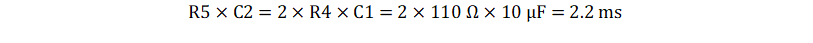SNOAA85 January 2022 LMP7704-SP
Design Steps
- Select resistors R2 and R3 to attenuate the 2.5-V output voltage of the TL1431-SP to 1.25 V. In this case, a value of R2 = R3 = 1 kΩ provides the necessary attenuation and ensures that the thermal noise generated by these resistors is insignificant compared to other noise sources and can be ignored.
- Use the following equation to calculate
the current flowing through resistors R2 and R3:
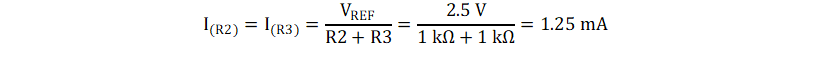
Use the following equation to calculate the maximum value of R1:
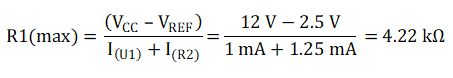
A value of 3.9 kΩ is therefore suitable for R1.
- Choose values for R4 and C1 that will
create a pole at the desired cutoff frequency. In this application, a cutoff frequency of
about 150 Hz was selected: this provides sufficient noise attenuation in the frequency
range of interest (1 kHz to 10 MHz). The op amp compensates for the voltage drop across
R4, so do not make it too big. As a general rule, it is recommended to make sure that the
voltage drop across R4 is less than 1 V at maximum output current.
Use the following equation to calculate the RC time constant needed for the desired cutoff frequency:
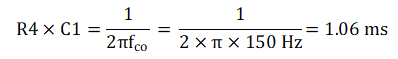
Using values of R4 = 110 Ω and C1 = 10 μF results in a cutoff frequency of 145 Hz.
- To minimize noise gain peaking close to
the cutoff frequency, choose R5 and C2 so that: