’s CDR the EQ becomes associated with that CDR’s register set. For example, if the cross point was configured to do point to point switching from the inputs of channel 0 to the output of channel 1 and the inputs of channel 1 to the outputs of channel 0, the EQ physically located at the pins for inputs of channel 0 would be accessible through the register set of channel 1.
A simplified diagram of the cross point switch is shown in Figure 3.
 Figure 3. Cross Point Switch Diagram
Figure 3. Cross Point Switch Diagram
In a typical point-to-point switching application users must configure the following for each channel:
- Control bus mux setting (ch reg 0x9B)
- Data path mux setting (ch reg 0x96)
- Enabling/Disabling the local or multi-drive buffers for each channel (ch reg 0x96)
- Cross point enable bit (ch reg 0x96)
- Perform a CDR reset and reset release (ch reg 0x0A)
Note, when using the cross point switch the local and multi-drive buffer should both be enabled regardless of the desired configuration.
The cross point switch can also be used to replicate data or perform a broadcast function. The options for this type of configuration include:
- 1:2 – any channel input to any 2 channels output
- 1:3 – any channel input to any 3 channels output
- 1:4 – any channel input to all 4 channels output
When the cross point switch is configured to replicate/broadcast data a master must be assigned during the cross point configuration. The master channel will have control over the CTLE adaption. All of the slave channels will be able to adapt their own DFE, but will not have control to adapt the CTLE. In this type of configuration there must be 1 channel assigned as a master. All other channels in the broadcast network must be assigned as slaves. There cannot be more than one master channel in a broadcast network.
In a typical data replication/broadcast application users must configure the following for each channel:
- Control bus mux setting (ch reg 0x9B)
- Data path mux setting (ch reg 0x96)
- Enabling/Disabling the local or multi-drive buffers for each channel (ch reg 0x96)
- Master/Slave assignment (ch reg 0x96)
- Cross point enable bit (ch reg 0x96)
- Perform a CDR reset and reset release (ch reg 0x0A)
6.3.1.4 DFE With VGA
A 5-tap DFE with a VGA can be enabled within the data path of each channel to assist with reducing the effects of cross talk, reflections, or post cursor inter-symbol interference (ISI). The DFE must be manually enabled, regardless of the selected adapt mode. Once the DFE has been enabled it can be configured to adapt only during lock acquisition or to adapt continuously. The DFE can also be manually configured to specified tap polarities and tap weights. However, when the DFE is configured manually the DFE auto-adaption should be disabled.
The DFE taps are all feedback taps with 1UI spacing. Each tap has a specified boost weight range and polarity bit.
| DFE PARAMETER | VALUE (mV) |
|---|---|
| Tap 1 Weight Range | 0 – 224 |
| Tap 2-5 Weight Range | 0 – 112 |
| Tap Weight Step Size | 7 |
A VGA is located at the input to the DFE block. The VGA has 2-bit control to allow for 4 levels of boost. The VGA can be used to assist in the recovery of extremely small signals. Note that the VGA is integrated within the DFE, so in order to use the VGA the DFE must be enabled.
6.3.1.5 Clock and Data Recovery
The CDR block consists of a Phase Locked Loop (PLL), reference clock based PPM counter, Input and Output Data Multiplexers (mux) and circuits to monitor single bit transitions and detect false locking. The CDR sampling position is fixed at the 0.5UI location for each bit.
By default, the equalized data is fed into the CDR for clock and data recovery. This data is then output to FIR filter and differential driver. Users can configure the CDR data to route the recovered clock and data to the PRBS checker. Users also have the option of configuring the output of the CDR to send raw non-retimed data, or data from the pattern generator.
The CDR requires the following in order to be properly configured:
- Input reference clock with proper reference clock divider setting to run the PPM counter.
- Expected data rates must be programmed into the CDR either through the rate/sub-rate table or entered manually with the corrected divider settings.
6.3.1.6 Reference Clock
The reference clock is not part of the CDR’s PLL. The reference clock is connected only to the PPM counter for each CDR. The PPM counter constrains the allowable lock ranges of the CDR according to the programmed values in the rate/sub-rate table or the manually entered data rates.
The reference clock can be set to any of the 3 allowable frequencies independant of the data rate of the high speed channel. The input reference clock can be single-ended or differential for the 25 MHz or 125 MHz settings. If the 312.5 MHz setting is used, the input signaling type should be differential. The reference clock can be output through the CLK_MON pins for observation or daisy chaining the reference clock to the next device. If the CLK_MON port is used for daisy chaining then the output frequency should be set to 25 MHz.
If the reference clock port is configured to operate in single-ended mode, the 2.5V LVCMOS clock signal should be applied to the REF_CLK_P pin. In this configuration the REF_CLK_N pin should be floated (N/C). In this case the LVCMOS clock signal should be DC coupled into the REF_CLK_P pin.
Configuring the reference clock frequency is done in share register 0x02[6:5]. Configuring the reference clock input port for single-ended or differential mode operation is done in share register 0x0B[4]. Enabling or disabling the CLK_MON port is done in share reg 0x0A[0]. Selecting the divided (25 MHz) or undivided (input frequency) is done in share register 0x04[7].
Table 1. Reference Clock Configurations
| INPUT FREQUENCY | INPUT CONFIGURATION | DEFAULT CLK_MON FREQUENCY | CLK_MON FREQUENCY FOR DAISY CHAINING |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 MHz | Single-ended or Differential | 25 MHz | 25 MHz |
| 125 MHz | Single-ended or Differential | 125 MHz | 25 MHz |
| 312.5 MHz | Differential | 312.5 MHz | 25 MHz |
6.3.1.7 Differential Driver With FIR Filter
The DS110DF1610 output driver can be manually powered off through SMBus register control. The outputs of the DS110DF1610 also have optional output termination resistors that can be enabled when the driver is manually powered down. These termination resistors can help reduce the effects of cross talk in high speed systems.
The DS110DF1610 uses a 3-tap FIR filter to assist with transmit equalization. The FIR filter consists of a pre cursor tap, a main cursor tap and a post cursor tap. Each tap has a polarity bit and 64 available levels. By default, the main cursor tap is set to a positive polarity, while the pre cursor and post cursor taps are set to a negative polarity. Users can invert the polarity of all 3 FIR taps to invert the polarity of the output data.
6.3.1.7.1 Setting the Output VOD
Users can control the output differential voltage (VOD) of the driver by manipulating the drv_sel_vod bits, DEM bits, and FIR main cursor tap. The table below shows various settings for VOD settings ranging from 150mVPP to 1200 mVPP. Using the FIR, DEM and drv_sel_vod bits is the recommended method for configuring the output VOD for the best signal integrity. The user also has the option of using only the drv_sel_vod bits to configure the output VOD, which is sometimes useful for slower datarates. If the FIR taps and DEM bits are set to 0x0, the drv_sel_vod bits can be used to set the output VOD from 50mVPP to 1400mVPP.
| VOD (mVPP) | DEM SETTING | DRV_SEL_VOD SETTING | FIR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | MAIN | POST | |||
| 1200 | 0 | 31 | 0 | 56 | -4 |
| 1150 | 0 | 31 | 0 | 52 | -4 |
| 1100 | 0 | 31 | 0 | 49 | -4 |
| 1050 | 0 | 31 | 0 | 45 | -4 |
| 1000 | 2 | 31 | 0 | 54 | -3 |
| 950 | 3 | 31 | 0 | 56 | -2 |
| 900 | 3 | 31 | 0 | 52 | -2 |
| 850 | 3 | 31 | 0 | 46 | -1 |
| 800 | 3 | 31 | 0 | 42 | -1 |
| 750 | 3 | 25 | 0 | 56 | -3 |
| 700 | 3 | 25 | 0 | 46 | -2 |
| 650 | 3 | 25 | 0 | 40 | -1 |
| 600 | 3 | 21 | 0 | 50 | -2 |
| 550 | 3 | 19 | 0 | 50 | -3 |
| 500 | 3 | 17 | 0 | 52 | -3 |
| 450 | 3 | 15 | 0 | 50 | -3 |
| 400 | 3 | 13 | 0 | 52 | -3 |
| 350 | 3 | 12 | 0 | 51 | -3 |
| 300 | 3 | 10 | 0 | 51 | -3 |
| 250 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 55 | -3 |
| 200 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 56 | -3 |
| 150 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 57 | -3 |
6.3.1.7.2 Output Driver Polarity Inversion
In some cases it may be necessary to invert the polarity of the data transmitted from the retimer. To invert the polarity of the data read back the FIR polarity settings for the pre, main and post cursor and then invert these bits.
6.3.1.7.3 Driver Output Rise/Fall Time
In some applications, a longer rise/fall time for the output signal is desired. This can reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) generated by fast switching waveforms. This is necessary in some applications for regulatory compliance. In others, it can reduce the crosstalk in the system.
The DS110DF1610 can be configured to operate with a nominal rise/fall time corresponding to the maximum slew rate of the output drivers into the load capacitance. Alternatively, the DS110DF1610 can be configured to operate with a slightly greater rise/fall time if desired. By default the DS110DF1610 is configured to use the fastest edge rate.
6.3.2 Debug Features
6.3.2.1 Pattern Generator
Each channel in the DS110DF1610 can be configured to generate a 16-bit user defined data pattern or a pseudo random bit sequence (PRBS). The user defined pattern can also be set to automatically invert every other 16-bit symbol for DC balancing purposes. The DS110DF1610 pattern generator supports the following PRBS sequences:
- PRBS – 7
- PRBS – 9
- PRBS – 15
- PRBS – 31
6.3.2.2 Pattern Checker
The pattern checker can be manually set to lock for specific PRBS sequences and polarities or it can be set to automatically detect the incoming pattern and polarity. If the pattern checker is meant to work with a user defined pattern, then it must be programmed to search for that exact pattern.
The pattern checker consists of a 47-bit bit counter and an 11-bit error counter. In order to read out the bit and error counters, the pattern checker must first be frozen. Continuous operation with simultaneous read out of the bit and error counters is not possible in this implementation.
6.3.2.3 Eye Opening Monitor
The DS110DF1610’s Eye Opening Monitor (EOM) can be used for 2 functions:
- Horizontal Eye Opening (HEO) and Vertical Eye Opening (VEO) measurement
- Full Eye Diagram Capture
The HEO measurement is made at the 0V crossing and is read in channel register 0x27. The VEO measurement is made at the 0.5 UI mark and is read in channel register 0x28. The HEO and VEO registers can be read from channel registers 0x27 and 0x28 at any time while the CDR is locked. The following equations are used to convert the contents of channel registers 0x27 and 0x28 into their appropriate units:
- HEO [UI] = ch reg 0x27 ÷ 64
- VEO [mV] = ch reg 0x28 x 3.125
A full eye diagram capture can be performed when the CDR is locked. The eye diagram is constructed within a 64 x 64 array, where each cell in the matrix consists of an 16-bit word. Users can manually adjust the vertical scaling of the EOM or allow the state machine to control the scaling which is the default option. The horizontal scaling controlled by the state machine and is always directly proportional to the data rate.
When a full eye diagram plot is captured, the retimer will shift out 4 16-bit words of junk data that should be discarded followed by 4096 16-bit words that make up the 64 x 64 eye plot. The first actual word of the eye plot from the retimer is for (X, Y) position (0,0). Each time the eye plot data is read out the voltage position is incremented. Once the voltage position has incremented to position 63, the next read will cause the voltage position to reset to 0 and the phase position to increment. This process will continue until the entire 64 x 64 matrix is read out. Figure 4 shows the EOM read out sequence overlaid on top of a simple eye opening plot. In this plot any hits are shown in green. This type of plot is helpful for quickly visualizing the HEO and VEO. Users can apply different algorithms to the output data to plot density or color gradients to the output data.
 Figure 4. EOM Full Eye Capture Readout
Figure 4. EOM Full Eye Capture Readout
To manually control the EOM vertical range, remove scaling control from the state machine then select the desired range:
- Channel Reg 0x2C[6] → 0
- See table:
| CH REG 0x11[7:6] VALUE | EOM VERTICAL RANGE [mV] |
|---|---|
| 2’b00 | ±100 |
| 2'b01 | ±200 |
| 2'b10 | ±300 |
| 2'b11 | ±400 |
The EOM operates as an under-sampled circuit. This allows the EOM to be useful in identifying over equalization, ringing and other gross signal conditioning issues. However, the EOM cannot be correlated to a bit error rate.
The EOM can be accessed in two ways to read out the entire eye plot:
- Multi-byte reads can be used such that data is repeatedly latched out from channel register 0x25.
- Or single byte reads. With single byte reads, the MSB are located in register 0x25 and the LSB are located in register 0x26. In this mode, the device must be addressed each time a new byte is read.
To perform a full eye capture with the EOM, follow these steps within the desired channel register set:
| STEP | REGISTER [BITS] |
VALUE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0x67[5] | 0 | Disable lock EOM lock monitoring | |
| 2 | 0x2C[6] 0x11[7:6] |
0 2'b-- |
Set the desired EOM vertical range | |
| 3 | 0x11[5] | 0 | Power on the EOM | |
| 4 | 0x24[7] | 1 | Enable fast EOM | |
| 5 | 0x24[0] 0x25 0x26 |
1 | Begin read out of the 64 x 64 array, discard first 4 words Ch reg 0x24[0] is self clearing. 0x25 is the MSB of the 16-bit word 0x26 is the LSB of the 16-bit word |
|
| 6 | 0x25 0x26 |
Continue reading information until the 64 x 64 array is complete. | ||
| 7 | 0x67[5] 0x2C[6] 0x11[5] 0x24[7,1] |
1 1 1 0 |
Return the EOM to its original state. Undo steps 1-4 | |
6.3.2.4 Interrupt Signals
The DS110DF1610 can be configured to report different events as interrupt signals. These interrupt signals do not impact the operation of the device, but merely report that the selected event has occurred. The interrupt bits in the register sets are all sticky bits. This means that when an event triggers an interrupt the status bit for that interrupt is set to logic HIGH. This interrupt status bit will remain at logic HIGH until the bit has been read. Once the bit has been read it will be automatically cleared, which allows for new interrupts to be detected. The DS110DF1610 will report the occurrence of an interrupt through the INTERR_IO pin. The INTERR_IO pin is an open drain output that will pull the line low when an interrupt signal is triggered.
Note that all available interrupts are disabled by default. Users must activate the various interrupts before they can be used.
The interrupts available in the DS110DF1610 are:
- CDR loss of lock
- CDR locked
- Signal detect loss
- Signal detected
- PRBS pattern generator lock up
- PRBS pattern checker bit error detected
- HEO/VEO threshold violation
When an interrupt occurs, share register 0x08 and 0x09 report which channel generated the interrupt request. Users can then select the channel(s) that generated the interrupt request and service the interrupt by reading the appropriate interrupt status bits in the corresponding channel registers.
6.3.3 Other Features
6.3.3.1 Lock Sequencer
A channel will temporarily consume a higher amount of power while its CDR is attempting to lock, compared to when the CDR is locked. In order to reduce the impact of a power consumption spike when data is transmitted to a DS110DF1610, the internal lock sequencer will limit the number of active channels that are simultaneously allowed to attempt to lock.
The lock sequencer grants tokens to various channels that have detected a signal at the input to the CTLE. Once a channel has achieved CDR lock, it returns its token to the lock sequencer. The lock sequencer will distribute any available tokens on a first come first serve basis to any channel that is allowed to attempt lock and that has detected a valid signal.
The lock sequencer is configurable in the share registers. Users can control which channels are allowed to attempt lock when a signal is present by configuring share registers 0x0F and 0x10. Users can also limit the number of channels that are allowed to simultaneously attempt to lock by configuring share register 0x05.
RESET_IO Pin
The RESET_IO pin in the DS110DF1610 emulates a power on reset (POR). This type of reset re-initializes the entire device including the SMBus address strap settings and restores both share and channel register defaults.
The RESET_IO pin triggers a reset on the rising edge of the signal. It is not recommended to hold the RESET_IO pin at a logic LOW state for an extended period of time. RESET_IO should be held at logic HIGH during power on. After power on, the RESET_IO pin should be pulsed low for a minimum of 10 µs to perform a reset.
6.4 Device Functional Modes
6.4.1 SMBus Slave Mode
6.4.1.1 SDA and SDC
In both SMBus master and SMBus slave mode, the DS110DF1610 is configured using the SMBus. The SMBus consists of two lines, the SDA or serial data line and the SCL or serial clock line. In the DS110DF1610 these pins are 3.3V tolerant. The SDA and SCL lines are both open-drain. They require a pull-up resistor to a supply voltage, which may be either 2.5V or 3.3V. A pull-up resistor in the 2KΩ to 5KΩ range will provide reliable SMBus operation.
6.4.1.2 Address Line
In either SMBus mode the DS110DF1610 must be assigned an SMBus address. A unique address should be assigned to each device on the SMBus.
The DS110DF1610 can be configured to respond to one of the sixteen SMBus addresses listed in the table below. GPIO1 and GPIO0 are configured to be four level inputs immediately after the device powers on. Logic 0 can be set by tying the pin to ground through a ≤1kΩ resistor. Logic R is set by tying the pin to ground through a 20kΩ resistor. Logic F is set by floating the pin. Logic 1 is set by tying the pin to VCC = 2.5V through a ≤1kΩ resistor.
| ADDR1(GPIO1) (PIN D5) | ADDR0(GPIO0) (PIN B6) | 7-BIT ADDRESS | 8-BIT WRITE ADDRESS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 7’h18 | 0x30 |
| 0 | R | 7’h19 | 0x32 |
| 0 | F | 7’h1A | 0x34 |
| 0 | 1 | 7’h1B | 0x36 |
| R | 0 | 7’h1C | 0x38 |
| R | R | 7’h1D | 0x3A |
| R | F | 7’h1E | 0x3C |
| R | 1 | 7’h1F | 0x3E |
| F | 0 | 7’h20 | 0x40 |
| F | R | 7’h21 | 0x42 |
| F | F | 7’h22 | 0x44 |
| F | 1 | 7’h23 | 0x46 |
| 1 | 0 | 7’h24 | 0x48 |
| 1 | R | 7’h25 | 0x4A |
| 1 | F | 7’h26 | 0x4C |
| 1 | 1 | 7’h27 | 0x4E |
When an SMBus device is addressed for reading or writing a bit is appended to the address a the least significant bit space. This bit is set to 0 for a write or to 1 for a read.
6.4.1.3 Device Configuration in SMBus Slave Mode
The configurable settings of the DS110DF1610 may be set independently for each channel at any time after power up using the SMBus. A register write is accomplished when the controller sends a START condition on the SMBus followed by the Write address of the DS110DF1610 to be configured. After sending the Write address of the DS110DF1610, the controller sends the register address byte followed by the register data byte. The DS110DF1610 acknowledges each byte written to the controller according to the data link protocol of the SMBus Version 2.0 Specification. See this specification for additional information on the operation of the SMBus.
There are 3 types of device registers in the DS110DF1610. These are the global registers, shared registers and the channel registers. The global registers are programmed to access the various channel registers or the shared registers. The shared registers control or allow observation of settings which affect the operation of all channels of the DS110DF1610 at the greater device level.
The channel registers are used to set all the configuration settings of the DS110DF1610. They provide independent control for each channel of the DS110DF1610 for all the settable device characteristics. Any registers not described in the tables that follow should be treated as reserved. The user should not try to write new values to these registers. The user-accessible registers described in the tables that follow provide a complete capability for customizing the operation of the DS110DF1610 on a channel-by-channel basis.
6.5 Programming
6.5.1 Bit Fields in the Register Set
Many of the registers in the DS110DF1610 are divided into bit fields. This allows a single register to serve multiple purposes, which may be unrelated. Often configuring the DS110DF1610 requires writing a bit field that makes up only part of a register value while leaving the remainder of the register value unchanged.
The procedure for accomplishing this is to read in the current value of the register to be written, modify only the desired bits in this value, and write the modified value back to the register. Of course, if the entire register is to be changed, rather than just a bit field within the register, it is not necessary to read in the current value of the register first. In all the register configuration procedures described in the following sections, this procedure should be kept in mind. In some cases, the entire register is to be modified. When only a part of the register is to be changed, however, the procedure described above should be used.
6.5.2 Writing to and Reading from the Global/Shared/Channel Registers
Global registers can be accessed from the shared register page and also the channel register pages. There are three global registers in the DS110DF1610:
- Register 0xFC
- Register 0xFD
- Register 0xFF
Registers 0xFC and 0xFD are used to select the channel registers to be written to. To select a channel write a 1 to its corresponding bit in these global registers. Note more than one channel may be written to by setting multiple bits in registers 0xFC and 0xFD. However, when performing an SMBus read transaction only one channel can be selected at a time. If multiple channels are selected when attempting to perform an SMBus read, the device will return 0x00.
| GLOBAL REGISTER | BIT | DESCRIPTION | CDR/TX PIN ASSIGNMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0xFD | 7 | Channel 15– Quad 3 Channel 3– Cross Point Ch D | TX_7B |
| 6 | Channel 14– Quad 3 Channel 2 – Cross Point Ch C | TX_7A | |
| 5 | Channel 13– Quad 3 Channel 1 – Cross Point Ch B | TX_6B | |
| 4 | Channel 12– Quad 3 Channel 0 – Cross Point Ch A | TX_6A | |
| 3 | Channel 11– Quad 2 Channel 3– Cross Point Ch D | TX_5B | |
| 2 | Channel 10– Quad 2 Channel 2 – Cross Point Ch C | TX_5A | |
| 1 | Channel 9– Quad 2 Channel 1 – Cross Point Ch B | TX_4B | |
| 0 | Channel 8– Quad 2 Channel 0 – Cross Point Ch A | TX_4A | |
| 0xFC | 7 | Channel 7– Quad 1 Channel 3– Cross Point Ch D | TX_3B |
| 6 | Channel 6– Quad 1 Channel 2 – Cross Point Ch C | TX_3A | |
| 5 | Channel 5– Quad 1 Channel 1 – Cross Point Ch B | TX_2B | |
| 4 | Channel 4– Quad 1 Channel 0 – Cross Point Ch A | TX_2A | |
| 3 | Channel 3– Quad 0 Channel 3 – Cross Point Ch D | TX_1B | |
| 2 | Channel 2– Quad 0 Channel 2 – Cross Point Ch C | TX_1A | |
| 1 | Channel 1– Quad 0 Channel 1 – Cross Point Ch B | TX_0B | |
| 0 | Channel 0 – Quad 0 Channel 0 – Cross Point Ch A | TX_0A |
Register 0xFF is used select the shared register page or the channel register page for the channels selected in registers 0xFC and 0xFD.
| GLOBAL REGISTER | BITS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0xFF | 0 | 1: Select Channel Registers 0: Select Share Registers |
6.6 Register Maps
6.6.1 Shared and Channel Registers
Table 2. Shared Registers
| ADDRESS (HEX) |
BITS | DEFAULT VALUE (HEX) |
MODE | EEPROM | FIELD NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7 | 0 | R | N | SMBus_Addr3 | SMBus Address Strapped 7-bit addres is 0x18 + SMBus_Addr[3:0] |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | SMBus_Addr2 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | SMBus_Addr1 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | SMBus_Addr0 | ||
| 3:0 | 0 | RESERVED | ||||
| 1 | 7 | 0 | R | N | Version2 | Device version |
| 6 | 1 | R | N | Version1 | ||
| 5 | 1 | R | N | Version0 | ||
| 4 | 1 | R | N | Device_ID4 | Device ID code for DS110DF1610 | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | Device_ID3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | Device_ID2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | Device_ID1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | Device_ID0 | ||
| 2 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | REFCLK_SEL1 | Sets the REFCLK input frequency 00: 25 MHz 01: 125 MHz 10: 312.5MHz 11: Reserved |
|
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | REFCLK_SEL0 | ||
| 4:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 3 | 7:0 | 0 | N | RESERVED | ||
| 4 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_REF_CLK_DIG_OUT_ANA | 1: Selects the divided clock 0: Selects the undivided clock |
| 6 | 0 | RWSC | N | RST_SMB_REGS | 1: Resets share registers | |
| 5 | 0 | RWSC | N | RST_SMB_MAS | 1: Resets SMBus Master controller | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | MR_DIS_LOCK_SEQR | 1: Disables the lock sequencer circuit 0: Normal operation, lock sequencer is enabled |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 5 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | CRC_EN | 1: Slave CRC Trigger | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 4 | 1 | R | N | EEPROM_READ_DONE | This bit is set to 1 when read from EEPROM is done | |
| 3 | 1 | RW | N | LIMIT_CONC_LOCKS3 | Sets max number of channels that can lock at any given time, defaults to 8 channels. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | LIMIT_CONC_LOCKS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | LIMIT_CONC_LOCKS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | LIMIT_CONC_LOCKS0 | ||
| 6 | 7:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 7 | 7:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 8 | 7 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q1C3 | Interrupt from quad 1, ch 3 |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q1C2 | Interrupt from quad 1, ch 2 | |
| 5 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q1C1 | Interrupt from quad 1, ch 1 | |
| 4 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q1C0 | Interrupt from quad 1, ch 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q0C3 | Interrupt from quad 0, ch 3 | |
| 2 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q0C2 | Interrupt from quad 0, ch 2 | |
| 1 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q0C1 | Interrupt from quad 0, ch 1 | |
| 0 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q0C0 | Interrupt from quad 0, ch 0 | |
| 9 | 7 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q3C3 | Interrupt from quad 3, ch 3 |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q3C2 | Interrupt from quad 3, ch 2 | |
| 5 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q3C1 | Interrupt from quad 3, ch 1 | |
| 4 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q3C0 | Interrupt from quad 3, ch 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q2C3 | Interrupt from quad 2, ch 3 | |
| 2 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q2C2 | Interrupt from quad 2, ch 2 | |
| 1 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q2C1 | Interrupt from quad 2, ch 1 | |
| 0 | 0 | R | N | INT_Q2C0 | Interrupt from quad 2, ch 0 | |
| A | 7 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_CLK_FROM_DIG | 1: selects ref clk from digital to transmit out 0: selects ref clk from analog loop chain to transmit out. All channels’ analog blocks must have ref clk loop through enabled to transmit ref clk out of device |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_REFCLK_TX_VCM1 | Sets the output common-mode voltage: 00: 800mV 01: 1000mV 10: 1200mV 11: Tracks VCC, bias at 1.2V |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_REFCLK_TX_VCM0 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_REFCLK_TX_VOD1 | Sets the output differential peak-to-peak voltage: 00: 400mV 01: 533mV 10: 667mV 11: 800mV |
|
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_REFCLK_TX_VOD0 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_REFCLK_TX_SCP | 1:disable 0:Ref-clk TX short-circuit protection |
|
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | DIS_REFCLK_OUT | 1: Disable REFCLK_OUT (TRI-STATE) 0: Enable REFCLK_OUT |
|
| B | 7 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | REFCLK_DET | This bit is set to 1 when refclk has been detected | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | REFCLK_SINGLE_END | 1: Reference clock input port configured as single-ended input 0: Normal operation, reference clock input port configured as differential input |
|
| 3:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| C | 7:3 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_RST | Resets SAR ADC | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_EN | Enables SAR ADC | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| D | 7 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_OUT7 | 10-bit SAR ADC Output[7:0] |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_OUT6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_OUT5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_OUT4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_OUT3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_OUT2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_OUT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | SAR_ADC_OUT0 | ||
| E | 7:2 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 1 | 0 | R | N | SAR_ADC_OUT9 | 10-bit SAR ADC Output[9:8] | |
| 0 | 0 | R | N | SAR_ADC_OUT8 | ||
| F | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK15 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK14 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK13 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK12 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK11 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK10 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK9 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK8 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 10 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK7 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK6 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK5 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK4 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK3 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK2 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK1 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_CH_LOCK0 | 1: Allows channel to lock 0: Channel not allowed to lock |
|
| 11 | 7:6 | 0 | R | N | EEPRM_LOAD_STATUS | 11: Not valid 10: EEPROM load completed successfully 01: EEPROM load failed after 64 attempts 00: EEPROM load in progress |
| 5 | 0 | R | N | EEPRM_ATMPT5 | Number of attempts made to load EEPROM image | |
| 4 | 0 | R | N | EEPRM_ATMPT4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | EEPRM_ATMPT3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | EEPRM_ATMPT2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | EEPRM_ATMPT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | EEPRM_ATMPT0 | ||
| FC | 7 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 7– Quad 1 Channel 3 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 7 |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 6– Quad 1 Channel 2 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 6 |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 5– Quad 1 Channel 1 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 5 |
|
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 4– Quad 1 Channel 0 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 4 |
|
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 3– Quad 0 Channel 3 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 3 |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 2– Quad 0 Channel 2 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 2 |
|
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 1– Quad 0 Channel 1 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 1 |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 0– Quad 0 Channel 0 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 0 |
|
| FD | 7 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 15– Quad 3 Channel 3 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 15 |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 14– Quad 3 Channel 2 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 14 |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 13– Quad 3 Channel 1 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 13 |
|
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 12– Quad 3 Channel 0 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 12 |
|
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 11– Quad 2 Channel 3 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 11 |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 10– Quad 2 Channel 2 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 10 |
|
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 9– Quad 2 Channel 1 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 9 |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | Channel 8– Quad 2 Channel 0 | 1: Enables SMBus access to channel 8 |
|
| FE | 7 | 0 | R | N | VENDOR_ID7 | |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | VENDOR_ID6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | VENDOR_ID5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | VENDOR_ID4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | VENDOR_ID3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | VENDOR_ID2 | ||
| 1 | 1 | R | N | VENDOR_ID1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | R | N | VENDOR_ID0 | ||
| FF | 7:2 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | WRITE_ALL_CH | 1: Write to all channels as if they are the same, but only allows to read back from a single channel specified in 0xFC and 0xFD. Note: EN_CH_SMB must be set to 1, or else this function is invalid. |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | EN_CH_SMB | 1: Enables SMBus access to the channels specified in 0xFC and 0xFD. 0: Enables SMBus access to the shared registers |
Table 3. Channel Registers, 0 to 1F
| ADDRESS (HEX) |
BITS | DEFAULT VALUE (HEX) |
MODE | EEPROM | FIELD NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | CLK_CORE_DIS | 1: Disables the primary digital clock, resets all state machines 0: Normal operation |
| 6:4 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | RST_CORE | 1: Reset core state machine 0: Normal Operation |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | RST_REGS | 1: Resets channel registers, restores default values 0: Normal Operation |
|
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | RST_VCO | 1: Resets PPM counter, EOM counter, FLD counter, SBT counter 0: Normal Operation |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | RST_REFCLK | 1: Reset PPM counter 0: Normal Operation |
|
| 1 | 7 | 0 | R | N | SIG_DET | 1: Signal is present on high speed inputs 0: No signal is detected on high speed inputs |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | POL_INV_DET | 1: PRBS checker detected polarity inversion 0: No pattern inversion detected | |
| 5 | 0 | R | N | CDR_LOCK_LOSS_INT | 1: indicates loss of CDR lock after having acquired it. Bit clears on read. |
|
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_SEQ_DET3 | 1: Indicates if the PRBS-31 sequence is locked | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_SEQ_DET2 | 1: Indicates if the PRBS-15 sequence is locked | |
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_SEQ_DET1 | 1: Indicates if the PRBS-9 sequence is locked | |
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_SEQ_DET0 | 1: Indicates if the PRBS-7 sequence is locked | |
| 0 | 0 | R | N | SIG_DET_LOSS_INT | Loss of signal indicator. Bit is set once signal is acquired and then lost. |
|
| 2 | 7:0 | 0 | R | N | MULTI_PURP_STATUS | Register configured by setting channel register 0x0C[7:4] |
| 3 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BST0[1] | This register can be used to force an EQ boost setting if used in conjuntion with channel register 0x2D[3] |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BST3[0] | ||
| 4 | 7:0 | 0x01 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 5 | 7:0 | 0x01 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 6 | 7:0 | 0x01 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 7 | 7:0 | 0x01 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 8 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_RNG_P2 | Positive cap dac range modifier |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_RNG_P1 | Positive cap dac range modifier | |
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_RNG_P0 | Positive cap dac range modifier | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_START4 | Starting VCO Cap Dac Setting 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_START3 | Starting VCO Cap Dac Setting 0 | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_START2 | Starting VCO Cap Dac Setting 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_START1 | Starting VCO Cap Dac Setting 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_START0 | Starting VCO Cap Dac Setting 0 | |
| 9 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_VCO_CAP_OV | Enable bit to override cap_cnt with value in register 0x0B[4:0] |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | SET_CP_LVL_LPF_OV | Enable bit to override lpf_dac_val with value in register 0x1F[4:0] | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | BYPASS_PFD_OV | Enable bit to override sel_retimed_loopthru and sel_raw_loopthru with values in reg 0x1E[7:5] | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_FD_PD_VCO_PDIQ_OV | Enable bit to override en_fd, pd_pd, pd_vco, pd_pdiq with reg 0x1E[0], reg 0x1E[2], reg 0x1C[0], reg 0x1C[1] | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_PD_CP_OV | Enable bit to override pd_fd_cp and pd_pd_cp with value in reg 0x1B[1:0] | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_OV | Enable bit to override divsel with value in reg 0x18[6:4] 1: Override enable 0: Normal operation |
|
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_FLD_OV | Enable to override pd_fld with value in reg 0x1E[1] | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | PFD_LOCK_ MODE_SM |
Enable fd in lock state | |
| A | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | SBT_EN | Enable bit to override sbt_en with value in reg 0x1D[7] |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_IDAC_PD_CP_OV EN_IDAC_FD_CP_OV |
Enable bit to overridephase detector charge pump settings with reg 0x1C[7:5] Enable bit to override frequency detector charge pump settings with reg 0x1C[4:2] |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | DAC_LPF_HIGH_ PHASE_OV DAC_LPF_LOW_ PHASE_OV |
Enable bit to override loop filter comparator trip voltage with reg 0x16[7:0] | |
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EN150_LPF_OV | Enable bit to override en150_lpf with value in reg 0x1F[6] | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | CDR_RESET_OV | Enable bit to override CDR reset with reg 0x0A[2] | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | CDR_RESET_SM | 1: CDR is put into reset 0: normal CDR operation |
|
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | CDR_LOCK_OV | Enable CDR lock signal override with reg 0x0A[0] | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | CDR_LOCK | CDR lock signal override bit | |
| B | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_RNG_N2 | Negative cap dac range modifier |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_RNG_N1 | Negative cap dac range modifier | |
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_RNG_N0 | Negative cap dac range modifier | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | CAP_DAC_START1[4] | Starting VCO cap dac setting 1 | |
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | CAP_DAC_START1[3] | Starting VCO cap dac setting 1 | |
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | CAP_DAC_START1[2] | Starting VCO cap dac setting 1 | |
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | CAP_DAC_START1[1] | Starting VCO cap dac setting 1 | |
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | CAP_DAC_START1[0] | Starting VCO cap dac setting 1 | |
| C | 7:4 | 0 | RW | N | STATUS_CONTROL | These bits repurpose channel register 0x02 to report different status signals |
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | SINGLE_BIT_LIMIT_CHECK_ON | 1: Normal operation, device checks for single bit transitions as a gate to achieving CDR lock | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_IDAC_FD_CP3 | Frequency detector charge pump setting bit 3 (MSB) LSB located in channel register 0x1C |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_IDAC_PD_CP3 | Phase detector charge pump setting bit 3 (MSB) LSB located in channel register 0x1C |
|
| D | 7 | 1 | RW | N | DES_PD | 1: Deserializer is powered down 0: Deserializer is enabled |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | DRV_SEL_VOD4 | Used in conjunction with 0x2D[2:0] to control the VOD levels of the high speed drivers | |
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | DRV_SEL_VOD3 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_RLOAD_MAX | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_SEL_NEG_GM | ||
| 1:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| E | 7:0 | 0x93 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| F | 7:0 | 0x69 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 10 | 7:0 | 0x3A | RW | Y | RESERVED | |
| 11 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_SEL_VRANGE1 | Manually set the EOM vertical range, used with channel register 0x2C[6] 00: ±100 mV 01: ±200 mV 10: ±300 mV 11: ±400 mV |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_SEL_VRANGE1 | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EOM_PD | 1: Normal operation | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_TAP2_POL | Bit forces DFE tap 2 polarity, manual DFE operation required to take effect | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_TAP3_POL | Bit forces DFE tap 3 polarity, manual DFE operation required to take effect | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_TAP4_POL | Bit forces DFE tap 4 polarity, manual DFE operation required to take effect | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_TAP5_POL | Bit forces DFE tap 5 polarity, manual DFE operation required to take effect | |
| 12 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_TAP1_POL | Bit forces DFE tap 1 polarity, manual DFE operation required to take effect |
| 6 | 1 | RW | N | SD_SEL_MUTEZ | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_SEL_NEG_GM | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT1[4] | Bits force DFE tap 1 weight, manual DFE operation required to take effect | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT1[3] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT1[2] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT1[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT1[0] | ||
| 13 | 7 | 1 | RW | N | EQ_PD_PEAKDET | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | EQ_PD_SD | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_EN_DC_OFF | 1: Normal operation | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_PD_EQ | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_LIMIT_EN | 1: Configures the final stage of the equalizer to be a limiting stage. 0: Normal operation, final stage of the equalizer is configured to be a linear stage. |
|
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | EQ_PD_CM | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 14 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_SD_PRESET | 1: Forces signal detect HIGH, and force enables the channel. Should not be set if bit 6 is set. 0: Normal Operation. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_SD_RESET | 1: Forces signal detect LOW and force disables the channel. Should not be set if bit 7 is set. 0: Normal Operation. |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_REFA_SEL1 | Controls the signal detect assert levels. | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_REFA_SEL0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_REFD_SEL1 | Controls the signal detect de-assert levels. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_REFD_SEL0 | ||
| 1:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 15 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_FORCE_EN | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | COMP_EN_HYST | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | COMP_EN | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | DRV_PD | 1: Powers down the high speed driver 0: Normal operation |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | Reserved | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | DRV_DEM1 | Degenerates the pre-driver degeneration 00: 0 dB 01: 1 dB 10: 2 dB 11: 3 dB |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | DRV_DEM0 | ||
| 16 | 7:0 | 0x7A | RW | Y | RESERVED | |
| 17 | 7:0 | 0x25 | RW | Y | RESERVED | |
| 18 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | PDIQ_SEL_DIV2 | These bits will force the divider setting if 0x09[2] is set. 000: Divide by 1 001: Divide by 2 010: Divide by 4 011: Divide by 8 100: Divide by 16 All other values are reserved. |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | PDIQ_SEL_DIV1 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | PDIQ_SEL_DIV0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | DRV_PD_R_EN | 1: Enables the shut down termination resistor to be present when the driver is powered down with channel register 0x15[3] 0: Normal operation, resistor is disconnected from output for propper driver operation |
|
| 1:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 19 | 7:6 | 0x20 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 5:0 | RW | Y | RESERVED | |||
| 1A | 7:4 | 0xA | RW | Y | RESERVED | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | DRV_SEL_VCM1 | Controls driver output common mode voltage. This feature is reserved for future use. |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | DRV_SEL_VCM0 | ||
| 1:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 1B | 7:2 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | CP_EN_CP_PD | 1: Normal operation | |
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | CP_EN_CP_FD | 1: Normal operation | |
| 1C | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_IDAC_PD_CP2 | Phase detector charge pump setting MSB located in channel register 0x0C[0] Override bit required for these bits to take effect |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_IDAC_PD_CP1 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_IDAC_PD_CP0 | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_IDAC_FD_CP2 | Frequency detector charge pump setting MSB located in channel register 0x0C[1] Override bit required for these bits to take effect |
|
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_IDAC_FD_CP1 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_IDAC_FD_CP0 | ||
| 1:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 1D | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | SBT_EN | SBT enable override 0: Normal operation |
| 6:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 1E | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | PFD_SEL_DATA_MUX2 | For these values to take effect, register 0x09[5] must be set to 1. 000: Raw Data* 001: Retimed Data 100: Pattern Generator 111: Mute All other values are reserved. *Note in this mode the FIR filter will not function. Data is routed only through the pre cursor tap. See Functional Description section for more information. |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | PFD_SEL_DATA_MUX1 | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | PFD_SEL_DATA_MUX0 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | SER_EN | 1: Enables the serializer for pattern generation 0: Disables the serializer |
|
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_PD | This bit must be cleared for the DFE to be functional in any adapt mode. 0: DFE enabled 1: DFE disabled |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | PFD_PD_PD | PFD phasee detector power down override | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | PFD_EN_FLD | PFD enable FLD override | |
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | PFD_EN_FD | PFD enable frequency detector override | |
| 1F | 7:0 | 0x55 | RW | Y | RESERVED |
Table 4. Channel Registers, 20 to 39
| ADDRESS
(HEX) |
BITS | DEFAULT
VALUE (HEX) |
MODE | EEPROM | FIELD NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT5[3] | Bits force DFE tap 5 weight, manual DFE operation required to take effect |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT5[2] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT5[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT5[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT4[3] | Bits force DFE tap 4 weight, manual DFE operation required to take effect | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT4[2] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT4[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT4[0] | ||
| 21 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT3[3] | Bits force DFE tap 3 weight, manual DFE operation required to take effect |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT3[2] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT3[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT3[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT2[3] | Bits force DFE tap 2 weight, manual DFE operation required to take effect | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT2[2] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT2[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_WT2[0] | ||
| 22 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | EOM_OV | 1: Override enable for EOM manual control 0: Normal operation |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | EOM_SEL_RATE_OV | 1: Override enable for EOM rate selection 0: Normal operation |
|
| 5:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 23 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | EOM_GET_HEO_VEO_OV | 1: Override enable for manual control of the HEO/VEO trigger 0: Normal operation |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_OV | 1: Normal operation, DFE must be enabled in channel register 0x1E[3] | |
| 5:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 24 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | FAST_EOM | 1: Enables fast EOM mode for fully eye capture. In this mode the phase DAC and voltage DAC of the EOM are automatically incremented through a 64 x 64 matrix. Values for each point are stored in channel registers 25 and 26. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | DFE_EQ_ERROR_NO_LOCK | DFE/CTLE SM quit due to loss of lock | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | GET_HEO_VEO_ERROR_ NO_HITS |
GET_HEO_VEO sees no hits at zero crossing | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | GET_HEO_VEO_ERROR_ NO_OPENING |
GET_HEO_VEO cannot see a vertical eye opening | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 2 | 0 | RWSC | N | DFE_ADAPT | 1: Manually start DFE adaption, self clearing. 0: Normal operation |
|
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | EOM_GET_HEO_VEO | 1: Manually triggers a HEO/VEO measurement. Must be enabled with channel register 0x23[7]. | |
| 0 | 0 | RWSC | N | EOM_START | 1: Starts EOM counter, self clearing | |
| 25 | 7 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT15 | MSBs of EOM counter |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT14 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT13 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT12 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT11 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT10 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT8 | ||
| 26 | 7 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT7 | LSBs of EOM counter |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | EOM_COUNT0 | ||
| 27 | 7 | 0 | R | N | HEO7 | HEO value, requires CDR to be locked for valid measurement |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | HEO6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | HEO5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | HEO4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | HEO3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | HEO2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | HEO1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | HEO0 | ||
| 28 | 7 | 0 | R | N | VEO7 | VEO value, requires CDR to be locked for valid measurement |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | VEO6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | VEO5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | VEO4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | VEO3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | VEO2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | VEO1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | VEO0 | ||
| 29 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | EOM_VRANGE_SETTING1 | Use these bits to read back the EOM voltage range setting 00: ±100 mV 01: ±200 mV 10: ±300 mV 11: ±400 mV |
|
| 5 | 0 | R | N | EOM_VRANGE_SETTING0 | ||
| 4:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 2A | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_TIMER_THR7 | Controls the amount of time the EOM samples each point in the eye for. The total counter bit width is 16-bits, this register is the upper 8-bits. The counter counts in 32-bit words, therefore, the total number of bits counted is 32 times this value. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_TIMER_THR6 | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EOM_TIMER_THR5 | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EOM_TIMER_THR4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_TIMER_THR3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_TIMER_THR2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_TIMER_THR1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_TIMER_THR0 | ||
| 2B | 7:6 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 5:4 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_MIN_REQ_HITS3 | These bits set the number of hits for a particular phase and voltage location in the EOM before the EOM will indicate a hit has occured. This filtering only affects the HEO measurement. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_MIN_REQ_HITS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_MIN_REQ_HITS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_MIN_REQ_HITS0 | ||
| 2C | 7 | 1 | RW | N | RELOAD_DFE_TAPS | 1: Reload DFE taps from last adapted value |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | VEO_SCALE | 1: Scale VEO based on EOM vertical range 0: Manual control of vertical range |
|
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_SM_FOM1 | 00: not valid 01: SM uses only HEO 10: SM uses only VEO 11: SM uses both HEO and VEO |
|
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_SM_FOM0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_ADAPT_COUNTER3 | Counter for incrementing taps when FoM decreases in EQ adaption | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_ADAPT_COUNTER2 | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_ADAPT_COUNTER1 | Counter for incrementing taps when FoM decreases in DFE adaption | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_ADAPT_COUNTER0 | ||
| 2D | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | PD_SCP | 1: Power down the short circuit protection for the high speed driver outputs 0: Normal operation, short circuit protection is enabled for the high speed driver outputs |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | SD_EN_FAST_OOB | Feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | SD_REF_HIGH | Feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | SD_GAIN | Feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BST_OV | Allow override control of the EQ setting by writing to channel register 0x03. Not recommended for normal operation. | |
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | DRV_SEL_VOD2 | Used in conjunction with 0x0D[5:4] to control the VOD levels of the high speed drivers | |
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | DRV_SEL_VOD1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | DRV_SEL_VOD0 | ||
| 2E | 7:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 2F | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | RATE1 | 4 bits determine standard. 0xF0: 8.625Gbps/4.3125 Gbps 0xE0: 9.95328Gbps 0xD0: 10.51875Gbps, 8.5Gbps, 4.25Gbps, 2.125Gbps 0xC0: 10.3125Gbps, 1.25Gbps 0x00: 5Gbps, 2.5Gbps |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | RATE0 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | SUBRATE1 | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | SUBRATE0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | INDEX_OV | If this bit is set to 1, reg 0x13 is to be used as a 5 bit index to the [31:0] array of EQ settings. | |
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_PPM_CHECK | 1: PPM check to be used as a qualifier when performing lock detect | |
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_FLD_CHECK | 1: False lock detector is used as a qualifier when performing lock detect | |
| 0 | 0 | RWSC | N | CTLE_ADAPT | Starts CTLE adaption, self clearing | |
| 30 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | FREEZE_PPM_CNT | 1: Freeze PPM counter to allow safe read asynchronously |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_SEARCH_OV_EN | Enables the EQ search bit to be force by channel register 0x13[2] | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | EN_PATT_INV | 1: Enables automatic pattern inversion of successive 16-bit words when using the user defined pattern generator option. |
|
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | RELOAD_PRBS_CHKR | Feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_EN_DIG_CLK | This bit enables the clock to operate the PRBS generator and/or the PRBS checker. Toggling this bit is the primary method to reset the PRBS pattern generator and PRBS checker. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_PROGPATT_EN | 1: Enable a fixed user defined pattern. Requires that the pattern generator be configured properly to be enabled | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_PATTERN_SEL1 | Selects the PRBS generator pattern to output. Requires that the pattern generator be configured properly. 00: PRBS-7 01: PRBS-9 10: PRBS-15 11: PRBS-31 |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_PATTERN_SEL0 | ||
| 31 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_INT_EN | 1: Enables interrupt for detection of PRBS errors. The PRBS checker must be properly configured for this feature to work |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | ADAPT_MODE1 | 00: no adaption 01: adapt CTLE only 10: adapt CTLE until optimal, then DFE, then CTLE again 11: adapt CTLE until lock, then DFE, then EQ until optimal |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | ADAPT_MODE0 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | EQ_SM_FOM1 | Sets the desired FoM for EQ adaption 00: not valid 01: SM uses HEO only 10: SM uses VEO only 11: SM uses both HEO and VEO |
|
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | EQ_SM_FOM0 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | CDR_LOCK_LOSS_INT_EN | 1: enables loss of CDR lock interrupt | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | SIG_DET_LOSS_INT_EN | 1: enable loss of signal detect interrupt | |
| 32 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | HEO_INT_THRESH3 | These bits set the threshold for the HEO and VEO interrupt. Each threshold bit represents 8 counts of HEO or VEO. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | HEO_INT_THRESH2 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | HEO_INT_THRESH1 | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | HEO_INT_THRESH0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | VEO_INT_THRESH3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | VEO_INT_THRESH2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | VEO_INT_THRESH1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | VEO_INT_THRESH0 | ||
| 33 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | HEO_THRESH3 | In adapt modes where the EQ adapts until lock and then adapts the DFE, this register sets the minimum HEO and VEO required before starting DFE adaption. This can be a max of 15 |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | HEO_THRESH2 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | HEO_THRESH1 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | HEO_THRESH0 | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | VEO_THRESH3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | VEO_THRESH2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | VEO_THRESH1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | VEO_THRESH0 | ||
| 34 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | PPM_ERR_RDY | 1: Indicates that a PPM error count is read to be read from channel register 0x3B and 0x3C |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | LOW_POWER_MODE_DISABLE | By default, all blocks (except signal detect) power down after 100ms after signal detect goes low. | |
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | LOCK_COUNTER1 | Afteer achieving lock, the CDR continues to monitor the lock criteria.If the lock criteria fail, the lock is checked for a total of N number of times before declaring an out of lock condition, where N is set by this the value in these registers, with a max value of +3, for a total of 4. If during the N lock checks, lock is regained, then the lock condition is left HI, and the counter is reset back to zero. | |
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | LOCK_COUNTER0 | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_MAX_TAP2_5[3] | These 4 bits are used to set the maximum value by which DFE taps 2-5 are able to adapt with each subsequent adaptation. Same used for both polarities. | |
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_MAX_TAP2_5[2] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_MAX_TAP2_5[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_MAX_TAP2_5[0] | ||
| 35 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | DATA_LOCK_PPM1 | Modifies the value of the ppm delta tolerance from channel register 0x64 00 - ppm_delta[7:0] =1 x ppm_delta[7:0] 01 - ppm_delta[7:0] =1 x ppm_delta[7:0] + ppm_delta[3:1] 10 - ppm_delta[7:0] =2 x ppm_delta[7:0] 11 - ppm_delta[7:0] =2 x ppm_delta[7:0] + ppm_delta[3:1] |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | DATA_LOCK_PPM0 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | GET_PPM_ERROR | Get ppm error from ppm_count - clears when done. Normally updates continuously, but can be manually triggered with read value from channel register 0x3B and 0x3C | |
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_MAX_TAP1[4] | Determins max tap limit for DFE tap 1 | |
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_MAX_TAP1[3] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_MAX_TAP1[2] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_MAX_TAP1[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | DFE_MAX_TAP1[0] | ||
| 36 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_INT_EN | Feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | HEO_VEO_INT_EN | 1: Enable HEO/VEO interrupt capability | |
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | REF_MODE1 | 11: Fast_lock all cap dac ref clock enabled (recommended) 10: Reserved 01: Reserved 00: referenceless all cap dac, for debug use only |
|
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | REF_MODE0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_6466B_LOCK_GATE | 1: Enables check for 64b66b encoding as a gate to lock 0: Normal operation |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_RNG_OV | Override enable for cap dac range | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | EN_6466B_RESTART | Feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | K28P5_6466_INT_EN | Feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 37 | 7 | 0 | R | N | CTLE_STATUS7 | Feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | CTLE_STATUS6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | CTLE_STATUS5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | CTLE_STATUS4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | CTLE_STATUS3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | CTLE_STATUS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | CTLE_STATUS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | CTLE_STATUS0 | ||
| 38 | 7 | 0 | R | N | DFE_STATUS7 | Feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | DFE_STATUS6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | DFE_STATUS5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | DFE_STATUS4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | DFE_STATUS3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | DFE_STATUS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | DFE_STATUS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | DFE_STATUS0 | ||
| 39 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | PRELOCK_COMPARATOR_ ABRT_MODE |
Feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_RATE1 | With eom_ov=1, these bits control the Eye Monitor Rate. 11 - Use for Full Rate, Fastest 10 - Use for 1/2 Rate 01 - Use for 1/4 Rate 00 - Use for 1/8 Rate, Slowest |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EOM_RATE0 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | START_INDEX4 | Start index for EQ adaptation | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | START_INDEX3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | START_INDEX2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | START_INDEX1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | START_INDEX0 |
Table 5. Channel Registers, 3A to 59
| ADDRESS (HEX) |
BITS | DEFAULT VALUE (HEX) |
MODE | EEPROM | FIELD NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3A | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | FIXED_EQ_BST0[1] | During adaptation, if the divider setting is >2, then a fixed EQ setting, from this register will be used. However, if channel register 0x6F[7] is enabled, then an EQ adaptation will be performed instead. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | FIXED_EQ_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | FIXED_EQ_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | FIXED_EQ_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | FIXED_EQ_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | FIXED_EQ_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | FIXED_EQ_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | FIXED_EQ_BST3[0] | |||
| 3B | 7 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT15 | PPM count MSB |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT14 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT13 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT12 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT11 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT10 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT8 | ||
| 3C | 7 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT7 | PPM count LSB |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PPM_COUNT0 | ||
| 3D | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_PD_pd | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_C0_SGN | FIR main cursor polarity 1: negative 0: positive |
|
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_C0[5] | FIR main cursor setting | |
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_C0[4] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_C0[3] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_C0[2] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_C0[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_C0[0] | ||
| 3E | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_PD_TX | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_CN1_SGN | FIR pre cursor polarity 1: negative 0: positive |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CN1[5] | FIR pre cursor setting | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CN1[4] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CN1[3] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CN1[2] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CN1[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CN1[0] | ||
| 3F | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_SEL_I_MAX | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_CP1_SGN | FIR post cursor polarity 1: negative 0: positive |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CP1[5] | FIR post cursor setting | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CP1[4] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CP1[3] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | FIR_CP1[2] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_CP1[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_CP1[0] | ||
| 40 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_0_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_0_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_0_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_0_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_0_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_0_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_0_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_0_BST3[0] | ||
| 41 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_1_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_1_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_1_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_1_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_1_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_1_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_1_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_1_BST3[0] | ||
| 42 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_2_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_2_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_2_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_2_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_2_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_2_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_2_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_2_BST3[0] | ||
| 43 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_3_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_3_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_3_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_3_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_3_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_3_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_3_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_3_BST3[0] | ||
| 44 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_4_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_4_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_4_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_4_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_4_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_4_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_4_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_4_BST3[0] | ||
| 45 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_5_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_5_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_5_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_5_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_5_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_5_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_5_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_5_BST3[0] | ||
| 46 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_6_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_6_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_6_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_6_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_6_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_6_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_6_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_6_BST3[0] | ||
| 47 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_7_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_7_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_7_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_7_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_7_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_7_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_7_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_7_BST3[0] | ||
| 48 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_8_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_8_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_8_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_8_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_8_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_8_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_8_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_8_BST3[0] | ||
| 49 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_9_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_9_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_9_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_9_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_9_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_9_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_9_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_9_BST3[0] | ||
| 4A | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_10_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_10_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_10_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_10_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_10_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_10_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_10_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_10_BST3[0] | ||
| 4B | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_11_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_11_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_11_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_11_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_11_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_11_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_11_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_11_BST3[0] | ||
| 4C | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_12_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_12_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_12_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_12_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_12_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_12_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_12_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_12_BST3[0] | ||
| 4D | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_13_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_13_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_13_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_13_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_13_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_13_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_13_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_13_BST3[0] | ||
| 4E | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_14_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_14_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_14_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_14_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_14_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_14_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_14_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_14_BST3[0] | ||
| 4F | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_15_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_15_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_15_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_15_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_15_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_15_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_15_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_15_BST3[0] | ||
| 50 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_16_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_16_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_16_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_16_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_16_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_16_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_16_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_16_BST3[0] | ||
| 51 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_17_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_17_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_17_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_17_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_17_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_17_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_17_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_17_BST3[0] | ||
| 52 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_18_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_18_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_18_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_18_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_18_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_18_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_18_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_18_BST3[0] | ||
| 53 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_19_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_19_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_19_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_19_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_19_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_19_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_19_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_19_BST3[0] | ||
| 54 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_20_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_20_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_20_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_20_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_20_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_20_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_20_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_20_BST3[0] | ||
| 55 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_21_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_21_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_21_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_21_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_21_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_21_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_21_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_21_BST3[0] | ||
| 56 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_22_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_22_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_22_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_22_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_22_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_22_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_22_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_22_BST3[0] | ||
| 57 | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_23_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_23_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_23_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_23_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_23_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_23_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_23_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_23_BST3[0] | ||
| 58 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_24_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_24_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_24_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_24_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_24_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_24_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_24_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_24_BST3[0] | ||
| 59 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_25_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_25_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_25_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_25_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_25_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_25_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_25_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_25_BST3[0] |
Table 6. Channel Registers, 5A to 9B
| ADDRESS (HEX) |
BITS | DEFAULT VALUE (HEX) |
MODE | EEPROM | FIELD NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5A | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_26_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_26_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_26_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_26_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_26_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_26_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_26_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_26_BST3[0] | ||
| 5B | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_27_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_27_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_27_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_27_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_27_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_27_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_27_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_27_BST3[0] | ||
| 5C | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_28_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_28_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_28_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_28_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_28_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_28_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_28_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_28_BST3[0] | ||
| 5D | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_29_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_29_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_29_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_29_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_29_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_29_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_29_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_29_BST3[0] | ||
| 5E | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_30_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_30_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_30_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_30_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_30_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_30_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_30_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_30_BST3[0] | ||
| 5F | 7 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_31_BST0[1] | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_31_BST0[0] | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_31_BST1[1] | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_31_BST1[0] | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_31_BST2[1] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_31_BST2[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_31_BST3[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_ARRAY_INDEX_31_BST3[0] | ||
| 60 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT7 | Group 0 count LSB |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT0 | ||
| 61 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | CNT_DLTA_OV_0 | Override enable for group 0 mannual data rate selection |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT14 | Group 0 count MSB | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT13 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT12 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT11 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT10 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_CNT8 | ||
| 62 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT7 | Group 1 count LSB |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT0 | ||
| 63 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | CNT_DLTA_OV_1 | Override enable for group 1 mannual data rate selection |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT14 | Group 1 count MSB | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT13 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT12 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT11 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT10 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_CNT8 | ||
| 64 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_DLTA3 | Sets the PPM delta tolerance for the PPM counter lock check for group 0. Must also program channel register 0x67[7]. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_DLTA2 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_DLTA1 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_DLTA0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_DLTA3 | Sets the PPM delta tolerance for the PPM counter lock check for group 1. Must also program channel register 0x67[6]. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_DLTA2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_DLTA1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_DLTA0 | ||
| 65 | 7:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 66 | 7:00 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 67 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP0_OV_DLTA4 | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | GRP1_OV_DLTA4 | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | HV_LOCKMON_EN | 1: Normal operation, HEO/VEO measurements are used for lock monitoring | |
| 4:1 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | LOCKMON_FRC_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 68 | 7:5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | ADPT_FRC_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | SCN_OBS_CTRL3 | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | SCN_OBS_CTRL2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | SCN_OBS_CTRL1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | SCN_OBS_CTRL0 | ||
| 69 | 7:5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | CTLE_ADPT_FRC_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | HV_LCKMON_CNT_MS3 | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | HV_LCKMON_CNT_MS2 | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | HV_LCKMON_CNT_MS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | HV_LCKMON_CNT_MS0 | ||
| 6A | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | VEO_LCK_THRSH3 | VEO threshold to meet before lock is established |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | VEO_LCK_THRSH2 | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | VEO_LCK_THRSH1 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | VEO_LCK_THRSH0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | HEO_LCK_THRSH3 | HEO threshold to meet before lock is established | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | HEO_LCK_THRSH2 | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | HEO_LCK_THRSH1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | HEO_LCK_THRSH0 | ||
| 6B | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_A7 | Alternate Figure of Merit variable A Max value for this register is 128, do not use the MSB |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | FOM_A6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_A5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_A4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_A3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_A2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_A1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_A0 | ||
| 6C | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_B7 | HEO adjustment for Alternate FoM, variable B |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | FOM_B6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_B5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_B4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_B3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_B2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_B1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_B0 | ||
| 6D | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_C7 | VEO adjustment for alternate FoM, variable C |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | FOM_C6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_C5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_C4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_C3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_C2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_C1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | FOM_C0 | ||
| 6E | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_NEW_FOM_CTLE | 1: CTLE adaption state machine will use the alternate FoM HEO_ALT = (HEO-B)*A*2 VEO_ALT = (VEO-C)*(1-A)*2 The values of A,B,C are set in channel register 0x6B, 0x6C, and 0x6D. The value of A is equal to the register value divided by 128 The Alternate FoM = (HEO-B)*A*2 + (VEO-C)*(1-A)*2 |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_NEW_FOM_DFE | 1: DFE adaption state machine will use the alternate FoM HEO_ALT = (HEO-B)*A*2 VEO_ALT = (VEO-C)*(1-A)*2 The values of A,B,C are set in channel register 0x6B, 0x6C, and 0x6D. The value of A is equal to the register value divided by 128 The Alternate FoM = (HEO-B)*A*2 + (VEO-C)*(1-A)*2 |
|
| 5:1 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | GET_HV_ST_FRC_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 6F | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_LOW_DIVSEL_EQ | 1: EQ adaption will be performed for all divider settings 0: EQ adaption will only be performed for dividers of 1 and 2 |
| 6:5 | 0 | RW | Y | RESERVED | ||
| 4:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 70 | 7:4 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_LB_CNT3 | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_LB_CNT2 | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_LB_CNT1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_LB_CNT0 | ||
| 71 | 7 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_INT | 1: Indicates that a PRBS stream has been detected. Requires the PRBS checker to be properly configured. This bit will stay set until it has been cleared by being read. This bit will clear after reading |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | K28P5_6466_COND_MET_INT | This feature only functions during intial lock if the k28.5 or 64b/66b lock conditions are enabled and met. 1: Indicates that the k28.5 or 64b/66b lock conditions were met |
|
| 5 | 0 | R | N | DFE_POL_1_OBS | Primary observation point for DFE tap 1 polarity | |
| 4 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT1_OBS4 | Primary observation point for DFE tap 1 weight | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT1_OBS3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT1_OBS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT1_OBS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT1_OBS0 | ||
| 72 | 7:5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 4 | 0 | R | N | DFE_POL_2_OBS | Primary observation point for DFE tap 2 polarity | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT2_OBS3 | Primary observation point for DFE tap 2 weight | |
| 2 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT2_OBS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT2_OBS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT2_OBS0 | ||
| 73 | 7:5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 4 | 0 | R | N | DFE_POL_3_OBS | Primary observation point for DFE tap 3 polarity | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT3_OBS3 | Primary observation point for DFE tap 3 weight | |
| 2 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT3_OBS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT3_OBS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT3_OBS0 | ||
| 74 | 7:5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 4 | 0 | R | N | DFE_POL_4_OBS | Primary observation point for DFE tap 4 polarity | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT4_OBS3 | Primary observation point for DFE tap 4 weight | |
| 2 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT4_OBS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT4_OBS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT4_OBS0 | ||
| 75 | 7:5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 4 | 0 | R | N | DFE_POL_5_OBS | Primary observation point for DFE tap 5 polarity | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT5_OBS3 | Primary observation point for DFE tap 5 weight | |
| 2 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT5_OBS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT5_OBS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | DFE_WT5_OBS0 | ||
| 76 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_VEO_THR3 | VEO threshold after lock is established |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_VEO_THR2 | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_VEO_THR1 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_VEO_THR0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_HEO_THR3 | HEO threshold after lock is established | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_HEO_THR2 | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_HEO_THR1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_HEO_THR0 | ||
| 77 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_GEN_POL_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. To invert the polarity of the PRBS data use the normal method of inverting of the sign bits for the FIR taps. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_START1[5] | This feature is reserved for future use | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | CDR_CAP_DAC_START0[5] | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_SBTTHR4 | SBT threshold after lock is established. | |
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_SBTTHR3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_SBTTHR2 | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_SBTTHR1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | POST_LOCK_SBTTHR0 | ||
| 78 | 7 | 0 | R | N | UNCORR_ERR_INT | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_LOCKUP_STATUS | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 5 | 0 | R | N | SD_STATUS | Primary observation point for signal detect status | |
| 4 | 0 | R | N | CDR_LOCK_STATUS | Primary observation point for CDR lock status | |
| 3 | 0 | R | N | CDR_LOCK_INT | Requires that channel register 0x79[1] be set. 1: Indicates CDR has achieved lock, lock goes from LOW to HIGH. This bit is cleared after reading. This bit will stay set until it has been cleared by reading. |
|
| 2 | 0 | R | N | SD_INT | Requires that channel register 0x79[0] be set. 1: Indicates signal detect status has changed. This will trigger when signal detect goes from LOW to HIGH or HIGH to LOW. This bit is cleared after reading. This bit will stay set until it has been cleared by reading. |
|
| 1 | 0 | R | N | EOM_VRANGE_LIMIT_ERROR | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 0 | 0 | R | N | HEO_VEO_INT | Requires that channel register 0x36[6] be set. 1: Indicates that HEO/VEO dropped below the limits set in channel register 0x76 This bit is cleared after reading. This bit will stay set until it has been cleared by reading. |
|
| 79 | 7 | 0 | R | N | PWDN_SD | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_CHKR_EN | 1: Enable the PRBS checker. 0: Disable the PRBS checker |
|
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_GEN_EN | 1: Enable the pattern generator 0: Disable the pattern generator |
|
| 4 | 1 | R | N | PRBS_LCKUP_EXIT_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 3 | 0 | R | Y | EN_K285 | 1: Enables K28.5 checking as a requirement for lock 0: Normal operation |
|
| 2 | 0 | R | Y | CAL_OVERRIDE | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 1 | 0 | R | N | CDR_LOCK_INT_EN | 1: Enable CDR lock interrupt, observable in channel register 0x78[3] 0: Disable CDR lock interrupt |
|
| 0 | 0 | R | N | SD_INT_EN | 1: Enable signal detect interrupt, observable in channel register 0x78[3] 0: Disable signal detect interrupt |
|
| 7A | 7 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_A7 | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_A6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_A5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_A4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_A3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_A2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_A1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_A0 | ||
| 7B | 7 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_D7 | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_D6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_D5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_D4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_D3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_D2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_D1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_D0 | ||
| 7C | 7 | 0 | W | N | PRBS_FIXED7 | Pattern generator user defined pattern LSB. MSB located at channel register 0x97. |
| 6 | 0 | W | N | PRBS_FIXED6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | W | N | PRBS_FIXED5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | W | N | PRBS_FIXED4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | W | N | PRBS_FIXED3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | W | N | PRBS_FIXED2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | W | N | PRBS_FIXED1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | W | N | PRBS_FIXED0 | ||
| 7D | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADAPT_HEO_CHNG_THRS3 | Limit for HEO change before triggering a DFE adaption while continous DFE adaption is enabled. |
| 6 | 1 | RW | Y | CONT_ADAPT_HEO_CHNG_THRS2 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADAPT_HEO_CHNG_THRS1 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADAPT_HEO_CHNG_THRS0 | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | CONT_ADAPT_VEO_CHNG_THRS3 | Limit for VEO change before triggering a DFE adaption while continous DFE adaption is enabled. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADAPT_VEO_CHNG_THRS2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADAPT_VEO_CHNG_THRS1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADAPT_VEO_CHNG_THRS0 | ||
| 7E | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_TAP_INCR3 | Limit of allowable DFE tap weight change from the previous base point |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_TAP_INCR2 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_TAP_INCR1 | ||
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_TAP_INCR0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_FOM_CHNG_THRS3 | Limit for FoM change before triggering a DFE adaption while continous DFE adaption is enabled. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_FOM_CHNG_THRS2 | ||
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_FOM_CHNG_THRS1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_FOM_CHNG_THRS0 | ||
| 7F | 7 | 0 | RW | N | EN_OBS_ALT_FOM | 1: Allows for alternate FoM calculation to be shown in channel registers 0x27, 0x28 and 0x29 instead of HEO and VEO |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | DIS_HV_CHK_FOR_CONT_ADAPT | 1: Ignore HEO/VEO lock condition checks during continous adaption. Normal operation for continous DFE adaption | |
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | EN_DFE_CONT_ADAPT | 1: Continous DFE adaption is enabled 0: DFE adapts only during lock and then freezes |
|
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_CMP_BOTH | 1: If continous DFE adaption is enabled, a DFE adaption will trigger if either HEO or VEO degrades | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_COUNT2 | Limit for number of weights the DFE can look ahead in continous adaption | |
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_COUNT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | CONT_ADPT_COUNT0 | ||
| 80 | 7 | 0 | R | N | HEO_CENTER7 | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | HEO_CENTER6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | HEO_CENTER5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | HEO_CENTER4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | HEO_CENTER3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | HEO_CENTER2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | HEO_CENTER1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | HEO_CENTER0 | ||
| 81 | 7:0 | 0 | R | N | RESERVED | |
| 82 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | FREEZE_PRBS_CNTR | 1: Freeze the PRBS bit and error counts to allow for read back 0: Normal operation. Both bit and error counters are allowed to increment if the PRBS checker is properly configured. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | RST_PRBS_CNTS | 1: Reset PRBS bit and error counts 0: Normal operation, counters are released from reset |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_PATT_OV | 1: Override PRBS pattern auto detection. Forces the pattern checker to only lock onto the pattern defined in bits 3 and 2 of this register. 0: Normal operation, pattern checker will automatically detect the PRBS pattern |
|
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_PATT1 | Usage is enabled with channel reg 0x82[4] Select PRBS pattern to be checked 00: PRBS-7 01: PRBS-9 10: PRBS-15 11: PRBS-31 |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_PATT0 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_POL_OV | 1: Override PRBS pattern auto polarity detection. Forces the pattern checker to only lock onto the polarity defined in bit 0 of this register. 0: Normal operation, pattern checker will automatically detect the PRBS pattern polarity |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | PRBS_POL | Usage is enabled with channel register 0x82[1] 0: Forced polarity = true 1 - Forced polarity = inverted |
|
| 83 | 7:3 | 0 | R | N | RESERVED | |
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT10 | PRBS error count MSB | |
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT8 | ||
| 84 | 7 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT7 | PRBS error count LSB |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_ERR_CNT0 | ||
| 85 | 7 | 0 | R | N | RESERVED | |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT46 | PRBS bit count, 47-bit word from channel registers 0x85 to 0x8A | |
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT45 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT44 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT43 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT42 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT41 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT40 | ||
| 86 | 7 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT39 | PRBS bit count, 47-bit word from channel registers 0x85 to 0x8A |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT38 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT37 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT36 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT35 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT34 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT33 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT32 | ||
| 87 | 7 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT31 | PRBS bit count, 47-bit word from channel registers 0x85 to 0x8A |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT30 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT29 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT28 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT27 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT26 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT25 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT24 | ||
| 88 | 7 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT23 | PRBS bit count, 47-bit word from channel registers 0x85 to 0x8A |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT22 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT21 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT20 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT19 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT18 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT17 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT16 | ||
| 89 | 7 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT15 | PRBS bit count, 47-bit word from channel registers 0x85 to 0x8A |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT14 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT13 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT12 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT11 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT10 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT8 | ||
| 8A | 7 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT7 | PRBS bit count, 47-bit word from channel registers 0x85 to 0x8A |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_DATA_CNT0 | ||
| 8B | 7 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT15 | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT14 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT13 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT12 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT11 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT10 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT8 | ||
| 8C | 7 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT7 | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | UNCORR_ERR_PATT0 | ||
| 8D | 7 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_EN_HR_MODE | Used with bit 2 to set Full rate, Mid rate or Half rate EQ bandwidth. Bit 6 is MSB. Bit 2 is LSB. 00: Full rate 01: Mid rate 11: Half rate |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | PFD_EN_HR_MODE | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | DIV_EN_HR_MODE | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | DIV_EN_HR_MODE | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_EN_MR_MODE | Used with bit 6 to set Full rate, Mid rate or Half rate EQ bandwidth. Bit 6 is MSB. Bit 2 is LSB. 00: Full rate 01: Mid rate 10: Alternate mid rate 11: Half rate |
|
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | SD_DC_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_SEL_LOOP_OUT | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 8E | 7 | 0 | RW | N | SD_CAL_RESET_LV | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | SEL_DIV48_LV | Output reference clock selection 1: Selects reference clock from in channel digital 0: Selects reference clock from adjacent channel output |
|
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | EN_CLK_LOOPTHRU_LV | 1: Enable the reference clock loop through mux | |
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_SEL_EDGE2 | Edge rate (slew rate) control | |
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_SEL_EDGE1 | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | FIR_SEL_EDGE0 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_SEL_GAIN1 | VGA gain control | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | DFE_SEL_GAIN0 | ||
| 8F | 7 | 0 | R | N | EQ_BST_TO_ANA7 | Primary observation point for the EQ boost setting. |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | EQ_BST_TO_ANA6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | EQ_BST_TO_ANA5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | EQ_BST_TO_ANA4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | EQ_BST_TO_ANA3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | EQ_BST_TO_ANA2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | EQ_BST_TO_ANA1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | EQ_BST_TO_ANA0 | ||
| 90 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | K28P5_COMPR_PERIOD3 | Used when one of these modes are enabled, k28.5 lock check(channel register 0x79[5]), 64b66b lock check(channel register 0x36[3]), k28.5 or 64b66b Interrupt(register 0x36[0]) k28.5_compr_period defines period within which k28.5 is expected to be seen. Also used for expected frequency of 64B66B transitions The number of bits to check is equal to 2^(min_k28.5_reqd[11:0]) * 32 Enable K28.5 checking with reg_79[3] |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | K28P5_COMPR_PERIOD2 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | K28P5_COMPR_PERIOD1 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | K28P5_COMPR_PERIOD0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD11 | Used when one of these modes are enabled, k28.5 lock check(channel register 0x79[5]), 64b66b lock check(channel register 0x36[3]), k28.5 or 64b66b Interrupt(register 0x36[0]) Channel register 0x90[3:0] together with channel register 0x91[7:0] defines number of k28.5+ patterns that need to be detected in the number of bits checked(set by channel register 0x90[7:4] Also used for expected frequency of 64B66B transitions Enable k28.5 checking with channel register 0x79[3] |
|
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD10 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD8 | ||
| 91 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD7 | See channel register 0x90[3:0] |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD6 | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD5 | ||
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD4 | ||
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD3 | ||
| 2 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD2 | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD1 | ||
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | MIN_K28P5_REQD0 | ||
| 92 | 7:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 93 | 7:0 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 94 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | DFE_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | DFE_DIS | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | EOM_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | EOM_DIS | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | DRV_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | DRV_DIS | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | PEAK_DET_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | PEAK_DET_DIS | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 95 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | SD_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | SD_DIS | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 5 | 0 | RW | N | DC_OFF_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 4 | 0 | RW | N | DC_OFF_DIS | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 3 | 0 | RW | N | EQ_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 2 | 0 | RW | N | EQ_DIS | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | N | COMP_EN | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 0 | 0 | RW | N | COMP_DIS | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 96 | 7 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 6 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | ||
| 5 | 0 | RW | Y | XPNT_SLAVE | A channel that it is configured in a 1-to-many xpnt setup must be slaved to the channel from which it is taking input data. 1: Channel is a slave 0: Channel is a master |
|
| 4 | 0 | RW | Y | XPNT_EN | 1: Cross Point is enabled 0: Cross Point is disabled |
|
| 3 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_BUFFER_EN[1] | Enable EQ output buffers: 00: Neither buffer in ON (not recommended) 01: Only local buffer is ON 10: Only multi-drive buffer is ON 11: Both buffers are ON |
|
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | EQ_BUFFER_EN[0] | ||
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_DATA_MUX_IN[1] | Select EQ data and signal detect bus from one channel: 00: channel A 01: Channel B 10: Channel C 11: Channel D Channel A = 0,4,8,12 Channel B = 1,5,9,13 Channel C = 2,6,10,14 Channel D = 3,7,11,15 |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_DATA_MUX_IN[0] | ||
| 97 | 7 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_FIXED15 | Pattern generator user defined pattern MSB. LSB located at channel register 0x7C. |
| 6 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_FIXED14 | ||
| 5 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_FIXED13 | ||
| 4 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_FIXED12 | ||
| 3 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_FIXED11 | ||
| 2 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_FIXED10 | ||
| 1 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_FIXED9 | ||
| 0 | 0 | R | N | PRBS_FIXED8 | ||
| 98 | 7:6 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 5:0 | 0 | RW | Y | RESERVED | ||
| 99 | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_START1_OV | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_STOP1_OV | ||
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_START2 | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_START1 | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_START0 | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_STOP2 | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_STOP1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_STOP0 | ||
| 9A | 7 | 0 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_START0_OV | This feature is reserved for future use. |
| 6 | 0 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_STOP0_OV | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 5 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_START0[2] | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 4 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_START0[1] | ||
| 3 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_START0[0] | ||
| 2 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_STOP0[2] | This feature is reserved for future use. | |
| 1 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_STOP0[1] | ||
| 0 | 1 | RW | Y | DIVSEL_STOP0[0] | ||
| 9B | 7:2 | 0 | RW | N | RESERVED | |
| 1 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_CTRL_MUX_IN[1] | Select EQ control bus from one channel: 00: channel A 01: Channel B 10: Channel C 11: Channel D Channel A = 0,4,8,12 Channel B = 1,5,9,13 Channel C = 2,6,10,14 Channel D = 3,7,11,15 |
|
| 0 | 0 | RW | Y | EQ_CTRL_MUX_IN[0] |
7 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
7.1 Typical Applications
Figure 5 and Figure 6 show a typical application of the DS110Df1610. In these diagrams, the DS110DF1610 is configured for SMBus slave mode programming. Power is supplied to the device through a single 2.5V plane. The power supply filtering shown in these diagrams may need to be adjusted to accommodate additional system power noise. The SMBus and LVCMOS signals in this example use 2.5V logic. A differential reference clock for the digital block is applied to the device through 1µF AC-coupling capacitors. In this example, the high speed signals are connected to the device in groups of four to allow for the system designer to make use of the 4x4 cross point switches. Note that since the device contains AC-coupling capacitors on the high speed receiver inputs, the signals can be directly connected to the device. The transmitter outputs of this device should connect to AC-coupling capacitors placed near the receive inputs of the receiving ASIC.
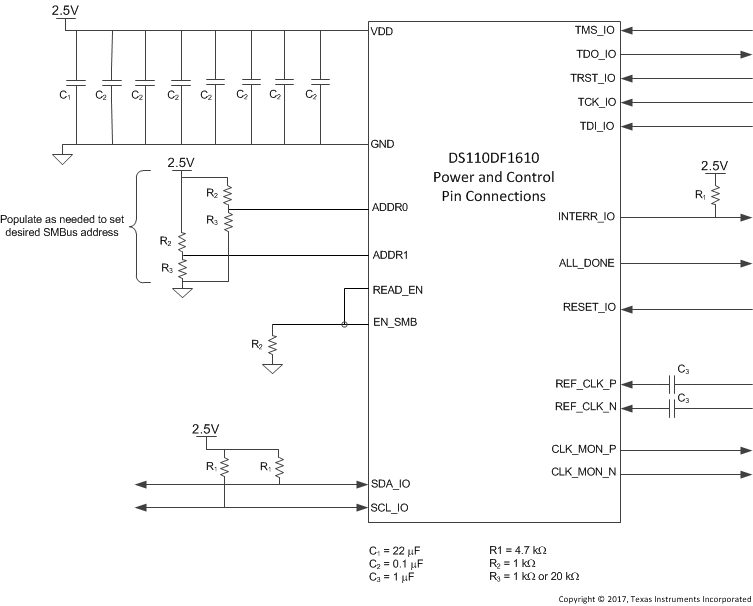 Figure 5. Typical Connection Diagram: Power and Control Pins
Figure 5. Typical Connection Diagram: Power and Control Pins
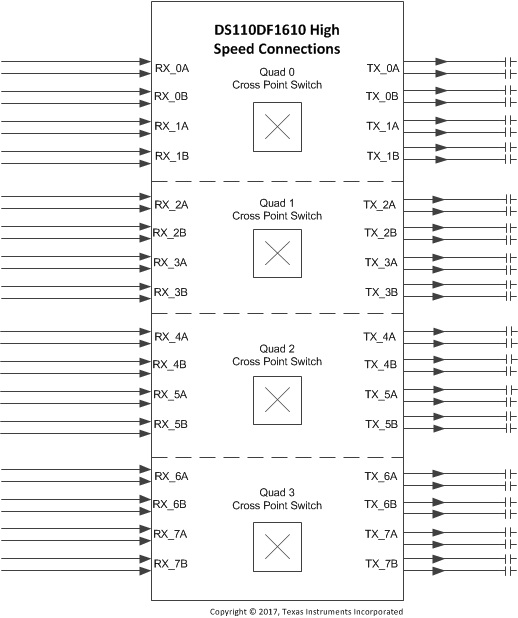 Figure 6. Typical Connection Diagram: High Speed Signals
Figure 6. Typical Connection Diagram: High Speed Signals
7.2 Initialization Setup
The typical device initialization sequence for a DS110DF1610 includes the following:
- Shared Register Configurations
- Reference Clock Divider Setting (default is 125MHz)
- Lock Sequencer Configuration (default is 8 channels allowed lock concurrently)
- Channel Register Configurations repeated for all desired channels:
- CDR reset
- Adapt Mode Configuration
- Data rate selection
- Output driver VOD and FIR configuration
- Optional Continuous DFE adaption configuration
- Optional Interrupt enable
- Optional Reference clock loop through enable
- Optional Cross point switch configuration
- CDR reset release
7.2.1 Data Rate Selection (Rate/Sub-Rate Table)
The data rates for the DS110DF1610 must be known and programmed into each desired channel. The DS110DF1610 will only lock to programmed data rates and the programmed divider settings. For ease of use several common data rates have been preprogrammed into the DS110DF1610 along with the associated sub-rates for those various standards. These rate/sub-rate settings comprise the Rate/Sub-rate Table. Note that each channel operates independently, so different channels in the DS110DF1610 can operate at different data rates at the same time.
The Rate/Sub-rate table for the DS110DF1610 shown below includes all of the available preprogrammed data rates and associated divider groupings.
| CHANNEL REGISTER 0x2F[7:4] SETTING | STANDARD | DATA RATES (Gbps) | FIRST GROUP DIVIDER SETTINGS | SECOND GROUP DIVIDER SETTINGS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | Custom 1 | 5.0, 2.5 | 2, 4 | 2, 4 |
| 0xC | Ethernet | 1.25, 10.3125 | 8 | 1 |
| 0xD | Fiber Channel | (2.125, 4.25, 8.5), 10.51875 | 1, 2, 4 | 1 |
| 0xE | SFF 8431 | 9.95328 | 1 | 1 |
| 0xF | Custom 2 | 8.625, 4.3125 | 1, 2 | 1, 2 |
7.2.2 Data Rate Selection (Manual Programming)
The DS110DF1610 is capable of supporting any data rate within the specified range of 8.5 Gbps to 11.3 Gbps including the divide by 2, 4, and 8 sub-rates of this range. If it is desired to operate the DS110DF1610 at a data rate or data rate and sub-rate combination that is not available in the Rate/Sub-rate Table, then these desired data rates can be programmed into the device manually.
The following procedure describes how to calculate and manually program data rates into the DS110DF1610.
- Select a divider grouping from the Rate/Sub-rate Table and program that value to channel register 0x2F. When manually programming the data rate into the device, other rate/sub-rate values may be used to allow for different divider and group combinations. A list of all preprogrammed divider, group combinations is shown in the table below.
- Calculate the first group settings:
- Calculate the second group settings:
| CHANNEL REGISTER 0x2F[7:4] SETTING |
FIRST GROUP DIVIDER SETTINGS | SECOND GROUP DIVIDER SETTINGS |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | 2, 4 | 2, 4 |
| 0x1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0x2 | 1, 2, 4 | 1, 2, 4 |
| 0x3 | 1, 2, 4 | 1, 2, 4 |
| 0x4 | 1 | 1 |
| 0x5 | 1 | 1 |
| 0x6 | 1 | 1 |
| 0x7 | 1, 2, 4 | 1, 2, 4 |
| 0x8 | 1, 2, 4 | 1, 2, 4 |
| 0x9 | 2, 4 | 2, 4 |
| 0xA | 1, 2, 4 | 1, 2, 4 |
| 0xB | 8 | 1 |
| 0xC | 8 | 1 |
| 0xD | 1, 2, 4 | 1 |
| 0xE | 1 | 1 |
| 0xF | 1, 2 | 1, 2 |
| PARAMETER | VALUE/EQUATION | COMMENT |
|---|---|---|
| Reference Clock | F0 = 25e6 | Internally the reference clock always operates at 25 MHz |
| Desired VCO Frequency | F1 | F1 is the frequency of the VC0 which is equal to the desired data rate. If the desired data rate uses dividers, be sure to multiply the data rate by the divide setting to get the correct VCO frequency |
| Number of Reference Clocks | N = 1024 | |
| VCO Freq ÷ 32 | F2 = F1 ÷ 32 | |
| Counts of VCO Freq ÷ 32 required | F3 = F2 x N ÷ F0 | |
| Counts of VCO Freq ÷ 32 required rounded | F4 | Round F3 to the nearest integer value. Convert this value to binary. Program the upper 8 bits to ch register 0x61 and the lower 8 bits to ch register 0x60. Be sure to set channel register 0x61[7] to 1 to enable the override function for manual programming. |
| PPM error due to rounding | Err = 1e6 x (F4 – F3) ÷ F3 | |
| Required PPM tolerance | T | Enter the desired PPM tolerance |
| VCO Freq ÷ 32 +PPM tolerance | F5 = (1+ T÷1e6) ÷ F2 | |
| Rounded Counts of the VCO Freq ÷ 32 +PPM tolerance required | F6 = F5 x N ÷ F0 | Round F6 to the nearest integer value |
| PPM Counts delta | F7 = F6 – F3 | Convert this value to binary. Program the most significant bit channel register 0x67[7] and the rest of the bits to channel register 0x64[7:4] |
| PARAMETER | VALUE/EQUATION | COMMENT |
|---|---|---|
| Reference Clock | F0 = 25e6 | Internally the reference clock always operates at 25 MHz |
| Desired VCO Frequency | F1 | F1 is the frequency of the VC0 which is equal to the desired data rate. If the desired data rate uses dividers, be sure to multiply the data rate by the divide setting to get the correct VCO frequency |
| Number of Reference Clocks | N = 1024 | |
| VCO Freq ÷ 32 | F2 = F1 ÷ 32 | |
| Counts of VCO Freq ÷ 32 required | F3 = F2 x N ÷ F0 | |
| Counts of VCO Freq ÷ 32 required rounded | F4 | Round F3 to the nearest integer value. Convert this value to binary. Program the upper 8 bits to ch register 0x63 and the lower 8 bits to ch register 0x62. Be sure to set channel register 0x63[7] to 1 to enable the override function for manual programming. |
| PPM error due to rounding | Err = 1e6 x (F4 – F3) ÷ F3 | |
| Required PPM tolerance | T | Enter the desired PPM tolerance |
| VCO Freq ÷ 32 +PPM tolerance | F5 = (1+ T÷1e6) ÷ F2 | |
| Rounded Counts of the VCO Freq ÷ 32 +PPM tolerance required | F6 = F5 x N ÷ F0 | Round F6 to the nearest integer value |
| PPM Counts delta | F7 = F6 – F3 | Convert this value to binary. Program the most significant bit channel register 0x67[6] and the rest of the bits to channel register 0x64[3:0] |
An example for setting group 0 and group 1 to 11.3 Gbps is shown in the table below.
| CHANNEL REGISTER (HEX) | VALUE |
|---|---|
| 0x60 | 0x80 |
| 0x61 | 0xB8 |
| 0x62 | 0x80 |
| 0x63 | 0xB8 |
| 0x64 | 0xEE |
| 0x67[7:6] | 2'b00 |