SNVSB07C July 2018 – April 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Integrated Power MOSFET
- 7.3.2 PSR Flyback Modes of Operation
- 7.3.3 Setting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.4 Control Loop Error Amplifier
- 7.3.5 Precision Enable
- 7.3.6 Configurable Soft Start
- 7.3.7 External Bias Supply
- 7.3.8 Minimum On-Time and Off-Time
- 7.3.9 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Design 1: Wide VIN, Low IQ PSR Flyback Converter Rated at 5 V, 1 A
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Custom Design With Excel Quickstart Tool
- 8.2.1.2.3 Flyback Transformer – T1
- 8.2.1.2.4 Flyback Diode – DFLY
- 8.2.1.2.5 Zener Clamp Circuit – DF, DCLAMP
- 8.2.1.2.6 Output Capacitor – COUT
- 8.2.1.2.7 Input Capacitor – CIN
- 8.2.1.2.8 Feedback Resistor – RFB
- 8.2.1.2.9 Thermal Compensation Resistor – RTC
- 8.2.1.2.10 UVLO Resistors – RUV1, RUV2
- 8.2.1.2.11 Soft-Start Capacitor – CSS
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Design 2: PSR Flyback Converter With Dual Outputs of 15 V and –7.7 V at 200 mA
- 8.2.3 Design 3: PSR Flyback Converter With Stacked Dual Outputs of 24 V and 5 V
- 8.2.1
Design 1: Wide VIN, Low IQ PSR Flyback Converter Rated at 5 V, 1 A
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.7 External Bias Supply
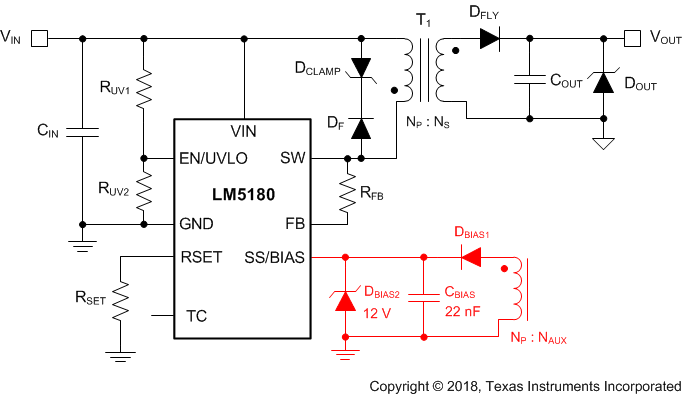 Figure 22. External Bias Supply Using Transformer Auxiliary Winding
Figure 22. External Bias Supply Using Transformer Auxiliary Winding The LM5180-Q1 has an external bias supply feature that reduces input quiescent current and increases efficiency. When the voltage at SS/BIAS exceeds a rising threshold of 5.5 V, bias power for the internal LDO regulator can be derived from an external voltage source or from a transformer auxiliary winding as shown in Figure 22. With a bias supply connected, the LM5180-Q1 then uses its internal soft-start ramp to control the primary current during start-up.
When using a transformer auxiliary winding for bias power, the total leakage current related to diodes DBIAS1 and DBIAS2 in Figure 22 should be less than 1 µA across the full operating temperature range.