-
TPS61193-Q1 Low-EMI Automotive LED Driver With Three 100-mA Channels
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Internal LDO Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Protection Electrical Characteristics
- 7.8 Current Sinks Electrical Characteristics
- 7.9 PWM Brightness Control Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 Boost and SEPIC Converter Characteristics
- 7.11 Logic Interface Characteristics
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
TPS61193-Q1 Low-EMI Automotive LED Driver With Three 100-mA Channels
1 Features
- Qualified for Automotive Applications
- AEC-Q100 Qualified With the Following Results:
- Device Temperature Grade 1: –40°C to +125°C Ambient Operating Temperature
- Input Voltage Operating Range 4.5 V to 40 V
- Three High-Precision Current Sinks
- Current Matching 1% (Typical)
- LED String Current up to 100 mA per Channel
- Outputs can be Combined Externally for Higher Current Capability
- High Dimming Ratio of 10 000:1 at 100 Hz
- Integrated Boost/SEPIC for LED String Power
- Output Voltage up to 45 V
- Switching Frequency 300 kHz to 2.2 MHz
- Switching Synchronization Input
- Spread Spectrum for Lower EMI
- Extensive Fault Detection Features
- Fault Output
- Input Voltage OVP, UVLO, and OCP
- Open and Shorted LED Fault Detection
- Thermal Shutdown
- Minimum Number of External Components
space
Simplified Schematic
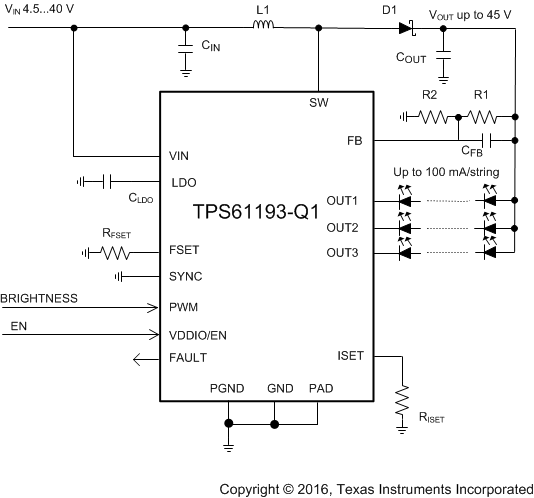
2 Applications
- Backlight for:
- Automotive Infotainment
- Automotive Instrument Clusters
- Smart Mirrors
- Heads-Up Displays (HUD)
- Central Information Displays (CID)
- Audio-Video Navigation (AVN)
3 Description
The TPS61193-Q1 is an automotive high-efficiency, low-EMI, easy-to-use LED driver with an integrated DC-DC converter. The DC-DC converter supports both boost and SEPIC mode operation. The device has three high-precision current sinks that can be combined for higher current capability.
The DC-DC converter has adaptive output voltage control based on the LED current sink headroom voltages. This feature minimizes the power consumption by adjusting the voltage to the lowest sufficient level in all conditions. For EMI reduction DC-DC supports spread spectrum for switching frequency and an external synchronization with dedicated pin. A wide-rage adjustable frequency allows the TPS61193-Q1 to avoid disturbance for AM radio bands.
The input voltage range for the TPS61193-Q1 is from 4.5 V to 40 V to support automotive stop/start and load dump condition. The TPS61193-Q1 integrates extensive fault detection features.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS61193-Q1 | HTSSOP (20) | 6.50 mm × 4.40 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
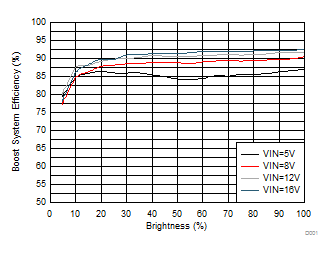
System Efficiency
4 Revision History
Changes from B Revision (April 2017) to C Revision
- Enhanced pin descriptions for pins 3, 10 and 16 in Pin FunctionsGo
- Deleted "Dimming ratio is calculated as ratio between the input PWM period and minimum on/off time (0.5 µs). " from Brightness ControlGo
Changes from A Revision (October 2016) to B Revision
- Deleted "IOUT = 100 mA" from tON/OFF row of Table 7.9Go
- Changed "0.5" from MAX to TYP column in tON/OFF row of Table 7.9 Go
- Added table note 1 for Tables 7.9 and 7.10Go
- Deleted "Initial DC-DC voltage is about 88% of VMAX BOOST." from Integrated DC-DC Converter; change wording in last sentence before equation 1.Go
- Changed eq. 1; added "K" eq definitions for eq. 1 and paragraph after Fig. 9 Go
- Added new paragraph before Internal LDOGo
Changes from * Revision (October 2015) to A Revision
- Changed several wording of several items in Features Go
- Changed "High Dimming Ratio of 10 000:1 at 200 Hz" to "High Dimming Ratio of 10 000:1 at 100 Hz"Go
- Changed some wording in Description - for clarity; additional several newApplicationsGo
- Added Device Comparison Table Go
- Added Figures 7 and 8 - new graphsGo
5 Device Comparison Table
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
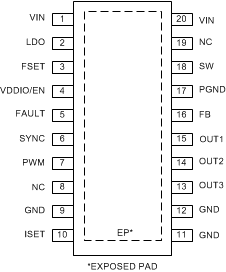
Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 1 | VIN | A | Input power pin |
| 2 | LDO | A | Output of internal LDO; connect a 1-μF decoupling capacitor between this pin and noise-free GND. |
| 3 | FSET | A | DC-DC (boost or SEPIC) switching frequency setting resistor; for normal operation, resistor value from 24 kΩ to 219 kΩ must be connected between this pin and ground. |
| 4 | VDDIO/EN | I | Enable input for the device as well as supply input (VDDIO) for digital pins |
| 5 | FAULT | OD | Fault signal output. If unused, the pin may be left floating. |
| 6 | SYNC | I | Input for synchronizing boost. If synchronization is not used, connect this pin to GND to disable spread spectrum or to VDDIO/EN to enable spread spectrum. |
| 7 | PWM | I | PWM dimming input. |
| 8 | NC | — | No connect |
| 9 | GND | G | Ground. |
| 10 | ISET | A | LED current setting resistor; for normal operation, resistor value from 24 kΩ to 129 kΩ must be connected between this pin and ground. |
| 11 | GND | G | Ground |
| 12 | GND | G | Ground |
| 13 | OUT3 | A | Current sink output; this pin must be connected to GND if not used. |
| 14 | OUT2 | A | Current sink output This pin must be connected to GND if not used. |
| 15 | OUT1 | A | Current sink output This pin must be connected to GND if not used. |
| 16 | FB | A | DC-DC (boost or SEPIC) feedback input; for normal operation this pin must be connected to the middle of a resistor divider between VOUT and ground using feedback resistor values from 5 kΩ to 150 kΩ. |
| 17 | PGND | G | DC-DC (boost or SEPIC) power ground |
| 18 | SW | A | DC-DC (boost or SEPIC) switch pin |
| 19 | NC | A | No connect |
| 20 | VIN | A | Input power pin |
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage on pins | VIN, SW, FB | –0.3 | 50 | V |
| OUT1, OUT2, OUT3 | –0.3 | 45 | ||
| LDO, SYNC, FSET, ISET, PWM, VDDIO/EN, FAULT | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||
| Continuous power dissipation(3) | Internally Limited | |||
| Ambient temperature range TA(4) | –40 | 125 | °C | |
| Junction temperature range TJ(4) | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| Maximum lead temperature (soldering) | See(5) | |||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | ±2000 | V | |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | All other pins | ±500 | |||
| Corner pins (1,10,11,20) | ±750 | ||||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage on pins | VIN | 4.5 | 45 | V |
| SW | 0 | 45 | ||
| OUT1, OUT2, OUT3 | 0 | 40 | ||
| FB, FSET, LDO, ISET, VDDIO/EN, FAULT | 0 | 5.25 | ||
| SYNC, PWM | 0 | VDDIO/EN | ||
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS61193-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PWP (TSSOP) | |||
| 20 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance(2) | 44.2 | °C/W |
| RθJCtop | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 26.5 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 22.4 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.9 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 22.2 | °C/W |
| RθJCbot | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 2.5 | °C/W |
7.5 Electrical Characteristics(1)(2)
TJ = −40°C to +125°C (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IQ | Standby supply current | Device disabled, VVDDIO/EN = 0 V, VIN = 12 V | 4.5 | 20 | μA | |
| Active supply current | VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 26 V, output current 80 mA/channel, converter ƒSW = 300 kHz | 5 | 12 | mA | ||
| VPOR_R | Power-on reset rising threshold | LDO pin voltage | 2.7 | V | ||
| VPOR_F | Power-on reset falling threshold | LDO pin voltage | 1.5 | V | ||
| TTSD | Thermal shutdown threshold | 150 | 165 | 175 | °C | |
| TTSD_HYST | Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 20 | °C | |||
7.6 Internal LDO Electrical Characteristics
TJ = −40°C to +125°C (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VLDO | Output voltage | VIN = 12 V | 4.15 | 4.3 | 4.55 | V |
| VDR | Dropout voltage | 120 | 300 | 430 | mV | |
| ISHORT | Short circuit current | 50 | mA | |||
7.7 Protection Electrical Characteristics
TJ = −40°C to +125°C (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOVP | VIN OVP threshold voltage | 41 | 42 | 44 | V | |
| VUVLO | VIN UVLO | 4 | V | |||
| VUVLO_HYST | VIN UVLO hysteresis | 100 | mV | |||
| LED short detection threshold | 5.6 | 6 | 7 | V | ||
7.8 Current Sinks Electrical Characteristics
TJ = −40°C to +125°C (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ILEAKAGE | Leakage current | Outputs OUT1 to OUT3 , VOUTx = 45 V | 0.1 | 5 | µA | |
| IMAX | Maximum current | OUT1, OUT2, OUT3 | 100 | mA | ||
| IOUT | Output current accuracy | IOUT = 100 mA | −5% | 5% | ||
| IMATCH | Output current matching(1) | IOUT = 100 mA, PWM duty =100% | 1% | 5% | ||
| VSAT | Saturation voltage(2) | IOUT = 100 mA | 0.4 | 0.7 | V | |
7.9 PWM Brightness Control Electrical Characteristics
TJ = −40°C to +125°C (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ƒPWM | PWM input frequency | 100 | 20 000 | Hz | ||
| tON/OFF | Minimum on/off time(1) | 0.5 | µs | |||
7.10 Boost and SEPIC Converter Characteristics
TJ = −40°C to +125°C (unless otherwise noted).Unless otherwise specified: VIN = 12 V, VEN/VDDIO = 3.3 V, L = 22 μH, CIN = 2 × 10-μF ceramic and 33-μF electrolytic,
COUT = 2 × 10-μF ceramic and 33-μF electrolytic, D = NRVB460MFS, ƒSW = 300 kHz.
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage | 4.5 | 40 | V | ||
| VOUT | Output voltage | 6 | 45 | |||
| ƒSW_MIN | Minimum switching frequency (central frequency if spread spectrum is enabled) | Defined by RFSET resistor | 300 | kHz | ||
| ƒSW_MAX | Maximum switching frequency (central frequency if spread spectrum is enabled) | 2 200 | kHz | |||
| VOUT/VIN | Conversion ratio | 10 | ||||
| TOFF | Minimum switch OFF time(1) | ƒSW ≥ 1.15 MHz | 55 | ns | ||
| ISW_MAX | SW current limit | 1.8 | 2 | 2.2 | A | |
| RDSON | FET RDSON | Pin-to-pin | 240 | 400 | mΩ | |
| fSYNC | External SYNC frequency | 300 | 2 200 | kHz | ||
| tSYNC_ON_MIN | External SYNC minimum on time(1) | 150 | ns | |||
| tSYNC_OFF_MIN | External SYNC minimum off time(1) | 150 | ns | |||
7.11 Logic Interface Characteristics
TJ = −40°C to +125°C (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOGIC INPUT VDDIO/EN | ||||||
| VIL | Input low level | 0.4 | V | |||
| VIH | Input high level | 1.65 | ||||
| II | Input current | −1 | 5 | 30 | µA | |
| LOGIC INPUT SYNC/FSET, PWM | ||||||
| VIL | Input low level | 0.2 × VDDIO/EN | V | |||
| VIH | Input high level | 0.8 × VDDIO/EN | ||||
| II | Input current | −1 | 1 | μA | ||
| LOGIC OUTPUT FAULT | ||||||
| VOL | Output low level | Pullup current 3 mA | 0.3 | 0.5 | V | |
| ILEAKAGE | Output leakage current | V = 5.5 V | 1 | μA | ||
7.12 Typical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified: D = NRVB460MFS, T = 25°C
| ƒSW = 300 kHz | L = 33 μH | DC Load (PWM = 100%) |
| CIN and COUT = 33 µF + 2 × 10 µF (ceramic) | ||

| ƒSW = 1.5 MHz | L = 8.2 μH | DC Load (PWM = 100%) | |
| CIN and COUT = 2 × 10 µF (ceramic) | |||


| ƒSW = 800 kHz | L = 15 μH | DC Load (PWM = 100%) |
| CIN and COUT = 2 ×10 µF (ceramic) | ||

| ƒSW = 2.2 MHz | L = 4.7 μH | DC Load (PWM = 100%) |
| CIN and COUT = 2 × 10 µF (ceramic) | ||


| RISET = 24 kΩ |
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The TPS61193-Q1 is a highly integrated LED driver for automotive infotainment, lighting systems, and medium-sized LCD backlight applications. It includes a DC-DC with an integrated FET, supporting both boost and SEPIC modes, an internal LDO enabling direct connection to battery without need for a pre-regulated supply and three LED current sinks. The VDDIO/EN pin provides the supply voltage for digital IOs (PWM and SYNC inputs) and at the same time enables the device.
The switching frequency on the DC-DC converter is set by a resistor connected to the FSET pin. The maximum voltage of the DC-DC is set by a resistive divider connected to the FB pin. For the best efficiency the output voltage is adapted automatically to the minimum necessary level needed to drive the LED strings. This is done by monitoring LED output voltage drop in real time. For EMI reduction and control two optional features are available:
- Spread spectrum, which reduces EMI noise around the switching frequency and its harmonic frequencies
- DC-DC can be synchronized to an external frequency connected to SYNC pin
The three constant current sinks OUT1, OUT2, and OUT3 provide LED current up to 100 mA. Value for the current per OUT pin is set with a resistor connected to ISET pin. Current sinks that are not used must be connected to ground. Grounded current sink is disabled and excluded from adaptive voltage detection loop.
Brightness is controlled with the PWM input. Frequency range for the input PWM is from 100 Hz to 20 kHz. LED output PWM follows the input PWM so the output frequency is equal to the input frequency.
TPS61193-Q1 has extensive fault detection features :
- Open-string and shorted LED detections
- LED fault detection prevents system overheating in case of open or short in some of the LED strings
- VIN input overvoltage protection
- Threshold sensing from VIN pin
- VIN input undervoltage protection
- Threshold sensing from VIN pin
- Thermal shutdown in case of die overtemperature
Fault condition is indicated through the FAULT output pin.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram

8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Integrated DC-DC Converter
The TPS61193-Q1 DC-DC converter generates supply voltage for the LEDs and can operate in boost mode or in SEPIC mode. The maximum output voltage VOUT_MAX is defined by an external resistive divider (R1, R2).
VOUT_MAX voltage should be chosen based on the maximum voltage required for LED strings. Recommended maximum voltage is about 30% higher than maximum LED string voltage. DC-DC output voltage is adjusted automatically based on LED current sink headroom voltage. Maximum, minimum, and initial boost voltages can be calculated with :

where
- VBG = 1.2 V
- R2 recommended value is 130 kΩ
- Resistor values are in kΩ
- K = 1 for maximum adaptive boost voltage (typical)
- K = 0 for minimum adaptive boost voltage (typical)
- K = 0.88 for initial boost voltage (typical)
 Figure 9. Maximum Converter Output Voltage vs R1 Resistance
Figure 9. Maximum Converter Output Voltage vs R1 Resistance
Alternatively, a T-divider can be used if resistance less than 100 kΩ is required for the external resistive divider. Refer to Using the TPS61193-Q1 Evaluation Module for details.
The converter is a current mode DC-DC converter, where the inductor current is measured and controlled with the feedback. Switching frequency is adjustable between 250 kHz and 2.2 MHz with RFSET resistor as Equation 2:
where
- ƒSW is switching frequency, kHz
- RFSET is frequency setting resistor, kΩ
In most cases lower frequency has higher system efficiency. DC-DC internal parameters are chosen automatically according to the selected switching frequency (see Table 2) to ensure stability. In boost mode a 15-pF capacitor CFB must be placed across resistor R1 when operating in 300-kHz to 500-kHz range (see Typical Application for 3 LED Strings). When operating in the 1.8-MHz to 2.2-MHz range CFB = 4.7 pF.
 Figure 10. Boost Block Diagram
Figure 10. Boost Block Diagram
DC-DC can be driven by an external SYNC signal between 300 kHz and 2.2 MHz. If the external synchronization input disappears, DC-DC continues operation at the frequency defined by RFSET resistor. When external frequency disappears and SYNC pin level is low, converter continues operation without spread spectrum immediately. If SYNC remains high, converter continues switching with spread spectrum enabled after 256 µs.
External SYNC frequency must be 1.2 to 1.5 times higher than the frequency defined by RFSET resistor. Minimum frequency setting with RFSET is 250 kHz to support 300-kHz switching with external clock.
The optional spread spectrum feature (±3% from central frequency, 1-kHz modulation frequency) reduces EMI noise at the switching frequency and its harmonic frequencies. When external synchronization is used, spread spectrum is not available.
Table 1. DC-DC Synchronization Mode
| SYNC PIN INPUT | MODE |
|---|---|
| Low | Spread spectrum disabled |
| High | Spread spectrum enabled |
| 300 to 2200 kHz frequency | Spread spectrum disabled, external synchronization mode |
Table 2. DC-DC Parameters(1)
| RANGE | FREQUENCY (kHz) | TYPICAL INDUCTANCE (µH) |
TYPICAL BOOST INPUT AND OUTPUT CAPACITORS (µF) |
MINIMUM SWITCH OFF TIME (ns)(2) |
BLANK TIME (ns) |
CURRENT RAMP (A/s) |
CURRENT RAMP DELAY (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 300 to 480 | 33 | 2 ×10 (cer.) + 33 (electr.) | 150 | 95 | 24 | 550 |
| 2 | 480 to 1150 | 15 | 10 (cer.) + 33 (electr.) | 60 | 95 | 43 | 300 |
| 3 | 1150 to 1650 | 10 | 3 × 10 (cer.) | 40 | 95 | 79 | 0 |
| 4 | 1650 to 2200 | 4.7 | 3 × 10 (cer.) | 40 | 70 | 145 | 0 |
The converter SW pin DC current is limited to 2 A (typical). To support warm-start transient conditions the current limit is automatically increased to 2.5 A for a short period of 1.5 seconds when a 2-A limit is reached.
NOTE
Application condition where the 2-A limit is exceeded continuously is not allowed. In this case the current limit would be 2 A for 1.5 seconds followed by 2.5-A limit for 1.5 seconds, and this 3-second period repeats.
To keep switching voltage within safe levels there is a 48-V limit comparator in the event that FB loop is broken.
8.3.2 Internal LDO
The internal LDO regulator converts the input voltage at VIN to a 4.3-V output voltage for internal use. Connect a minimum of 1-µF ceramic capacitor from LDO pin to ground, as close to the LDO pin as possible.
8.3.3 LED Current Sinks
8.3.3.1 Output Configuration
TPS61193-Q1 detects LED output configuration during start-up. Any current sink output connected to ground is disabled and excluded from the adaptive voltage control of the DC-DC and fault detections.
8.3.3.2 Current Setting
Maximum current for the LED outputs is controlled with external RISET resistor. RISET value for target maximum current can be calculated using Equation 3:

where
- RISET is current setting resistor, kΩ
- ILED is output current per output, mA
8.3.4 Protection and Fault Detections
The TPS61193-Q1 has fault detection for LED open and short, VIN input overvoltage protection (VIN_OVP) , VIN undervoltage lockout (VIN_UVLO), and thermal shutdown (TSD).
8.3.4.1 Adaptive DC-DC Voltage Control and Functionality of LED Fault Comparators
Adaptive voltage control function adjusts the DC-DC output voltage to the minimum sufficient voltage for proper LED current sink operation. The current sink with highest VF LED string is detected and DC-DC output voltage adjusted accordingly. DC-DC adaptive control voltage step size is defined by maximum voltage setting, VSTEP = (VOUT_MAX – VOUT_MIN) / 256. Periodic down pressure is applied to the target voltage to achieve better system efficiency.
Every LED current sink has 3 comparators for the adaptive DC-DC control and LED fault detections. Comparator outputs are filtered, filtering time is 1 µs.
 Figure 11. Comparators for Adaptive Voltage Control and LED Fault Detection
Figure 11. Comparators for Adaptive Voltage Control and LED Fault Detection
Figure 12 shows different cases which cause DC-DC voltage increase, decrease, or generate faults. In normal operation voltage at all the OUT# pins is between LOW_COMP and MID_COMP levels, and boost voltage stays constant. LOW_COMP level is the minimum for proper LED current sink operation, 1.1 × VSAT + 0.2 V (typical). MID_COMP level is 1.1 × VSAT + 1.2 V (typical) so typical headroom window is 1 V.
When voltage at all the OUT# pins increases above MID_COMP level, DC-DC voltage adapts downwards.
When voltage at any of the OUT# pins falls below LOW_COMP threshold, DC-DC voltage adapts upwards. In the condition where DC-DC voltage reaches the maximum and there are one or more outputs still below LOW_COMP level, an open LED fault is detected.
HIGH_COMP level, 6 V typical, is the threshold for shorted LED detection. When the voltage of one or more of the OUT# pins increases above HIGH_COMP level and at least one of the other outputs is within the normal headroom window, shorted LED fault is detected.
 Figure 12. Protection and DC-DC Voltage Adaptation Algorithms
Figure 12. Protection and DC-DC Voltage Adaptation Algorithms
8.3.4.2 Overview of the Fault/Protection Schemes
A summary of the TPS61193-Q1 fault detection behavior is shown in Table 3. Detected faults (excluding LED open or short) cause device to enter FAULT_RECOVERY state. In FAULT_RECOVERY the DC-DC and LED current sinks of the device are disabled, and the FAULT pin is pulled low. The device recovers automatically and enters normal operating mode (ACTIVE) after a recovery time of 100 ms if the fault condition has disappeared. When recovery is succesful, FAULT pin is released.
If a LED fault is detected, the device continues normal operation and only the faulty string is disabled. The fault is indicated via the FAULT pin which can be released by toggling VDDIO/EN pin low for a short period of 2 µs to 20 µs. LEDs are turned off for this period but the device stays in ACTIVE mode. If VDDIO/EN is low longer, the device goes to STANDBY and restarts when EN goes high again.
Table 3. Fault Detections
| FAULT/ PROTECTION |
FAULT NAME | THRESHOLD | FAULT PIN | FAULT_ RECOVERY STATE |
ACTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN overvoltage protection | VIN_OVP | 1. VIN > 42 V 2. VOUT > VSET_DCDC + 6..10 V. VSET_DCDC is voltage value defined by logic during adaptation |
Yes | Yes | 1. Overvoltage is monitored from the beginning of soft start. Fault is detected if the duration of overvoltage condition is 100 µs minimum. 2. Overvoltage is monitored from the beginning of normal operation (ACTIVE mode). Fault is detected if over-voltage condition duration is 560 ms minimum (tfilter). After the first fault, detection filter time is reduced to 50 ms for following recovery cycles. When the device recovers and has been in ACTIVE mode for 160 ms, filter time is increased back to 560 ms . |
| VIN undervoltage lockout | VIN_UVLO | Falling 3.9 V Rising 4 V |
Yes | Yes | Detects undervoltage condition at VIN pin. Sensed in all operating modes. Fault is detected if undervoltage condition duration is 100 µs minimum. |
| Open LED fault | OPEN_LED | LOW_COMP threshold | Yes | No | Detected if the voltage of one or more current sinks is below threshold level, and DC-DC adaptive control has reached maximum voltage. Open string is removed from the DC-DC voltage control loop and current sink is disabled. Fault pin is released by toggling VDDIO/EN pin. If VDDIO/EN is low for a period of 2 µs to 20 µs, LEDs are turned off for this period but device stays ACTIVE. If VDDIO/EN is low longer, device goes to STANDBY and restarts when EN goes high again. |
| Shorted LED fault | SHORT_LED | Shorted string detection level 6 V | Yes | No | Detected if the voltage of one or more current sinks is above shorted string detection level and at least one OUTx voltage is within headroom window. Shorted string is removed from the DC-DC voltage control loop and current sink is disabled. Fault pin is released by toggling VDDIO/EN pin. If VDDIO/EN is low for a period of 2…20 µs, LEDs are turned off for this period but device stays ACTIVE. If VDDIO/EN is low longer, device goes to STANDBY and restarts when EN goes high again.. |
| Thermal protection | TSD | 165ºC Thermal shutdown hysteresis 20ºC |
Yes | Yes | Thermal shutdown is monitored from the beginning of soft start. Die temperature must decrease by 20ºC for device to recover. |
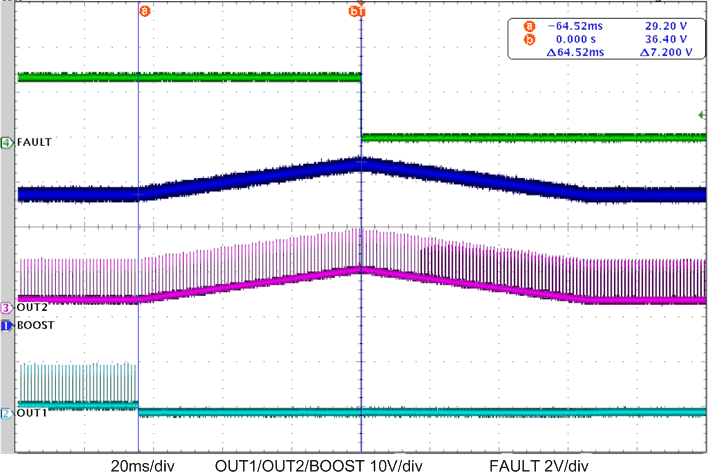
 Figure 13. VIN Overvoltage Protection (DC-DC OVP)
Figure 13. VIN Overvoltage Protection (DC-DC OVP)
 Figure 14. VIN Overvoltage Protection (VIN OVP)
Figure 14. VIN Overvoltage Protection (VIN OVP)
 Figure 15. VIN Undervoltage Lockout
Figure 15. VIN Undervoltage Lockout
 Figure 16. LED Open Fault
Figure 16. LED Open Fault
 Figure 17. LED Short Fault
Figure 17. LED Short Fault
8.4 Device Functional Modes
8.4.1 Device States
The TPS61193-Q1 enters STANDBY mode when the internal LDO output rises above the power-on reset level, VLDO > VPOR. In STANDBY mode the device is able to detect VDDIO/EN signal. When VDDIO/EN is pulled high, the device powers up. After start LED outputs are sensed to detect grounded outputs. Grounded outputs are disabled and excluded from the adaptive voltage control loop of the DC-DC.
If a fault condition is detected, the device enters FAULT_RECOVERY state. Faults that cause the device to enter FAULT_RECOVERY are listed in Table 3. When LED open or short is detected, the faulty string is disabled, but device stays in ACTIVE mode.
 Figure 18. State Diagram
Figure 18. State Diagram
 Figure 19. Timing Diagram for the Typical Start-Up and Shutdown
Figure 19. Timing Diagram for the Typical Start-Up and Shutdown
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The TPS61193-Q1 is designed for automotive applications, and an input voltage (VIN), intended to be connected to the automotive battery, supports input voltage range from 4.5 V to 40 V. Device internal circuitry is powered from the integrated LDO.
The TPS61193-Q1 uses a simple four-wire control:
- VDDIO/EN for enable
- PWM input for brightness control
- SYNC pin for boost synchronisation (optional)
- FAULT output to indicate fault condition (optional)
9.2 Typical Applications
9.2.1 Typical Application for 3 LED Strings
Figure 20 shows the typical application for TPS61193-Q1 which supports 3 LED strings with maximum current 100 mA, with a boost switching frequency of 300 kHz.
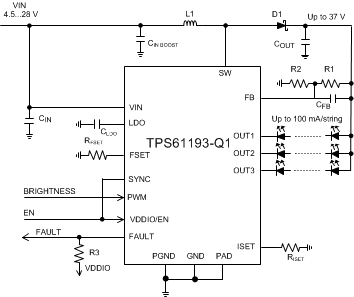 Figure 20. Three Strings 100 mA/String Configuration
Figure 20. Three Strings 100 mA/String Configuration
9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
| DESIGN PARAMETER | VALUE |
|---|---|
| VIN voltage range | 4.5 V – 28 V |
| LED string | 3P8S LEDs (30 V) |
| LED string current | 100 mA |
| Maximum boost voltage | 37 V |
| Boost switching frequency | 300 kHz |
| External boost sync | not used |
| Boost spread spectrum | enabled |
| L1 | 33 μH |
| CIN | 100 µF, 50 V |
| CIN BOOST | 2 × (10-µF, 50-V ceramic) + 33-µF, 50-V electrolytic |
| COUT | 2 × (10-µF, 50-V ceramic) + 33-µF, 50-V electrolytic |
| CFB | 15 pF |
| CLDO | 1 µF, 10 V |
| RISET | 24 kΩ |
| RFSET | 210 kΩ |
| R1 | 750 kΩ |
| R2 | 130 kΩ |
| R3 | 10 kΩ |
9.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
9.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
There are two main considerations when choosing an inductor; the inductor must not saturate, and the inductor current ripple must be small enough to achieve the desired output voltage ripple. Different saturation current rating specifications are followed by different manufacturers so attention must be given to details. Saturation current ratings are typically specified at 25°C. However, ratings at the maximum ambient temperature of application should be requested from the manufacturer. Shielded inductors radiate less noise and are preferred. The saturation current must be greater than the sum of the maximum load current, and the worst case average-to-peak inductor current. Equation 4 shows the worst case conditions
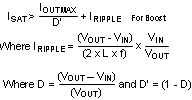
where
- IRIPPLE - peak inductor current
- IOUTMAX - maximum load current
- VIN - minimum input voltage in application
- L - min inductor value including worst case tolerances
- f - minimum switching frequency
- VOUT - output voltage
- D - Duty Cycle for CCM Operation
As a result, the inductor should be selected according to the ISAT. A more conservative and recommended approach is to choose an inductor that has a saturation current rating greater than the maximum current limit. A saturation current rating of at least 2.5 A is recommended for most applications. See Table 2 for recommended inductance value for the different switching frequency ranges. The inductor’s resistance should be less than
300 mΩ for good efficiency.
See detailed information in Understanding Boost Power Stages in Switch Mode Power Supplies. Power Stage Designer™ Tool can be used for the boost calculation: http://www.ti.com/tool/powerstage-designer.
9.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
A ceramic capacitor with 2 × VMAX BOOST or more voltage rating is recommended for the output capacitor. The DC-bias effect can reduce the effective capacitance by up to 80%, which needs to be considered in capacitance value selection. Capacitance recommendations for different switching frequencies are shown in Table 2. To minimize audible noise of ceramic capacitors their physical size should typically be minimized.
9.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
A ceramic capacitor with 2 × VIN MAX or more voltage rating is recommended for the input capacitor. The DC-bias effect can reduce the effective capacitance by up to 80%, which needs to be considered in capacitance value selection. Capacitance recommendations for different boost switching frequencies are shown in Table 2.
9.2.1.2.4 LDO Output Capacitor
A ceramic capacitor with at least 10-V voltage rating is recommended for the output capacitor of the LDO. The DC-bias effect can reduce the effective capacitance by up to 80%, which needs to be considered in capacitance value selection. Typically a 1-µF capacitor is sufficient.
9.2.1.2.5 Diode
A Schottky diode should be used for the boost output diode. Do not use ordinary rectifier diodes because slow switching speeds and long recovery times degrade the efficiency and the load regulation. Diode rating for peak repetitive current should be greater than inductor peak current (up to 3 A) to ensure reliable operation in boost mode. Average current rating should be greater than the maximum output current. Schottky diodes with a low forward drop and fast switching speeds are ideal for increasing efficiency. Choose a reverse breakdown voltage of the Schottky diode significantly larger than the output voltage.
9.2.1.3 Application Curves
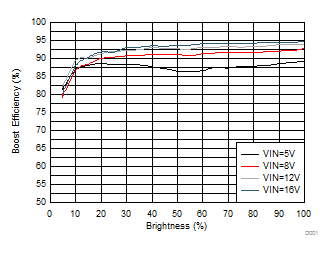
| Load 3 strings, 8 LEDs per string | ƒsw = 300 kHz, 33 μH | |
| 100 mA/string for VIN = 12 V and VIN = 16 V | ||
| 60 mA/string for VIN = 8 V | ||
| 50 mA/string for VIN = 5 V | ||
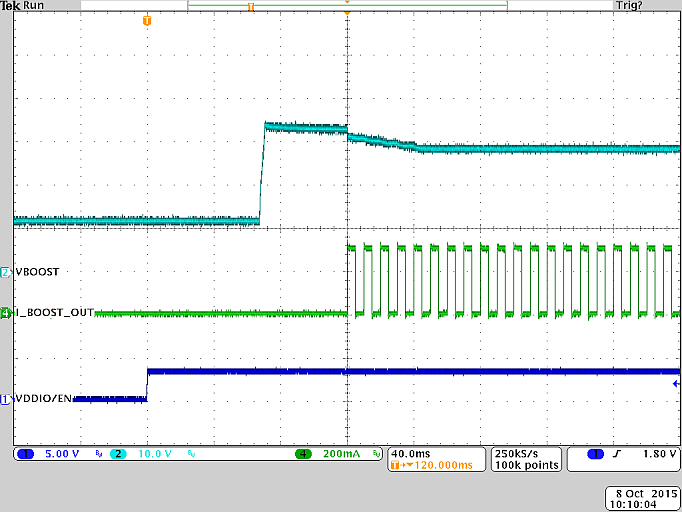 Figure 23. Typical Start-Up
Figure 23. Typical Start-Up

| Load 3 strings, 8 LEDs per string | ƒsw = 300 kHz, 33 μH | |
| 100 mA/string for VIN = 12 V and VIN = 16 V | ||
| 60 mA/string for VIN = 8 V | ||
| 50 mA/string for VIN = 5 V | ||
9.2.2 SEPIC Mode Application
When LED string voltage can be above or below VIN voltage, SEPIC configuration can be used. In this example, two separate coils are used for SEPIC. This can enable lower height external components to be used, compared to a coupled coil solution. On the other hand, coupled coil typically maximizes the efficiency. Also, in this example, an external clock is used to synchronize SEPIC switching frequency. External clock input can be modulated to spread switching frequency spectrum.
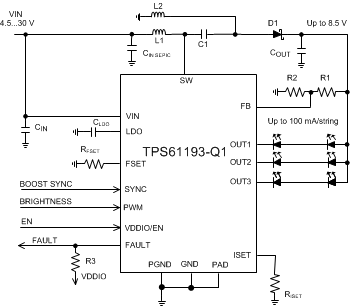 Figure 25. SEPIC Mode, 3 Strings, 100 mA/String Configuration
Figure 25. SEPIC Mode, 3 Strings, 100 mA/String Configuration
9.2.2.1 Design Requirements
| DESIGN PARAMETER | VALUE |
|---|---|
| VIN voltage range | 4.5 V – 30 V |
| LED string | 3P2S LEDs (7.2 V) |
| LED string current | 100 mA |
| Maxmum output voltage | 10 V |
| SEPIC switching frequency | 2.2 MHz |
| External sync for SEPIC | used |
| Spread spectrum | Internal spread spectrum disabled (external sync used) |
| L1, L2 | 10 µH |
| CIN | 10 µF 50 V |
| CIN SEPIC | 2 × 10-µF, 50-V ceramic + 33 µF 50-V electrolytic |
| C1 | 10-µF 50-V ceramic |
| COUT | 2 × 10-µF, 50-V ceramic + 33 µF 50-V electrolytic |
| CLDO | 1 µF, 10 V |
| RISET | 24 kΩ |
| RFSET | 24 kΩ |
| R1 | 184 kΩ |
| R2 | 130 kΩ |
| R3 | 10 kΩ |
9.2.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
In SEPIC mode the maximum voltage at the SW pin is equal to the sum of the input voltage and the output voltage. Because of this, the maximum sum of input and output voltage must be limited below 50 V. See Detailed Design Procedure for general external component guidelines. Main differences of SEPIC compared to boost are described below.
Power Stage Designer™ Tool can be used for modeling SEPIC behavior: http://www.ti.com/tool/powerstage-designer. For detailed explanation on SEPIC see Texas Instruments Analog Applications Journal Designing DC/DC Converters Based on SEPIC Topology.
9.2.2.2.1 Inductor
In SEPIC mode, currents flowing through the coupled inductors or the two separate inductors L1 and L2 are the input current and output current, respectively. Values can be calculated using Power Stage Designer™ Tool or using equations in Designing DC/DC Converters Based on SEPIC Topology.
9.2.2.2.2 Diode
In SEPIC mode diode peak current is equal to the sum of input and output currents. Diode rating for peak repetitive current should be greater than SW pin current limit (up to 3 A for transients) to ensure reliable operation in boost mode. Average current rating should be greater than the maximum output current. Diode voltage rating must be higher than sum of input and output voltages.
9.2.2.2.3 Capacitor C1
Ti recommends a ceramic capacitor with low ESR. Diode voltage rating must be higher than maximum input voltage.
9.2.2.3 Application Curves
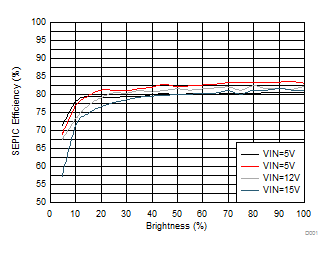
| Load 100mA per string, 3 strings, 2 LEDs per string | ||
| ƒsw = 2.2 MHz | ||
| 2 × 10 μH, IHLP2525BDER100M | ||
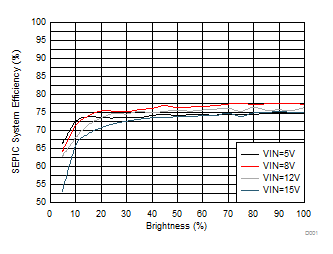
| Load 100mA per string, 3 strings, 2 LEDs per string | |
| ƒsw = 2.2 MHz | |
| 2 × 10 μH, IHLP2525BDER100M |
10 Power Supply Recommendations
The device is designed to operate from an automotive battery. Device should be protected from reversal voltage and voltage dump over 50 V. The resistance of the input supply rail must be low enough so that the input current transient does not cause too high drop at TPS61193-Q1 VIN pin. If the input supply is connected by using long wires additional bulk capacitance may be required in addition to the ceramic bypass capacitors in the VIN line.
