SPRADI0A July 2024 – November 2024
3.1 Simulink Tool Optimization
 Figure 3-1 Hardware Settings
Figure 3-1 Hardware SettingsOpen model configuration parameters by selecting the Hardware settings option under the Hardware tab of Simulink window. Code optimization configurations are available in the Optimization tab available in the Code Generation drop down as shown in Figure 3-2.
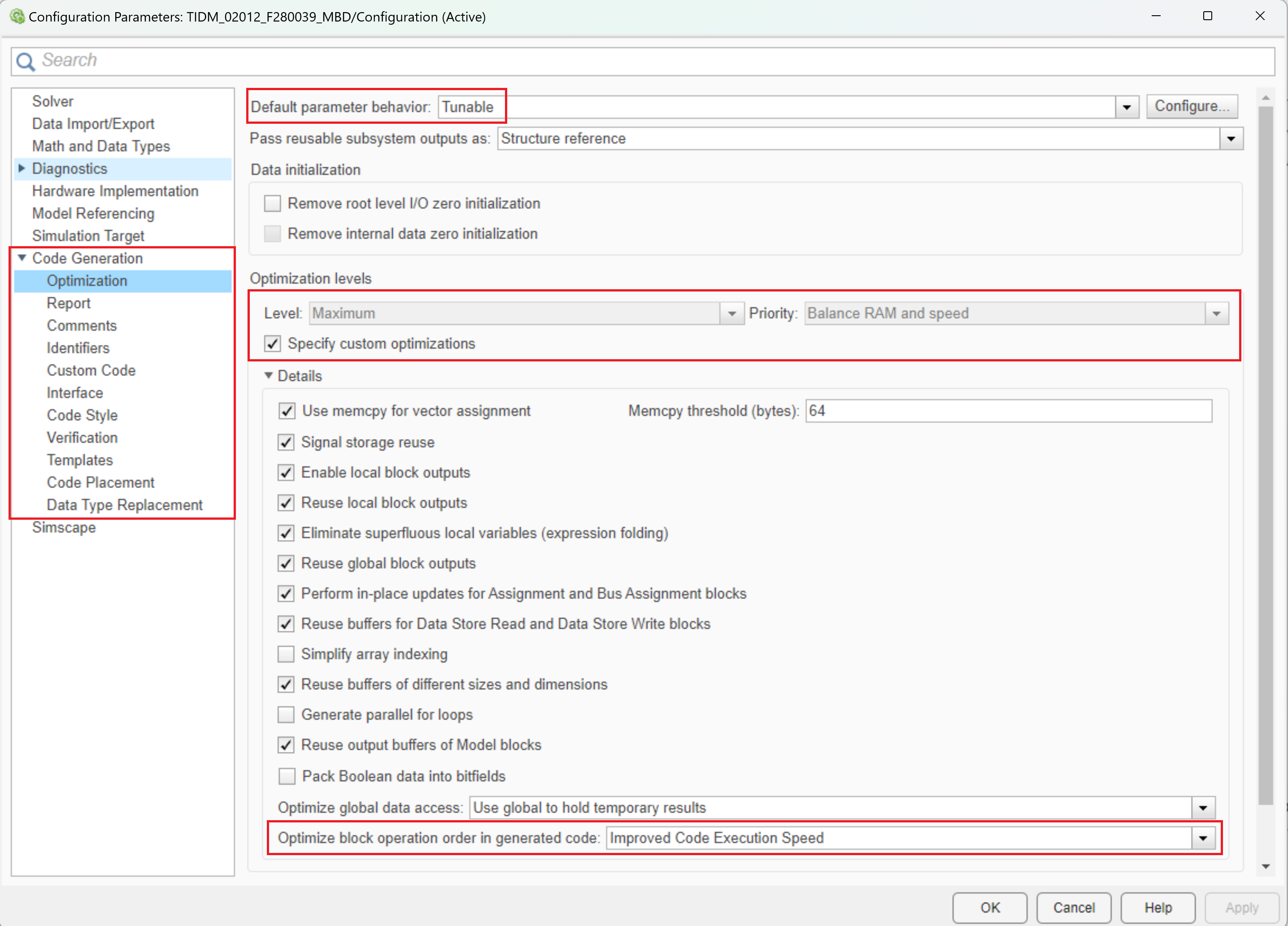 Figure 3-2 Configuration
Parameters
Figure 3-2 Configuration
ParametersConfigurations to be made to ensure optimal code generation for C2000 are as shown in Table 3-1.
| Simulink Tab | Specific Setting | Default Configuration | Optimized Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code Generation | Build configuration | Faster Builds | Faster Runs |
| Prioritized objectives | Unspecified | Execution efficiency | |
| Optimization | Priority | Balance RAM and speed | Speed |
| Specify custom optimization | On | Off | |
| Default parameter behavior | Tunable | Inlined | |
| Efficient Map of Float to Int | Off | On | |
| Interface | Support absolute time | On | Off |
| Support complex | On | Off | |
| Support non finite | On | Off | |
| Math and Data Types | Life span | auto | 1 |
All the mentioned configurations can be configured manually by selecting appropriate options in the Model configuration section as shown in Figure 3-2. Alternatively, a MATLAB .m script containing the above configuration can be integrated with the application example to ensure that the optimized configurations are invoked.
The script to integrate with the application is available with the TIDM_2012_F280039_MBD example with the name - TIDM_02012_F280039C_MBD_optimconfigs.m.
Code Generation:
- Build Configuration: Faster
runs
The build configuration of faster runs ensures the C2000 tool chain configuration is updated to use compiler optimization -O2 in place of default -O0.
- Objective priorities: Execution
efficiency
Keeping execution efficiency as the highest priority in the objective priority ensures the code generation from MATLAB is focused on the execution speed. Other parameters such as RAM, ROM efficiency are also available as a part of objective priorities that can be invoked based on the requirement, but may impact the performance. Default configuration is none.
Optimization:
- Optimization priority: Maximize speed
User is allowed to configure the optimization priority to either maximize the speed, minimize the memory (RAM) or to balance between minimizing RAM and maximizing speed. To generate code focused on better performance in terms of execution speed, the optimization priority is to be set to maximize the speed. The default behavior is to optimize keeping a balance between RAM and speed.
Change Configuration Parameters > Code Generation > Optimization > Optimization levels > Priority to Maximize Execution Speed. This applies code generation settings to maximize execution speed.
- Optimization customization: Off
If the optimization customization is unchecked, the default configurations under the Details tab is auto-populated with the block operation optimized for improving code execution speed.
Uncheck the Specify custom optimizations in Configuration Parameters > Code Generation > Optimization > Optimization levels. This disables the parameters in the Details section, so that you cannot individually select or clear these parameters.
- Default parameter behavior: Inlined
Boost performance by changing Configuration Parameters > Code Generation > Optimization > Default parameter behavior to Inlined, optimizing default parameter behavior.
Also, check the Inline invariant signals checkbox in Configuration Parameters > Code Generation > Optimization > Advanced parameters. This uses the numerical values of model parameters, instead of their symbolic names, in generated code.
- Efficient Map of Float to Int: On
Datatype mapping from float to int is to be enabled. This configuration removes code that handles floating-point to integer conversion results for NaN values.
Check the Remove code from floating-point to integer conversions with saturation that maps NaN to zero checkbox in Configuration Parameters > Code Generation > Optimization > Advanced parameters. This removes code that handles floating-point to integer conversion results for NaN values.
Interface:
Under the interface tab, the support for all the data type configurations that are noto going to be in use can be disabled. For generating efficient code, the configuration support for absolute time, non-finite numbers and complex numbers can be removed. Additional checks for the selected configurations in the Support tab is enabled, which may add additional number of cycles in run time application code.
Uncheck the Support: absolute time, non-finite numbers and complex numbers checkbox in Configuration Parameters > Interface > Software environment. This causes the support for blocks that depend on absolute time, non-finite numbers and complex numbers. Deselecting unused configurations under the Support tab ensures better run-time code efficiency.
Set the Application lifespan (days) field in Configuration Parameters > Math and Data Types > Advanced parameters. This specifies how long, in days, an application that depends on elapsed time can execute before timer overflow occurs.