SPRUI33H November 2015 – June 2024 TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C-Q1
- 1
- Read This First
- 1 C2000™ Microcontrollers Software Support
- 2 C28x Processor
-
3 System Control and
Interrupts
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 Power Management
- 3.3 Device Identification and Configuration Registers
- 3.4 Resets
- 3.5 Peripheral Interrupts
- 3.6 Exceptions and Non-Maskable Interrupts
- 3.7
Clocking
- 3.7.1 Clock Sources
- 3.7.2 Derived Clocks
- 3.7.3 Device Clock Domains
- 3.7.4 XCLKOUT
- 3.7.5 Clock Connectivity
- 3.7.6 Clock Source and PLL Setup
- 3.7.7 Using an External Crystal or Resonator
- 3.7.8 Using an External Oscillator
- 3.7.9 Choosing PLL Settings
- 3.7.10 System Clock Setup
- 3.7.11 Clock Configuration Examples
- 3.7.12 Missing Clock Detection
- 3.8 32-Bit CPU Timers 0/1/2
- 3.9 Watchdog Timer
- 3.10 Low-Power Modes
- 3.11
Memory Controller Module
- 3.11.1
Functional Description
- 3.11.1.1 Dedicated RAM (Mx RAM)
- 3.11.1.2 Local Shared RAM (LSx RAM)
- 3.11.1.3 Global Shared RAM (GSx RAM)
- 3.11.1.4 Message RAM (CLA MSGRAM)
- 3.11.1.5 Access Arbitration
- 3.11.1.6 Access Protection
- 3.11.1.7 Memory Error Detection, Correction and Error Handling
- 3.11.1.8 Application Test Hooks for Error Detection and Correction
- 3.11.1.9 RAM Initialization
- 3.11.1
Functional Description
- 3.12
Flash and OTP Memory
- 3.12.1 Features
- 3.12.2 Flash Tools
- 3.12.3 Default Flash Configuration
- 3.12.4 Flash Bank, OTP and Pump
- 3.12.5 Flash Module Controller (FMC)
- 3.12.6 Flash and OTP and Wakeup Power-Down Modes
- 3.12.7 Flash and OTP Performance
- 3.12.8 Flash Access Interface
- 3.12.9 Erase/Program Flash
- 3.12.10 Error Correction Code (ECC) Protection
- 3.12.11 Reserved Locations Within Flash and OTP
- 3.12.12 Procedure to Change the Flash Control Registers
- 3.12.13 Simple Procedure to Modify an Application from RAM Configuration to Flash Configuration
- 3.13
Dual Code Security Module (DCSM)
- 3.13.1 Functional Description
- 3.13.2 C Code Example to Get Zone Select Block Addr for Zone1 in BANK0
- 3.13.3 Flash and OTP Erase/Program
- 3.13.4 Safe Copy Code
- 3.13.5 SafeCRC
- 3.13.6 CSM Impact on Other On-Chip Resources
- 3.13.7
Incorporating Code Security in User Applications
- 3.13.7.1 Environments That Require Security Unlocking
- 3.13.7.2 CSM Password Match Flow
- 3.13.7.3 C Code Example to Unsecure C28x Zone1
- 3.13.7.4 C Code Example to Resecure C28x Zone1
- 3.13.7.5 Environments That Require ECSL Unlocking
- 3.13.7.6 ECSL Password Match Flow
- 3.13.7.7 ECSL Disable Considerations for any Zone
- 3.13.7.8 Device Unique ID
- 3.14 System Control Register Configuration Restrictions
- 3.15
System Control Registers
- 3.15.1 System Control Base Address Table
- 3.15.2 CPUTIMER_REGS Registers
- 3.15.3 PIE_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 3.15.4 WD_REGS Registers
- 3.15.5 NMI_INTRUPT_REGS Registers
- 3.15.6 XINT_REGS Registers
- 3.15.7 DMA_CLA_SRC_SEL_REGS Registers
- 3.15.8 DEV_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.15.9 CLK_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.15.10 CPU_SYS_REGS Registers
- 3.15.11 PERIPH_AC_REGS Registers
- 3.15.12 DCSM_BANK0_Z1_REGS Registers
- 3.15.13 DCSM_BANK0_Z2_REGS Registers
- 3.15.14 DCSM_COMMON_REGS Registers
- 3.15.15 DCSM_BANK1_Z1_REGS Registers
- 3.15.16 DCSM_BANK1_Z2_REGS Registers
- 3.15.17 MEM_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.15.18 ACCESS_PROTECTION_REGS Registers
- 3.15.19 MEMORY_ERROR_REGS Registers
- 3.15.20 FLASH_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 3.15.21 FLASH_ECC_REGS Registers
- 3.15.22 UID_REGS Registers
- 3.15.23 DCSM_BANK0_Z1_OTP Registers
- 3.15.24 DCSM_BANK0_Z2_OTP Registers
- 3.15.25 DCSM_BANK1_Z1_OTP Registers
- 3.15.26 DCSM_BANK1_Z2_OTP Registers
- 3.15.27
Register to Driverlib Function Mapping
- 3.15.27.1 ASYSCTL Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.2 CPUTIMER Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.3 DCSM Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.4 FLASH Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.5 MEMCFG Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.6 NMI Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.7 PIE Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.8 SYSCTL Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.15.27.9 XINT Registers to Driverlib Functions
-
4 ROM Code and Peripheral Booting
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Device Boot Sequence
- 4.3 Device Boot Modes
- 4.4 Device Boot Flow Diagrams
- 4.5 Device Reset and Exception Handling
- 4.6
Boot ROM Description
- 4.6.1 Boot ROM Registers
- 4.6.2 Boot ROM User OTP
- 4.6.3 Entry Points
- 4.6.4 Wait Points
- 4.6.5 Memory Maps
- 4.6.6 ROM Tables
- 4.6.7 Boot Modes
- 4.6.8 Boot Data Stream Structure
- 4.6.9 GPIO Assignments
- 4.6.10 Secure ROM Function APIs
- 4.6.11 DCSM Usage
- 4.6.12 Clock Initialization
- 4.6.13 Boot Status Information
- 4.6.14 ROM Version
- 4.7 The C2000 Hex Utility
-
5 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 CLA Interface
- 5.3 CLA, DMA, and CPU Arbitration
- 5.4 CLA Configuration and Debug
- 5.5 Pipeline
- 5.6
Software
- 5.6.1
CLA Examples
- 5.6.1.1 CLA arcsine(x) using a lookup table (cla_asin_cpu01)
- 5.6.1.2 CLA arctangent(x) using a lookup table (cla_atan_cpu01)
- 5.6.1.3 CLA background nesting task
- 5.6.1.4 Controlling PWM output using CLA
- 5.6.1.5 Just-in-time ADC sampling with CLA
- 5.6.1.6 Optimal offloading of control algorithms to CLA
- 5.6.1.7 Handling shared resources across C28x and CLA
- 5.6.1
CLA Examples
- 5.7
Instruction Set
- 5.7.1 Instruction Descriptions
- 5.7.2 Addressing Modes and Encoding
- 5.7.3
Instructions
- MABSF32 MRa, MRb
- MADD32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MADDF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MADDF32 MRa, MRb, #16FHi
- MADDF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MAND32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MASR32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MBCNDD 16BitDest [, CNDF]
- MCCNDD 16BitDest [, CNDF]
- MCLRC BGINTM
- MCMP32 MRa, MRb
- MCMPF32 MRa, MRb
- MCMPF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MDEBUGSTOP
- MDEBUGSTOP1
- MEALLOW
- MEDIS
- MEINVF32 MRa, MRb
- MEISQRTF32 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI16 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI16R MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI32 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI16 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI16R MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI32 MRa, MRb
- MFRACF32 MRa, MRb
- MI16TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MI16TOF32 MRa, mem16
- MI32TOF32 MRa, mem32
- MI32TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MLSL32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MLSR32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MMACF32 MR3, MR2, MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MMAXF32 MRa, MRb
- MMAXF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MMINF32 MRa, MRb
- MMINF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MMOV16 MARx, MRa, #16I
- MMOV16 MARx, mem16
- MMOV16 mem16, MARx
- MMOV16 mem16, MRa
- MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MMOV32 mem32, MSTF
- MMOV32 MRa, mem32 [, CNDF]
- MMOV32 MRa, MRb [, CNDF]
- MMOV32 MSTF, mem32
- MMOVD32 MRa, mem32
- MMOVF32 MRa, #32F
- MMOVI16 MARx, #16I
- MMOVI32 MRa, #32FHex
- MMOVIZ MRa, #16FHi
- MMOVZ16 MRa, mem16
- MMOVXI MRa, #16FLoHex
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MMPYF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, #16FHi
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc||MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf
- MMPYF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MMPYF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc ||MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf
- MNEGF32 MRa, MRb[, CNDF]
- MNOP
- MOR32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MRCNDD [CNDF]
- MSETC BGINTM
- MSETFLG FLAG, VALUE
- MSTOP
- MSUB32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MSUBF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MSUBF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MSWAPF MRa, MRb [, CNDF]
- MTESTTF CNDF
- MUI16TOF32 MRa, mem16
- MUI16TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MUI32TOF32 MRa, mem32
- MUI32TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MXOR32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- 5.8 CLA Registers
- 6 Dual-Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 7 CLA Program ROM CRC (CLAPROMCRC)
- 8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 9 Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 10Direct Memory Access (DMA)
-
11Embedded Real-time Analysis and Diagnostic (ERAD)
- 11.1 Introduction
- 11.2 Enhanced Bus Comparator Unit
- 11.3 System Event Counter Unit
- 11.4 ERAD Ownership, Initialization and Reset
- 11.5 ERAD Programming Sequence
- 11.6
Software
- 11.6.1
ERAD Examples
- 11.6.1.1 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 11.6.1.2 ERAD Profile Function
- 11.6.1.3 ERAD Profile Function
- 11.6.1.4 ERAD HWBP Monitor Program Counter
- 11.6.1.5 ERAD HWBP Monitor Program Counter
- 11.6.1.6 ERAD Profile Function
- 11.6.1.7 ERAD HWBP Stack Overflow Detection
- 11.6.1.8 ERAD HWBP Stack Overflow Detection
- 11.6.1.9 ERAD Stack Overflow
- 11.6.1.10 ERAD Profile Interrupts CLA
- 11.6.1.11 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 11.6.1.12 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 11.6.1.13 ERAD MEMORY ACCESS RESTRICT
- 11.6.1.14 ERAD INTERRUPT ORDER
- 11.6.1.15 ERAD AND CLB
- 11.6.1.16 ERAD PWM PROTECTION
- 11.6.1
ERAD Examples
- 11.7 ERAD Registers
- 12Analog Subsystem
-
13Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 13.1 Introduction
- 13.2 ADC Configurability
- 13.3 SOC Principle of Operation
- 13.4 SOC Configuration Examples
- 13.5 ADC Conversion Priority
- 13.6 Burst Mode
- 13.7 EOC and Interrupt Operation
- 13.8 Post-Processing Blocks
- 13.9 Opens/Shorts Detection Circuit (OSDETECT)
- 13.10 Power-Up Sequence
- 13.11 ADC Calibration
- 13.12 ADC Timings
- 13.13
Additional Information
- 13.13.1 Ensuring Synchronous Operation
- 13.13.2 Choosing an Acquisition Window Duration
- 13.13.3 Achieving Simultaneous Sampling
- 13.13.4 Result Register Mapping
- 13.13.5 Internal Temperature Sensor
- 13.13.6 Designing an External Reference Circuit
- 13.13.7 ADC-DAC Loopback Testing
- 13.13.8 Internal Test Mode
- 13.13.9 ADC Gain and Offset Calibration
- 13.14
Software
- 13.14.1
ADC Examples
- 13.14.1.1 ADC Software Triggering
- 13.14.1.2 ADC ePWM Triggering
- 13.14.1.3 ADC Temperature Sensor Conversion
- 13.14.1.4 ADC Synchronous SOC Software Force (adc_soc_software_sync)
- 13.14.1.5 ADC Continuous Triggering (adc_soc_continuous)
- 13.14.1.6 ADC Continuous Conversions Read by DMA (adc_soc_continuous_dma)
- 13.14.1.7 ADC PPB Offset (adc_ppb_offset)
- 13.14.1.8 ADC PPB Limits (adc_ppb_limits)
- 13.14.1.9 ADC PPB Delay Capture (adc_ppb_delay)
- 13.14.1.10 ADC ePWM Triggering Multiple SOC
- 13.14.1.11 ADC Burst Mode
- 13.14.1.12 ADC Burst Mode Oversampling
- 13.14.1.13 ADC SOC Oversampling
- 13.14.1.14 ADC PPB PWM trip (adc_ppb_pwm_trip)
- 13.14.1.15 ADC Open Shorts Detection (adc_open_shorts_detection)
- 13.14.1
ADC Examples
- 13.15 ADC Registers
-
14Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA)
- 14.1 Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) Overview
- 14.2 Linear Output Range
- 14.3 Gain Modes
- 14.4 External Filtering
- 14.5 Error Calibration
- 14.6 Ground Routing
- 14.7 Enabling and Disabling the PGA Clock
- 14.8 Lock Register
- 14.9 Examples
- 14.10 Analog Front End Integration
- 14.11 Software
- 14.12 PGA Registers
- 15Buffered Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
- 16Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS)
- 17Sigma Delta Filter Module (SDFM)
-
18Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 18.1 Introduction
- 18.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 18.3 ePWM Modules Overview
- 18.4
Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 18.4.1 Purpose of the Time-Base Submodule
- 18.4.2 Controlling and Monitoring the Time-Base Submodule
- 18.4.3 Calculating PWM Period and Frequency
- 18.4.4 Phase Locking the Time-Base Clocks of Multiple ePWM Modules
- 18.4.5 Simultaneous Writes to TBPRD and CMPx Registers Between ePWM Modules
- 18.4.6 Time-Base Counter Modes and Timing Waveforms
- 18.4.7 Global Load
- 18.5 Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 18.6 Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 18.7 Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 18.8 PWM Chopper (PC) Submodule
- 18.9 Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 18.10 Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 18.11 Digital Compare (DC) Submodule
- 18.12 ePWM Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 18.13
Applications to Power Topologies
- 18.13.1 Overview of Multiple Modules
- 18.13.2 Key Configuration Capabilities
- 18.13.3 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Independent Frequencies
- 18.13.4 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Same Frequencies
- 18.13.5 Controlling Multiple Half H-Bridge (HHB) Converters
- 18.13.6 Controlling Dual 3-Phase Inverters for Motors (ACI and PMSM)
- 18.13.7 Practical Applications Using Phase Control Between PWM Modules
- 18.13.8 Controlling a 3-Phase Interleaved DC/DC Converter
- 18.13.9 Controlling Zero Voltage Switched Full Bridge (ZVSFB) Converter
- 18.13.10 Controlling a Peak Current Mode Controlled Buck Module
- 18.13.11 Controlling H-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter
- 18.14 Register Lock Protection
- 18.15
High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 18.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 18.15.1.1 Controlling the HRPWM Capabilities
- 18.15.1.2 HRPWM Source Clock
- 18.15.1.3 Configuring the HRPWM
- 18.15.1.4 Configuring High-Resolution in Deadband Rising-Edge and Falling-Edge Delay
- 18.15.1.5 Principle of Operation
- 18.15.1.6 Deadband High-Resolution Operation
- 18.15.1.7 Scale Factor Optimizing Software (SFO)
- 18.15.1.8 HRPWM Examples Using Optimized Assembly Code
- 18.15.2 SFO Library Software - SFO_TI_Build_V8.lib
- 18.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 18.16
Software
- 18.16.1
EPWM Examples
- 18.16.1.1 ePWM Trip Zone
- 18.16.1.2 ePWM Up Down Count Action Qualifier
- 18.16.1.3 ePWM Synchronization
- 18.16.1.4 ePWM Digital Compare
- 18.16.1.5 ePWM Digital Compare Event Filter Blanking Window
- 18.16.1.6 ePWM Valley Switching
- 18.16.1.7 ePWM Digital Compare Edge Filter
- 18.16.1.8 ePWM Deadband
- 18.16.1.9 ePWM DMA
- 18.16.1.10 ePWM Chopper
- 18.16.1.11 EPWM Configure Signal
- 18.16.1.12 Realization of Monoshot mode
- 18.16.1.13 EPWM Action Qualifier (epwm_up_aq)
- 18.16.2 HRPWM Examples
- 18.16.1
EPWM Examples
- 18.17 ePWM Registers
-
19Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 19.1 Introduction
- 19.2 Description
- 19.3 Configuring Device Pins for the eCAP
- 19.4 Capture and APWM Operating Mode
- 19.5
Capture Mode Description
- 19.5.1 Event Prescaler
- 19.5.2 Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 19.5.3 Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 19.5.4 32-Bit Counter and Phase Control
- 19.5.5 CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 19.5.6 eCAP Synchronization
- 19.5.7 Interrupt Control
- 19.5.8 DMA Interrupt
- 19.5.9 Shadow Load and Lockout Control
- 19.5.10 APWM Mode Operation
- 19.6
Application of the eCAP Module
- 19.6.1 Example 1 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 19.6.2 Example 2 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 19.6.3 Example 3 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 19.6.4 Example 4 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 19.7 Application of the APWM Mode
- 19.8 Software
- 19.9 eCAP Registers
- 20High Resolution Capture (HRCAP)
-
21Enhanced Quadrature
Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 21.1 Introduction
- 21.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 21.3 Description
- 21.4 Quadrature Decoder Unit (QDU)
- 21.5 Position Counter and Control Unit (PCCU)
- 21.6 eQEP Edge Capture Unit
- 21.7 eQEP Watchdog
- 21.8 eQEP Unit Timer Base
- 21.9 QMA Module
- 21.10 eQEP Interrupt Structure
- 21.11 eQEP Registers
-
22Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 22.1 Introduction
- 22.2 System-Level Integration
- 22.3 SPI Operation
- 22.4 Programming Procedure
- 22.5 Software
- 22.6 SPI Registers
-
23Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 23.1 Introduction
- 23.2 Architecture
- 23.3 SCI Module Signal Summary
- 23.4 Configuring Device Pins
- 23.5 Multiprocessor and Asynchronous Communication Modes
- 23.6 SCI Programmable Data Format
- 23.7 SCI Multiprocessor Communication
- 23.8 Idle-Line Multiprocessor Mode
- 23.9 Address-Bit Multiprocessor Mode
- 23.10 SCI Communication Format
- 23.11 SCI Port Interrupts
- 23.12 SCI Baud Rate Calculations
- 23.13 SCI Enhanced Features
- 23.14 Software
- 23.15 SCI Registers
-
24Inter-Integrated Circuit Module (I2C)
- 24.1 Introduction
- 24.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 24.3
I2C Module Operational Details
- 24.3.1 Input and Output Voltage Levels
- 24.3.2 Selecting Pullup Resistors
- 24.3.3 Data Validity
- 24.3.4 Operating Modes
- 24.3.5 I2C Module START and STOP Conditions
- 24.3.6 Non-repeat Mode versus Repeat Mode
- 24.3.7 Serial Data Formats
- 24.3.8 Clock Synchronization
- 24.3.9 Arbitration
- 24.3.10 Digital Loopback Mode
- 24.3.11 NACK Bit Generation
- 24.4 Interrupt Requests Generated by the I2C Module
- 24.5 Resetting or Disabling the I2C Module
- 24.6 Software
- 24.7 I2C Registers
-
25Power Management Bus Module (PMBus)
- 25.1 Introduction
- 25.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 25.3
Slave Mode
Operation
- 25.3.1 Configuration
- 25.3.2
Message Handling
- 25.3.2.1 Quick Command
- 25.3.2.2 Send Byte
- 25.3.2.3 Receive Byte
- 25.3.2.4 Write Byte and Write Word
- 25.3.2.5 Read Byte and Read Word
- 25.3.2.6 Process Call
- 25.3.2.7 Block Write
- 25.3.2.8 Block Read
- 25.3.2.9 Block Write-Block Read Process Call
- 25.3.2.10 Alert Response
- 25.3.2.11 Extended Command
- 25.3.2.12 Group Command
- 25.4
Master Mode
Operation
- 25.4.1 Configuration
- 25.4.2
Message Handling
- 25.4.2.1 Quick Command
- 25.4.2.2 Send Byte
- 25.4.2.3 Receive Byte
- 25.4.2.4 Write Byte and Write Word
- 25.4.2.5 Read Byte and Read Word
- 25.4.2.6 Process Call
- 25.4.2.7 Block Write
- 25.4.2.8 Block Read
- 25.4.2.9 Block Write-Block Read Process Call
- 25.4.2.10 Alert Response
- 25.4.2.11 Extended Command
- 25.4.2.12 Group Command
- 25.5 PMBus Registers
-
26Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 26.1 Introduction
- 26.2 Functional Description
- 26.3 Operating Modes
- 26.4 Multiple Clock Source
- 26.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 26.6 DMA Functionality
- 26.7 Parity Check Mechanism
- 26.8 Debug Mode
- 26.9 Module Initialization
- 26.10 Configuration of Message Objects
- 26.11
Message Handling
- 26.11.1 Message Handler Overview
- 26.11.2 Receive/Transmit Priority
- 26.11.3 Transmission of Messages in Event Driven CAN Communication
- 26.11.4 Updating a Transmit Object
- 26.11.5 Changing a Transmit Object
- 26.11.6 Acceptance Filtering of Received Messages
- 26.11.7 Reception of Data Frames
- 26.11.8 Reception of Remote Frames
- 26.11.9 Reading Received Messages
- 26.11.10 Requesting New Data for a Receive Object
- 26.11.11 Storing Received Messages in FIFO Buffers
- 26.11.12 Reading from a FIFO Buffer
- 26.12 CAN Bit Timing
- 26.13 Message Interface Register Sets
- 26.14 Message RAM
- 26.15
Software
- 26.15.1
CAN Examples
- 26.15.1.1 CAN External Loopback
- 26.15.1.2 CAN External Loopback with Interrupts
- 26.15.1.3 CAN-A to CAN-B External Transmit
- 26.15.1.4 CAN External Loopback with DMA
- 26.15.1.5 CAN Transmit and Receive Configurations
- 26.15.1.6 CAN Error Generation Example
- 26.15.1.7 CAN Remote Request Loopback
- 26.15.1.8 CAN example that illustrates the usage of Mask registers
- 26.15.1
CAN Examples
- 26.16 CAN Registers
-
27Local Interconnect Network
(LIN)
- 27.1 Introduction
- 27.2 Serial Communications Interface Module
- 27.3
Local Interconnect Network Module
- 27.3.1
LIN Communication Formats
- 27.3.1.1 LIN Standards
- 27.3.1.2 Message Frame
- 27.3.1.3 Synchronizer
- 27.3.1.4 Baud Rate
- 27.3.1.5 Header Generation
- 27.3.1.6 Extended Frames Handling
- 27.3.1.7 Timeout Control
- 27.3.1.8 TXRX Error Detector (TED)
- 27.3.1.9 Message Filtering and Validation
- 27.3.1.10 Receive Buffers
- 27.3.1.11 Transmit Buffers
- 27.3.2 LIN Interrupts
- 27.3.3 Servicing LIN Interrupts
- 27.3.4 LIN DMA Interface
- 27.3.5 LIN Configurations
- 27.3.1
LIN Communication Formats
- 27.4 Low-Power Mode
- 27.5 Emulation Mode
- 27.6 Software
- 27.7 SCI/LIN Registers
-
28Fast Serial Interface
(FSI)
- 28.1 Introduction
- 28.2 System-level Integration
- 28.3
FSI Functional Description
- 28.3.1 Introduction to Operation
- 28.3.2 FSI Transmitter Module
- 28.3.3
FSI Receiver Module
- 28.3.3.1 Initialization
- 28.3.3.2 FSI_RX Clocking
- 28.3.3.3 Receiving Frames
- 28.3.3.4 Ping Frame Watchdog
- 28.3.3.5 Frame Watchdog
- 28.3.3.6 Delay Line Control
- 28.3.3.7 Buffer Management
- 28.3.3.8 CRC Submodule
- 28.3.3.9 Using the Zero Bits of the Receiver Tag Registers
- 28.3.3.10 Conditions in Which the Receiver Must Undergo a Soft Reset
- 28.3.3.11 FSI_RX Reset
- 28.3.4 Frame Format
- 28.3.5 Flush Sequence
- 28.3.6 Internal Loopback
- 28.3.7 CRC Generation
- 28.3.8 ECC Module
- 28.3.9 FSI Trigger Generation
- 28.3.10 FSI-SPI Compatibility Mode
- 28.4 FSI Programing Guide
- 28.5
Software
- 28.5.1
FSI Examples
- 28.5.1.1 FSI Loopback:CPU Control
- 28.5.1.2 FSI Loopback CLA control
- 28.5.1.3 FSI DMA frame transfers:DMA Control
- 28.5.1.4 FSI data transfer by external trigger
- 28.5.1.5 FSI data transfers upon CPU Timer event
- 28.5.1.6 FSI and SPI communication(fsi_ex6_spi_main_tx)
- 28.5.1.7 FSI and SPI communication(fsi_ex7_spi_remote_rx)
- 28.5.1.8 FSI P2Point Connection:Rx Side
- 28.5.1.9 FSI P2Point Connection:Tx Side
- 28.5.1.10 FSI and SPI communication (fsi_ex9_spi_master_tx_drivers)
- 28.5.1.11 FSI and SPI communication (fsi_ex10_spi_slave_rx_driver)
- 28.5.1.12 FSI and SPI communication full-duplex
- 28.5.1.13 FSI Receive Skew Compensation Block Element Delays
- 28.5.1.14 FSI Skew Calibration in Single Data Line Mode (RX Device)
- 28.5.1.15 FSI Skew Calibration in Single Data Line Mode (TX Device)
- 28.5.1.16 FSI Skew Calibration in Dual Data Line Mode (RX Device)
- 28.5.1.17 FSI Skew Calibration in Dual Data Line Mode (TX Device)
- 28.5.1.18 FSI Find Optimal Number of Delay Elements Activated For FSIRX
- 28.5.1.19 FSI Find Optimal Number of Delay Elements Activated For FSIRX
- 28.5.1.20 FSI daisy chain topology, lead device example
- 28.5.1.21 FSI daisy chain topology, node device example
- 28.5.1
FSI Examples
- 28.6 FSI Registers
-
29Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 29.1 Introduction
- 29.2 Description
- 29.3 CLB Input/Output Connection
- 29.4 CLB Tile
- 29.5 CPU Interface
- 29.6 DMA Access
- 29.7
Software
- 29.7.1
CLB Examples
- 29.7.1.1 CLB Empty Project
- 29.7.1.2 CLB Combinational Logic
- 29.7.1.3 CLB GPIO Input Filter
- 29.7.1.4 CLB Auxilary PWM
- 29.7.1.5 CLB PWM Protection
- 29.7.1.6 CLB Event Window
- 29.7.1.7 CLB Signal Generator
- 29.7.1.8 CLB State Machine
- 29.7.1.9 CLB External Signal AND Gate
- 29.7.1.10 CLB Timer
- 29.7.1.11 CLB Timer Two States
- 29.7.1.12 CLB Interrupt Tag
- 29.7.1.13 CLB Output Intersect
- 29.7.1.14 CLB PUSH PULL
- 29.7.1.15 CLB Multi Tile
- 29.7.1.16 CLB Glue Logic
- 29.7.1.17 CLB based One-shot PWM
- 29.7.1.18 CLB AOC Control
- 29.7.1.19 CLB AOC Release Control
- 29.7.1.20 CLB AOC Control
- 29.7.1.21 CLB Serializer
- 29.7.1.22 CLB LFSR
- 29.7.1.23 CLB Trip Zone Timestamp
- 29.7.1.24 CLB CRC
- 29.7.1
CLB Examples
- 29.8 CLB Registers
- 30Revision History
18.15.1 Operational Description of HRPWM
The HRPWM is based on micro-edge positioner (MEP) technology. MEP logic is capable of positioning an edge very finely by sub-dividing one coarse system clock of a conventional PWM generator. The time step accuracy is on the order of 150ps. See the device data sheet for the typical MEP step size on a particular device. The HRPWM also has a self-check software diagnostics mode to check if the MEP logic is running as designed under all operating conditions. Details on software diagnostics and functions are in Section 18.15.1.7.
Figure 18-82 shows the relationship between one coarse system clock and edge position in terms of MEP steps, which are controlled using an 8-bit field in the Compare A extension register (CMPAHR). The same operating logic applies to CMPBHR as well.
To generate an HRPWM waveform, configure the ePWM registers to generate a conventional PWM of a given frequency and polarity. The HRPWM works together with the ePWM registers to extend edge resolution. Although many programming combinations are possible, only a few are needed and practical. These methods are described in Section 18.15.1.8.
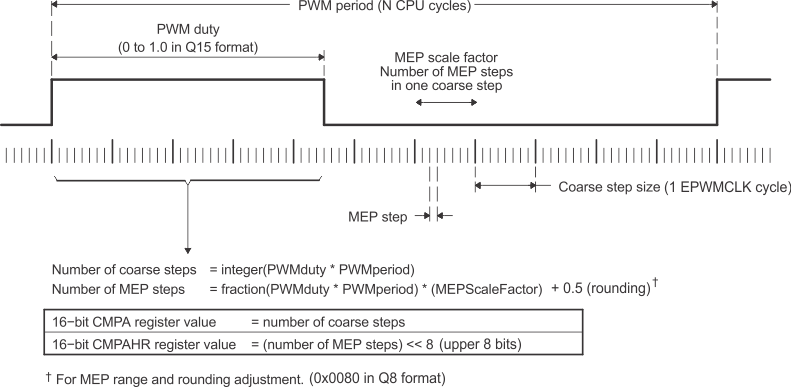 Figure 18-82 Operating Logic Using MEP
Figure 18-82 Operating Logic Using MEP