SPRACX9 July 2021 DRA829J , DRA829J-Q1 , DRA829V , DRA829V-Q1 , TDA4VM , TDA4VM-Q1
3 The Vision Pre-Processing Accelerator
The Vision Pre-processing Accelerator (VPAC) subsystem is a set of common vision primitive functions, performing pixel data processing tasks, such as: color processing and enhancement, noise filtering, wide dynamic range (WDR) processing, lens distortion correction, pixel remap for de-warping, on-the-fly scale generation, and on-the-fly pyramid generation. The VPAC offloads these common tasks from the main SoC processors (ARM, DSP, and so forth), so these CPUs can be utilized for differentiated high-level algorithms. The VPAC is designed to support multiple cameras by working in time-multiplexing mode. The VPAC works as a front end to vision processing pipeline and provides for further processing by other vision accelerators or processor cores inside the SoC.
Figure 3-1 shows the VPAC high-level block diagram.
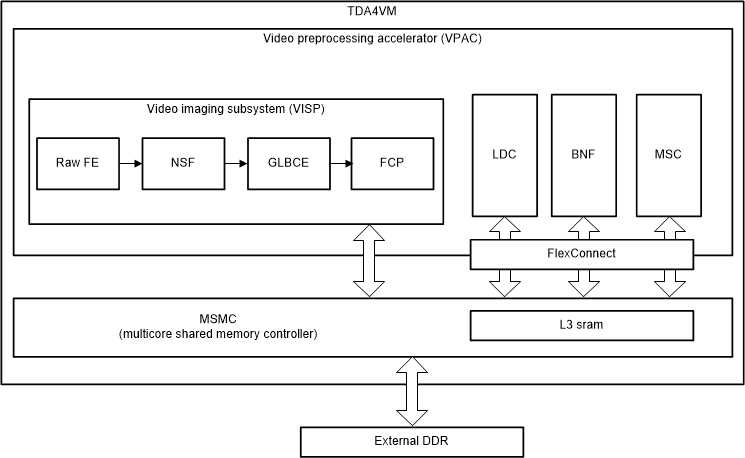 Figure 3-1 VPAC Block Diagram
Figure 3-1 VPAC Block DiagramThe VPAC is composed on following major blocks:
- Video Imaging Subsystem (VISS)
- Lens Distortion Correction (LDC)
- Bilinear Noise Filter (BNF)
- Multi-scaler (MSC)