SPNU151W January 1998 – March 2023 66AK2E05 , 66AK2H06 , 66AK2H12 , 66AK2H14 , AM1705 , AM1707 , AM1802 , AM1806 , AM1808 , AM1810 , AM5K2E04 , OMAP-L132 , OMAP-L137 , OMAP-L138 , SM470R1B1M-HT , TMS470R1A288 , TMS470R1A384 , TMS470R1A64 , TMS470R1B1M , TMS470R1B512 , TMS470R1B768
- Read This First
- 1Introduction to the Software Development Tools
-
2Using the C/C++ Compiler
- 2.1 About the Compiler
- 2.2 Invoking the C/C++ Compiler
- 2.3
Changing the Compiler's Behavior with Options
- 2.3.1 Linker Options
- 2.3.2 Frequently Used Options
- 2.3.3 Miscellaneous Useful Options
- 2.3.4 Run-Time Model Options
- 2.3.5 Symbolic Debugging and Profiling Options
- 2.3.6 Specifying Filenames
- 2.3.7 Changing How the Compiler Interprets Filenames
- 2.3.8 Changing How the Compiler Processes C Files
- 2.3.9 Changing How the Compiler Interprets and Names Extensions
- 2.3.10 Specifying Directories
- 2.3.11 Assembler Options
- 2.3.12 Deprecated Options
- 2.4 Controlling the Compiler Through Environment Variables
- 2.5
Controlling the Preprocessor
- 2.5.1 Predefined Macro Names
- 2.5.2 The Search Path for #include Files
- 2.5.3 Support for the #warning and #warn Directives
- 2.5.4 Generating a Preprocessed Listing File (--preproc_only Option)
- 2.5.5 Continuing Compilation After Preprocessing (--preproc_with_compile Option)
- 2.5.6 Generating a Preprocessed Listing File with Comments (--preproc_with_comment Option)
- 2.5.7 Generating Preprocessed Listing with Line-Control Details (--preproc_with_line Option)
- 2.5.8 Generating Preprocessed Output for a Make Utility (--preproc_dependency Option)
- 2.5.9 Generating a List of Files Included with #include (--preproc_includes Option)
- 2.5.10 Generating a List of Macros in a File (--preproc_macros Option)
- 2.6 Passing Arguments to main()
- 2.7 Understanding Diagnostic Messages
- 2.8 Other Messages
- 2.9 Generating Cross-Reference Listing Information (--gen_cross_reference_listing Option)
- 2.10 Generating a Raw Listing File (--gen_preprocessor_listing Option)
- 2.11 Using Inline Function Expansion
- 2.12 Using Interlist
- 2.13 Controlling Application Binary Interface
- 2.14 VFP Support
- 2.15 Enabling Entry Hook and Exit Hook Functions
-
3Optimizing Your Code
- 3.1 Invoking Optimization
- 3.2 Controlling Code Size Versus Speed
- 3.3 Performing File-Level Optimization (--opt_level=3 option)
- 3.4 Program-Level Optimization (--program_level_compile and --opt_level=3 options)
- 3.5 Automatic Inline Expansion (--auto_inline Option)
- 3.6 Link-Time Optimization (--opt_level=4 Option)
- 3.7
Using Feedback Directed Optimization
- 3.7.1
Feedback Directed Optimization
- 3.7.1.1 Phase 1 -- Collect Program Profile Information
- 3.7.1.2 Phase 2 -- Use Application Profile Information for Optimization
- 3.7.1.3 Generating and Using Profile Information
- 3.7.1.4 Example Use of Feedback Directed Optimization
- 3.7.1.5 The .ppdata Section
- 3.7.1.6 Feedback Directed Optimization and Code Size Tune
- 3.7.1.7 Instrumented Program Execution Overhead
- 3.7.1.8 Invalid Profile Data
- 3.7.2 Profile Data Decoder
- 3.7.3 Feedback Directed Optimization API
- 3.7.4 Feedback Directed Optimization Summary
- 3.7.1
Feedback Directed Optimization
- 3.8 Using Profile Information to Analyze Code Coverage
- 3.9 Accessing Aliased Variables in Optimized Code
- 3.10 Use Caution With asm Statements in Optimized Code
- 3.11 Using the Interlist Feature With Optimization
- 3.12 Debugging and Profiling Optimized Code
- 3.13
What Kind of Optimization Is Being
Performed?
- 3.13.1 Cost-Based Register Allocation
- 3.13.2 Alias Disambiguation
- 3.13.3 Branch Optimizations and Control-Flow Simplification
- 3.13.4 Data Flow Optimizations
- 3.13.5 Expression Simplification
- 3.13.6 Inline Expansion of Functions
- 3.13.7 Function Symbol Aliasing
- 3.13.8 Induction Variables and Strength Reduction
- 3.13.9 Loop-Invariant Code Motion
- 3.13.10 Loop Rotation
- 3.13.11 Instruction Scheduling
- 3.13.12 Tail Merging
- 3.13.13 Autoincrement Addressing
- 3.13.14 Block Conditionalizing
- 3.13.15 Epilog Inlining
- 3.13.16 Removing Comparisons to Zero
- 3.13.17 Integer Division With Constant Divisor
- 3.13.18 Branch Chaining
-
4Linking C/C++ Code
- 4.1 Invoking the Linker Through the Compiler (-z Option)
- 4.2 Linker Code Optimizations
- 4.3
Controlling the Linking Process
- 4.3.1 Including the Run-Time-Support Library
- 4.3.2 Run-Time Initialization
- 4.3.3 Initialization of Cinit and Watchdog Timer Hold
- 4.3.4 Global Object Constructors
- 4.3.5 Specifying the Type of Global Variable Initialization
- 4.3.6 Specifying Where to Allocate Sections in Memory
- 4.3.7 A Sample Linker Command File
-
5C/C++ Language
Implementation
- 5.1 Characteristics of ARM C
- 5.2 Characteristics of ARM C++
- 5.3 Using MISRA C 2004
- 5.4 Using the ULP Advisor
- 5.5 Data Types
- 5.6 File Encodings and Character Sets
- 5.7 Keywords
- 5.8 C++ Exception Handling
- 5.9 Register Variables and Parameters
- 5.10 The __asm Statement
- 5.11
Pragma Directives
- 5.11.1 The CALLS Pragma
- 5.11.2 The CHECK_MISRA Pragma
- 5.11.3 The CHECK_ULP Pragma
- 5.11.4 The CODE_SECTION Pragma
- 5.11.5 The CODE_STATE Pragma
- 5.11.6 The DATA_ALIGN Pragma
- 5.11.7 The DATA_SECTION Pragma
- 5.11.8 The Diagnostic Message Pragmas
- 5.11.9 The DUAL_STATE Pragma
- 5.11.10 The FORCEINLINE Pragma
- 5.11.11 The FORCEINLINE_RECURSIVE Pragma
- 5.11.12 The FUNC_ALWAYS_INLINE Pragma
- 5.11.13 The FUNC_CANNOT_INLINE Pragma
- 5.11.14 The FUNC_EXT_CALLED Pragma
- 5.11.15 The FUNCTION_OPTIONS Pragma
- 5.11.16 The INTERRUPT Pragma
- 5.11.17 The LOCATION Pragma
- 5.11.18 The MUST_ITERATE Pragma
- 5.11.19 The NOINIT and PERSISTENT Pragmas
- 5.11.20 The NOINLINE Pragma
- 5.11.21 The NO_HOOKS Pragma
- 5.11.22 The once Pragma
- 5.11.23 The pack Pragma
- 5.11.24 The PROB_ITERATE Pragma
- 5.11.25 The RESET_MISRA Pragma
- 5.11.26 The RESET_ULP Pragma
- 5.11.27 The RETAIN Pragma
- 5.11.28 The SET_CODE_SECTION and SET_DATA_SECTION Pragmas
- 5.11.29 The SWI_ALIAS Pragma
- 5.11.30 The TASK Pragma
- 5.11.31 The UNROLL Pragma
- 5.11.32 The WEAK Pragma
- 5.12 The _Pragma Operator
- 5.13 Application Binary Interface
- 5.14 ARM Instruction Intrinsics
- 5.15 Object File Symbol Naming Conventions (Linknames)
- 5.16 Changing the ANSI/ISO C/C++ Language Mode
- 5.17 GNU , Clang, and ACLE Language Extensions
- 5.18 AUTOSAR
- 5.19 Compiler Limits
-
6Run-Time Environment
- 6.1 Memory Model
- 6.2
Object Representation
- 6.2.1
Data Type Storage
- 6.2.1.1 char and short Data Types (signed and unsigned)
- 6.2.1.2 float, int, and long Data Types (signed and unsigned)
- 6.2.1.3 double, long double, and long long Data Types (signed and unsigned)
- 6.2.1.4 Pointer to Data Member Types
- 6.2.1.5 Pointer to Member Function Types
- 6.2.1.6 Structure and Array Alignment
- 6.2.2 Bit Fields
- 6.2.3 Character String Constants
- 6.2.1
Data Type Storage
- 6.3 Register Conventions
- 6.4 Function Structure and Calling Conventions
- 6.5 Accessing Linker Symbols in C and C++
- 6.6
Interfacing C and C++ With Assembly Language
- 6.6.1 Using Assembly Language Modules With C/C++ Code
- 6.6.2 Accessing Assembly Language Functions From C/C++
- 6.6.3 Accessing Assembly Language Variables From C/C++
- 6.6.4 Sharing C/C++ Header Files With Assembly Source
- 6.6.5 Using Inline Assembly Language
- 6.6.6 Modifying Compiler Output
- 6.7 Interrupt Handling
- 6.8 Intrinsic Run-Time-Support Arithmetic and Conversion Routines
- 6.9 Built-In Functions
- 6.10
System Initialization
- 6.10.1 Boot Hook Functions for System Pre-Initialization
- 6.10.2 Run-Time Stack
- 6.10.3 Automatic Initialization of Variables
- 6.10.4 Initialization Tables
- 6.11 Dual-State Interworking Under TIABI (Deprecated)
-
7Using Run-Time-Support Functions and Building Libraries
- 7.1
C and C++ Run-Time Support Libraries
- 7.1.1 Linking Code With the Object Library
- 7.1.2 Header Files
- 7.1.3 Modifying a Library Function
- 7.1.4 Support for String Handling
- 7.1.5 Minimal Support for Internationalization
- 7.1.6 Support for Time and Clock Functions
- 7.1.7 Allowable Number of Open Files
- 7.1.8 Nonstandard Header Files in the Source Tree
- 7.1.9 Library Naming Conventions
- 7.2 The C I/O Functions
- 7.3 Handling Reentrancy (_register_lock() and _register_unlock() Functions)
- 7.4 Library-Build Process
- 7.1
C and C++ Run-Time Support Libraries
- 8C++ Name Demangler
- A Glossary
- B Revision History
- B Earlier Revisions
6.4 Function Structure and Calling Conventions
The C/C++ compiler imposes a strict set of rules on function calls. Except for special run-time support functions, any function that calls or is called by a C/C++ function must follow these rules. Failure to adhere to these rules can disrupt the C/C++ environment and cause a program to fail.
The following sections use this terminology to describe the function-calling conventions of the C/C++ compiler:
- Argument block. The part of the local frame used to pass arguments to other functions. Arguments are passed to a function by moving them into the argument block rather than pushing them on the stack. The local frame and argument block are allocated at the same time.
- Register save area. The part of the local frame that is used to save the registers when the program calls the function and restore them when the program exits the function.
- Save-on-call registers. Registers R0-R3 and R12 (alternate names are A1-A4 and V9). The called function does not preserve the values in these registers; therefore, the calling function must save them if their values need to be preserved.
- Save-on-entry registers. Registers R4-R11 and R14 (alternate names are V1-V8 and LR). It is the called function's responsibility to preserve values in these registers. If the called function modifies these registers, it saves them when it gains control and preserves them when it returns control to the calling function.
For details on the calling conventions in EABI mode or when using a VFP coprocessor, refer to the EABI documentation located in the ARM Information Center.
Figure 6-5 illustrates a typical function call. In this example, arguments are passed to the function, and the function uses local variables and calls another function. The first four arguments are passed to registers R0-R3. This example also shows allocation of a local frame and argument block for the called function. Functions that have no local variables and do not require an argument block do not allocate a local frame.
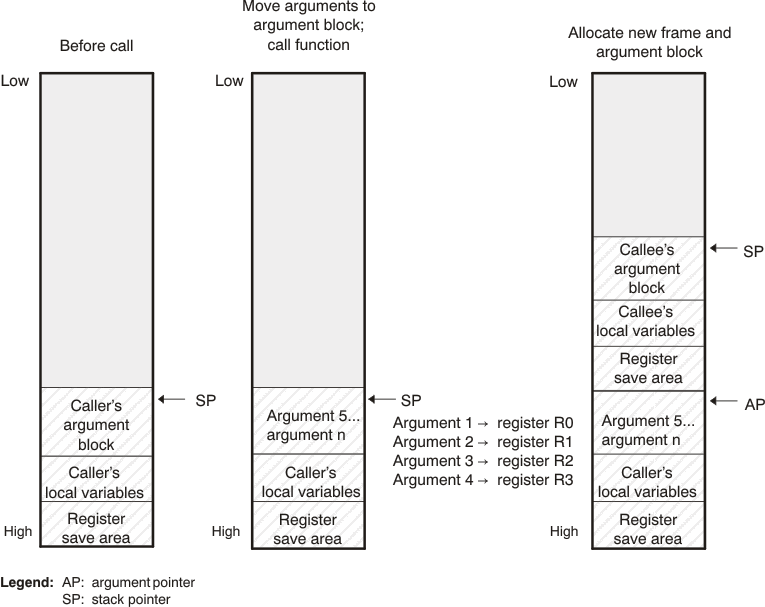 Figure 6-5 Use of the Stack
During a Function Call
Figure 6-5 Use of the Stack
During a Function Call