SPRACV1B February 2022 – January 2024 AM2434 , AM6411 , AM6412 , AM6421 , AM6441 , AM6442
1 Introduction
The benchmarks were measured on the Cortex®-A53 and Cortex-R5F cores. For up to date results, refer to the Performance Guide and the Benchmark Demo application in the Processor SDK for AM64x. The benchmarking was produced using the following: TMDS64GPEVM, SK-AM64X, and LP-AM243. The key board parameters for the evaluation were 1GHz clock speed for the Cortex-A53 cores, 800MHz for the Cortex-R5F cores, and a 16-bit wide DDR4 or LPDDR4 at a speed of 1600MT/s. AM64x adds a dual core Cortex-A53 including a 256kB L2 cache, but otherwise the devices are identical. For reference, see Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2.
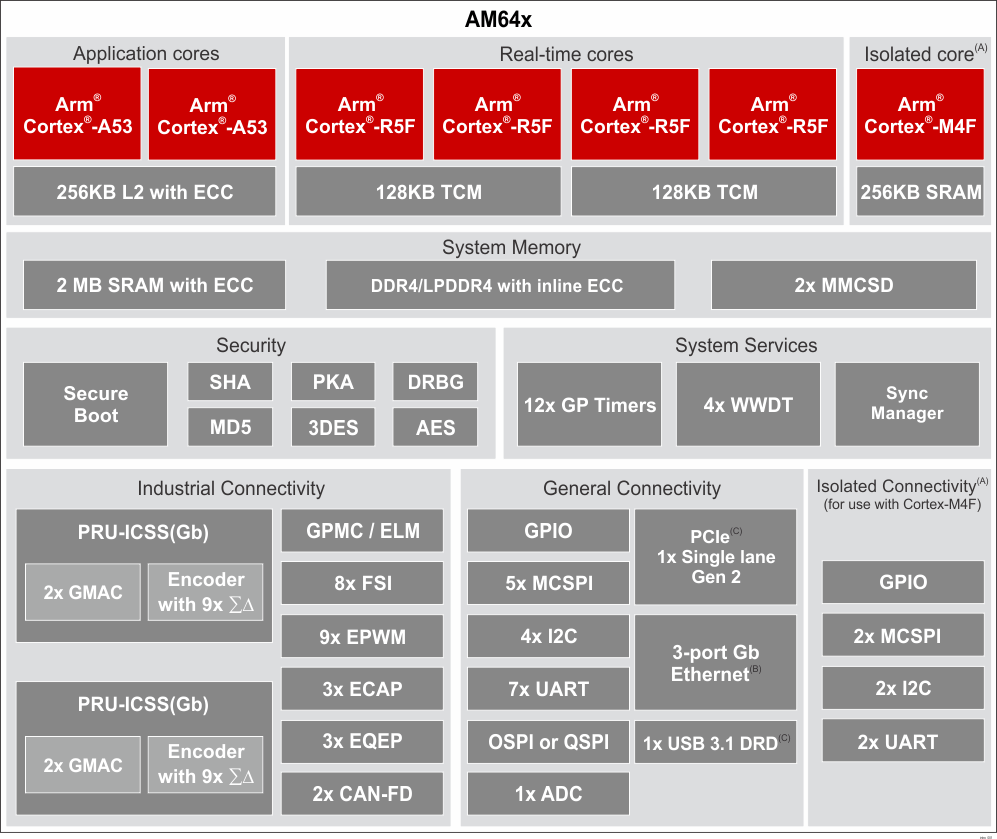
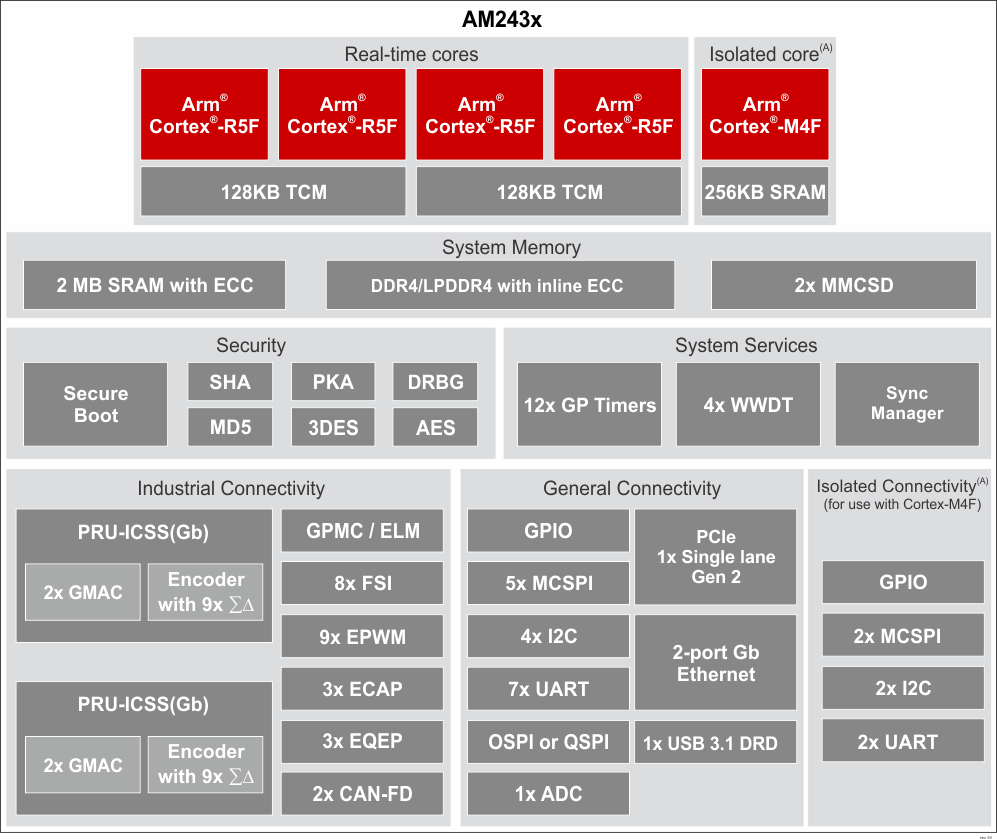 Figure 1-2 Functional Block Diagram:
AM243x
Figure 1-2 Functional Block Diagram:
AM243x