SNVSA72 February 2015 LP8728D-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
- AVDD and BYP pins must be bypassed to ground. 1-µF ceramic capacitor is recommended. Place the capacitors close to the AVDD, BYP, and AGND pins.
- AGND pin must be tied to the PCB ground plane. Use multiple vias to minimize the inductance.
- AVDD pin must be connected to PCB VIN plane. Use multiple vias to minimize the inductance.
- Place the buck converter input capacitors as close to the buck input voltage and buck ground pins as possible.
- Place the buck converter output capacitors and inductors so that the buck converter switching loops can be routed on top layer. Try to minimize the area of the switching loops.
- Keep the trace width from switch pin to inductor wide enough to withstand the switching currents. Avoid any excess copper on the switch node to minimize parasitic switch node capacitance.
- Connect the exposed thermal pad to ground plane with multiple thermal vias.
- Avoid routing digital signals directly under the switching loops to avoid interferences.
10.2 Layout Example
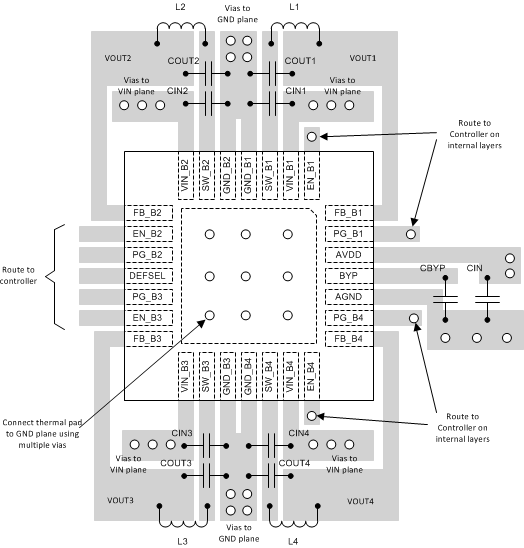 Figure 21. LP8728D-Q1 Layout Example
Figure 21. LP8728D-Q1 Layout Example