SPRUHZ7K August 2015 – April 2024 AM5706 , AM5708 , AM5716 , AM5718 , AM5718-HIREL
- 1
- Preface
-
1 Introduction
- 1.1 AM571x, AM570x Overview
- 1.2 AM571x, AM570x Environment
- 1.3
AM571x, AM570x Description
- 1.3.1 MPU Subsystem
- 1.3.2 DSP Subsystem
- 1.3.3 PRU-ICSS
- 1.3.4 IPU Subsystems
- 1.3.5 IVA-HD Subsystem
- 1.3.6 Display Subsystem
- 1.3.7 Video Processing Subsystem
- 1.3.8 Video Capture
- 1.3.9 3D GPU Subsystem
- 1.3.10 BB2D Subsystem
- 1.3.11 Camera Interface Subsystem
- 1.3.12 On-Chip Debug Support
- 1.3.13 Power, Reset, and Clock Management
- 1.3.14 On-Chip Memory
- 1.3.15 Memory Management
- 1.3.16 External Memory Interfaces
- 1.3.17 System and Connectivity Peripherals
- 1.4 AM571x, AM570x Family
- 1.5 AM571x, AM570x Device Identification
- 1.6 AM571x, AM570x Package Characteristics Overview
- 2 Memory Mapping
-
3 Power, Reset, and Clock Management
- 3.1
Device Power Management Introduction
- 3.1.1
Device Power-Management Architecture Building Blocks
- 3.1.1.1 Clock Management
- 3.1.1.2 Power Management
- 3.1.1.3 Voltage Management
- 3.1.2 Power-Management Techniques
- 3.1.1
Device Power-Management Architecture Building Blocks
- 3.2 PRCM Subsystem Overview
- 3.3 PRCM Subsystem Environment
- 3.4 PRCM Subsystem Integration
- 3.5
Reset Management Functional Description
- 3.5.1 Overview
- 3.5.2 General Characteristics of Reset Signals
- 3.5.3 Reset Sources
- 3.5.4 Reset Logging
- 3.5.5 Reset Domains
- 3.5.6
Reset Sequences
- 3.5.6.1 MPU Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.2 MPU Subsystem Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.3 MPU Subsystem Reset Sequence on Sleep and Wake-Up Transitions From RETENTION State
- 3.5.6.4 IVA Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.5 IVA Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.6 DSP1 Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.7 DSP1 Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.8 IPU1 Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.9 IPU1 Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.10 IPU2 Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.11 IPU2 Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.12 Global Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.6
Clock Management Functional Description
- 3.6.1 Overview
- 3.6.2 External Clock Inputs
- 3.6.3
Internal Clock Sources and Generators
- 3.6.3.1 PRM Clock Source
- 3.6.3.2 CM Clock Source
- 3.6.3.3 Generic DPLL Overview
- 3.6.3.4 DPLL_PER Description
- 3.6.3.5 DPLL_CORE Description
- 3.6.3.6 DPLL_ABE Description
- 3.6.3.7 DPLL_MPU Description
- 3.6.3.8 DPLL_IVA Description
- 3.6.3.9 DPLL_USB Description
- 3.6.3.10 DPLL_DSP Description
- 3.6.3.11 DPLL_GMAC Description
- 3.6.3.12 DPLL_GPU Description
- 3.6.3.13 DPLL_DDR Description
- 3.6.3.14 DPLL_PCIE_REF Description
- 3.6.3.15 APLL_PCIE Description
- 3.6.4
Clock Domains
- 3.6.4.1 CD_WKUPAON Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.2 CD_DSP1 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.3 CD_CUSTEFUSE Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.4 CD_MPU Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.5 CD_L4PER1 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.6 CD_L4PER2 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.7 CD_L4PER3 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.8 CD_L4SEC Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.9 CD_L3INIT Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.10 CD_IVA Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.11 CD_GPU Description
- 3.6.4.12 CD_EMU Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.13 CD_DSS Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.14 CD_L4_CFG Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.15 CD_L3_INSTR Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.16 CD_L3_MAIN1 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.17 CD_EMIF Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.18 CD_IPU Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.19 CD_IPU1 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.20 CD_IPU2 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.21 CD_DMA Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.22 CD_ATL Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.23 CD_CAM Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.24 CD_GMAC Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.25 CD_VPE Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.26 CD_RTC Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.27 CD_PCIE Clock Domain
- 3.7
Power Management Functional Description
- 3.7.1 PD_WKUPAON Description
- 3.7.2 PD_DSP1 Description
- 3.7.3 PD_CUSTEFUSE Description
- 3.7.4 PD_MPU Description
- 3.7.5 PD_IPU Description
- 3.7.6 PD_L3INIT Description
- 3.7.7 PD_L4PER Description
- 3.7.8 PD_IVA Description
- 3.7.9 PD_GPU Description
- 3.7.10 PD_EMU Description
- 3.7.11 PD_DSS Description
- 3.7.12 PD_CORE Description
- 3.7.13 PD_CAM Description
- 3.7.14 PD_MPUAON Description
- 3.7.15 PD_MMAON Description
- 3.7.16 PD_COREAON Description
- 3.7.17 PD_VPE Description
- 3.7.18 PD_RTC Description
- 3.8 Voltage-Management Functional Description
- 3.9 Device Low-Power States
- 3.10
PRCM Module Programming Guide
- 3.10.1 DPLLs Low-Level Programming Models
- 3.10.2 Clock Management Low-Level Programming Models
- 3.10.3 Power Management Low-Level Programming Models
- 3.11 497
- 3.12 PRCM Software Configuration for OPP_PLUS
- 3.13
PRCM Register Manual
- 3.13.1 Not Supported Functionality (Registers and Bits)
- 3.13.2 PRCM Instance Summary
- 3.13.3 CM_CORE_AON__CKGEN Registers
- 3.13.4 CM_CORE_AON__DSP1 Registers
- 3.13.5 CM_CORE_AON__DSP2 Registers
- 3.13.6 CM_CORE_AON__EVE1 Registers
- 3.13.7 CM_CORE_AON__EVE2 Registers
- 3.13.8 CM_CORE_AON__EVE3 Registers
- 3.13.9 CM_CORE_AON__EVE4 Registers
- 3.13.10 CM_CORE_AON__INSTR Registers
- 3.13.11 CM_CORE_AON__IPU Registers
- 3.13.12 CM_CORE_AON__MPU Registers
- 3.13.13 CM_CORE_AON__OCP_SOCKET Registers
- 3.13.14 CM_CORE_AON__RESTORE Registers
- 3.13.15 CM_CORE_AON__RTC Registers
- 3.13.16 CM_CORE_AON__VPE Registers
- 3.13.17 CM_CORE__CAM Registers
- 3.13.18 CM_CORE__CKGEN Registers
- 3.13.19 CM_CORE__COREAON Registers
- 3.13.20 CM_CORE__CORE Registers
- 3.13.21 CM_CORE__CUSTEFUSE Registers
- 3.13.22 CM_CORE__DSS Registers
- 3.13.23 CM_CORE__GPU Registers
- 3.13.24 CM_CORE__IVA Registers
- 3.13.25 CM_CORE__L3INIT Registers
- 3.13.26 CM_CORE__L4PER Registers
- 3.13.27 CM_CORE__OCP_SOCKET Registers
- 3.13.28 CM_CORE__RESTORE Registers
- 3.13.29 SMARTREFLEX Registers
- 3.13.30 CAM_PRM Registers
- 3.13.31 CKGEN_PRM Registers
- 3.13.32 COREAON_PRM Registers
- 3.13.33 CORE_PRM Registers
- 3.13.34 CUSTEFUSE_PRM Registers
- 3.13.35 DEVICE_PRM Registers
- 3.13.36 DSP1_PRM registers
- 3.13.37 DSP2_PRM Registers
- 3.13.38 DSS_PRM Registers
- 3.13.39 EMU_CM Registers
- 3.13.40 EMU_PRM Registers
- 3.13.41 EVE1_PRM Registers
- 3.13.42 EVE2_PRM Registers
- 3.13.43 EVE3_PRM Registers
- 3.13.44 EVE4_PRM Registers
- 3.13.45 GPU_PRM Registers
- 3.13.46 INSTR_PRM Registers
- 3.13.47 IPU_PRM registers
- 3.13.48 IVA_PRM Registers
- 3.13.49 L3INIT_PRM Registers
- 3.13.50 L4PER_PRM Registers
- 3.13.51 MPU_PRM Registers
- 3.13.52 OCP_SOCKET_PRM Registers
- 3.13.53 RTC_PRM Registers
- 3.13.54 VPE_PRM Registers
- 3.13.55 WKUPAON_CM Registers
- 3.13.56 WKUPAON_PRM registers
- 3.1
Device Power Management Introduction
-
4 Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem
- 4.1 Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Overview
- 4.2 Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Integration
- 4.3
Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Functional Description
- 4.3.1 MPU Subsystem Block Diagram
- 4.3.2 Cortex-A15 MPCore (MPU_CLUSTER)
- 4.3.3 MPU_AXI2OCP
- 4.3.4 Memory Adapter
- 4.3.5 Realtime Counter (Master Counter)
- 4.3.6 MPU Watchdog Timer
- 4.3.7 MPU Subsystem Power Management
- 4.3.8 MPU Subsystem AMBA Interface Configuration
- 4.4
Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Register Manual
- 4.4.1 Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Instance Summary
- 4.4.2 MPU_CS_STM Registers
- 4.4.3 MPU_INTC Registers
- 4.4.4 MPU_PRCM_OCP_SOCKET Registers
- 4.4.5 MPU_PRCM_DEVICE Registers
- 4.4.6 MPU_PRCM_PRM_C0 Registers
- 4.4.7 MPU_PRCM_CM_C0 Registers
- 4.4.8 MPU_WUGEN Registers
- 4.4.9 MPU_WD_TIMER Registers
- 4.4.10 MPU_AXI2OCP_MISC Registers
- 4.4.11 MPU_MA_LSM Registers
- 4.4.12 MPU_MA_WP Registers
-
5 DSP Subsystem
- 5.1 DSP Subsystem Overview
- 5.2 DSP Subsystem Integration
- 5.3
DSP Subsystem Functional Description
- 5.3.1 DSP Subsystem Block Diagram
- 5.3.2
DSP Subsystem Components
- 5.3.2.1 C66x DSP Subsystem Introduction
- 5.3.2.2
DSP TMS320C66x CorePac
- 5.3.2.2.1 DSP TMS320C66x CorePac CPU
- 5.3.2.2.2 DSP TMS320C66x CorePac Internal Memory Controllers and Memories
- 5.3.2.2.3
DSP C66x CorePac Internal Peripherals
- 5.3.2.2.3.1 DSP C66x CorePac Interrupt Controller (DSP INTC)
- 5.3.2.2.3.2 DSP C66x CorePac Power-Down Controller (DSP PDC)
- 5.3.2.2.3.3 DSP C66x CorePac Bandwidth Manager (BWM)
- 5.3.2.2.3.4 DSP C66x CorePac Memory Protection Hardware
- 5.3.2.2.3.5 DSP C66x CorePac Internal DMA (IDMA) Controller
- 5.3.2.2.3.6 DSP C66x CorePac External Memory Controller
- 5.3.2.2.3.7 DSP C66x CorePac Extended Memory Controller
- 5.3.2.2.3.8 L1P Memory Error Detection Logic
- 5.3.2.2.3.9 L2 Memory Error Detection and Correction Logic
- 5.3.2.3 DSP Debug and Trace Support
- 5.3.3 DSP System Control Logic
- 5.3.4 DSP Interrupt Requests
- 5.3.5 DSP DMA Requests
- 5.3.6 DSP Intergated Memory Management Units
- 5.3.7 DSP Integrated EDMA Subsystem
- 5.3.8 DSP L2 interconnect Network
- 5.3.9 DSP Boot Configuration
- 5.3.10 DSP Internal and External Memory Views
- 5.4 DSP Subsystem Register Manual
- 6 IVA Subsystem
-
7 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem
- 7.1 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem Overview
- 7.2 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem Integration
- 7.3 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem Functional Description
- 7.4 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem Register Manual
-
8 Camera Interface Subsystem
- 8.1 CAMSS Overview
- 8.2 CAMSS Environment
- 8.3 CAMSS Integration
- 8.4
CAMSS Functional Description
- 8.4.1 CAMSS Hardware and Software Reset
- 8.4.2 CAMSS Clock Configuration
- 8.4.3 CAMSS Power Management
- 8.4.4 CAMSS Interrupt Events
- 8.4.5 CSI2 PHY Functional Description
- 8.4.6
CAL Functional Description
- 8.4.6.1 CAL Block Diagram
- 8.4.6.2
CSI2 Low Level Protocol
- 8.4.6.2.1 CSI2 Physical Layer
- 8.4.6.2.2 CSI2 Multi-lane Layer and Lane Merger
- 8.4.6.2.3
CSI2 Protocol Layer
- 8.4.6.2.3.1 CSI2 Short Packet
- 8.4.6.2.3.2 CSI2 Long Packet
- 8.4.6.2.3.3 CSI2 ECC and Checksum Generation
- 8.4.6.2.3.4 CSI2 Alignment Constraints
- 8.4.6.2.3.5 CSI2 Data Identifier
- 8.4.6.2.3.6 CSI2 Virtual Channel ID
- 8.4.6.2.3.7 CSI2 Synchronization Codes
- 8.4.6.2.3.8 CSI2 Generic Short Packet Codes
- 8.4.6.2.3.9 CSI2 Frame Structure and Data
- 8.4.6.2.3.10 CSI2 Virtual Channel and Context
- 8.4.6.2.4 CSI2 TAG Generation FSM
- 8.4.6.3 CAL Data Stream Merger
- 8.4.6.4 CAL Pixel Extraction
- 8.4.6.5 CAL DPCM Decoding and Encoding
- 8.4.6.6 CAL Stream Interleaving
- 8.4.6.7 CAL Pixel Packing
- 8.4.6.8 CAL Write DMA
- 8.4.6.9 CAL Video Port
- 8.4.6.10 CAL Registers Shadowing
- 8.5 CAMSS Register Manual
-
9 Video Input Port
- 9.1 VIP Overview
- 9.2 VIP Environment
- 9.3 VIP Integration
- 9.4
VIP Functional Description
- 9.4.1 VIP Block Diagram
- 9.4.2 VIP Software Reset
- 9.4.3 VIP Power and Clocks Management
- 9.4.4
VIP Slice
- 9.4.4.1 VIP Slice Processing Path Overview
- 9.4.4.2 VIP Slice Processing Path Multiplexers
- 9.4.4.3
VIP Slice Processing Path Examples
- 9.4.4.3.1 Input: A=RGB, B=YUV422; Output: A=RGB, B=RGB
- 9.4.4.3.2 Input: A=YUV422 8/16, B=YUV422; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, B=RGB
- 9.4.4.3.3 Input: A=RGB, B=YUV422; Output: A=RGB, B=Scaled YUV420
- 9.4.4.3.4 Input: A=YUV444, B=YUV422; Output: A=YUV422, A=Scaled YUV422, B=YUV422
- 9.4.4.3.5 Input: A=YUV444; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, A=YUV420
- 9.4.4.3.6 Input: A=YUV444; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, A=YUV444
- 9.4.4.3.7 Input: A=YUV422 8/16; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, A=YUV444
- 9.4.4.3.8 Input: A=YUV422 8/16, B=YUV422; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, B=YUV420
- 9.4.4.3.9 Input: A=YUV422 8/16, B=YUV422; Output: A=YUV420, B=YUV420
- 9.4.5
VIP Parser
- 9.4.5.1 Features
- 9.4.5.2 Repacker
- 9.4.5.3 Analog Video
- 9.4.5.4 Digitized Video
- 9.4.5.5 Frame Buffers
- 9.4.5.6
Input Data Interface
- 9.4.5.6.1 8b Interface Mode
- 9.4.5.6.2 16b Interface Mode
- 9.4.5.6.3 24b Interface Mode
- 9.4.5.6.4 Signal Relationships
- 9.4.5.6.5 General 5 Pin Interfaces
- 9.4.5.6.6 Signal Subsets—4 Pin VSYNC, ACTVID, and FID
- 9.4.5.6.7 Signal Subsets—4 Pin VSYNC, HSYNC, and FID
- 9.4.5.6.8 Vertical Sync
- 9.4.5.6.9 Field ID Determination Using Dedicated Signal
- 9.4.5.6.10 Field ID Determination Using VSYNC Skew
- 9.4.5.6.11 Rationale for FID Determination By VSYNC Skew
- 9.4.5.6.12 ACTVID Framing
- 9.4.5.6.13 Ancillary Data Storage in Descrete Sync Mode
- 9.4.5.7 BT.656 Style Embedded Sync
- 9.4.5.8
Source Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.1 Multiplexing Scenarios
- 9.4.5.8.2 2-Way Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.3 4-Way Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.4 Line Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.5 Super Frame Concept in Line Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.6 8-bit Data Interface in Line Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.7 16-bit Data Interface in Line Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.8 Split Lines in Line Multiplex Mode
- 9.4.5.8.9 Meta Data
- 9.4.5.8.10 TI Line Mux Mode, Split Lines, and Channel ID Remapping
- 9.4.5.9 Channel ID Extraction for 2x/4x Multiplexed Source
- 9.4.5.10 Embedded Sync Mux Modes and Data Bus Widths
- 9.4.5.11 Ancillary and Active Video Cropping
- 9.4.5.12 Interrupts
- 9.4.5.13 VDET Interrupt
- 9.4.5.14 Source Video Size
- 9.4.5.15 Clipping
- 9.4.5.16 Current and Last FID Value
- 9.4.5.17 Disable Handling
- 9.4.5.18 Picture Size Interrupt
- 9.4.5.19 Discrete Sync Signals
- 9.4.5.20 VIP Overflow Detection and Recovery
- 9.4.6 VIP Color Space Converter (CSC)
- 9.4.7
VIP Scaler (SC)
- 9.4.7.1 SC Features
- 9.4.7.2 SC Functional Description
- 9.4.7.3 SC Code
- 9.4.7.4
SC Coefficient Data Files
- 9.4.7.4.1
HS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 9.4.7.4.1.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_1_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_8div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_9div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_10div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_11div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.6 ppfcoef_scale_eq_12div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.7 ppfcoef_scale_eq_13div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.8 ppfcoef_scale_eq_14div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.9 ppfcoef_scale_eq_15div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2
VS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 9.4.7.4.2.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_1_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_3_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_4_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_5_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_6_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6
ppfcoef_scale_eq_7_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_8div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_9div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_10div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_11div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_12div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.6 ppfcoef_scale_eq_13div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.7 ppfcoef_scale_eq_14div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.8 ppfcoef_scale_eq_15div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.3 VS (Bilinear Filter Coefficients)
- 9.4.7.4.1
HS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 9.4.8
VIP Video Port Direct Memory Access (VPDMA)
- 9.4.8.1 VPDMA Introduction
- 9.4.8.2 VPDMA Basic Definitions
- 9.4.8.3 1107
- 9.4.8.4 VPDMA Client Buffering and Functionality
- 9.4.8.5 VPDMA Channels Assignment
- 9.4.8.6 VPDMA MFLAG Mechanism
- 9.4.8.7 VPDMA Interrupts
- 9.4.8.8
VPDMA Descriptors
- 9.4.8.8.1 Data Transfer Descriptors
- 9.4.8.8.2 Configuration Descriptor
- 9.4.8.8.3 Control Descriptor
- 9.4.8.9 VPDMA Configuration
- 9.4.8.10
VPDMA Data Formats
- 9.4.8.10.1
YUV Data Formats
- 9.4.8.10.1.1 Y 4:4:4 (Data Type 0)
- 9.4.8.10.1.2 Y 4:2:2 (Data Type 1)
- 9.4.8.10.1.3 Y 4:2:0 (Data Type 2)
- 9.4.8.10.1.4 C 4:4:4 (Data Type 4)
- 9.4.8.10.1.5 C 4:2:2 (Data Type 5)
- 9.4.8.10.1.6 C 4:2:0 (Data Type 6)
- 9.4.8.10.1.7 YC 4:2:2 (Data Type 7)
- 9.4.8.10.1.8 YC 4:4:4 (Data Type 8)
- 9.4.8.10.1.9 CY 4:2:2 (Data Type 23)
- 9.4.8.10.2
RGB Data Formats
- 9.4.8.10.2.1 RGB16-565 (Data Type 0)
- 9.4.8.10.2.2 ARGB-1555 (Data Type 1)
- 9.4.8.10.2.3 ARGB-4444 (Data Type 2)
- 9.4.8.10.2.4 RGBA-5551 (Data Type 3)
- 9.4.8.10.2.5 RGBA-4444 (Data Type 4)
- 9.4.8.10.2.6 ARGB24-6666 (Data Type 5)
- 9.4.8.10.2.7 RGB24-888 (Data Type 6)
- 9.4.8.10.2.8 ARGB32-8888 (Data Type 7)
- 9.4.8.10.2.9 RGBA24-6666 (Data Type 8)
- 9.4.8.10.2.10 RGBA32-8888 (Data Type 9)
- 9.4.8.10.3 Miscellaneous Data Type
- 9.4.8.10.1
YUV Data Formats
- 9.5 VIP Register Manual
-
10Video Processing Engine
- 10.1 VPE Overview
- 10.2 VPE Integration
- 10.3
VPE Functional Description
- 10.3.1 VPE Block Diagram
- 10.3.2 VPE VC1 Range Mapping/Range Reduction
- 10.3.3 VPE Deinterlacer (DEI)
- 10.3.4
VPE Scaler (SC)
- 10.3.4.1 SC Features
- 10.3.4.2 SC Functional Description
- 10.3.4.3 SC Code
- 10.3.4.4
SC Coefficient Data Files
- 10.3.4.4.1
HS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 10.3.4.4.1.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_1_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_8div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_9div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_10div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_11div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.6 ppfcoef_scale_eq_12div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.7 ppfcoef_scale_eq_13div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.8 ppfcoef_scale_eq_14div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.9 ppfcoef_scale_eq_15div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2
VS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 10.3.4.4.2.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_1_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_3_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_4_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_5_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_6_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6
ppfcoef_scale_eq_7_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_8div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_9div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_10div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_11div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_12div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.6 ppfcoef_scale_eq_13div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.7 ppfcoef_scale_eq_14div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.8 ppfcoef_scale_eq_15div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.9 ppcoef_scale_1x_ver_5tap.dat
- 10.3.4.4.3 VS (Bilinear Filter Coefficients)
- 10.3.4.4.1
HS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 10.3.5 VPE Color Space Converter (CSC)
- 10.3.6 VPE Chroma Up-Sampler (CHR_US)
- 10.3.7 VPE Chroma Down-Sampler (CHR_DS)
- 10.3.8 VPE YUV422 to YUV444 Conversion
- 10.3.9
VPE Video Port Direct Memory Access (VPDMA)
- 10.3.9.1 VPDMA Introduction
- 10.3.9.2 VPDMA Basic Definitions
- 10.3.9.3 VPDMA Client Buffering and Functionality
- 10.3.9.4 VPDMA Channels Assignment
- 10.3.9.5 VPDMA Interrupts
- 10.3.9.6
VPDMA Descriptors
- 10.3.9.6.1
Data Transfer Descriptors
- 10.3.9.6.1.1 Data Packet Descriptor Word 0 (Data)
- 10.3.9.6.1.2 Data Packet Descriptor Word 1
- 10.3.9.6.1.3 Data Packet Descriptor Word 2
- 10.3.9.6.1.4 Data Packet Descriptor Word 3
- 10.3.9.6.1.5 Data Packet Descriptor Word 4
- 10.3.9.6.1.6 Data Packet Descriptor Word 5
- 10.3.9.6.1.7 Data Packet Descriptor Word 6/7 (Data)
- 10.3.9.6.2 Configuration Descriptor
- 10.3.9.6.3 Control Descriptor
- 10.3.9.6.1
Data Transfer Descriptors
- 10.3.9.7 VPDMA Configuration
- 10.3.9.8
VPDMA Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.1
YUV Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.1.1 Y 4:4:4 (Data Type 0)
- 10.3.9.8.1.2 Y 4:2:2 (Data Type 1)
- 10.3.9.8.1.3 Y 4:2:0 (Data Type 2)
- 10.3.9.8.1.4 C 4:4:4 (Data Type 4)
- 10.3.9.8.1.5 C 4:2:2 (Data Type 5)
- 10.3.9.8.1.6 C 4:2:0 (Data Type 6)
- 10.3.9.8.1.7 YC 4:2:2 (Data Type 7)
- 10.3.9.8.1.8 YC 4:4:4 (Data Type 8)
- 10.3.9.8.1.9 CY 4:2:2 (Data Type 23)
- 10.3.9.8.2
RGB Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.2.1
Input Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.1 RGB16-565 (Data Type 0)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.2 ARGB-1555 (Data Type 1)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.3 ARGB-4444 (Data Type 2)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.4 RGBA-5551 (Data Type 3)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.5 RGBA-4444 (Data Type 4)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.6 ARGB24-6666 (Data Type 5)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.7 RGB24-888 (Data Type 6)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.8 ARGB32-8888 (Data Type 7)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.9 RGBA24-6666 (Data Type 8)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.10 RGBA32-8888 (Data Type 9)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2
Output Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.1 RGB16-565 (Data Type 0)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.2 ARGB-1555 (Data Type 1)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.3 ARGB-4444 (Data Type 2)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.4 RGBA-5551 (Data Type 3)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.5 RGBA-4444 (Data Type 4)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.6 ARGB24-6666 (Data Type 5)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.7 RGB24-888 (Data Type 6)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.8 ARGB32-8888 (Data Type 7)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.9 RGBA24-6666 (Data Type 8)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.10 RGBA32-8888 (Data Type 9)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1
Input Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.3 Miscellaneous Data Type
- 10.3.9.8.1
YUV Data Formats
- 10.3.10 VPE Software Reset
- 10.3.11 VPE Power and Clocks Management
- 10.4 VPE Register Manual
-
11Display Subsystem
- 11.1
Display Subsystem Overview
- 11.1.1 Display Subsystem Environment
- 11.1.2 Display Subsystem Integration
- 11.1.3
Display Subsystem DPLL Controllers Functional Description
- 11.1.3.1 DPLL Controllers Overview
- 11.1.3.2 OCP2SCP2 Functional Description
- 11.1.3.3
DPLL_VIDEO Functional Description
- 11.1.3.3.1 DPLL_VIDEO Controller Architecture
- 11.1.3.3.2 DPLL_VIDEO Operations
- 11.1.3.3.3 DPLL_VIDEO Error Handling
- 11.1.3.3.4 DPLL_VIDEO Software Reset
- 11.1.3.3.5 DPLL_VIDEO Power Management
- 11.1.3.3.6 DPLL_VIDEO HSDIVIDER Loading Operation
- 11.1.3.3.7 DPLL_VIDEO Clock Sequence
- 11.1.3.3.8 DPLL_VIDEO Go Sequence
- 11.1.3.3.9 DPLL_VIDEO Recommended Values
- 11.1.3.4
DPLL_HDMI Functional Description
- 11.1.3.4.1 DPLL_HDMI and PLLCTRL_HDMI Overview
- 11.1.3.4.2 DPLL_HDMI and PLLCTRL_HDMI Architecture
- 11.1.3.4.3 DPLL_HDMI Operations
- 11.1.3.4.4 DPLL_HDMI Register Access
- 11.1.3.4.5 DPLL_HDMI Error Handling
- 11.1.3.4.6 DPLL_HDMI Software Reset
- 11.1.3.4.7 DPLL_HDMI Power Management
- 11.1.3.4.8 DPLL_HDMI Lock Sequence
- 11.1.3.4.9 DPLL_HDMI Go Sequence
- 11.1.3.4.10 DPLL_HDMI Recommended Values
- 11.1.4 Display Subsystem Programming Guide
- 11.1.5 Display Subsystem Register Manual
- 11.2
Display Controller
- 11.2.1 DISPC Overview
- 11.2.2 DISPC Environment
- 11.2.3 DISPC Integration
- 11.2.4
DISPC Functional Description
- 11.2.4.1 DISPC Clock Configuration
- 11.2.4.2 DISPC Software Reset
- 11.2.4.3 DISPC Power Management
- 11.2.4.4 DISPC Interrupt Requests
- 11.2.4.5 DISPC DMA Requests
- 11.2.4.6
DISPC DMA Engine
- 11.2.4.6.1 DISPC Addressing and Bursts
- 11.2.4.6.2 DISPC Immediate Base Address Flip Mechanism
- 11.2.4.6.3 DISPC DMA Buffers
- 11.2.4.6.4 DISPC MFLAG Mechanism and Arbitration
- 11.2.4.6.5 DISPC Predecimation
- 11.2.4.6.6 DISPC Progressive-to-Interlaced Format Conversion
- 11.2.4.6.7 DISPC Arbitration
- 11.2.4.6.8 DISPC DMA Power Modes
- 11.2.4.7 DISPC Rotation and Mirroring
- 11.2.4.8 DISPC Memory Format
- 11.2.4.9 DISPC Graphics Pipeline
- 11.2.4.10 DISPC Video Pipelines
- 11.2.4.11 DISPC Write-Back Pipeline
- 11.2.4.12 DISPC Hardware Cursor
- 11.2.4.13
DISPC LCD Outputs
- 11.2.4.13.1 DISPC Overlay Manager
- 11.2.4.13.2 DISPC Gamma Correction Unit
- 11.2.4.13.3 DISPC Color Phase Rotation Unit
- 11.2.4.13.4 DISPC Color Space Conversion
- 11.2.4.13.5 DISPC BT.656 and BT.1120 Modes
- 11.2.4.13.6 DISPC Active Matrix
- 11.2.4.13.7 DISPC Synchronized Buffer Update
- 11.2.4.13.8 DISPC Timing Generator and Panel Settings
- 11.2.4.14 DISPC TV Output
- 11.2.4.15 DISPC Frame Width Considerations
- 11.2.4.16 DISPC Extended 3D Support
- 11.2.4.17 DISPC Shadow Registers
- 11.2.5
DISPC Programming Guide
- 11.2.5.1
DISPC Low-Level Programming Models
- 11.2.5.1.1 DISPC Global Initialization
- 11.2.5.1.2
DISPC Operational Modes Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.1 DISPC DMA Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.2 DISPC GFX Pipeline Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.3
DISPC Video Pipeline Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.1 DISPC Main Sequence – Configure the Video Pipeline
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.2 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Window
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.3 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Pipeline Processing
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.4 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the VC-1 Range Mapping
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.5 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Color Space Conversion
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.6 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Scaler Unit
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.7 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Pipeline Layer Output
- 11.2.5.1.2.4 DISPC WB Pipeline Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.5
DISPC LCD Output Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.1 DISPC Main Sequence – Configure the LCD Output
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.2 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Overlay Manager
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.3 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Gamma Table for Gamma Correction
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.4 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Color Phase Rotation
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.5 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the LCD Panel Timings and Parameters
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.6 DISPC Subsequence – Configure BT.656 or BT.1120 Mode
- 11.2.5.1.2.6 DISPC TV Output Configuration
- 11.2.5.1
DISPC Low-Level Programming Models
- 11.2.6 DISPC Register Manual
- 11.3 High-Definition Multimedia Interface
- 11.1
Display Subsystem Overview
- 123D Graphics Accelerator
- 132D Graphics Accelerator
-
14Interconnect
- 14.1 Interconnect Overview
- 14.2
L3_MAIN Interconnect
- 14.2.1 L3_MAIN Interconnect Overview
- 14.2.2 L3_MAIN Interconnect Integration
- 14.2.3
L3_MAIN Interconnect Functional Description
- 14.2.3.1 Module Use in L3_MAIN Interconnect
- 14.2.3.2 Module Distribution
- 14.2.3.3 Bandwidth Regulators
- 14.2.3.4 Bandwidth Limiters
- 14.2.3.5 Flag Muxing
- 14.2.3.6 Statistic Collectors Group
- 14.2.3.7 L3_MAIN Protection and Firewalls
- 14.2.3.8 L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Handling
- 14.2.4
L3_MAIN Interconnect Programming Guide
- 14.2.4.1 L3 _MAIN Interconnect Low-Level Programming Models
- 14.2.4.2
Operational Modes Configuration
- 14.2.4.2.1
L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.2.4.2.1.1
Main Sequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.2.4.2.1.1.1 Subsequence: L3_MAIN Custom Error Identification
- 14.2.4.2.1.1.2 Subsequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect Protection Violation Error Identification
- 14.2.4.2.1.1.3 Subsequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect Standard Error Identification
- 14.2.4.2.1.1.4 Subsequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect FLAGMUX Configuration
- 14.2.4.2.1.1
Main Sequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.2.4.2.1
L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.2.5
L3_MAIN Interconnect Register Manual
- 14.2.5.1
L3_MAIN Register Group Summary
- 14.2.5.1.1 L3_MAIN Firewall Registers Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.2 L3_MAIN Host Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.3 L3_MAIN TARG Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.4 L3_MAIN FLAGMUX Registers Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.5 L3_MAIN FLAGMUX CLK1MERGE Registers Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.6 L3_MAIN FLAGMUX TIMEOUT Registers Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.7 L3_MAIN BW Regulator Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.8 L3_MAIN Bandwidth Limiter Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.9 L3_MAIN STATCOLL Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1
L3_MAIN Register Group Summary
- 14.3
L4 Interconnects
- 14.3.1 L4 Interconnect Overview
- 14.3.2 L4 Interconnect Integration
- 14.3.3 L4 Interconnect Functional Description
- 14.3.4
L4 Interconnect Programming Guide
- 14.3.4.1
L4 Interconnect Low-level Programming Models
- 14.3.4.1.1 Global Initialization
- 14.3.4.1.2
Operational Modes Configuration
- 14.3.4.1.2.1
L4 Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.3.4.1.2.1.1 Main Sequence: L4 Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.3.4.1.2.1.2 Subsequence: L4 Interconnect Protection Violation Error Identification
- 14.3.4.1.2.1.3 Subsequence: L4 Interconnect Unsupported Command/Address Hole Error Identification
- 14.3.4.1.2.1.4 Subsequence: L4 Interconnect Reset TA and Module
- 14.3.4.1.2.2 L4 Interconnect Time-Out Configuration Mode
- 14.3.4.1.2.3 L4 Interconnect Firewall Configuration Mode
- 14.3.4.1.2.1
L4 Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.3.4.1
L4 Interconnect Low-level Programming Models
- 14.3.5 L4 Interconnects Register Manual
-
15Memory Subsystem
- 15.1 Memory Subsystem Overview
- 15.2
Dynamic Memory Manager
- 15.2.1 DMM Overview
- 15.2.2 DMM Integration
- 15.2.3
DMM Functional Description
- 15.2.3.1 DMM Block Diagram
- 15.2.3.2 DMM Clock Configuration
- 15.2.3.3 DMM Power Management
- 15.2.3.4 DMM Interrupt Requests
- 15.2.3.5 DMM
- 15.2.3.6
TILER
- 15.2.3.6.1
TILER Concepts
- 15.2.3.6.1.1
TILER Rationale
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.1 The TILER is a 4-GiB Virtual Address Space Composed of Eight Views
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.2 A View is a 512-MiB Virtual Address Space Composed of Four Containers
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.3 A Container is a 128-MiB Virtual Address Space
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.4 A Page is a 4-kiB Virtual Address Space
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.5 A Tile is a 1-kiB Address Space
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.6 1851
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.7 A Subtile is a 128-Bit Address Space
- 15.2.3.6.1.2 TILER Modes
- 15.2.3.6.1.3 Object Container Definition
- 15.2.3.6.1.4 Page Definition
- 15.2.3.6.1.5 Orientation
- 15.2.3.6.1.6 Tile Definition
- 15.2.3.6.1.7 Subtiles
- 15.2.3.6.1.8
TILER Virtual Addressing
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.1 Page Mode Virtual Addressing and Characteristics
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.2 Tiled Mode Virtual Addressing and Characteristics
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3
Element Ordering in the TILER Container
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.1 Natural View or 0-Degree View (Orientation 0)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.2 0-Degree View With Vertical Mirror or 180-Degree View With Horizontal Mirror (Orientation 1)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.3 0-Degree View With Horizontal Mirror or 180-Degree View With Vertical Mirror (Orientation 2)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.4 180-Degree View (Orientation 3)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.5 90-Degree View With Vertical Mirror or 270-Degree View With Horizontal Mirror (Orientation 4)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.6 270-Degree View (Orientation 5)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.7 90-Degree View (Orientation 6)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.8 90-Degree View With Horizontal Mirror or 270-Degree View With Vertical Mirror (Orientation 7)
- 15.2.3.6.1.1
TILER Rationale
- 15.2.3.6.2 TILER Macro-Architecture
- 15.2.3.6.3 TILER Guidelines for Initiators
- 15.2.3.6.1
TILER Concepts
- 15.2.4 DMM Use Cases and Tips
- 15.2.5
DMM Basic Programming Model
- 15.2.5.1 Global Initialization
- 15.2.5.2 DMM Module Global Initialization
- 15.2.5.3 DMM Operational Modes Configuration
- 15.2.5.4 Addressing an Object in Tiled Mode
- 15.2.5.5 Addressing an Object in Page Mode
- 15.2.5.6 Sharing Containers Between Different Modes
- 15.2.6 DMM Register Manual
- 15.3
EMIF Controller
- 15.3.1 EMIF Controller Overview
- 15.3.2 EMIF Module Environment
- 15.3.3 EMIF Module Integration
- 15.3.4
EMIF Functional Description
- 15.3.4.1 Block Diagram
- 15.3.4.2 Clock Management
- 15.3.4.3 Reset
- 15.3.4.4 System Power Management
- 15.3.4.5 Interrupt Requests
- 15.3.4.6 SDRAM Refresh Scheduling
- 15.3.4.7 SDRAM Initialization
- 15.3.4.8 DDR3/DDR3L Read-Write Leveling
- 15.3.4.9 EMIF Access Cycles
- 15.3.4.10 Turnaround Time
- 15.3.4.11 PHY DLL Calibration
- 15.3.4.12
SDRAM Address Mapping
- 15.3.4.12.1 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 0 and EBANK_POS = 0
- 15.3.4.12.2 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 1 and EBANK_POS = 0
- 15.3.4.12.3 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 2 and EBANK_POS = 0
- 15.3.4.12.4 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 3 and EBANK_POS = 0
- 15.3.4.12.5 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 0 and EBANK_POS = 1
- 15.3.4.12.6 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 1 and EBANK_POS = 1
- 15.3.4.12.7 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 2 and EBANK_POS = 1
- 15.3.4.12.8 1949
- 15.3.4.12.9 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 3 and EBANK_POS = 1
- 15.3.4.12.10 1951
- 15.3.4.13 DDR3/DDR3L Output Impedance Calibration
- 15.3.4.14 Error Correction And Detection Feature
- 15.3.4.15 Class of Service
- 15.3.4.16 Performance Counters
- 15.3.4.17 Forcing CKE to tri-state
- 15.3.5 EMIF Programming Guide
- 15.3.6 EMIF Register Manual
- 15.4
General-Purpose Memory Controller
- 15.4.1 GPMC Overview
- 15.4.2 GPMC Environment
- 15.4.3 GPMC Integration
- 15.4.4
GPMC Functional Description
- 15.4.4.1 GPMC Block Diagram
- 15.4.4.2 GPMC Clock Configuration
- 15.4.4.3 GPMC Software Reset
- 15.4.4.4 GPMC Power Management
- 15.4.4.5 GPMC Interrupt Requests
- 15.4.4.6 L3 Interconnect Interface
- 15.4.4.7 GPMC Address and Data Bus
- 15.4.4.8
Address Decoder and Chip-Select Configuration
- 15.4.4.8.1 Chip-Select Base Address and Region Size
- 15.4.4.8.2 Access Protocol
- 15.4.4.8.3
External Signals
- 15.4.4.8.3.1
Wait Pin Monitoring Control
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.1 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Read Access
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.2 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Write Access
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.3 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Read Access
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.4 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Write Access
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.5 Wait With NAND Device
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.6 Idle Cycle Control Between Successive Accesses
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.7 Slow Device Support (TIMEPARAGRANULARITY Parameter)
- 15.4.4.8.3.2 Reset
- 15.4.4.8.3.3 Byte Enable (nBE1/nBE0)
- 15.4.4.8.3.1
Wait Pin Monitoring Control
- 15.4.4.8.4 Error Handling
- 15.4.4.9
Timing Setting
- 15.4.4.9.1 Read Cycle Time and Write Cycle Time (RDCYCLETIME / WRCYCLETIME)
- 15.4.4.9.2 nCS: Chip-Select Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (CSONTIME / CSRDOFFTIME / CSWROFFTIME / CSEXTRADELAY)
- 15.4.4.9.3 nADV/ALE: Address Valid/Address Latch Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (ADVONTIME / ADVRDOFFTIME / ADVWROFFTIME / ADVEXTRADELAY/ADVAADMUXONTIME/ADVAADMUXRDOFFTIME/ADVAADMUXWROFFTIME)
- 15.4.4.9.4 nOE/nRE: Output Enable/Read Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (OEONTIME / OEOFFTIME / OEEXTRADELAY / OEAADMUXONTIME / OEAADMUXOFFTIME)
- 15.4.4.9.5 nWE: Write Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (WEONTIME / WEOFFTIME / WEEXTRADELAY)
- 15.4.4.9.6 GPMC_CLK
- 15.4.4.9.7 GPMC_CLK and Control Signals Setup and Hold
- 15.4.4.9.8 Access Time (RDACCESSTIME / WRACCESSTIME)
- 15.4.4.9.9 Page Burst Access Time (PAGEBURSTACCESSTIME)
- 15.4.4.9.10 Bus Keeping Support
- 15.4.4.10
NOR Access Description
- 15.4.4.10.1 Asynchronous Access Description
- 15.4.4.10.2 Synchronous Access Description
- 15.4.4.10.3
Asynchronous and Synchronous Accesses in Nonmultiplexed Mode
- 15.4.4.10.3.1 Asynchronous Single-Read Operation on Nonmultiplexed Device
- 15.4.4.10.3.2 Asynchronous Single-Write Operation on Nonmultiplexed Device
- 15.4.4.10.3.3 Asynchronous Multiple (Page Mode) Read Operation on Nonmultiplexed Device
- 15.4.4.10.3.4 Synchronous Operations on a Nonmultiplexed Device
- 15.4.4.10.4 Page and Burst Support
- 15.4.4.10.5 System Burst vs External Device Burst Support
- 15.4.4.11 pSRAM Access Specificities
- 15.4.4.12
NAND Access Description
- 15.4.4.12.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 15.4.4.12.1.1 Chip-Select Configuration for NAND Interfacing in Byte or Word Stream Mode
- 15.4.4.12.1.2 NAND Device Command and Address Phase Control
- 15.4.4.12.1.3 Command Latch Cycle
- 15.4.4.12.1.4 Address Latch Cycle
- 15.4.4.12.1.5 NAND Device Data Read and Write Phase Control in Stream Mode
- 15.4.4.12.1.6 NAND Device General Chip-Select Timing Control Requirement
- 15.4.4.12.1.7 Read and Write Access Size Adaptation
- 15.4.4.12.2 NAND Device-Ready Pin
- 15.4.4.12.3
ECC Calculator
- 15.4.4.12.3.1 Hamming Code
- 15.4.4.12.3.2
BCH Code
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.1 Requirements
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.2
Memory Mapping of BCH Codeword
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.2.1 Memory Mapping of Data Message
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.2.2 Memory-Mapping of the ECC
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.2.3
Wrapping Modes
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.1 Manual Mode (0x0)
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.2 Mode 0x1
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.3 Mode 0xA (10)
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.4 Mode 0x2
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.5 Mode 0x3
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.6 Mode 0x7
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.7 Mode 0x8
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.8 Mode 0x4
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.9 Mode 0x9
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.10 Mode 0x5
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.11 Mode 0xB (11)
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.12 Mode 0x6
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.3 Supported NAND Page Mappings and ECC Schemes
- 15.4.4.12.4
Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 15.4.4.12.4.1 General Facts About the Engine Configuration
- 15.4.4.12.4.2 Prefetch Mode
- 15.4.4.12.4.3 FIFO Control in Prefetch Mode
- 15.4.4.12.4.4 Write-Posting Mode
- 15.4.4.12.4.5 FIFO Control in Write-Posting Mode
- 15.4.4.12.4.6 Optimizing NAND Access Using the Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 15.4.4.12.4.7 Interleaved Accesses Between Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine and Other Chip-Selects
- 15.4.4.12.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 15.4.5 GPMC Basic Programming Model
- 15.4.6 GPMC Use Cases and Tips
- 15.4.7 GPMC Register Manual
- 15.5 Error Location Module
- 15.6
On-Chip Memory (OCM) Subsystem
- 15.6.1 OCM Subsystem Overview
- 15.6.2 OCM Subsystem Integration
- 15.6.3
OCM Subsystem Functional Desctiption
- 15.6.3.1 Block Diagram
- 15.6.3.2 Resets
- 15.6.3.3 Clock Management
- 15.6.3.4 Interrupt Requests
- 15.6.3.5 OCM Subsystem Memory Regions
- 15.6.3.6 OCM Controller Modes Of Operation
- 15.6.3.7 ECC Associated FIFOs
- 15.6.3.8 ECC Counters And Corrected Bit Distribution Register
- 15.6.3.9 ECC Support
- 15.6.3.10 Circular Buffer (CBUF) Support
- 15.6.3.11 CBUF Mode Error Handling
- 15.6.3.12 Status Reporting
- 15.6.4 OCM Subsystem Register Manual
-
16DMA Controllers
- 16.1
System DMA
- 16.1.1 DMA_SYSTEM Module Overview
- 16.1.2 DMA_SYSTEM Controller Environment
- 16.1.3 DMA_SYSTEM Module Integration
- 16.1.4
DMA_SYSTEM Functional Description
- 16.1.4.1 DMA_SYSTEM Controller Power Management
- 16.1.4.2 DMA_SYSTEM Controller Interrupt Requests
- 16.1.4.3 Logical Channel Transfer Overview
- 16.1.4.4 FIFO Queue Memory Pool
- 16.1.4.5 Addressing Modes
- 16.1.4.6 Packed Accesses
- 16.1.4.7 Burst Transactions
- 16.1.4.8 Endianism Conversion
- 16.1.4.9 Transfer Synchronization
- 16.1.4.10 Thread Budget Allocation
- 16.1.4.11 FIFO Budget Allocation
- 16.1.4.12 Chained Logical Channel Transfers
- 16.1.4.13 Reprogramming an Active Channel
- 16.1.4.14 Packet Synchronization
- 16.1.4.15 Graphics Acceleration Support
- 16.1.4.16 Supervisor Modes
- 16.1.4.17 Posted and Nonposted Writes
- 16.1.4.18 Disabling a Channel During Transfer
- 16.1.4.19 FIFO Draining Mechanism
- 16.1.4.20
Linked List
- 16.1.4.20.1 Overview
- 16.1.4.20.2 Link-List Transfer Profile
- 16.1.4.20.3 Descriptors
- 16.1.4.20.4
Linked-List Control and Monitoring
- 16.1.4.20.4.1 Transfer Mode Setting
- 16.1.4.20.4.2 Starting a Linked List
- 16.1.4.20.4.3 Monitoring a Linked-List Progression
- 16.1.4.20.4.4 Interrupt During Linked-List Execution
- 16.1.4.20.4.5 Pause a Linked List
- 16.1.4.20.4.6 Stop a Linked List (Abort or Drain)
- 16.1.4.20.4.7 Status Bit Behavior
- 16.1.4.20.4.8 Linked-List Channel Linking
- 16.1.5
DMA_SYSTEM Basic Programming Model
- 16.1.5.1 Setup Configuration
- 16.1.5.2 Software-Triggered (Nonsynchronized) Transfer
- 16.1.5.3 Hardware-Synchronized Transfer
- 16.1.5.4 Synchronized Transfer Monitoring Using CDAC
- 16.1.5.5 Concurrent Software and Hardware Synchronization
- 16.1.5.6 Chained Transfer
- 16.1.5.7 90-Degree Clockwise Image Rotation
- 16.1.5.8 Graphic Operations
- 16.1.5.9 Linked-List Programming Guidelines
- 16.1.6 DMA_SYSTEM Register Manual
- 16.2
Enhanced DMA
- 16.2.1 EDMA Module Overview
- 16.2.2 EDMA Controller Environment
- 16.2.3 EDMA Controller Integration
- 16.2.4
EDMA Controller Functional Description
- 16.2.4.1 Block Diagram
- 16.2.4.2 Types of EDMA controller Transfers
- 16.2.4.3
Parameter RAM (PaRAM)
- 16.2.4.3.1 PaRAM
- 16.2.4.3.2
EDMA Channel PaRAM Set Entry Fields
- 16.2.4.3.2.1 Channel Options Parameter (OPT)
- 16.2.4.3.2.2 Channel Source Address (SRC)
- 16.2.4.3.2.3 Channel Destination Address (DST)
- 16.2.4.3.2.4 Count for 1st Dimension (ACNT)
- 16.2.4.3.2.5 Count for 2nd Dimension (BCNT)
- 16.2.4.3.2.6 Count for 3rd Dimension (CCNT)
- 16.2.4.3.2.7 BCNT Reload (BCNTRLD)
- 16.2.4.3.2.8 Source B Index (SBIDX)
- 16.2.4.3.2.9 Destination B Index (DBIDX)
- 16.2.4.3.2.10 Source C Index (SCIDX)
- 16.2.4.3.2.11 Destination C Index (DCIDX)
- 16.2.4.3.2.12 Link Address (LINK)
- 16.2.4.3.3 Null PaRAM Set
- 16.2.4.3.4 Dummy PaRAM Set
- 16.2.4.3.5 Dummy Versus Null Transfer Comparison
- 16.2.4.3.6 Parameter Set Updates
- 16.2.4.3.7 Linking Transfers
- 16.2.4.3.8 Constant Addressing Mode Transfers/Alignment Issues
- 16.2.4.3.9 Element Size
- 16.2.4.4 Initiating a DMA Transfer
- 16.2.4.5 Completion of a DMA Transfer
- 16.2.4.6 Event, Channel, and PaRAM Mapping
- 16.2.4.7 EDMA Channel Controller Regions
- 16.2.4.8 Chaining EDMA Channels
- 16.2.4.9 EDMA Interrupts
- 16.2.4.10 Memory Protection
- 16.2.4.11 Event Queue(s)
- 16.2.4.12 EDMA Transfer Controller (EDMA_TPTC)
- 16.2.4.13 Event Dataflow
- 16.2.4.14 EDMA controller Prioritization
- 16.2.4.15 EDMA Power, Reset and Clock Management
- 16.2.4.16 Emulation Considerations
- 16.2.5
EDMA Transfer Examples
- 16.2.5.1 Block Move Example
- 16.2.5.2 Subframe Extraction Example
- 16.2.5.3 Data Sorting Example
- 16.2.5.4 Peripheral Servicing Example
- 16.2.5.5 Setting Up an EDMA Transfer
- 16.2.6 EDMA Debug Checklist and Programming Tips
- 16.2.7 EDMA Register Manual
- 16.1
System DMA
-
17Interrupt Controllers
- 17.1 Interrupt Controllers Overview
- 17.2 Interrupt Controllers Environment
- 17.3
Interrupt Controllers Integration
- 17.3.1 Interrupt Requests to MPU_INTC
- 17.3.2 Interrupt Requests to DSP1_INTC
- 17.3.3 Interrupt Requests to IPU1_Cx_INTC
- 17.3.4 Interrupt Requests to IPU2_Cx_INTC
- 17.3.5 Interrupt Requests to PRUSS1_INTC
- 17.3.6 Interrupt Requests to PRUSS2_INTC
- 17.3.7 Mapping of Device Interrupts to IRQ_CROSSBAR Inputs
- 17.4 Interrupt Controllers Functional Description
-
18Control Module
- 18.1 Control Module Overview
- 18.2 Control Module Environment
- 18.3 Control Module Integration
- 18.4
Control Module Functional Description
- 18.4.1 Control Module Clock Configuration
- 18.4.2 Control Module Resets
- 18.4.3 Control Module Power Management
- 18.4.4 Hardware Requests
- 18.4.5 Control Module Initialization
- 18.4.6
Functional Description Of The Various Register Types In CTRL_MODULE_CORE Submodule
- 18.4.6.1 Pad Configuration
- 18.4.6.2
Thermal Management Related Registers
- 18.4.6.2.1 Temperature Sensors Control Registers
- 18.4.6.2.2 Registers For The Thermal Alert Comparators
- 18.4.6.2.3 Thermal Shutdown Comparators
- 18.4.6.2.4 Temperature Timestamp Registers
- 18.4.6.2.5 Other Thermal Management Related Registers
- 18.4.6.2.6 Summary Of The Thermal Management Related Registers
- 18.4.6.2.7 ADC Values Versus Temperature
- 18.4.6.3 PBIAS Cell And MMC1 I/O Cells Control Registers
- 18.4.6.4 IRQ_CROSSBAR Module Functional Description
- 18.4.6.5 DMA_CROSSBAR Module Functional Description
- 18.4.6.6 SDRAM Initiator Priority Registers
- 18.4.6.7 L3_MAIN Initiator Priority Registers
- 18.4.6.8 Memory Region Lock Registers
- 18.4.6.9 NMI Mapping To Respective Cores
- 18.4.6.10 Software Controls for the DDR3 I/O Cells
- 18.4.6.11 Reference Voltage for the Device DDR3 Receivers
- 18.4.6.12 AVS Class 0 Associated Registers
- 18.4.6.13 ABB Associated Registers
- 18.4.6.14 Registers For Other Miscellaneous Functions
- 18.4.7 Functional Description Of The Various Register Types In CTRL_MODULE_WKUP Submodule
- 18.5 Control Module Register Manual
- 18.6 IODELAYCONFIG Module Integration
- 18.7 IODELAYCONFIG Module Register Manual
-
19Mailbox
- 19.1 Mailbox Overview
- 19.2 Mailbox Integration
- 19.3 Mailbox Functional Description
- 19.4 Mailbox Programming Guide
- 19.5 Mailbox Register Manual
-
20Memory Management Units
- 20.1 MMU Overview
- 20.2 MMU Integration
- 20.3
MMU Functional Description
- 20.3.1 MMU Block Diagram
- 20.3.2 MMU Software Reset
- 20.3.3 MMU Power Management
- 20.3.4 MMU Interrupt Requests
- 20.3.5 MMU Error Handling
- 20.4 MMU Low-level Programming Models
- 20.5 MMU Register Manual
- 21Spinlock
-
22Timers
- 22.1 Timers Overview
- 22.2
General-Purpose Timers
- 22.2.1 General-Purpose Timers Overview
- 22.2.2 GP Timer Environment
- 22.2.3 GP Timer Integration
- 22.2.4
GP Timer Functional Description
- 22.2.4.1 GP Timer Block Diagram
- 22.2.4.2 TIMER1, TIMER2 and TIMER10 Power Management
- 22.2.4.3 Power Management of Other GP Timers
- 22.2.4.4 Software Reset
- 22.2.4.5 GP Timer Interrupts
- 22.2.4.6 Timer Mode Functionality
- 22.2.4.7 Capture Mode Functionality
- 22.2.4.8 Compare Mode Functionality
- 22.2.4.9 Prescaler Functionality
- 22.2.4.10 Pulse-Width Modulation
- 22.2.4.11 Timer Counting Rate
- 22.2.4.12 Timer Under Emulation
- 22.2.4.13 Accessing GP Timer Registers
- 22.2.4.14 Posted Mode Selection
- 22.2.5 GP Timer Low-Level Programming Models
- 22.2.6 GP Timer Register Manual
- 22.3 32-kHz Synchronized Timer (COUNTER_32K)
- 22.4
Watchdog Timer
- 22.4.1 Watchdog Timer Overview
- 22.4.2 Watchdog Timer Integration
- 22.4.3
Watchdog Timer Functional Description
- 22.4.3.1 Power Management
- 22.4.3.2 Interrupts
- 22.4.3.3 General Watchdog Timer Operation
- 22.4.3.4 Reset Context
- 22.4.3.5 Overflow/Reset Generation
- 22.4.3.6 Prescaler Value/Timer Reset Frequency
- 22.4.3.7 Triggering a Timer Reload
- 22.4.3.8 Start/Stop Sequence for Watchdog Timer (Using the WSPR Register)
- 22.4.3.9 Modifying Timer Count/Load Values and Prescaler Setting
- 22.4.3.10 Watchdog Counter Register Access Restriction (WCRR)
- 22.4.3.11 Watchdog Timer Interrupt Generation
- 22.4.3.12 Watchdog Timer Under Emulation
- 22.4.3.13 Accessing Watchdog Timer Registers
- 22.4.4 Watchdog Timer Low-Level Programming Model
- 22.4.5 Watchdog Timer Register Manual
-
23Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- 23.1 RTC Overview
- 23.2 RTC Environment
- 23.3 RTC Integration
- 23.4 RTC Functional Description
- 23.5 RTC Low-Level Programming Guide
- 23.6 RTC Register Manual
-
24Serial Communication Interfaces
- 24.1
Multimaster High-Speed I2C Controller
- 24.1.1 HS I2C Overview
- 24.1.2
HS I2C Environment
- 24.1.2.1 HS I2C Typical Application
- 24.1.2.2
HS I2C Typical Connection Protocol and Data Format
- 24.1.2.2.1 HS I2C Serial Data Format
- 24.1.2.2.2 HS I2C Data Validity
- 24.1.2.2.3 HS I2C Start and Stop Conditions
- 24.1.2.2.4 HS I2C Addressing
- 24.1.2.2.5 HS I2C Master Transmitter
- 24.1.2.2.6 HS I2C Master Receiver
- 24.1.2.2.7 HS I2C Slave Transmitter
- 24.1.2.2.8 HS I2C Slave Receiver
- 24.1.2.2.9 HS I2C Bus Arbitration
- 24.1.2.2.10 HS I2C Clock Generation and Synchronization
- 24.1.3 HS I2C Integration
- 24.1.4
HS I2C Functional Description
- 24.1.4.1 HS I2C Block Diagram
- 24.1.4.2 HS I2C Clocks
- 24.1.4.3 HS I2C Software Reset
- 24.1.4.4 HS I2C Power Management
- 24.1.4.5 HS I2C Interrupt Requests
- 24.1.4.6 HS I2C DMA Requests
- 24.1.4.7 HS I2C Programmable Multislave Channel Feature
- 24.1.4.8 HS I2C FIFO Management
- 24.1.4.9 HS I2C Noise Filter
- 24.1.4.10 HS I2C System Test Mode
- 24.1.5 HS I2C Programming Guide
- 24.1.6 HS I2C Register Manual
- 24.2
HDQ/1-Wire
- 24.2.1 HDQ1W Overview
- 24.2.2 HDQ1W Environment
- 24.2.3 HDQ1W Integration
- 24.2.4 HDQ1W Functional Description
- 24.2.5 HDQ1W Low-Level Programming Model
- 24.2.6 HDQ1W Register Manual
- 24.3
UART/IrDA/CIR
- 24.3.1 UART/IrDA/CIR Overview
- 24.3.2
UART/IrDA/CIR Environment
- 24.3.2.1 UART Interface
- 24.3.2.2 IrDA Functional Interfaces
- 24.3.2.3 CIR Functional Interfaces
- 24.3.3 UART/IrDA/CIR Integration
- 24.3.4
UART/IrDA/CIR Functional Description
- 24.3.4.1 Block Diagram
- 24.3.4.2 Clock Configuration
- 24.3.4.3 Software Reset
- 24.3.4.4 Power Management
- 24.3.4.5 Interrupt Requests
- 24.3.4.6 FIFO Management
- 24.3.4.7 Mode Selection
- 24.3.4.8
Protocol Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 24.3.4.8.1.1 UART Clock Generation: Baud Rate Generation
- 24.3.4.8.1.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 24.3.4.8.1.3 UART Data Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.2
IrDA Mode (UART3 Only)
- 24.3.4.8.2.1 IrDA Clock Generation: Baud Generator
- 24.3.4.8.2.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 24.3.4.8.2.3
IrDA Data Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.1 IR RX Polarity Control
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.2 IrDA Reception Control
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.3 IR Address Checking
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.4 Frame Closing
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.5 Store and Controlled Transmission
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.6 Error Detection
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.7 Underrun During Transmission
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.8 Overrun During Receive
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.9 Status FIFO
- 24.3.4.8.2.4 SIR Mode Data Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.2.5 MIR and FIR Mode Data Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.3 CIR Mode (UART3 Only)
- 24.3.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 24.3.5 UART/IrDA/CIR Basic Programming Model
- 24.3.6 UART/IrDA/CIR Register Manual
- 24.4
Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface
- 24.4.1 McSPI Overview
- 24.4.2 McSPI Environment
- 24.4.3 McSPI Integration
- 24.4.4
McSPI Functional Description
- 24.4.4.1 McSPI Block Diagram
- 24.4.4.2 Reset
- 24.4.4.3
Master Mode
- 24.4.4.3.1 Master Mode Features
- 24.4.4.3.2 Master Transmit-and-Receive Mode (Full Duplex)
- 24.4.4.3.3 Master Transmit-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 24.4.4.3.4 Master Receive-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 24.4.4.3.5 Single-Channel Master Mode
- 24.4.4.3.6 Start-Bit Mode
- 24.4.4.3.7 Chip-Select Timing Control
- 24.4.4.3.8 Programmable SPI Clock
- 24.4.4.4 Slave Mode
- 24.4.4.5 3-Pin or 4-Pin Mode
- 24.4.4.6 FIFO Buffer Management
- 24.4.4.7 Interrupts
- 24.4.4.8 DMA Requests
- 24.4.4.9 Power Saving Management
- 24.4.5
McSPI Programming Guide
- 24.4.5.1 Global Initialization
- 24.4.5.2
Operational Mode Configuration
- 24.4.5.2.1
McSPI Operational Modes
- 24.4.5.2.1.1 Common Transfer Sequence
- 24.4.5.2.1.2 End of Transfer Sequences
- 24.4.5.2.1.3 Transmit-and-Receive (Master and Slave)
- 24.4.5.2.1.4 Transmit-Only (Master and Slave)
- 24.4.5.2.1.5 Master Normal Receive-Only
- 24.4.5.2.1.6 Master Turbo Receive-Only
- 24.4.5.2.1.7 Slave Receive-Only
- 24.4.5.2.1.8
Transfer Procedures With FIFO
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.1 Common Transfer Sequence in FIFO Mode
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.2 End of Transfer Sequences in FIFO Mode
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.3 Transmit-and-Receive With Word Count
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.4 Transmit-and-Receive Without Word Count
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.5 Transmit-Only
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.6 Receive-Only With Word Count
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.7 Receive-Only Without Word Count
- 24.4.5.2.1
McSPI Operational Modes
- 24.4.5.3 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 24.4.6 McSPI Register Manual
- 24.5 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface
- 24.6
Multichannel Audio Serial Port
- 24.6.1 McASP Overview
- 24.6.2 McASP Environment
- 24.6.3 McASP Integration
- 24.6.4
McASP Functional Description
- 24.6.4.1 McASP Block Diagram
- 24.6.4.2 McASP Clock and Frame-Sync Configurations
- 24.6.4.3 Serializers
- 24.6.4.4 Format Units
- 24.6.4.5 State-Machines
- 24.6.4.6 TDM Sequencers
- 24.6.4.7 McASP Software Reset
- 24.6.4.8 McASP Power Management
- 24.6.4.9 Transfer Modes
- 24.6.4.10 Data Transmission and Reception
- 24.6.4.11 McASP Audio FIFO (AFIFO)
- 24.6.4.12 McASP Events and Interrupt Requests
- 24.6.4.13 DMA Requests
- 24.6.4.14 Loopback Modes
- 24.6.4.15 Error Reporting
- 24.6.5
McASP Low-Level Programming Model
- 24.6.5.1
Global Initialization
- 24.6.5.1.1 Surrounding Modules Global Initialization
- 24.6.5.1.2
McASP Global Initialization
- 24.6.5.1.2.1
Main Sequence – McASP Global Initialization for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.1 Subsequence – Transmit Format Unit Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.2 Subsequence – Transmit Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.3 Subsequence – Transmit Clock Generator Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.4 Subsequence - McASP Pins Functional Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.5 Subsequence – DIT-specific Subframe Fields Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.2
Main Sequence – McASP Global Initialization for TDM-Reception
- 24.6.5.1.2.2.1 Subsequence – Receive Format Unit Configuration in TDM Mode
- 24.6.5.1.2.2.2 Subsequence – Receive Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration in TDM Mode
- 24.6.5.1.2.2.3 Subsequence – Receive Clock Generator Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.2.4 Subsequence—McASP Receiver Pins Functional Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.3
Main Sequence – McASP Global Initialization for TDM -Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.3.1 Subsequence – Transmit Format Unit Configuration in TDM Mode
- 24.6.5.1.2.3.2 Subsequence – Transmit Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration in TDM Mode
- 24.6.5.1.2.3.3 Subsequence – Transmit Clock Generator Configuration for TDM Cases
- 24.6.5.1.2.3.4 Subsequence—McASP Transmit Pins Functional Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.1
Main Sequence – McASP Global Initialization for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.2 Operational Modes Configuration
- 24.6.5.1
Global Initialization
- 24.6.6 McASP Register Manual
- 24.7 SuperSpeed USB DRD
- 24.8
SATA Controller
- 24.8.1 SATA Controller Overview
- 24.8.2 SATA Controller Environment
- 24.8.3 SATA Controller Integration
- 24.8.4
SATA Controller Functional Description
- 24.8.4.1 SATA Controller Block Diagram
- 24.8.4.2 SATA Controller Link Layer Protocol and Data Format
- 24.8.4.3 Resets
- 24.8.4.4 Power Management
- 24.8.4.5
Interrupt Requests
- 24.8.4.5.1 Interrupt Generation
- 24.8.4.5.2 Levels of Interrupt Control
- 24.8.4.5.3
Interrupt Events Description
- 24.8.4.5.3.1 Task File Error Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.2 Host Bus Fatal Error
- 24.8.4.5.3.3 Interface Fatal Error Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.4 Interface Non-Fatal Error Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.5 Overflow Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.6 Incorrect Port Multiplier Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.7 PHYReady Change Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.8 Port Connect Change Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.9 Descriptor Processed
- 24.8.4.5.3.10 Unknown FIS Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.3.11 Set Device Bits Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.3.12 DMA Setup FIS Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.3.13 PIO Setup FIS Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.3.14 Device to Host Register FIS Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.4 Interrupt Condition Control
- 24.8.4.5.5 Command Completion Coalescing Interrupts
- 24.8.4.6 System Memory FIS Descriptors
- 24.8.4.7 Transport Layer FIS-Based Interactions
- 24.8.4.8 DMA Port Configuration
- 24.8.4.9 Port Multiplier Operation
- 24.8.4.10 Activity LED Generation Functionality
- 24.8.4.11 Supported Types of SATA Transfers
- 24.8.4.12 SATA Controller AHCI Hardware Register Interface
- 24.8.5 SATA Controller Low Level Programming Model
- 24.8.6 SATA Controller Register Manual
- 24.9
PCIe Controller
- 24.9.1 PCIe Controller Subsystem Overview
- 24.9.2 PCIe Controller Environment
- 24.9.3 PCIe Controllers Integration
- 24.9.4
PCIe SS Controller Functional Description
- 24.9.4.1 PCIe Controller Functional Block Diagram
- 24.9.4.2 PCIe Traffics
- 24.9.4.3 PCIe Controller Ports on L3_MAIN Interconnect
- 24.9.4.4 PCIe Controller Reset Management
- 24.9.4.5 PCIe Controller Power Management
- 24.9.4.6
PCIe Controller Interrupt Requests
- 24.9.4.6.1 PCIe Controller Main Hardware Management
- 24.9.4.6.2 PCIe Controller Legacy and MSI Virtual Interrupts Management
- 24.9.4.6.3 PCIe Controller MSI Hardware Interrupt Events
- 24.9.4.7 PCIe Controller Address Spaces and Address Translation
- 24.9.4.8 PCIe Traffic Requesting and Responding
- 24.9.4.9 PCIe Programming Register Interface
- 24.9.5 PCIe Controller Low Level Programming Model
- 24.9.6 PCIe Standard Registers vs PCIe Subsystem Hardware Registers Mapping
- 24.9.7
PCIe Controller Register Manual
- 24.9.7.1 PCIe Controller Instance Summary
- 24.9.7.2 PCIe_SS_EP_CFG_PCIe Registers
- 24.9.7.3 PCIe_SS_EP_CFG_DBICS Registers
- 24.9.7.4 PCIe_SS_RC_CFG_DBICS Registers
- 24.9.7.5 PCIe_SS_PL_CONF Registers
- 24.9.7.6 PCIe_SS_EP_CFG_DBICS2 Registers
- 24.9.7.7 PCIe_SS_RC_CFG_DBICS2 Registers
- 24.9.7.8 PCIe_SS_TI_CONF Registers
- 24.10
DCAN
- 24.10.1 DCAN Overview
- 24.10.2 DCAN Environment
- 24.10.3 DCAN Integration
- 24.10.4
DCAN Functional Description
- 24.10.4.1 Module Clocking Requirements
- 24.10.4.2 Interrupt Functionality
- 24.10.4.3 DMA Functionality
- 24.10.4.4 Local Power-Down Mode
- 24.10.4.5 Parity Check Mechanism
- 24.10.4.6 Debug/Suspend Mode
- 24.10.4.7
Configuration of Message Objects Description
- 24.10.4.7.1 Configuration of a Transmit Object for Data Frames
- 24.10.4.7.2 Configuration of a Transmit Object for Remote Frames
- 24.10.4.7.3 Configuration of a Single Receive Object for Data Frames
- 24.10.4.7.4 Configuration of a Single Receive Object for Remote Frames
- 24.10.4.7.5 Configuration of a FIFO Buffer
- 24.10.4.8
Message Handling
- 24.10.4.8.1 Message Handler Overview
- 24.10.4.8.2 Receive/Transmit Priority
- 24.10.4.8.3 Transmission of Messages in Event Driven CAN Communication
- 24.10.4.8.4 Updating a Transmit Object
- 24.10.4.8.5 Changing a Transmit Object
- 24.10.4.8.6 Acceptance Filtering of Received Messages
- 24.10.4.8.7 Reception of Data Frames
- 24.10.4.8.8 Reception of Remote Frames
- 24.10.4.8.9 Reading Received Messages
- 24.10.4.8.10 Requesting New Data for a Receive Object
- 24.10.4.8.11 Storing Received Messages in FIFO Buffers
- 24.10.4.8.12 Reading From a FIFO Buffer
- 24.10.4.9 CAN Bit Timing
- 24.10.4.10 Message Interface Register Sets
- 24.10.4.11 Message RAM
- 24.10.4.12 CAN Operation
- 24.10.4.13 GPIO Support
- 24.10.5 DCAN Register Manual
- 24.11
Gigabit Ethernet Switch (GMAC_SW)
- 24.11.1 GMAC_SW Overview
- 24.11.2 GMAC_SW Environment
- 24.11.3 GMAC_SW Integration
- 24.11.4
GMAC_SW Functional Description
- 24.11.4.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 24.11.4.2 GMAC_SW Ports
- 24.11.4.3 Clocking
- 24.11.4.4 Software IDLE
- 24.11.4.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 24.11.4.6 Reset Isolation
- 24.11.4.7 Software Reset
- 24.11.4.8
CPSW_3G
- 24.11.4.8.1 CPDMA RX and TX Interfaces
- 24.11.4.8.2
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 24.11.4.8.2.1
Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.1 Free Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.2 Multicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.3 VLAN/Multicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.4 Unicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.5 OUI Unicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.6 VLAN/Unicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.7 VLAN Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.2 Packet Forwarding Processes
- 24.11.4.8.2.3 Learning Process
- 24.11.4.8.2.4 VLAN Aware Mode
- 24.11.4.8.2.5 VLAN Unaware Mode
- 24.11.4.8.2.1
Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.3 Packet Priority Handling
- 24.11.4.8.4 FIFO Memory Control
- 24.11.4.8.5 FIFO Transmit Queue Control
- 24.11.4.8.6 Audio Video Bridging
- 24.11.4.8.7
Ethernet MAC Sliver (CPGMAC_SL)
- 24.11.4.8.7.1
G/MII Media Independent Interface
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.1 Data Reception
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2
Data Transmission
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.1 Transmit Control
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.2 CRC Insertion
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.3 MTXER
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.4 Adaptive Performance Optimization (APO)
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.5 Inter-Packet-Gap Enforcement
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.6 Back Off
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.7 Programmable Transmit Inter-Packet Gap
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.8 Speed, Duplex and Pause Frame Support Negotiation
- 24.11.4.8.7.2 RMII Interface
- 24.11.4.8.7.3 RGMII Interface
- 24.11.4.8.7.4 Frame Classification
- 24.11.4.8.7.1
G/MII Media Independent Interface
- 24.11.4.8.8 Embedded Memories
- 24.11.4.8.9 Flow Control
- 24.11.4.8.10 Short Gap
- 24.11.4.8.11 Switch Latency
- 24.11.4.8.12 Emulation Control
- 24.11.4.8.13 FIFO Loopback
- 24.11.4.8.14 Device Level Ring (DLR) Support
- 24.11.4.8.15 Energy Efficient Ethernet Support (802.3az)
- 24.11.4.8.16 CPSW_3G Network Statistics
- 24.11.4.9
Static Packet Filter (SPF)
- 24.11.4.9.1 SPF Overview
- 24.11.4.9.2 SPF Functional Description
- 24.11.4.9.3 Programming Guide
- 24.11.4.10 Common Platform Time Sync (CPTS)
- 24.11.4.11 CPPI Buffer Descriptors
- 24.11.4.12 MDIO
- 24.11.5 GMAC_SW Programming Guide
- 24.11.6
GMAC_SW Register Manual
- 24.11.6.1 GMAC_SW Instance Summary
- 24.11.6.2 SS Registers
- 24.11.6.3 PORT Registers
- 24.11.6.4 CPDMA registers
- 24.11.6.5 STATS Registers
- 24.11.6.6 STATERAM Registers
- 24.11.6.7 CPTS registers
- 24.11.6.8 ALE registers
- 24.11.6.9 SL registers
- 24.11.6.10 MDIO registers
- 24.11.6.11 WR registers
- 24.11.6.12 SPF Registers
- 24.12 Media Local Bus (MLB)
- 24.1
Multimaster High-Speed I2C Controller
-
25eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 25.1 eMMC/SD/SDIO Overview
- 25.2 eMMC/SD/SDIO Environment
- 25.3 eMMC/SD/SDIO Integration
- 25.4
eMMC/SD/SDIO Functional Description
- 25.4.1 Block Diagram
- 25.4.2 Resets
- 25.4.3 Power Management
- 25.4.4 Interrupt Requests
- 25.4.5 DMA Modes
- 25.4.6 Mode Selection
- 25.4.7 Buffer Management
- 25.4.8 Transfer Process
- 25.4.9 Transfer or Command Status and Errors Reporting
- 25.4.10 Auto Command 12 Timings
- 25.4.11 Transfer Stop
- 25.4.12 Output Signals Generation
- 25.4.13 Sampling Clock Tuning
- 25.4.14 Card Boot Mode Management
- 25.4.15 MMC CE-ATA Command Completion Disable Management
- 25.4.16 Test Registers
- 25.4.17 eMMC/SD/SDIO Hardware Status Features
- 25.5
eMMC/SD/SDIO Programming Guide
- 25.5.1
Low-Level Programming Models
- 25.5.1.1 Global Initialization
- 25.5.1.2
Operational Modes Configuration
- 25.5.1.2.1
Basic Operations for eMMC/SD/SDIO Host Controller
- 25.5.1.2.1.1 Card Detection, Identification, and Selection
- 25.5.1.2.1.2 Read/Write Transfer Flow in DMA Mode With Interrupt
- 25.5.1.2.1.3 Read/Write Transfer Flow in DMA Mode With Polling
- 25.5.1.2.1.4 Read/Write Transfer Flow Without DMA With Polling
- 25.5.1.2.1.5 Read/Write Transfer Flow in CE-ATA Mode
- 25.5.1.2.1.6 Suspend-Resume Flow
- 25.5.1.2.1.7 Basic Operations – Steps Detailed
- 25.5.1.2.2 Bus Voltage Selection
- 25.5.1.2.3 Boot Mode Configuration
- 25.5.1.2.4 SDR104/HS200 DLL Tuning Procedure
- 25.5.1.2.1
Basic Operations for eMMC/SD/SDIO Host Controller
- 25.5.1
Low-Level Programming Models
- 25.6 eMMC/SD/SDIO Register Manual
-
26Shared PHY Component Subsystem
- 26.1
SATA PHY Subsystem
- 26.1.1 SATA PHY Subsystem Overview
- 26.1.2 SATA PHY Subsystem Environment
- 26.1.3 SATA PHY Subsystem Integration
- 26.1.4
SATA PHY Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.1.4.1 SATA PLL Controller L4 Interface Adapter Functional Description
- 26.1.4.2 SATA PHY Serializer and Deserializer Functional Descriptions
- 26.1.4.3
SATA Clock Generator Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.1.4.3.1 SATA DPLL Clock Generator Overview
- 26.1.4.3.2 SATA DPLL Clock Generator Reset
- 26.1.4.3.3 SATA DPLL Low-Power Modes
- 26.1.4.3.4 SATA DPLL Clocks Configuration
- 26.1.4.3.5 SATA DPLL Subsystem Architecture
- 26.1.4.3.6 SATA DPLL Clock Generator Modes and State Transitions
- 26.1.4.3.7 SATA PLL Controller Functions
- 26.1.5 SATA PHY Subsystem Low-Level Programming Model
- 26.2
USB3_PHY Subsystem
- 26.2.1 USB3_PHY Subsystem Overview
- 26.2.2 USB3_PHY Subsystem Environment
- 26.2.3 USB3_PHY Subsystem Integration
- 26.2.4
USB3_PHY Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.2.4.1 Super-Speed USB PLL Controller L4 Interface Adapter Functional Description
- 26.2.4.2 USB3_PHY Serializer and Deserializer Functional Descriptions
- 26.2.4.3
USB3_PHY Clock Generator Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.2.4.3.1 USB3_PHY DPLL Clock Generator Overview
- 26.2.4.3.2 USB3_PHY DPLL Clock Generator Reset
- 26.2.4.3.3 USB3_PHY DPLL Low-Power Modes
- 26.2.4.3.4 USB3_PHY DPLL Clocks Configuration
- 26.2.4.3.5 USB3_PHY DPLL Subsystem Architecture
- 26.2.4.3.6 USB3_PHY DPLL Clock Generator Modes and State Transitions
- 26.2.4.3.7 USB3_PHY PLL Controller Functions
- 26.2.5 USB3_PHY Subsystem Low-Level Programming Model
- 26.3 USB3 PHY and SATA PHY Register Manual
- 26.4
PCIe PHY Subsystem
- 26.4.1 PCIe PHY Subsystem Overview
- 26.4.2 PCIe PHY Subsystem Environment
- 26.4.3 PCIe Shared PHY Subsystem Integration
- 26.4.4
PCIe PHY Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.4.4.1 PCIe PHY Subsystem Block Diagram
- 26.4.4.2 OCP2SCP Functional Description
- 26.4.4.3 PCIe PHY Serializer and Deserializer Functional Descriptions
- 26.4.4.4
PCIe PHY Clock Generator Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.4.4.4.1
PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator
- 26.4.4.4.1.1 PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator Overview
- 26.4.4.4.1.2 PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator Reset
- 26.4.4.4.1.3 PCIe PHY DPLL Low-Power Modes
- 26.4.4.4.1.4 PCIe PHY DPLL Clocks Configuration
- 26.4.4.4.1.5 PCIe PHY DPLL Subsystem Architecture
- 26.4.4.4.1.6
PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator Modes and State Transitions
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.1 PCIe PHY Clock Generator Power Up
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.2 PCIe PHY DPLL Sequences
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.3 PCIe PHY DPLL Locked Mode
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.4 PCIe PHY DPLL Idle-Bypass Mode
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.5 PCIe PHY DPLL Low Power Stop Mode
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.6 PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Programming Sequence
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.7 PCIe PHY DPLL Recommended Values
- 26.4.4.4.2
PCIe PHY APLL Clock Generator
- 26.4.4.4.2.1 PCIe PHY APLL Clock Generator Overview
- 26.4.4.4.2.2 PCIe PHY APLL Clock Generator Reset
- 26.4.4.4.2.3 PCIe PHY APLL Low-Power Mode
- 26.4.4.4.2.4 PCIe PHY APLL Clocks Configuration
- 26.4.4.4.2.5 PCIe PHY APLL Subsystem Architecture
- 26.4.4.4.2.6 PCIe PHY APLL Clock Generator Modes and State Transitions
- 26.4.4.4.3 ACSPCIE reference clock buffer
- 26.4.4.4.1
PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator
- 26.4.5 PCIePHY Subsystem Low-Level Programming Model
- 26.4.6 PCIe PHY Subsystem Register Manual
- 26.1
SATA PHY Subsystem
-
27General-Purpose Interface
- 27.1 General-Purpose Interface Overview
- 27.2 General-Purpose Interface Environment
- 27.3 General-Purpose Interface Integration
- 27.4
General-Purpose Interface Functional Description
- 27.4.1 General-Purpose Interface Block Diagram
- 27.4.2 General-Purpose Interface Interrupt and Wake-Up Features
- 27.4.3 General-Purpose Interface Clock Configuration
- 27.4.4 General-Purpose Interface Hardware and Software Reset
- 27.4.5 General-Purpose Interface Power Management
- 27.4.6 General-Purpose Interface Interrupt and Wake-Up Requests
- 27.4.7 General-Purpose Interface Channels Description
- 27.4.8 General-Purpose Interface Data Input/Output Capabilities
- 27.4.9 General-Purpose Interface Set-and-Clear Protocol
- 27.5 General-Purpose Interface Programming Guide
- 27.6 General-Purpose Interface Register Manual
-
28Keyboard Controller
- 28.1 Keyboard Controller Overview
- 28.2 Keyboard Controller Environment
- 28.3 Keyboard Controller Integration
- 28.4
Keyboard Controller Functional Description
- 28.4.1 Keyboard Controller Block Diagram
- 28.4.2 Keyboard Controller Software Reset
- 28.4.3 Keyboard Controller Power Management
- 28.4.4 Keyboard Controller Interrupt Requests
- 28.4.5 Keyboard Controller Software Mode
- 28.4.6 Keyboard Controller Hardware Decoding Modes
- 28.4.7 Keyboard Controller Key Coding Registers
- 28.4.8 Keyboard Controller Register Access
- 28.5
Keyboard Controller Programming Guide
- 28.5.1
Keyboard Controller Low-Level Programming Models
- 28.5.1.1 Global Initialization
- 28.5.1.2 Operational Modes Configuration
- 28.5.1.3 Keyboard Controller Events Servicing
- 28.5.1
Keyboard Controller Low-Level Programming Models
- 28.6 Keyboard Controller Register Manual
-
29Pulse-Width Modulation Subsystem
- 29.1 PWM Subsystem Resources
- 29.2 Enhanced PWM (ePWM) Module
- 29.3 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Module
- 29.4 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP) Module
-
30Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem and Industrial Communication Subsystem
- 30.1 PRU-ICSS Overview
- 30.2 PRU-ICSS Environment
- 30.3 PRU-ICSS Integration
- 30.4 PRU-ICSS Level Resources Functional Description
- 30.5 PRU-ICSS PRU Cores
- 30.6
PRU-ICSS Local Interrupt Controller
- 30.6.1 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Overview
- 30.6.2
PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Functional Description
- 30.6.2.1 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller System Events
- 30.6.2.2 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller System Events Flow
- 30.6.2.3 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Disabling
- 30.6.3 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Basic Programming Model
- 30.6.4 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Requests Mapping
- 30.6.5 PRU-ICSS Interrupt Controller Register Manual
- 30.7
PRU-ICSS UART Module
- 30.7.1 PRU-ICSS UART Module Overview
- 30.7.2 PRU-ICSS UART Environment
- 30.7.3
PRU-ICSS UART Module Functional Description
- 30.7.3.1 PRU-ICSS UART Functional Block Diagram
- 30.7.3.2 PRU-ICSS UART Reset Considerations
- 30.7.3.3 PRU-ICSS UART Power Management
- 30.7.3.4 PRU-ICSS UART Interrupt Support
- 30.7.3.5 4061
- 30.7.3.6 PRU-ICSS UART DMA Event Support
- 30.7.3.7 PRU-ICSS UART Operations
- 30.7.3.8 PRU-ICSS UART Initialization
- 30.7.3.9 PRU-ICSS UART Exception Processing
- 30.7.4 PRUSS_UART Register Manual
- 30.8 PRU-ICSS eCAP Module
- 30.9
PRU-ICSS MII RT Module
- 30.9.1 Introduction
- 30.9.2 Functional Description
- 30.9.3 PRU-ICSS MII RT Module Register Manual
- 30.10 PRU-ICSS MII MDIO Module
- 30.11
PRU-ICSS Industrial Ethernet Peripheral (IEP)
- 30.11.1 PRU-ICSS IEP Overview
- 30.11.2 PRU-ICSS IEP Functional Description
- 30.11.3 PRUSS_IEP Register Manual
- 31Viterbi-Decoder Coprocessor
- 32Audio Tracking Logic
-
33Initialization
- 33.1 Initialization Overview
- 33.2 Preinitialization
- 33.3
Device Initialization by ROM Code
- 33.3.1 Booting Overview
- 33.3.2 Memory Maps
- 33.3.3 Overall Booting Sequence
- 33.3.4 Startup and Configuration
- 33.3.5 Peripheral Booting
- 33.3.6 Fast External Booting
- 33.3.7
Memory Booting
- 33.3.7.1 Overview
- 33.3.7.2 Non-XIP Memory
- 33.3.7.3 XIP Memory
- 33.3.7.4 NAND
- 33.3.7.5 SPI/QSPI Flash Devices
- 33.3.7.6
eMMC Memories and SD Cards
- 33.3.7.6.1 eMMC Memories
- 33.3.7.6.2 SD Cards
- 33.3.7.6.3 Initialization and Detection
- 33.3.7.6.4 Read Sector Procedure
- 33.3.7.6.5 File System Handling
- 33.3.7.7 SATA Device Boot Operation
- 33.3.8 Image Format
- 33.3.9 Tracing
- 33.4 Services for HLOS Support
-
34On-Chip Debug Support
- 34.1 Introduction
- 34.2 Debug Interfaces
- 34.3 Debugger Connection
- 34.4 Primary Debug Support
- 34.5 Real-Time Debug
- 34.6 Power, Reset, and Clock Management Debug Support
- 34.7 Performance Monitoring
- 34.8 MPU Memory Adaptor (MPU_MA) Watchpoint
- 34.9 Processor Trace
- 34.10
System Instrumentation
- 34.10.1 MIPI STM (CT_STM)
- 34.10.2 System Trace Export
- 34.10.3 Software Instrumentation
- 34.10.4 OCP Watchpoint
- 34.10.5 IVA Pipeline
- 34.10.6
L3 NOC Statistics Collector
- 34.10.6.1 L3 Target Load Monitoring
- 34.10.6.2
L3 Master Latency Monitoring
- 34.10.6.2.1 SC_LAT0 Configuration
- 34.10.6.2.2 SC_LAT1 Configuration
- 34.10.6.2.3 SC_LAT2 Configuration
- 34.10.6.2.4 SC_LAT3 Configuration
- 34.10.6.2.5 SC_LAT4 Configuration
- 34.10.6.2.6 SC_LAT5 Configuration
- 34.10.6.2.7 SC_LAT6 Configuration
- 34.10.6.2.8 SC_LAT7 Configuration
- 34.10.6.2.9 SC_LAT8 Configuration
- 34.10.6.2.10 Statistics Collector Alarm Mode
- 34.10.6.2.11 Statistics Collector Suspend Mode
- 34.10.7 PM Instrumentation
- 34.10.8 CM Instrumentation
- 34.10.9 Master-ID Encoding
- 34.11 Concurrent Debug Modes
- 34.12 DRM Register Manual
- 35Glossary
- 36Revision History
18.2 Control Module Environment
One of the control module functions is to control the multiplexing of certain signals from the device internal modules. Using the correct pad configuration settings, the control module maps these observability lines to the device boundary and a set of user selected internal module signals are available to be observed on the device pads. In addition, there are also two lines intended for observation of any of the device interrupt requests connected to the inputs of the IRQ_CROSSBAR module and two lines intended for observation of any of the DMA requests connected to the inputs of the DMA_CROSSBAR module. For more information, see Section 18.4.6.4, IRQ_CROSSBAR Module Functional Description and Section 18.4.6.5, DMA_CROSSBAR Module Functional Description.
An external non-maskable interrupt signal is also present. Using the appropriate registers the NMI can be mapped to different device cores. For more information, see Section 18.4.6.9, NMI Mapping to respective cores.
Figure 18-2 is an overview of the control module environment.
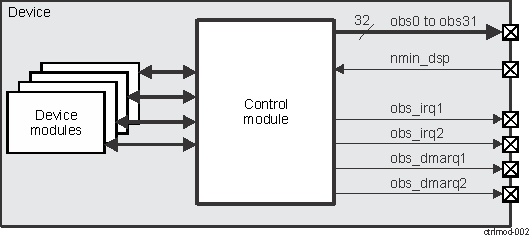 Figure 18-2 Control Module Environment
Figure 18-2 Control Module EnvironmentTable 18-1 shows the NMI input signal and observability outputs used to observe different signals of the device modules.
| Signal | I/O(1) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| obs[31:0] | O | 32 internal hardware observability signals |
| nmin_dsp | I | External non-maskable interrupt signal |
| obs_irq1 | O | Two signals intended for IRQ observation |
| obs_irq2 | O | |
| obs_dmarq1 | O | Two signals intended for DREQ observation |
| obs_dmarq2 | O |