SPRUIV7B May 2022 – September 2023 AM620-Q1 , AM623 , AM625 , AM625-Q1 , AM625SIP
- 1
- Read This First
-
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Device Overview
- 1.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 1.3 Module Allocation and Instances within Device Domains
- 1.4
Device MAIN Domain
- 1.4.1 Arm Cortex-A53 Subsystem (A53SS)
- 1.4.2 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS)
- 1.4.3 DDR 16-bit Subsystem (DDR16)
- 1.4.4 Region-based Address Translation Module (RAT)
- 1.4.5 Data Movement Subsystem (DMSS)
- 1.4.6 Mailbox (MAILBOX)
- 1.4.7 Spinlock (SPINLOCK)
- 1.4.8 General Purpose Input/Output Interface (GPIO)
- 1.4.9 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 1.4.10 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 1.4.11 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 1.4.12 3-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW3G)
- 1.4.13 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Subsystem 2.0
- 1.4.14 General Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 1.4.15 Error Location Module (ELM)
- 1.4.16 Flash Subsystem (FSS) with Octal Serial Peripheral Interface (OSPI)
- 1.4.17 Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital Interface (MMCSD)
- 1.4.18 Enhanced Capture Module (ECAP)
- 1.4.19 Enhanced Pulse-Width Modulation Module (EPWM)
- 1.4.20 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Module (EQEP)
- 1.4.21 Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 1.4.22 Timers
- 1.4.23 Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 1.5
Device MCU Domain
- 1.5.1 MCU Arm Cortex M4F Subsystem (MCU_M4FSS)
- 1.5.2 MCU General Purpose Input/Output Interface (MCU_GPIO)
- 1.5.3 MCU Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (MCU_I2C)
- 1.5.4 MCU Multi-channel Serial Peripheral Interface (MCU_SPI)
- 1.5.5 MCU Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (MCU_UART)
- 1.5.6 MCU Timers
- 1.5.7 MCU Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 1.6 Device WKUP Domain
- 1.7 Device Identification
- 2 Memory Map
-
3 System Interconnect
- 3.1
System Interconnect Overview
- 3.1.1 Domain Partition
- 3.1.2 IO Coherency Support
- 3.1.3 Timeout Gasket
- 3.1.4 Route ID Allocation
- 3.1.5 Quality of Service (QoS)
- 3.1.6 Initiator-Side Security Controls and Firewalls
- 3.1.7 Interconnect Error Reporting Feature
- 3.1.8 Connectivity Table
- 3.1.9 QoS Programming Guide
- 3.1.10 Performance Considerations
- 3.1
System Interconnect Overview
-
4 Module Integration
- 4.1 Memory Controllers
- 4.2 Processors and Accelerators
- 4.3 Interprocessor Communication
- 4.4 Device Configuration
- 4.5 Data Movement Architecture
- 4.6 Audio
- 4.7 General Connectivity
- 4.8 High-speed Serial Interfaces
- 4.9 Memory Interfaces
- 4.10 Industrial and Control Interfaces
- 4.11 Camera Subsystem
- 4.12 Timer Modules
- 4.13 Internal Diagnostic Modules
- 4.14 Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
- 4.15 Display Subsystem (DSS)
- 4.16 Spinlock
-
5 Initialization
- 5.1 Initialization Overview
- 5.2 Boot Process
- 5.3 Boot Mode Pins
- 5.4
Boot Modes
- 5.4.1 OSPI\xSPI\QSPI\SPI Boot
- 5.4.2 I2C Boot
- 5.4.3 SD Card Boot
- 5.4.4 eMMC Boot
- 5.4.5 Ethernet Boot
- 5.4.6 USB Boot
- 5.4.7 UART Boot
- 5.4.8 GPMC NOR Boot
- 5.4.9 GPMC NAND Boot
- 5.4.10 Serial NAND Boot
- 5.4.11 No boot/Development boot
- 5.5 PLL Configuration
- 5.6
Boot Parameter Tables
- 5.6.1 Common Header
- 5.6.2 PLL Setup
- 5.6.3 OSPI/QSPI/SPI Boot Parameter Table
- 5.6.4 UART Boot Parameter Table
- 5.6.5 I2C Boot Parameter Table
- 5.6.6 MMCSD/eMMC Boot Parameter Table
- 5.6.7 Ethernet Boot Parameter Table
- 5.6.8 xSPI Boot Parameter Table
- 5.6.9 USB DFU Boot Parameter Table
- 5.6.10 USB MSC Boot Parameter Table
- 5.6.11 GPMC NOR Boot Parameter Table
- 5.6.12 GPMC NAND Boot Parameter Table
- 5.7 Boot Image Format
- 5.8 Boot Memory Maps
-
6 Device Configuration
- 6.1 Memory Mapped Control Register Modules (CTRL_MMR)
- 6.2
Power
- 6.2.1 Power Management Overview
- 6.2.2 Power Control Modules
- 6.2.3 Power Management Techniques
- 6.2.4
Power Modes
- 6.2.4.1 Active
- 6.2.4.2 Standby
- 6.2.4.3 MCU-Only
- 6.2.4.4 DeepSleep
- 6.2.4.5 Partial I/O
- 6.2.4.6 Power States and Transitions
- 6.2.4.7 Wakeup Sources/Events
- 6.2.4.8 USB Wakeup Scenarios
- 6.2.4.9 Main Oscillator Control During DeepSleep
- 6.2.4.10 Low Power Mode Sequencing with Device Manager
- 6.2.4.11 I/O Power Management and Daisy Chaining
- 6.2.5 Power Supply Modules
- 6.3
Reset
- 6.3.1 Overview
- 6.3.2 Reset Sources
- 6.3.3 Reset Status
- 6.3.4 Reset Controls
- 6.3.5 Reset Details
- 6.4
Clocking
- 6.4.1 Overview
- 6.4.2 Clock Inputs
- 6.4.3 Clock Outputs
- 6.4.4 Device Oscillators
- 6.4.5
PLLs
- 6.4.5.1 MCU Domain PLL Overview
- 6.4.5.2 MAIN Domain PLLs Overview
- 6.4.5.3 PLL Reference Clocks
- 6.4.5.4 Generic PLL Overview
- 6.4.5.5 PLLs Device-Specific Information
- 6.4.5.6 PLL Controller (PLLCTRL)
- 6.4.5.7 PLL, PLLCTRL, and HSDIV Controllers Programming Guide
-
7 Processors and
Accelerators
- 7.1
Arm Cortex-A53 Subsystem (A53SS)
- 7.1.1 A53SS Overview
- 7.1.2
A53SS Functional
Description
- 7.1.2.1 A53SS Block Diagram
- 7.1.2.2 Arm Cortex-A53 Cluster
- 7.1.2.3 A53SS Interfaces and Async Bridges
- 7.1.2.4 A53SS Interrupts
- 7.1.2.5 A53SS Power Management and Clocking
- 7.1.2.6 A53SS Debug
- 7.1.2.7 A53SS Global and Debug Timestamps
- 7.1.2.8 A53SS Watchdog
- 7.1.2.9 A53SS Functional Safety - ECC Error Injection Support
- 7.1.2.10 A53SS Boot
- 7.1.2.11 A53SS Interprocessor Communication
- 7.2
Device
Manager Cortex R5F Subsystem (WKUP_R5FSS)
- 7.2.1 WKUP_R5FSS Overview
- 7.2.2
WKUP_R5FSS Functional Description
- 7.2.2.1 WKUP_R5FSS Block Diagram
- 7.2.2.2 WKUP_R5FSS Cortex-R5F Core
- 7.2.2.3 WKUP_R5FSS Interfaces
- 7.2.2.4 WKUP_R5FSS Power, Clocking and Reset
- 7.2.2.5 WKUP_R5FSS Vectored Interrupt Manager (VIM)
- 7.2.2.6 WKUP_R5FSS Region Address Translation (RAT)
- 7.2.2.7 WKUP_R5FSS ECC Support
- 7.2.2.8 WKUP_R5FSS Memory View
- 7.2.2.9 WKUP_R5FSS Interrupts
- 7.2.2.10 WKUP_R5FSS Debug and Trace
- 7.2.2.11 WKUP_R5FSS Boot Options
- 7.2.2.12 WKUP_R5FSS Core Memory ECC Events
- 7.2.3 Vectored Interrupt Manager (VIM)
- 7.3
Cortex-M4F Subsystem
(MCU_M4FSS)
- 7.3.1 MCU_M4FSS Overview
- 7.3.2
MCU_M4FSS Functional Description
- 7.3.2.1 MCU_M4FSS Block Diagram
- 7.3.2.2 MCU_M4FSS Processor
- 7.3.2.3 MCU_M4FSS Internal RAMs
- 7.3.2.4 MCU_M4FSS Interfaces
- 7.3.2.5 MCU_M4FSS Power, Clocking and Reset
- 7.3.2.6 MCU_M4FSS Memory View
- 7.3.2.7 MCU_M4FSS RAT
- 7.3.2.8 MCU_M4FSS ECC Support
- 7.3.2.9 MCU_M4FSS Interrupts
- 7.3.2.10 MCU_M4FSS Debug and Trace
- 7.3.2.11 MCU_M4FSS Time Sync
- 7.3.2.12 MCU_M4FSS SysTick
- 7.3.2.13 MCU_M4FSS Initialization
- 7.4
Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS)
- 7.4.1 PRUSS Overview
- 7.4.2 PRUSS Environment
- 7.4.3 PRUSS Top Level Resources Functional Description
- 7.4.4
PRUSS PRU Cores
- 7.4.4.1 PRU Cores Overview
- 7.4.4.2
PRU Cores Functional Description
- 7.4.4.2.1 PRU Constant Table
- 7.4.4.2.2
PRU Module Interface
- 7.4.4.2.2.1 Real-Time Status Interface Mapping (R31): Interrupt Events Input
- 7.4.4.2.2.2 Event Interface Mapping (R31): PRU System Events
- 7.4.4.2.2.3
General-Purpose Inputs (R31): Enhanced PRU GP Module
- 7.4.4.2.2.3.1 PRU EGPIs Direct Input
- 7.4.4.2.2.3.2 PRU EGPIs 16-Bit Parallel Capture
- 7.4.4.2.2.3.3 PRU EGPIs 28-Bit Shift In
- 7.4.4.2.2.3.4 General-Purpose Outputs (R30): Enhanced PRU GP Module
- 7.4.4.2.2.3.5 Sigma Delta (SD) Decimation Filtering
- 7.4.4.2.2.3.6 Three Channel Peripheral Interface
- 7.4.4.3 PRUSS RAM Index Allocation
- 7.4.5
PRUSS Broadside Accelerators
- 7.4.5.1 PRUSS Broadside Accelerators Overview
- 7.4.5.2 PRUSS Data Processing Accelerators Functional
- 7.4.5.3 PRUSS Data Movement Accelerators Functional
- 7.4.6
PRUSS Local INTC
- 7.4.6.1
PRUSS Interrupt Controller Functional Description
- 7.4.6.1.1 PRUSS Interrupt Controller Events
- 7.4.6.1.2 PRUSS Interrupt Controller System Events Flow
- 7.4.6.1.3 PRUSS Interrupt Disabling
- 7.4.6.2 PRUSS Interrupt Controller Basic Programming Model
- 7.4.6.3 PRUSS Interrupt Requests Mapping
- 7.4.6.1
PRUSS Interrupt Controller Functional Description
- 7.4.7
PRUSS
UART Module
- 7.4.7.1 PRUSS UART Overview
- 7.4.7.2 PRUSS UART Environment
- 7.4.7.3
PRUSS UART Functional Description
- 7.4.7.3.1 PRUSS UART Functional Block Diagram
- 7.4.7.3.2 PRUSS UART Reset Considerations
- 7.4.7.3.3 PRUSS UART Power Management
- 7.4.7.3.4 PRUSS UART Interrupt Support
- 7.4.7.3.5 808
- 7.4.7.3.6 PRUSS UART DMA Event Support
- 7.4.7.3.7 PRUSS UART Operations
- 7.4.7.3.8 PRUSS UART Emulation Considerations
- 7.4.7.3.9 PRUSS UART Exception Processing
- 7.4.8 PRUSS ECAP Module
- 7.4.9
PRUSS IEP
- 7.4.9.1 PRUSS IEP Overview
- 7.4.9.2 PRUSS IEP Functional Description
- 7.1
Arm Cortex-A53 Subsystem (A53SS)
-
8 Interprocessor Communication (IPC)
- 8.1
Inter-processor Communication Scheme
(IPC)
- 8.1.1
Mailbox
- 8.1.1.1 Mailbox Overview
- 8.1.1.2 Mailbox Functional Description
- 8.1.1.3 Mailbox Programming Guide
- 8.1.2 Spinlock
- 8.1.3 Secure Proxy (SEC_PROXY)
- 8.1.1
Mailbox
- 8.1
Inter-processor Communication Scheme
(IPC)
-
9 Memory Controllers
- 9.1
DDR Subsystem (DDRSS)
- 9.1.1 DDRSS Overview
- 9.1.2 DDRSS Environment
- 9.1.3
DDRSS Functional Description
- 9.1.3.1 Class of Service (CoS)
- 9.1.3.2 AXI Write Data All-Strobes
- 9.1.3.3 Inline ECC for SDRAM Data
- 9.1.3.4 Address Alias Prevention
- 9.1.3.5 AXI Bus Timeout
- 9.1.3.6 DDRSS Interrupts
- 9.1.3.7 DDRSS Memory Regions
- 9.1.3.8 DDRSS Dynamic Frequency Change Interface
- 9.1.3.9 DDR Controller Functional Description
- 9.2 Region-based Address Translation (RAT) Module
- 9.1
DDR Subsystem (DDRSS)
-
10Interrupts
- 10.1
Interrupt Architecture
- 10.1.1 ESM Connectivity
- 10.1.2 Events
- 10.1.3 Interrupt Router (INTROUTER)
- 10.1.4 Time Synchronization Support
- 10.1.5 GPIO Interrupt Handling
- 10.1.6 Utilizing Miscellaneous Signals as Interrupt
- 10.1.7 Interrupt Connections for MCUSS NVIC
- 10.1.8 Interrupt Connections for GICSS
- 10.1.9 Interrupt Connections for R5FSS
- 10.1.10 Interrupt Connection for HSM
- 10.1.11 Interrupt Connection for ICSSM
- 10.1.12 Interrupt Connections Summary
- 10.1
Interrupt Architecture
-
11Data Movement Architecture
- 11.1
Data Movement Architecture Overview
- 11.1.1
Overview
- 11.1.1.1 Ring Accelerator (RINGACC)
- 11.1.1.2 Secure Proxy (SEC_PROXY)
- 11.1.1.3 Interrupt Aggregator (INTAGGR)
- 11.1.1.4
Packet DMA (PKTDMA)
- 11.1.1.4.1
PKTDMA Submodule Descriptions
- 11.1.1.4.1.1 Bus Interface Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.2 Config CR
- 11.1.1.4.1.3 Configuration Registers
- 11.1.1.4.1.4 Tx Packet DMA Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.5 Tx Packet Coherency Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.6 Tx Per Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.4.1.7 Rx Per Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.4.1.8 Rx Packet DMA Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.9 Rx Packet Coherency Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.10 Event Handler
- 11.1.1.4.2 Channel Classes
- 11.1.1.4.1
PKTDMA Submodule Descriptions
- 11.1.1.5
Block Copy DMA (BCDMA)
- 11.1.1.5.1
BCDMA Submodule Descriptions
- 11.1.1.5.1.1 Bus Interface Unit
- 11.1.1.5.1.2 Config CR
- 11.1.1.5.1.3 Configuration Registers
- 11.1.1.5.1.4 Read Unit(s)
- 11.1.1.5.1.5 TR Coherency Unit
- 11.1.1.5.1.6 Per-Copy-Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.5.1.7 Tx Per-Split-Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.5.1.8 Rx Per-Split-Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.5.1.9 Write Unit(s)
- 11.1.1.5.1.10 Event Coherency Unit
- 11.1.1.5.1.11 Event Handler
- 11.1.1.5.2 Channel Classes
- 11.1.1.5.1
BCDMA Submodule Descriptions
- 11.1.2 Definition of Terms
- 11.1.3
DMSS Hardware/Software Interface
- 11.1.3.1 Data Buffers
- 11.1.3.2 Descriptors
- 11.1.3.3
Transfer Request Record
- 11.1.3.3.1 Overview
- 11.1.3.3.2 Addressing Algorithm
- 11.1.3.3.3 Transfer Request Formats
- 11.1.3.3.4 Flags Field Definition
- 11.1.3.3.5
TR Address and Size Attributes
- 11.1.3.3.5.1 ICNT0
- 11.1.3.3.5.2 ICNT1
- 11.1.3.3.5.3 ADDR
- 11.1.3.3.5.4 DIM1
- 11.1.3.3.5.5 ICNT2
- 11.1.3.3.5.6 ICNT3
- 11.1.3.3.5.7 DIM2
- 11.1.3.3.5.8 DIM3
- 11.1.3.3.5.9 DDIM1
- 11.1.3.3.5.10 DADDR
- 11.1.3.3.5.11 DDIM2
- 11.1.3.3.5.12 DDIM3
- 11.1.3.3.5.13 DICNT0
- 11.1.3.3.5.14 DICNT1
- 11.1.3.3.5.15 DICNT2
- 11.1.3.3.5.16 DICNT3
- 11.1.3.4 Transfer Response Record
- 11.1.3.5 Channels
- 11.1.3.6 Flows
- 11.1.3.7 Queues
- 11.1.4
Operational Description
- 11.1.4.1 Resource Allocation
- 11.1.4.2 PKTDMA/BCDMA - Ring Operation
- 11.1.4.3 PKTDMA/BCDMA - Output Event Generation
- 11.1.4.4 PKTDMA - Transmit Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.5 PKTDMA - Transmit Channel Pause
- 11.1.4.6 PKTDMA - Transmit Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.7 PKTDMA - Transmit Operation
- 11.1.4.8 PKTDMA - Receive Free Descriptor / Buffer Queue Setup
- 11.1.4.9 PKTDMA - Receive Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.10 PKTDMA - Receive Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.11 PKTDMA - Receive Channel Pause
- 11.1.4.12 PKTDMA - Receive Operation
- 11.1.4.13 BCDMA - Block Copy Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.14 BCDMA - Block Copy Channel Pause
- 11.1.4.15 BCDMA - Block Copy Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.16 BCDMA - Block Copy Operation (TR Packet)
- 11.1.4.17 BCDMA - Block Copy Error/Exception Handling
- 11.1.4.18 BCDMA - Split Transmit Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.19 BCDMA - Split Transmit Operation Pause
- 11.1.4.20 BCDMA - Split Transmit Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.21 BCDMA - Split Transmit Operation (TR Packet)
- 11.1.4.22 BCDMA - Split Transmit Error / Exception Handling
- 11.1.4.23 BCDMA - Split Receive Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.24 BCDMA - Split Receive Channel Pause
- 11.1.4.25 BCDMA - Split Receive Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.26 BCDMA - Split Receive Operation (TR Packet)
- 11.1.4.27 BCDMA - Split Receive Error / Exception Handling
- 11.1.1
Overview
- 11.2
Data Movement
Subsystem (DMSS)
- 11.2.1 Data Movement Subsystem (DMSS)
- 11.2.2
Ring Accelerator (RINGACC)
- 11.2.2.1 RINGACC Overview
- 11.2.2.2
RINGACC Functional Description
- 11.2.2.2.1
Block Diagram
- 11.2.2.2.1.1 Configuration Registers
- 11.2.2.2.1.2 Source Command FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.3 Source Write Data FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.4 Source Read Data FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.5 Source Write Status FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.6 Main State Machine
- 11.2.2.2.1.7 Destination Command FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.8 Destination Write Data FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.9 Destination Read Data FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.10 Destination Write Status FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.2
RINGACC Functional Operation
- 11.2.2.2.2.1 Queue Modes
- 11.2.2.2.2.2 VBUSM Target Ring Operations
- 11.2.2.2.2.3 VBUSM Initiator Interface Command ID Selection
- 11.2.2.2.2.4 Ring Push Operation (VBUSM Write to Source Interface)
- 11.2.2.2.2.5 Ring Pop Operation (VBUSM Read from Source Interface)
- 11.2.2.2.2.6 Host Doorbell Access
- 11.2.2.2.2.7 Queue Push Operation (VBUSM Write to Source Interface)
- 11.2.2.2.2.8 Queue Pop Operation (VBUSM Read from Source Interface)
- 11.2.2.2.2.9 Mismatched Element Size Handling
- 11.2.2.2.3 Events
- 11.2.2.2.4 Bus Error Handling
- 11.2.2.2.5 Monitors
- 11.2.2.2.1
Block Diagram
- 11.2.3
Secure
Proxy (SEC_PROXY)
- 11.2.3.1 Secure Proxy Overview
- 11.2.3.2
Secure Proxy Functional Description
- 11.2.3.2.1 Targets
- 11.2.3.2.2 Buffers
- 11.2.3.2.3 Proxy Credits
- 11.2.3.2.4 Proxy Private Word
- 11.2.3.2.5 Completion Byte
- 11.2.3.2.6 Proxy Thread Sizes
- 11.2.3.2.7 Proxy Thread Interleaving
- 11.2.3.2.8 Proxy States
- 11.2.3.2.9 Proxy Host Access
- 11.2.3.2.10 Proxy Host Writes
- 11.2.3.2.11 Proxy Host Reads
- 11.2.3.2.12 Buffer Accesses
- 11.2.3.2.13 Target Access
- 11.2.3.2.14 Error State
- 11.2.3.2.15 Permission Inheritance
- 11.2.3.2.16 Resource Association
- 11.2.3.2.17 Direction
- 11.2.3.2.18 Threshold Events
- 11.2.3.2.19 Error Events
- 11.2.3.2.20 Bus Error and Credits
- 11.2.3.2.21 Debug
- 11.2.4 Interrupt Aggregator (INTAGGR)
- 11.2.5 Packet Streaming Interface Link (PSI-L)
- 11.3
Peripheral DMA (PDMA)
- 11.3.1
PDMA Controller
- 11.3.1.1 PDMA Overview
- 1202
- 11.3.1.2
Functional Description - SPI
- 11.3.1.2.1 Compliance to Standards
- 11.3.1.2.2
Functional Operation
- 11.3.1.2.2.1 Submodule Descriptions
- 11.3.1.2.2.2 General Functionality (Applicable to All Functions/Modes)
- 11.3.1.2.2.3 Events and Flow Control
- 11.3.1.2.2.4
Transmit Operation
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.1 Destination (Tx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.2 Destination (Tx) Channel Out of Band Signals
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.3 Destination Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.4 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.5 Transmit PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.6 Tx Pause
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.7 Tx Teardown
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.8 Tx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.9 Tx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.2.2.5
Receive Operation
- 11.3.1.2.2.5.1 Source (Rx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.2.2.5.2 Source Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.2.2.5.3 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.2.2.5.4 Receive PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.2.2.5.5 Rx Pause
- 11.3.1.2.2.5.6 Rx Teardown
- 11.3.1.2.2.5.7 Rx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.2.2.5.8 Rx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.3
Functional Description - UART
- 11.3.1.3.1 Compliance to Standards
- 11.3.1.3.2
Functional Operation
- 11.3.1.3.2.1 Submodule Descriptions
- 11.3.1.3.2.2 General Functionality (Applicable to All Functions/Modes)
- 11.3.1.3.2.3 Events and Flow Control
- 11.3.1.3.2.4
Transmit Operation
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.1 Destination (Tx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.2 Destination (Tx) Channel Out of Band Signals
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.3 Destination Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.4 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.5 Transmit PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.6 Tx Pause
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.7 Tx Teardown
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.8 Tx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.9 Tx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.3.2.5
Receive Operation
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.1 Source (Rx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.2 Source Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.3 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.4 Receive PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.5 Rx Pause
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.6 Rx Teardown
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.7 Rx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.8 Rx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.4
Functional Description - McASP
- 11.3.1.4.1 Compliance to Standards
- 11.3.1.4.2
Functional Operation
- 11.3.1.4.2.1 Submodule Descriptions
- 11.3.1.4.2.2 General Functionality (Applicable to All Functions/Modes)
- 11.3.1.4.2.3 Events and Flow Control
- 11.3.1.4.2.4
Transmit Operation
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.1 Destination (Tx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.2 Destination (Tx) Channel Out of Band Signals
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.3 Destination Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.4 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.5 Transmit PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.6 Tx Pause
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.7 Tx Teardown
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.8 Tx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.9 Tx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.4.2.5
Receive Operation
- 11.3.1.4.2.5.1 Source (Rx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.4.2.5.2 Source Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.4.2.5.3 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.4.2.5.4 Receive PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.4.2.5.5 Rx Pause
- 11.3.1.4.2.5.6 Rx Teardown
- 11.3.1.4.2.5.7 Rx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.4.2.5.8 Rx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.5 PDMA Registers
- 11.3.1
PDMA Controller
- 11.1
Data Movement Architecture Overview
-
12Peripherals
- 12.1
Audio Peripherals
- 12.1.1
Multichannel Audio Serial Port (MCASP)
- 12.1.1.1 MCASP Overview
- 12.1.1.2 MCASP Environment
- 12.1.1.3 Integration
- 12.1.1.4
MCASP Functional Description
- 12.1.1.4.1 MCASP Block Diagram
- 12.1.1.4.2 MCASP Clock and Frame-Sync Configurations
- 12.1.1.4.3 MCASP Serializers
- 12.1.1.4.4 MCASP Format Units
- 12.1.1.4.5 MCASP State-Machines
- 12.1.1.4.6 MCASP TDM Sequencers
- 12.1.1.4.7 MCASP Software Reset
- 12.1.1.4.8 MCASP Power Management
- 12.1.1.4.9 MCASP Transfer Modes
- 12.1.1.4.10 MCASP Data Transmission and Reception
- 12.1.1.4.11 MCASP Audio FIFO (AFIFO)
- 12.1.1.4.12 MCASP Events and Interrupt Requests
- 12.1.1.4.13 MCASP DMA Requests
- 12.1.1.4.14 MCASP Loopback Modes
- 12.1.1.4.15 MCASP Error Reporting
- 12.1.1.5
MCASP Programming Guide
- 12.1.1.5.1
MCASP Global Initialization
- 12.1.1.5.1.1 Surrounding Modules Global Initialization
- 12.1.1.5.1.2
MCASP Global Initialization
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.1
Main Sequence – MCASP Global Initialization for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.1.1 Subsequence – Transmit Format Unit Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.1.2 Subsequence – Transmit Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.1.3 Subsequence – Transmit Clock Generator Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.1.4 Subsequence - MCASP Pins Functional Configuration
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.1.5 Subsequence – DIT-specific Subframe Fields Configuration
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.2
Main Sequence – MCASP Global Initialization for TDM-Reception
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.2.1 Subsequence – Receive Format Unit Configuration in TDM Mode
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.2.2 Subsequence – Receive Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration in TDM Mode
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.2.3 Subsequence – Receive Clock Generator Configuration
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.2.4 Subsequence—MCASP Receiver Pins Functional Configuration
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.3
Main Sequence – MCASP Global Initialization for TDM -Transmission
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.3.1 Subsequence – Transmit Format Unit Configuration in TDM Mode
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.3.2 Subsequence – Transmit Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration in TDM Mode
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.3.3 Subsequence – Transmit Clock Generator Configuration for TDM Cases
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.3.4 Subsequence—MCASP Transmit Pins Functional Configuration
- 12.1.1.5.1.2.1
Main Sequence – MCASP Global Initialization for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.1.5.2 MCASP Operational Modes Configuration
- 12.1.1.5.1
MCASP Global Initialization
- 12.1.1
Multichannel Audio Serial Port (MCASP)
- 12.2
General Connectivity Peripherals
- 12.2.1
General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 12.2.1.1 GPIO Overview
- 12.2.1.2 GPIO Environment
- 12.2.1.3 Integration
- 12.2.1.4 GPIO Functional Description
- 12.2.1.5 GPIO Programming Guide
- 12.2.2
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface
- 12.2.2.1 I2C Overview
- 12.2.2.2
I2C Environment
- 12.2.2.2.1 I2C Typical Application
- 12.2.2.2.2
I2C Typical Connection Protocol and Data Format
- 12.2.2.2.2.1 I2C Serial Data Format
- 12.2.2.2.2.2 I2C Data Validity
- 12.2.2.2.2.3 I2C Start and Stop Conditions
- 12.2.2.2.2.4 I2C Addressing
- 12.2.2.2.2.5 I2C Controller Transmitter
- 12.2.2.2.2.6 I2C Controller Receiver
- 12.2.2.2.2.7 I2C Target Transmitter
- 12.2.2.2.2.8 I2C Target Receiver
- 12.2.2.2.2.9 I2C Bus Arbitration
- 12.2.2.2.2.10 I2C Clock Generation and Synchronization
- 12.2.2.3 I2C Functional Description
- 12.2.2.4 I2C Programming Guide
- 12.2.3
Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (MCSPI)
- 12.2.3.1 MCSPI Overview
- 12.2.3.2 MCSPI Environment
- 12.2.3.3 Integration
- 12.2.3.4
MCSPI Functional Description
- 12.2.3.4.1 MCSPI Block Diagram
- 12.2.3.4.2 MCSPI Reset
- 12.2.3.4.3
MCSPI Controller Mode
- 12.2.3.4.3.1 Controller Mode Features
- 12.2.3.4.3.2 Controller Transmit-and-Receive Mode (Full Duplex)
- 12.2.3.4.3.3 Controller Transmit-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 12.2.3.4.3.4 Controller Receive-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 12.2.3.4.3.5 Single-Channel Controller Mode
- 12.2.3.4.3.6 Start-Bit Mode
- 12.2.3.4.3.7 Chip-Select Timing Control
- 12.2.3.4.3.8 Programmable MCSPI Clock (SPICLK)
- 12.2.3.4.4 MCSPI Peripheral Mode
- 12.2.3.4.5 MCSPI 3-Pin or 4-Pin Mode
- 12.2.3.4.6 MCSPI FIFO Buffer Management
- 12.2.3.4.7 MCSPI Interrupts
- 12.2.3.4.8 MCSPI DMA Requests
- 12.2.3.4.9 MCSPI Power Saving Management
- 12.2.3.5
MCSPI Programming Guide
- 12.2.3.5.1 MCSPI Global Initialization
- 12.2.3.5.2
MCSPI Operational Mode Configuration
- 12.2.3.5.2.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.1 Common Transfer Sequence
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.2 End of Transfer Sequences
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.3 Transmit-and-Receive (Controller and Peripheral)
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.4 Transmit-Only (Controller and Peripheral)
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.5 Controller Normal Receive-Only
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.6 Controller Turbo Receive-Only
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.7 Peripheral Receive-Only
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8
Transfer Procedures With FIFO
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.1 Common Transfer Sequence in FIFO Mode
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.2 End of Transfer Sequences in FIFO Mode
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.3 Transmit-and-Receive With Word Count
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.4 Transmit-and-Receive Without Word Count
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.5 Transmit-Only
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.6 Receive-Only With Word Count
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.7 Receive-Only Without Word Count
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.9 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 12.2.3.5.2.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 12.2.3.5.3 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 12.2.4
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 12.2.4.1 UART Overview
- 12.2.4.2
UART Environment
- 12.2.4.2.1 UART Functional Interfaces
- 12.2.4.2.2 RS-485 Functional Interfaces
- 12.2.4.2.3 IrDA Functional Interfaces
- 12.2.4.2.4 CIR Functional Interfaces
- 12.2.4.3 Integration
- 12.2.4.4
UART Functional Description
- 12.2.4.4.1 UART Block Diagram
- 12.2.4.4.2 UART Clock Configuration
- 12.2.4.4.3 UART Software Reset
- 12.2.4.4.4 UART Power Management
- 12.2.4.4.5 UART Interrupt Requests
- 12.2.4.4.6 UART FIFO Management
- 12.2.4.4.7 UART Mode Selection
- 12.2.4.4.8
UART Protocol Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 12.2.4.4.8.1.1 UART Clock Generation: Baud Rate Generation
- 12.2.4.4.8.1.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 12.2.4.4.8.1.3 UART Data Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.2 RS-485 Mode
- 12.2.4.4.8.3
IrDA Mode
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.1 IrDA Clock Generation: Baud Generator
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3
IrDA Data Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.1 IR RX Polarity Control
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.2 IrDA Reception Control
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.3 IR Address Checking
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.4 Frame Closing
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.5 Store and Controlled Transmission
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.6 Error Detection
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.7 Underrun During Transmission
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.8 Overrun During Receive
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.9 Status FIFO
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.10 Multi-drop Parity Mode with Address Match
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.11 Time-guard
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.4 SIR Mode Data Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.5 MIR and FIR Mode Data Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.4 CIR Mode
- 12.2.4.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 12.2.4.5
UART Programming Guide
- 12.2.4.5.1 UART Global Initialization
- 12.2.4.5.2 UART Mode selection
- 12.2.4.5.3 UART Submode selection
- 12.2.4.5.4 UART Load FIFO trigger and DMA mode settings
- 12.2.4.5.5 UART Protocol, Baud rate and interrupt settings
- 12.2.4.5.6 UART Hardware and Software Flow Control Configuration
- 12.2.4.5.7 IrDA Programming Model
- 12.2.1
General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 12.3
High-speed Serial Interfaces
- 12.3.1
Gigabit Ethernet Switch
(CPSW3G)
- 12.3.1.1 CPSW0 Overview
- 12.3.1.2 CPSW0 Environment
- 12.3.1.3 Integration
- 12.3.1.4
CPSW0 Functional Description
- 12.3.1.4.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 12.3.1.4.2 CPSW Ports
- 12.3.1.4.3 Clocking
- 12.3.1.4.4 Software IDLE
- 12.3.1.4.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 12.3.1.4.6
CPSW_3G
- 12.3.1.4.6.1
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.1 Error Handling
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.2 Bypass Operations
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.3 OUI Deny or Accept
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.4 Statistics Counting
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.5 Automotive Security Features
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.6 CPSW Switching Solutions
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.7 VLAN Routing and OAM Operations
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.8 Supervisory packets
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9
Address Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.1 Multicast Address Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.2 OUI Unicast Address Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.3 Unicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40 == 0)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.4 Multicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40==1)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.5 VLAN/Unicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40 == 0)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.6 VLAN/Multicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40==1)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.7 Inner VLAN Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.8 Outer VLAN Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.9 EtherType Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.10 IPv4 Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.11 IPv6 Table Entry High
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.12 IPv6 Table Entry Low
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.10 Multicast Address
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.11 Aging and Auto Aging
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.12 ALE Policing and Classification
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.13 Mirroring
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.14 Trunking
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.15 DSCP
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.16 Packet Forwarding Processes
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.17 VLAN Aware Mode
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.18 VLAN Unaware Mode
- 12.3.1.4.6.2 Packet Priority Handling
- 12.3.1.4.6.3 CPPI Port Ingress
- 12.3.1.4.6.4 Packet CRC Handling
- 12.3.1.4.6.5 FIFO Memory Control
- 12.3.1.4.6.6 FIFO Transmit Queue Control
- 12.3.1.4.6.7 Intersperced Express Traffic (IET – P802.3br/D2.0)
- 12.3.1.4.6.8
Enhanced Scheduled Traffic (EST – P802.1Qbv/D2.2)
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.1 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Overview
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.2 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Fetch RAM
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.3 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Time Interval
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.4 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Fetch Values
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.5 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Packet Fill
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.6 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Time Stamp
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.7 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Packets Per Priority
- 12.3.1.4.6.9 Audio Video Bridging
- 12.3.1.4.6.10
Ethernet MAC Sliver
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1
Ethernet MAC Sliver
Overview
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.1 CRC Insertion
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.2 MTXER
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.3 Adaptive Performance Optimization (APO)
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.4 Inter-Packet-Gap Enforcement
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.5 Back Off
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.6 Programmable Transmit Inter-Packet Gap
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.7 Speed, Duplex and Pause Frame Support Negotiation
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.2 RMII Interface
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.3 RGMII Interface
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.4 Frame Classification
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.5 Receive FIFO Architecture
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1
Ethernet MAC Sliver
Overview
- 12.3.1.4.6.11 Embedded Memories
- 12.3.1.4.6.12 Memory Error Detection and Correction
- 12.3.1.4.6.13 Ethernet Port Flow Control
- 12.3.1.4.6.14 Energy Efficient Ethernet Support (802.3az)
- 12.3.1.4.6.15 Ethernet Switch Latency
- 12.3.1.4.6.16 MAC Emulation Control
- 12.3.1.4.6.17 MAC Command IDLE
- 12.3.1.4.6.18
CPSW Network Statistics
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1
Rx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.1 Good Rx Frames (Offset = 3A000h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.2 Broadcast Rx Frames (Offset = 3A004h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.3 Multicast Rx Frames (Offset = 3A008h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.4 Pause Rx Frames (Offset = 3A00Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.5 Rx CRC Errors (Offset = 3A010h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.6 Rx Align/Code Errors (Offset = 3A014h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.7 Oversize Rx Frames (Offset = 3A018h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.8 Rx Jabbers (Offset = 3A01Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.9 Undersize (Short) Rx Frames (Offset = 3A020h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.10 Rx Fragments (Offset = 3A024h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.11 RX IPG Error (Offset = 3A05Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.12 ALE Drop (Offset = 3A028h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.13 ALE Overrun Drop (Offset = 3A02Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.14 Rx Octets (Offset = 3A030h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.15 Rx Bottom of FIFO Drop (Offset = 3A084h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.16 Portmask Drop (Offset = 3A088h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.17 Rx Top of FIFO Drop (Offset = 3A08Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.18 ALE Rate Limit Drop (Offset = 3A090h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.19
ALE VLAN Ingress Check Drop (Offset = 3A094h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.1 ALE DA=SA Drop (Offset = 3A098h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.2 Block Address Drop (Offset = 3A09Ch)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.3 ALE Secure Drop (Offset = 3A0A0h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.4 ALE Authentication Drop (Offset = 3A0A4h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.5 ALE Unknown Unicast (Offset = 3A0A8h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.6 ALE Unknown Unicast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0ACh)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.7 ALE Unknown Multicast (Offset = 3A0B0h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.8 ALE Unknown Multicast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0B4h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.9 ALE Unknown Broadcast (Offset = 3A0B8h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.10 ALE Unknown Broadcast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0BCh)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.11 ALE Policer/Classifier Match (Offset = 3A0C0h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.2 ALE Policer Match Red (Offset = 3A0C4h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.3 ALE Policer Match Yellow (Offset = 3A0C8h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.4 IET Receive Assembly Error (Offset = 3A140h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.5 IET Receive Assembly OK (Offset = 3A144h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.6 IET Receive SMD Error (Offset = 3A148h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.7 IET Receive Merge Fragment Count (Offset = 3A14Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.8 Rx Cut Thru with No Delay
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.9 Rx Cut Thru with Delay
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.10 Rx Cut Thru Store-and-Forward
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11
Tx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.1 Good Tx Frames (Offset = 3A034h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.2 Broadcast Tx Frames (Offset = 3A038h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.3 Multicast Tx Frames (Offset = 3A03Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.4 Pause Tx Frames (Offset = 3A040h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.5 Deferred Tx Frames (Offset = 3A044h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.6 Collisions (Offset = 3A048h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.7 Single Collision Tx Frames (Offset = 3A04Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.8 Multiple Collision Tx Frames (Offset = 3A050h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.9 Excessive Collisions (Offset = 3A054h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.10 Late Collisions (Offset = 3A058h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.11 Carrier Sense Errors (Offset = 3A060h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.12 Tx Octets (Offset = 3A064h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.13 Transmit Priority 0-7 (Offset = 3A180h to 3A1A8h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.14 Transmit Priority 0-7 Drop (Offset = 3A1C0h to 3A1E8)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.15 Tx Memory Protect Errors (Offset = 3A17Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.16 IET Transmit Merge Hold Count (Offset = 3A150h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.17 IET Transmit Merge Fragment Count (Offset = 3A14Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.18 Tx CRC Errors
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.19 Tx Cut Thru
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.20 Tx Cut Thru Store-and-Forward
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12
Rx- and Tx (Shared) Statistics Descriptions
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.1 Rx + Tx 64 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A068h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.2 Rx + Tx 65–127 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A06Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.3 Rx + Tx 128–255 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A070h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.4 Rx + Tx 256–511 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A074h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.5 Rx + Tx 512–1023 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A078h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.6 Rx + Tx 1024_Up Octet Frames (Offset = 3A07Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.7 Net Octets (Offset = 3A080h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.13 2104
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1
Rx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 12.3.1.4.6.1
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 12.3.1.4.7
Common Platform Time Sync (CPTS)
- 12.3.1.4.7.1 CPSW0 CPTS Integration
- 12.3.1.4.7.2 CPTS Architecture
- 12.3.1.4.7.3 CPTS Initialization
- 12.3.1.4.7.4 32-bit Time Stamp Value
- 12.3.1.4.7.5 64-bit Time Stamp Value
- 12.3.1.4.7.6 64-Bit Timestamp Nudge
- 12.3.1.4.7.7 64-bit Timestamp PPM
- 12.3.1.4.7.8 Event FIFO
- 12.3.1.4.7.9 Timestamp Compare Output
- 12.3.1.4.7.10 Timestamp Sync Output
- 12.3.1.4.7.11 Timestamp GENFn Output
- 12.3.1.4.7.12 Timestamp ESTFn
- 12.3.1.4.7.13 Time Sync Events
- 12.3.1.4.7.14 Timestamp Compare Event
- 12.3.1.4.7.15 Host Transmit Event
- 12.3.1.4.7.16 CPTS Interrupt Handling
- 12.3.1.4.8
CPPI Streaming Packet Interface
- 12.3.1.4.8.1 Port 0 CPPI Transmit Packet Streaming Interface (CPSW_3G Egress)
- 12.3.1.4.8.2 Port 0 CPPI Receive Packet Streaming Interface (CPSW_3G Ingress)
- 12.3.1.4.8.3 Cut-Thru
- 12.3.1.4.8.4 Port Speed
- 12.3.1.4.8.5 CPPI Checksum Offload
- 12.3.1.4.8.6 CPPI Receive Checksum Offload
- 12.3.1.4.8.7 Egress Packet Operations
- 12.3.1.4.9 MII Management Interface (MDIO)
- 12.3.1.5 CPSW0 Programming Guide
- 12.3.2 Universal Serial Bus Subsystem (USBSS)
- 12.3.1
Gigabit Ethernet Switch
(CPSW3G)
- 12.4
Memory Interfaces
- 12.4.1 Flash Subsystem (FSS)
- 12.4.2
Octal Serial Peripheral Interface (OSPI)
- 12.4.2.1 OSPI Overview
- 12.4.2.2 OSPI Environment
- 12.4.2.3 Integration
- 12.4.2.4
OSPI Functional Description
- 12.4.2.4.1 OSPI Block Diagram
- 12.4.2.4.2 OSPI Modes
- 12.4.2.4.3 OSPI Power Management
- 12.4.2.4.4 Auto HW Polling
- 12.4.2.4.5 Flash Reset
- 12.4.2.4.6 OSPI Memory Regions
- 12.4.2.4.7 OSPI Interrupt Requests
- 12.4.2.4.8 OSPI Data Interface
- 12.4.2.4.9 OSPI Direct Access Controller (DAC)
- 12.4.2.4.10 OSPI Indirect Access Controller (INDAC)
- 12.4.2.4.11 OSPI Software-Triggered Instruction Generator (STIG)
- 12.4.2.4.12 OSPI Arbitration Between Direct / Indirect Access Controller and STIG
- 12.4.2.4.13 OSPI Command Translation
- 12.4.2.4.14 Selecting the Flash Instruction Type
- 12.4.2.4.15 OSPI Data Interface
- 12.4.2.4.16 OSPI PHY Module
- 12.4.2.5
OSPI Programming Guide
- 12.4.2.5.1 Configuring the OSPI Controller for Use After Reset
- 12.4.2.5.2 Configuring the OSPI Controller for Optimal Use
- 12.4.2.5.3 Using the Flash Command Control Register (STIG Operation)
- 12.4.2.5.4 Using SPI Legacy Mode
- 12.4.2.5.5 Entering XIP Mode from POR
- 12.4.2.5.6 Entering XIP Mode Otherwise
- 12.4.2.5.7 Exiting XIP Mode
- 12.4.3
General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 12.4.3.1 GPMC Overview
- 12.4.3.2 GPMC Environment
- 12.4.3.3 Integration
- 12.4.3.4
GPMC Functional Description
- 12.4.3.4.1 GPMC Block Diagram
- 12.4.3.4.2 GPMC Clock Configuration
- 12.4.3.4.3 GPMC Power Management
- 12.4.3.4.4 GPMC Interrupt Requests
- 12.4.3.4.5 GPMC Interconnect Port Interface
- 12.4.3.4.6 GPMC Address and Data Bus
- 12.4.3.4.7
GPMC Address Decoder and Chip-Select Configuration
- 12.4.3.4.7.1 Chip-Select Base Address and Region Size
- 12.4.3.4.7.2 Access Protocol
- 12.4.3.4.7.3
External Signals
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.1
WAIT Pin Monitoring Control
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.1.1 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Read Access
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.1.2 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Write Access
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.1.3 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Read Access
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.1.4 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Write Access
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.1.5 Wait With NAND Device
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.1.6 Idle Cycle Control Between Successive Accesses
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.1.7 Slow Device Support (TIMEPARAGRANULARITY Parameter)
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.2 DIR Pin
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.3 Reset
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.4 Write Protect Signal (nWP)
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.5 Byte Enable (nBE1/nBE0)
- 12.4.3.4.7.3.1
WAIT Pin Monitoring Control
- 12.4.3.4.7.4 Error Handling
- 12.4.3.4.8
GPMC Timing Setting
- 12.4.3.4.8.1 Read Cycle Time and Write Cycle Time (RDCYCLETIME / WRCYCLETIME)
- 12.4.3.4.8.2 nCS: Chip-Select Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (CSONTIME / CSRDOFFTIME / CSWROFFTIME / CSEXTRADELAY)
- 12.4.3.4.8.3 nADV/ALE: Address Valid/Address Latch Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (ADVONTIME / ADVRDOFFTIME / ADVWROFFTIME / ADVEXTRADELAY/ADVAADMUXONTIME/ADVAADMUXRDOFFTIME/ADVAADMUXWROFFTIME)
- 12.4.3.4.8.4 nOE/nRE: Output Enable/Read Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (OEONTIME / OEOFFTIME / OEEXTRADELAY / OEAADMUXONTIME / OEAADMUXOFFTIME)
- 12.4.3.4.8.5 nWE: Write Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (WEONTIME / WEOFFTIME / WEEXTRADELAY)
- 12.4.3.4.8.6 GPMC_CLKOUT
- 12.4.3.4.8.7 GPMC Output Clock and Control Signals Setup and Hold
- 12.4.3.4.8.8 Access Time (RDACCESSTIME / WRACCESSTIME)
- 12.4.3.4.8.9 Page Burst Access Time (PAGEBURSTACCESSTIME)
- 12.4.3.4.8.10 Bus Keeping Support
- 12.4.3.4.9
GPMC NOR Access Description
- 12.4.3.4.9.1 Asynchronous Access Description
- 12.4.3.4.9.2 Synchronous Access Description
- 12.4.3.4.9.3
Asynchronous and Synchronous Accesses in non-multiplexed Mode
- 12.4.3.4.9.3.1 Asynchronous Single-Read Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 12.4.3.4.9.3.2 Asynchronous Single-Write Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 12.4.3.4.9.3.3 Asynchronous Multiple (Page Mode) Read Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 12.4.3.4.9.3.4 Synchronous Operations on a non-multiplexed Device
- 12.4.3.4.9.4 Page and Burst Support
- 12.4.3.4.9.5 System Burst vs External Device Burst Support
- 12.4.3.4.10 GPMC pSRAM Access Specificities
- 12.4.3.4.11
GPMC NAND Access Description
- 12.4.3.4.11.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 12.4.3.4.11.1.1 Chip-Select Configuration for NAND Interfacing in Byte or Word Stream Mode
- 12.4.3.4.11.1.2 NAND Device Command and Address Phase Control
- 12.4.3.4.11.1.3 Command Latch Cycle
- 12.4.3.4.11.1.4 Address Latch Cycle
- 12.4.3.4.11.1.5 NAND Device Data Read and Write Phase Control in Stream Mode
- 12.4.3.4.11.1.6 NAND Device General Chip-Select Timing Control Requirement
- 12.4.3.4.11.1.7 Read and Write Access Size Adaptation
- 12.4.3.4.11.2 NAND Device-Ready Pin
- 12.4.3.4.11.3
ECC Calculator
- 12.4.3.4.11.3.1 Hamming Code
- 12.4.3.4.11.3.2
BCH Code
- 12.4.3.4.11.3.2.1 Requirements
- 12.4.3.4.11.3.2.2
Memory Mapping of BCH Codeword
- 4.3.4.11.3.2.2.1 Memory Mapping of Data Message
- 4.3.4.11.3.2.2.2 Memory-Mapping of the ECC
- 4.3.4.11.3.2.2.3
Wrapping Modes
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.1 Manual Mode (0x0)
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.2 Mode 0x1
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.3 Mode 0xA (10)
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.4 Mode 0x2
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.5 Mode 0x3
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.6 Mode 0x7
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.7 Mode 0x8
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.8 Mode 0x4
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.9 Mode 0x9
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.10 Mode 0x5
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.11 Mode 0xB (11)
- 3.4.11.3.2.2.3.12 Mode 0x6
- 12.4.3.4.11.3.2.3 Supported NAND Page Mappings and ECC Schemes
- 12.4.3.4.11.4
Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 12.4.3.4.11.4.1 General Facts About the Engine Configuration
- 12.4.3.4.11.4.2 Prefetch Mode
- 12.4.3.4.11.4.3 FIFO Control in Prefetch Mode
- 12.4.3.4.11.4.4 Write-Posting Mode
- 12.4.3.4.11.4.5 FIFO Control in Write-Posting Mode
- 12.4.3.4.11.4.6 Optimizing NAND Access Using the Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 12.4.3.4.11.4.7 Interleaved Accesses Between Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine and Other Chip-Selects
- 12.4.3.4.11.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 12.4.3.4.12 GPMC Use Cases and Tips
- 12.4.3.5 GPMC Basic Programming Model
- 12.4.4 Error Location Module (ELM)
- 12.4.5
Multi-Media Card Secure Digital (MMCSD) Interface
- 12.4.5.1 MMCSD Overview
- 12.4.5.2 MMCSD Environment
- 12.4.5.3 Integration
- 12.4.5.4 MMCSD Functional Description
- 12.4.5.5
MMCSD Programming Guide
- 12.4.5.5.1
Sequences
- 12.4.5.5.1.1 SD Card Detection
- 12.4.5.5.1.2 SD Clock Control
- 12.4.5.5.1.3 SD Bus Power Control
- 12.4.5.5.1.4 Changing Bus Width
- 12.4.5.5.1.5 Timeout Setting on DAT Line
- 12.4.5.5.1.6 Card Initialization and Identification (for SD I/F)
- 12.4.5.5.1.7 SD Transaction Generation
- 12.4.5.5.1.8 Abort Transaction
- 12.4.5.5.1.9 Changing Bus Speed Mode
- 12.4.5.5.1.10 Error Recovery
- 12.4.5.5.1.11 Wakeup Control (Optional)
- 12.4.5.5.1.12 Suspend/Resume (Optional, Not Supported from Version 4.00)
- 12.4.5.5.2 Driver Flow Sequence
- 12.4.5.5.1
Sequences
- 12.5
Industrial and Control Interfaces
- 12.5.1
Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 12.5.1.1 MCAN Overview
- 12.5.1.2 MCAN Environment
- 12.5.1.3 Integration
- 12.5.1.4
MCAN Functional Description
- 12.5.1.4.1 Module Clocking Requirements
- 12.5.1.4.2 Interrupt and DMA Requests
- 12.5.1.4.3
Operating Modes
- 12.5.1.4.3.1 Software Initialization
- 12.5.1.4.3.2 Normal Operation
- 12.5.1.4.3.3 CAN FD Operation
- 12.5.1.4.3.4 Transmitter Delay Compensation
- 12.5.1.4.3.5 Restricted Operation Mode
- 12.5.1.4.3.6 Bus Monitoring Mode
- 12.5.1.4.3.7 Disabled Automatic Retransmission (DAR) Mode
- 12.5.1.4.3.8 Power Down (Sleep Mode)
- 12.5.1.4.3.9 Test Modes
- 12.5.1.4.4 Timestamp Generation
- 12.5.1.4.5 Timeout Counter
- 12.5.1.4.6 ECC Support
- 12.5.1.4.7 Rx Handling
- 12.5.1.4.8 Tx Handling
- 12.5.1.4.9 FIFO Acknowledge Handling
- 12.5.1.4.10 Message RAM
- 12.5.2
Enhanced Capture (ECAP) Module
- 12.5.2.1 ECAP Overview
- 12.5.2.2 ECAP Environment
- 12.5.2.3 Integration
- 12.5.2.4
ECAP Functional Description
- 12.5.2.4.1
Capture and APWM Operating Modes
- 12.5.2.4.1.1
ECAP Capture Mode Description
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.1 ECAP Event Prescaler
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.2 ECAP Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.3 ECAP Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.4 ECAP 32-Bit Counter and Phase Control
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.5 CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.6 ECAP Interrupt Control
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.7 ECAP Shadow Load and Lockout Control
- 12.5.2.4.1.2 ECAP APWM Mode Operation
- 12.5.2.4.1.1
ECAP Capture Mode Description
- 12.5.2.4.2 Summary of ECAP Functional Registers
- 12.5.2.4.1
Capture and APWM Operating Modes
- 12.5.2.5
ECAP Use Cases
- 12.5.2.5.1 Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising Edge Trigger Example
- 12.5.2.5.2 Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising and Falling Edge Trigger Example
- 12.5.2.5.3 Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising Edge Trigger Example
- 12.5.2.5.4 Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising and Falling Edge Trigger Example
- 12.5.2.5.5 Application of the APWM Mode
- 12.5.3
Enhanced Pulse Width Modulation (EPWM) Module
- 12.5.3.1 EPWM Overview
- 12.5.3.2 EPWM Environment
- 12.5.3.3 Integration
- 12.5.3.4
EPWM Functional Description
- 12.5.3.4.1 EPWM Submodule Features
- 12.5.3.4.2 EPWM Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.3 EPWM Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.4 EPWM Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.5 EPWM Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.6 EPWM-Chopper (PC) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.7 EPWM Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.8 EPWM Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.9 EPWM Functional Register Groups
- 12.5.3.4.10 Proper EPWM Interrupt Initialization Procedure
- 12.5.4
Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (EQEP) Module
- 12.5.4.1 EQEP Overview
- 12.5.4.2 EQEP Environment
- 12.5.4.3 Integration
- 12.5.4.4
EQEP Functional Description
- 12.5.4.4.1 EQEP Inputs
- 12.5.4.4.2 EQEP Quadrature Decoder Unit (QDU)
- 12.5.4.4.3
EQEP Position Counter and Control Unit (PCCU)
- 12.5.4.4.3.1
EQEP Position Counter Operating Modes
- 12.5.4.4.3.1.1 EQEP Position Counter Reset on Index Event (EQEP_QDEC_QEP_CTL[29-28] PCRM] = 0b00)
- 12.5.4.4.3.1.2 EQEP Position Counter Reset on Maximum Position (EQEP_QDEC_QEP_CTL[29-28] PCRM = 0b01)
- 12.5.4.4.3.1.3 Position Counter Reset on the First Index Event (EQEP_QDEC_QEP_CTL[29-28] PCRM = 0b10)
- 12.5.4.4.3.1.4 Position Counter Reset on Unit Time out Event (EQEP_QDEC_QEP_CTL[29-28] PCRM = 0b11)
- 12.5.4.4.3.2 EQEP Position Counter Latch
- 12.5.4.4.3.3 EQEP Position Counter Initialization
- 12.5.4.4.3.4 EQEP Position-Compare Unit
- 12.5.4.4.3.1
EQEP Position Counter Operating Modes
- 12.5.4.4.4 EQEP Edge Capture Unit
- 12.5.4.4.5 EQEP Watchdog
- 12.5.4.4.6 Unit Timer Base
- 12.5.4.4.7 EQEP Interrupt Structure
- 12.5.4.4.8 Summary of EQEP Functional Registers
- 12.5.1
Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 12.6
Camera Subsystem
- 12.6.1
Camera Serial Interface Receiver
(CSI_RX_IF)
- 12.6.1.1 CSI_RX_IF Overview
- 12.6.1.2 CSI_RX_IF Environment
- 12.6.1.3 Integration
- 12.6.1.4
CSI_RX_IF Functional Description
- 12.6.1.4.1 CSI_RX_IF Block Diagram
- 12.6.1.4.2 CSI_RX_IF Hardware and Software Reset
- 12.6.1.4.3 CSI_RX_IF Clock Configuration
- 12.6.1.4.4 CSI_RX_IF Interrupt Events
- 12.6.1.4.5 CSI_RX_IF Data Memory Organization Details
- 12.6.1.4.6 CSI_RX_IF PSI_L (DMA) Interface
- 12.6.1.4.7 CSI_RX_IF ECC Protection Support
- 12.6.1.4.8
CSI_RX_IF Programming Guide
- 12.6.1.4.8.1 Overview
- 12.6.1.4.8.2 Controller Configuration
- 12.6.1.4.8.3 Power on Configuration
- 12.6.1.4.8.4 Stream Start and Stop
- 12.6.1.4.8.5 Error Control With Soft Resets
- 12.6.1.4.8.6 Stream Error Detected – No Error Bypass Mode
- 12.6.1.4.8.7 Stream Error Detected – Error Bypass Mode
- 12.6.1.4.8.8 Stream Error Detected – Soft Reset Recovery
- 12.6.1.4.8.9 Stream Monitor Configuration
- 12.6.1.4.8.10 Stream Monitor Frame Capture Control
- 12.6.1.4.8.11 Stream Monitor Timer interrupt
- 12.6.1.4.8.12 Stream Monitor Line/Byte Counters Interrupt
- 12.6.1.4.8.13 Example Controller Programming Sequence (Single Stream Operation)
- 12.6.1.4.8.14 CSI_RX_IF Programming Restrictions
- 12.6.1.4.8.15 CSI_RX_IF Real-time operating requirements
- 12.6.2 MIPI D-PHY Receiver (DPHY_RX)
- 12.6.1
Camera Serial Interface Receiver
(CSI_RX_IF)
- 12.7
Timer Modules
- 12.7.1 Global Timebase Counter (GTC)
- 12.7.2 RTI-Windowed Watchdog Timer (WWDT)
- 12.7.3 Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- 12.7.4
Timers
- 12.7.4.1 Timers Overview
- 12.7.4.2 Timers Environment
- 12.7.4.3 Integration
- 12.7.4.4
Timers Functional Description
- 12.7.4.4.1 Timer Block Diagram
- 12.7.4.4.2 Timer Power Management
- 12.7.4.4.3 Timer Software Reset
- 12.7.4.4.4 Timer Interrupts
- 12.7.4.4.5 Timer Mode Functionality
- 12.7.4.4.6 Timer Capture Mode Functionality
- 12.7.4.4.7 Timer Compare Mode Functionality
- 12.7.4.4.8 Timer Prescaler Functionality
- 12.7.4.4.9 Timer Pulse-Width Modulation
- 12.7.4.4.10 Timer Counting Rate
- 12.7.4.4.11 Timer Under Emulation
- 12.7.4.4.12 Accessing Timer Registers
- 12.7.4.4.13 Timer Posted Mode Selection
- 12.7.4.5 Timers Low-Level Programming Models
- 12.8
Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 12.8.1
Dual Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 12.8.1.1 DCC Overview
- 12.8.1.2
DCC Functional Description
- 12.8.1.2.1 DCC Counter Operation
- 12.8.1.2.2 DCC Low Power Mode Operation
- 12.8.1.2.3 DCC Suspend Mode Behavior
- 12.8.1.2.4 DCC Single-Shot Mode
- 12.8.1.2.5 DCC Continuous mode
- 12.8.1.2.6 DCC Control and count hand-off across clock domains
- 12.8.1.2.7 DCC Error Trajectory record
- 12.8.1.2.8 DCC Count read registers
- 12.8.2
Error Signaling Module (ESM)
- 12.8.2.1 ESM Overview
- 12.8.2.2 ESM Environment
- 12.8.2.3 Integration
- 12.8.2.4
ESM Functional Description
- 12.8.2.4.1 ESM Interrupt Requests
- 12.8.2.4.2 ESM Error Event Inputs
- 12.8.2.4.3 ESM Error Pin Output
- 12.8.2.4.4 PWM Mode
- 12.8.2.4.5 ESM Minimum Time Interval
- 12.8.2.4.6 ESM Protection for Registers
- 12.8.2.4.7 ESM Clock Stop
- 12.8.3
Memory Cyclic Redundancy Check (MCRC) Controller
- 12.8.3.1 MCRC Overview
- 12.8.3.2
MCRC Functional Description
- 12.8.3.2.1 MCRC Block Diagram
- 12.8.3.2.2 MCRC General Operation
- 12.8.3.2.3 MCRC Modes of Operation
- 12.8.3.2.4 PSA Signature Register
- 12.8.3.2.5 PSA Sector Signature Register
- 12.8.3.2.6 CRC Value Register
- 12.8.3.2.7 Raw Data Register
- 12.8.3.2.8 Example DMA Controller Setup
- 12.8.3.2.9 Pattern Count Register
- 12.8.3.2.10 Sector Count Register/Current Sector Register
- 12.8.3.2.11 Interrupts
- 12.8.3.2.12 Power Down Mode
- 12.8.3.2.13 Emulation
- 12.8.3.3 MCRC Programming Examples
- 12.8.4 ECC Aggregator
- 12.8.1
Dual Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 12.9
Display Subsystem (DSS) and Peripherals
- 12.9.1
Display Subsystem (DSS)
- 12.9.1.1 DSS Overview
- 12.9.1.2 DSS Environment
- 12.9.1.3 Integration
- 12.9.1.4
DSS Functional Description
- 12.9.1.4.1
DISPC Functional Description
- 12.9.1.4.1.1 DISPC Overview
- 12.9.1.4.1.2 DISPC Clocks
- 12.9.1.4.1.3 DISPC Resets
- 12.9.1.4.1.4 DISPC Power Management
- 12.9.1.4.1.5 DISPC Interrupt Requests
- 12.9.1.4.1.6
DISPC DMA Engine
- 12.9.1.4.1.6.1 DISPC DMA Addressing and Bursts
- 12.9.1.4.1.6.2 DISPC Read DMA Buffers
- 12.9.1.4.1.6.3 DISPC Flip/Mirror Support
- 12.9.1.4.1.6.4 DISPC DMA Predecimation
- 12.9.1.4.1.6.5 DISPC DMA MFLAG Mechanism
- 12.9.1.4.1.6.6 DISPC DMA Priority Requests Control
- 12.9.1.4.1.6.7 DISPC DMA Arbitration
- 12.9.1.4.1.6.8 DISPC DMA Power Modes
- 12.9.1.4.1.7 DISPC Pixel Data Formats
- 12.9.1.4.1.8
DISPC Video Pipelines
- 12.9.1.4.1.8.1 DISPC VID Replication Logic
- 12.9.1.4.1.8.2 DISPC VID VC-1 Range Mapping Unit
- 12.9.1.4.1.8.3 DISPC VID Color Look-Up Table (CLUT)
- 12.9.1.4.1.8.4 DISPC VID Chrominance Resampling
- 12.9.1.4.1.8.5 DISPC VID Scaler Unit
- 12.9.1.4.1.8.6 DISPC VID Color Space Conversion YUV to RGB
- 12.9.1.4.1.8.7 DISPC VID Brightness/Contrast/Saturation/Hue Control
- 12.9.1.4.1.8.8 DISPC VID Luma Key Support
- 12.9.1.4.1.9 DISPC Overlay Managers
- 12.9.1.4.1.10
DISPC Video Port Outputs
- 12.9.1.4.1.10.1 DISPC VP Gamma Correction Unit
- 12.9.1.4.1.10.2 DISPC VP Color Phase Rotation Unit
- 12.9.1.4.1.10.3 DISPC VP Color Space Conversion - RGB to YUV
- 12.9.1.4.1.10.4 DISPC VP BT.656 and BT.1120 Modes
- 12.9.1.4.1.10.5 DISPC VP Spatial/Temporal Dithering
- 12.9.1.4.1.10.6 DISPC VP Multiple Cycle Output Format (TDM)
- 12.9.1.4.1.10.7 DISPC VP Timing Generator and Display Panel Settings
- 12.9.1.4.1.11 DISPC Safety Features
- 12.9.1.4.1.12 DISPC Security Management
- 12.9.1.4.1.13 DISPC Shadow Registers
- 12.9.1.4.2 OLDITX Functional Description
- 12.9.1.4.1
DISPC Functional Description
- 12.9.2 Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
- 12.9.1
Display Subsystem (DSS)
- 12.1
Audio Peripherals
-
13On-Chip Debug
- 13.1 On-Chip Debug Overview
- 13.2 On-Chip Debug Features
- 3031
- 13.3
On-Chip Debug Functional Description
- 13.3.1 On-Chip Debug Block Diagram
- 13.3.2 Device Interfaces
- 13.3.3 Debug and Boundary Scan Access and Control
- 13.3.4 Debug Boot Modes and Boundary Scan Compliance
- 13.3.5 Power, Reset, Clock Management
- 13.3.6 Debug Cross Triggering
- 13.3.7 WKUP_R5F Debug
- 13.3.8 SMS0_HSM and MCU_M4F Debug
- 13.3.9 A53SS0 Debug
- 13.3.10 PRUSS Debug
- 13.3.11 SoC Debug and Trace
- 13.3.12 Trace Traffic
- 13.3.13 Application Support
-
14Registers
- 14.1
System Interconnect Registers
- 14.1.1
CBASS Registers
- 14.1.1.1 ERR_PID Registers
- 14.1.1.2 ERR_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.1.3 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.1.4 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.1.5 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.1.6 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.1.7 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.1.8 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.1.9 ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Registers
- 14.1.1.10 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Registers
- 14.1.1.11 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.1.1.12 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.1.1.13 ERR_EOI Registers
- 14.1.1.14 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.15 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.16 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.17 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.18 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.19 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.20 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.21 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.22 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.23 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.24 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.25 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.26 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.27 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.28 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.29 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.30 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.31 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.32 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.33 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.34 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.35 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.36 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.37 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.38 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.39 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.40 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.41 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.42 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.43 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.44 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.45 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.46 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.47 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.48 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.49 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.50 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.51 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.52 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.53 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.54 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.55 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.56 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.57 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.58 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.59 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.60 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.61 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.62 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.63 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.64 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.65 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.66 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.67 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.68 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.69 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.70 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.71 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.72 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.73 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.74 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.75 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.76 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.77 FW_ISAM62_DDR_WRAP_MAIN_0_DDRSS_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.78 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.79 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.80 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.81 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.82 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.83 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.84 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.85 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.86 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.87 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.88 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.89 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.90 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.91 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.92 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.93 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.94 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.95 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.96 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.97 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.98 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.99 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.100 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.101 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.102 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.103 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.104 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.105 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.106 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.107 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.108 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.109 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.110 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.111 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.112 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.113 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.114 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.115 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.116 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.117 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.118 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.119 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.120 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.121 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.122 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.123 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.124 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.125 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.126 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.127 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.128 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.129 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.130 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.131 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.132 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.133 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.134 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.135 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.136 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.137 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.138 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.139 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.140 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.141 FW_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_ACP_W_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.142 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.143 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.144 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.145 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.146 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.147 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.148 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.149 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.150 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.151 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.152 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.153 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.154 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.155 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.156 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.157 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.158 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.159 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.160 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.161 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.162 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.163 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.164 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.165 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.166 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.167 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.168 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.169 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.170 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.171 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.172 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.173 FW_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CFG_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.174 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.175 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.176 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.177 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.178 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.179 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.180 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.181 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.182 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.183 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.184 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.185 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.186 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.187 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.188 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.189 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.190 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.191 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.192 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.193 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.194 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.195 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.196 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.197 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.198 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.199 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.200 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.201 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.202 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.203 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.204 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.205 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.206 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.207 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.208 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.209 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.210 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.211 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.212 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.213 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.214 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.215 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.216 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.217 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.218 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.219 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.220 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.221 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.222 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.223 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.224 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.225 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.226 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.227 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.228 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.229 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.230 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.231 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.232 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.233 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.234 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.235 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.236 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.237 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_DATA_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.238 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.239 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.240 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.241 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.242 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.243 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.244 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.245 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.246 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.247 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.248 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.249 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.250 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.251 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.252 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.253 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.254 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.255 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.256 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.257 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.258 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.259 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.260 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.261 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.262 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.263 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.264 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.265 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.266 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.267 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.268 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.269 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.270 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.271 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.272 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.273 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.274 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.275 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.276 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.277 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.278 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.279 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.280 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.281 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.282 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.283 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.284 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.285 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.286 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.287 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.288 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.289 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.290 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.291 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.292 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.293 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.294 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.295 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.296 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.297 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.298 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.299 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.300 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.301 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.302 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_8_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.303 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.304 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.305 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.306 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.307 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.308 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.309 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.310 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_9_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.311 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.312 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.313 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.314 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.315 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.316 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.317 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.318 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_10_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.319 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.320 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.321 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.322 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.323 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.324 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.325 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.326 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_11_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.327 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.328 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.329 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.330 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.331 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.332 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.333 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.334 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_12_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.335 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.336 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.337 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.338 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.339 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.340 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.341 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.342 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_13_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.343 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.344 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.345 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.346 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.347 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.348 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.349 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.350 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_14_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.351 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.352 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.353 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.354 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.355 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.356 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.357 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.358 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_15_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.359 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.360 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.361 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.362 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.363 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.364 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.365 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.366 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_16_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.367 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_16_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.368 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_16_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.369 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_16_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.370 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_16_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.371 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_16_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.372 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_16_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.373 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_16_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.374 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_17_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.375 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_17_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.376 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_17_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.377 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_17_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.378 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_17_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.379 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_17_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.380 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_17_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.381 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_17_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.382 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_18_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.383 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_18_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.384 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_18_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.385 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_18_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.386 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_18_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.387 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_18_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.388 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_18_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.389 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_18_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.390 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_19_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.391 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_19_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.392 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_19_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.393 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_19_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.394 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_19_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.395 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_19_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.396 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_19_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.397 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_19_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.398 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_20_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.399 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_20_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.400 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_20_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.401 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_20_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.402 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_20_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.403 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_20_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.404 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_20_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.405 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_20_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.406 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_21_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.407 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_21_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.408 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_21_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.409 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_21_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.410 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_21_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.411 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_21_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.412 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_21_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.413 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_21_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.414 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_22_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.415 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_22_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.416 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_22_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.417 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_22_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.418 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_22_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.419 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_22_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.420 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_22_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.421 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_22_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.422 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_23_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.423 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_23_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.424 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_23_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.425 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_23_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.426 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_23_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.427 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_23_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.428 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_23_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.429 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK2_DMA_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_23_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.430 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.431 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.432 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.433 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.434 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.435 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.436 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.437 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.438 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.439 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.440 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.441 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.442 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.443 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.444 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.445 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.446 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.447 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.448 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.449 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.450 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.451 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.452 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.453 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.454 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.455 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.456 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.457 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.458 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.459 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.460 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.461 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.462 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.463 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.464 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.465 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.466 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.467 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.468 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.469 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.470 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.471 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.472 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.473 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.474 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.475 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.476 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.477 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.478 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.479 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.480 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.481 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.482 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.483 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.484 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.485 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.486 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.487 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.488 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.489 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.490 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.491 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.492 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.493 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_CLK4_CFG_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.494 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.495 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.496 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.497 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.498 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.499 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.500 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.501 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.502 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.503 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.504 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.505 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.506 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.507 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.508 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.509 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.510 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.511 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.512 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.513 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.514 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.515 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.516 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.517 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.518 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.519 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.520 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.521 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.522 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.523 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.524 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.525 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.526 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.527 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.528 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.529 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.530 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.531 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.532 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.533 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.534 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.535 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.536 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.537 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.538 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.539 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.540 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.541 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.542 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.543 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.544 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.545 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.546 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.547 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.548 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.549 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.550 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.551 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.552 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.553 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.554 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.555 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.556 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.557 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.558 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_8_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.559 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.560 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.561 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.562 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.563 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.564 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.565 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.566 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_9_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.567 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.568 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.569 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.570 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.571 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.572 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.573 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.574 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_10_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.575 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.576 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.577 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.578 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.579 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.580 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.581 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.582 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_11_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.583 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.584 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.585 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.586 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.587 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.588 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.589 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.590 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_12_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.591 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.592 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.593 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.594 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.595 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.596 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.597 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.598 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_13_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.599 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.600 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.601 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.602 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.603 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.604 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.605 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.606 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_14_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.607 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.608 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.609 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.610 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.611 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.612 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.613 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.614 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_15_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.615 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.616 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.617 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.618 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.619 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.620 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.621 FW_BR_SCRM_64B_CLK2_TO_SCRP_32_CLK2_MISC_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.622 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_R_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.623 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_R_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.624 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_R_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.625 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_R_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.626 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_R_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.627 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_R_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.628 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_W_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.629 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_W_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.630 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_W_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.631 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_W_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.632 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_W_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.633 ISC_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_W_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.634 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.635 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.636 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.637 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.638 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.639 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.640 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.641 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.642 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.643 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.644 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.645 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.646 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.647 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.648 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.649 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.650 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.651 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.652 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.653 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.654 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.655 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.656 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.657 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.658 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.659 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.660 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.661 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.662 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.663 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.664 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.665 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.666 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.667 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.668 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.669 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.670 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.671 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.672 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.673 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.674 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.675 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.676 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.677 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.678 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.679 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.680 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.681 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.682 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.683 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.684 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.685 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.686 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.687 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.688 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.689 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.690 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.691 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.692 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.693 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.694 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.695 ISC_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.696 ISC_IK3_LED2VBUS_MAIN_0_VBUSP_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.697 ISC_IK3_LED2VBUS_MAIN_0_VBUSP_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.698 ISC_IK3_LED2VBUS_MAIN_0_VBUSP_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.699 ISC_IK3_LED2VBUS_MAIN_0_VBUSP_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.700 ISC_IK3_LED2VBUS_MAIN_0_VBUSP_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.701 ISC_IK3_LED2VBUS_MAIN_0_VBUSP_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.702 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMW_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.703 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.704 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.705 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.706 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.707 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMW_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.708 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMR_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.709 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.710 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.711 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.712 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.713 ISC_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMR_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.714 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_WR_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.715 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_WR_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.716 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_WR_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.717 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_WR_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.718 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_WR_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.719 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_WR_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.720 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_RD_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.721 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_RD_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.722 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_RD_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.723 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_RD_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.724 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_RD_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.725 ISC_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_RD_VBUSM_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.726 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.727 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.728 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.729 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.730 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.731 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.732 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.733 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.734 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.735 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.736 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.737 ISC_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.738 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.739 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.740 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.741 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.742 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.743 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.744 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.745 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.746 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.747 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.748 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.749 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.750 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.751 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.752 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.753 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.754 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.755 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_WR_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.756 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.757 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.758 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.759 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.760 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.761 ISC_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_RD_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.762 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.763 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.764 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.765 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.766 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.767 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.768 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.769 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.770 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.771 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.772 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.773 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.774 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.775 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.776 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.777 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.778 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.779 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTR0_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.780 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.781 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.782 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.783 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.784 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.785 ISC_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTW0_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.786 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.787 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.788 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.789 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.790 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.791 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.792 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.793 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.794 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.795 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.796 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.797 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.798 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.799 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.800 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.801 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.802 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.803 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.804 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.805 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.806 ISC_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.807 ISC_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_CTXCACH_EXT_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.808 ISC_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_CTXCACH_EXT_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.809 ISC_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_CTXCACH_EXT_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.810 ISC_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_CTXCACH_EXT_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.811 ISC_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_CTXCACH_EXT_DMA_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.812 ISC_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_CTXCACH_EXT_DMA_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.813 GLB_PID Registers
- 14.1.1.814 GLB_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.1.815 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.816 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.1.817 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.1.818 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.1.819 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.1.820 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.1.821 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.1.822 GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Registers
- 14.1.1.823 GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Registers
- 14.1.1.824 QOS_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_R_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.825 QOS_ISAM62_A53_512KB_WRAP_MAIN_0_A53_QUAD_WRAP_CBA_AXI_W_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.826 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.827 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_MAP1 Registers
- 14.1.1.828 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_MAP2 Registers
- 14.1.1.829 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_MAP3 Registers
- 14.1.1.830 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_MAP4 Registers
- 14.1.1.831 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_W_MAP5 Registers
- 14.1.1.832 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.833 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_MAP1 Registers
- 14.1.1.834 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_MAP2 Registers
- 14.1.1.835 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_MAP3 Registers
- 14.1.1.836 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_MAP4 Registers
- 14.1.1.837 QOS_IK3_GPU_AXE116M_MAIN_0_K3_GPU_M_VBUSM_R_MAP5 Registers
- 14.1.1.838 QOS_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMW_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.839 QOS_IDEBUGSS_K3_WRAP_CV0_MAIN_0_VBUSMR_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.840 QOS_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_WR_VBUSM_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.841 QOS_IGIC500SS_1_4_MAIN_0_MEM_RD_VBUSM_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.842 QOS_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.843 QOS_IEMMCSD8SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.844 QOS_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_RD_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.845 QOS_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_0_EMMCSDSS_WR_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.846 QOS_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_WR_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.847 QOS_IEMMCSD4SS_MAIN_1_EMMCSDSS_RD_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.848 QOS_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTW0_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.849 QOS_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_0_MSTR0_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.850 QOS_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTR0_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.851 QOS_IUSB2SS_16FFC_MAIN_1_MSTW0_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.852 QOS_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.853 QOS_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_MAP1 Registers
- 14.1.1.854 QOS_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_MAP2 Registers
- 14.1.1.855 QOS_IK3_DSS_UL_MAIN_0_VBUSM_DMA_MAP3 Registers
- 14.1.1.856 QOS_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_CTXCACH_EXT_DMA_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.857 ISC_IBLAZAR_MCU_0_VBUSP_M_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.858 ISC_IBLAZAR_MCU_0_VBUSP_M_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.859 ISC_IBLAZAR_MCU_0_VBUSP_M_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.860 ISC_IBLAZAR_MCU_0_VBUSP_M_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.861 ISC_IBLAZAR_MCU_0_VBUSP_M_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.862 ISC_IBLAZAR_MCU_0_VBUSP_M_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.863 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.864 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.865 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.866 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.867 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.868 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.869 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.870 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.871 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.872 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.873 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.874 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.875 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.876 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.877 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.878 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.879 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.880 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.881 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.882 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.883 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.884 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.885 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.886 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.887 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.888 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.889 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.890 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.891 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.892 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.893 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.894 FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.895 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.896 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.897 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.898 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.899 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.900 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.901 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.902 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.903 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.904 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.905 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.906 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.907 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.908 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.909 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.910 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.911 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.912 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.913 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.914 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.915 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.916 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.917 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.918 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.919 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.920 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.921 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.922 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.923 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.924 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.925 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.926 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.927 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.928 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.929 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.930 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.931 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.932 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.933 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.934 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.935 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.936 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.937 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.938 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.939 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.940 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.941 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.942 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.943 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.944 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.945 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.946 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.947 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.948 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.949 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.950 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.951 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.952 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.953 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.954 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.955 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.956 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.957 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.958 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.959 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.960 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.961 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.962 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.963 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.964 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.965 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.966 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.967 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.968 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.969 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.970 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.971 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.972 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.973 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.974 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.975 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.976 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.977 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.978 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.979 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.980 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.981 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.982 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.983 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.984 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.985 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.986 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.987 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.988 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.989 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.990 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.991 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.992 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.993 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.994 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.995 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.996 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.997 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.998 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.999 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1000 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1001 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1002 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1003 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1004 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1005 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1006 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1007 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1008 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1009 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1010 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1011 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1012 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1013 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1014 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1015 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1016 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1017 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1018 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1019 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1020 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1021 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1022 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1023 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1024 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1025 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1026 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1027 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1028 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1029 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1030 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1031 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1032 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1033 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1034 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1035 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1036 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1037 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1038 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1039 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1040 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1041 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1042 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1043 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1044 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1045 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1046 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1047 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1048 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1049 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1050 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1051 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1052 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1053 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1054 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1055 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1056 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1057 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1058 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1059 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1060 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1061 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1062 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1063 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1064 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1065 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1066 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1067 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1068 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1069 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1070 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1071 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1072 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1073 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1074 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1075 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1076 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1077 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1078 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1079 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1080 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1081 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1082 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1083 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1084 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1085 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1086 FW_BR_SCRM_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32B_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1087 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1088 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1089 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1090 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1091 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1092 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1093 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1094 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1095 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1096 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1097 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1098 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1099 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1100 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1101 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1102 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1103 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1104 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1105 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1106 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1107 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1108 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1109 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1110 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1111 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1112 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1113 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1114 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1115 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1116 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1117 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1118 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1119 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1120 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1121 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1122 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1123 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1124 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1125 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1126 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1127 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1128 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1129 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1130 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1131 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1132 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1133 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1134 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1135 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1136 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1137 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1138 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1139 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1140 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1141 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1142 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1143 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1144 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1145 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1146 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1147 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1148 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1149 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1150 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1151 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1152 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1153 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1154 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1155 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1156 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1157 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1158 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1159 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1160 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1161 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1162 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1163 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1164 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1165 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1166 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1167 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1168 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1169 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1170 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1171 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1172 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1173 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1174 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1175 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1176 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1177 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1178 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1179 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1180 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1181 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1182 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1183 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1184 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1185 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1186 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1187 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1188 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1189 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1190 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1191 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1192 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1193 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1194 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1195 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1196 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1197 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1198 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1199 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1200 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1201 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1202 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1203 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1204 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1205 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1206 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1207 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1208 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1209 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.1.1210 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.1.1211 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1212 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1213 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1214 FW_EXPORT_AM62_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM62_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1215 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1216 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1217 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1218 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1219 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1220 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1221 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1222 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1223 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1224 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1225 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1226 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1227 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1228 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1229 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1230 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1231 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1232 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1233 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1234 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1235 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1236 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1237 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1238 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1239 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1240 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1241 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1242 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1243 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1244 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1245 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1246 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1247 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1248 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1249 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1250 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1251 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1252 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1253 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1254 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1255 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1256 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1257 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1258 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1259 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1260 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1261 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1262 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1263 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1264 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1265 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1266 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1267 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1268 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1269 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1270 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1271 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1272 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1273 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1274 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1275 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.1.1276 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.1.1277 ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.1.1278 QOS_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1279 QOS_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1280 QOS_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.1.1281 Access Table
- 14.1.2
CBASS_CENTRAL Registers
- 14.1.2.1 ERR_PID Registers
- 14.1.2.2 ERR_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.2.3 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.2.4 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.2.5 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.2.6 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.2.7 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.2.8 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.2.9 ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Registers
- 14.1.2.10 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Registers
- 14.1.2.11 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.1.2.12 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.1.2.13 ERR_EOI Registers
- 14.1.2.14 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.15 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.16 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.17 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.18 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.19 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.20 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.21 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.22 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.23 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.24 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.25 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.26 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.27 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.28 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.29 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.30 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.31 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.32 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.33 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.34 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.35 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.36 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.37 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.38 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.39 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.40 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.41 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.42 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.43 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.44 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.45 FW_IPSRAM16KX32E_MAIN_0_RAM_VB_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.46 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.47 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.48 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.49 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.50 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.51 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.52 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.53 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.54 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.55 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.56 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.57 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.58 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.59 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.60 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.61 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.62 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.63 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.64 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.65 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.66 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.67 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.68 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.69 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.70 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.71 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.72 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.73 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.74 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.75 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.76 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.77 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.78 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.79 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.80 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.81 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.82 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.83 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.84 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.85 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.86 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.87 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.88 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.89 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.90 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.91 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.92 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.93 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.94 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.95 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.96 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.97 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.98 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.99 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.100 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.101 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.102 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.103 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.104 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.105 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.106 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.107 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.108 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.109 FW_EXPORT_AM62_MAIN_CENTRAL_CBASS_TO_AM62_MCU_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.110 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.111 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.112 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.113 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.114 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.115 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.116 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.117 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.118 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.119 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.120 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.121 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.122 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.123 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.124 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.125 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.126 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.127 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.128 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.129 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.130 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.131 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.132 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.133 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.134 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.135 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.2.136 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.2.137 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.2.138 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.139 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.140 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.141 FW_BR_SCRP_32B_DMSC_HSM_TO_SCRP_HSM_CLK2_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.142 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP0_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.143 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.144 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP0_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.145 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.146 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP0_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.147 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP0_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.148 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP1_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.149 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP1_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.150 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP1_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.151 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP1_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.2.152 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP1_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.2.153 ISC_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP1_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.154 GLB_PID Registers
- 14.1.2.155 GLB_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.2.156 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.2.157 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.2.158 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.2.159 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.2.160 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.2.161 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.2.162 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.2.163 GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Registers
- 14.1.2.164 GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Registers
- 14.1.2.165 QOS_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP0_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.2.166 QOS_IICSS_M_MAIN_0_PR1_MST_VBUSP1_MAP0 Registers
- 14.1.2.167 Access Table
- 14.1.3
CBASS_DBG Registers
- 14.1.3.1 ERR_PID Registers
- 14.1.3.2 ERR_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.3.3 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.3.4 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.3.5 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.3.6 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.3.7 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.3.8 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.3.9 ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Registers
- 14.1.3.10 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Registers
- 14.1.3.11 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.1.3.12 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.1.3.13 ERR_EOI Registers
- 14.1.3.14 Access Table
- 14.1.4
CBASS_FW Registers
- 14.1.4.1 ERR_PID Registers
- 14.1.4.2 ERR_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.4.3 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.4.4 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.4.5 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.4.6 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.4.7 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.4.8 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.4.9 ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Registers
- 14.1.4.10 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Registers
- 14.1.4.11 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.1.4.12 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.1.4.13 ERR_EOI Registers
- 14.1.4.14 Access Table
- 14.1.5
CBASS_INFRA Registers
- 14.1.5.1 ERR_PID Registers
- 14.1.5.2 ERR_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.5.3 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.5.4 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.5.5 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.5.6 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.5.7 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.5.8 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.5.9 ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Registers
- 14.1.5.10 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Registers
- 14.1.5.11 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.1.5.12 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.1.5.13 ERR_EOI Registers
- 14.1.5.14 Access Table
- 14.1.6
CBASS_IPCSS Registers
- 14.1.6.1 ERR_PID Registers
- 14.1.6.2 ERR_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.6.3 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.6.4 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.6.5 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.6.6 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.6.7 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.6.8 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.6.9 ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Registers
- 14.1.6.10 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Registers
- 14.1.6.11 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.1.6.12 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.1.6.13 ERR_EOI Registers
- 14.1.6.14 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.15 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.16 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.17 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.18 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.19 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.20 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.21 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.22 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.23 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.24 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.25 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.26 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.27 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.28 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.29 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.30 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.31 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.32 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.33 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.34 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.35 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.36 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.37 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.38 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.39 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.40 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.41 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.42 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.43 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.44 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.45 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.46 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.47 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.48 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.49 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.50 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.51 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.52 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.53 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.54 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.55 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.56 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.57 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.58 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.59 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.60 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.61 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.62 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.63 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.64 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.65 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.66 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.67 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.68 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.69 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.70 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.71 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.72 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.73 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.74 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.75 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.76 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.77 FW_IDMSS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.78 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.79 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.80 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.81 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.82 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.83 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.84 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.85 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.86 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.87 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.88 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.89 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.90 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.91 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.92 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.93 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.94 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.95 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.96 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.97 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.98 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.99 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.100 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.101 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.102 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.103 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.104 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.105 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.106 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.107 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.108 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.109 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.110 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.111 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.112 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.113 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.114 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.115 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.116 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.117 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.118 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.119 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.120 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.121 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.122 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.123 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.124 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.125 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.126 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.127 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.128 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.129 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.130 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.131 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.132 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.133 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.134 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.135 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.1.6.136 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.1.6.137 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.1.6.138 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.139 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.140 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Registers
- 14.1.6.141 FW_ISA3SS_AM62_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Registers
- 14.1.6.142 GLB_PID Registers
- 14.1.6.143 GLB_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.6.144 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Registers
- 14.1.6.145 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.6.146 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.6.147 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.6.148 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.6.149 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.6.150 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.6.151 GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Registers
- 14.1.6.152 GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Registers
- 14.1.6.153 Access Table
- 14.1.7
CBASS_MCASP Registers
- 14.1.7.1 ERR_PID Registers
- 14.1.7.2 ERR_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.7.3 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.7.4 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.7.5 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.7.6 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.7.7 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.7.8 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.7.9 ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Registers
- 14.1.7.10 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Registers
- 14.1.7.11 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.1.7.12 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.1.7.13 ERR_EOI Registers
- 14.1.7.14 Access Table
- 14.1.8
CBASS_MISC_PERI Registers
- 14.1.8.1 ERR_PID Registers
- 14.1.8.2 ERR_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.8.3 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.8.4 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.8.5 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.8.6 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.8.7 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.8.8 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.8.9 ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Registers
- 14.1.8.10 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Registers
- 14.1.8.11 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.1.8.12 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.1.8.13 ERR_EOI Registers
- 14.1.8.14 Access Table
- 14.1.9
CBASS_SAFE Registers
- 14.1.9.1 ERR_PID Registers
- 14.1.9.2 ERR_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.1.9.3 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.1.9.4 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.1.9.5 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.1.9.6 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.1.9.7 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.1.9.8 ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.1.9.9 ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Registers
- 14.1.9.10 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Registers
- 14.1.9.11 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.1.9.12 ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.1.9.13 ERR_EOI Registers
- 14.1.9.14 Access Table
- 14.1.1
CBASS Registers
- 14.2
Device Configuration Registers
- 14.2.1
CTRL_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.1
General Purpose Control Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1
CTRL_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.1 CFG0_PID Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.2 CFG0_MMR_CFG1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.3 CFG0_LOCK0_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.4 CFG0_LOCK0_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.5 CFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.6 CFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.7 CFG0_INTR_ENABLE Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.8 CFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.9 CFG0_EOI Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.10 CFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.11 CFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.12 CFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.13 CFG0_FAULT_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.14 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.15 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.16 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.17 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.18 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.19 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.20 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.21 CFG0_PID_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.22 CFG0_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.23 CFG0_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.24 CFG0_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.25 CFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.26 CFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.27 CFG0_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.28 CFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.29 CFG0_EOI_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.30 CFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.31 CFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.32 CFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.33 CFG0_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.34 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.35 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.36 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.37 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.38 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.39 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.40 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.41 CFG0_ENET1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.42 CFG0_ENET2_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.43 CFG0_ICSSM0_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.44 CFG0_EPWM_TB_CLKEN Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.45 CFG0_EPWM0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.46 CFG0_EPWM1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.47 CFG0_EPWM2_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.48 CFG0_SOCA_SEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.49 CFG0_SOCB_SEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.50 CFG0_EQEP0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.51 CFG0_EQEP1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.52 CFG0_EQEP2_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.53 CFG0_EQEP_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.54 CFG0_TIMER1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.55 CFG0_TIMER3_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.56 CFG0_TIMER5_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.57 CFG0_TIMER7_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.58 CFG0_EMMC0_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.59 CFG0_EMMC1_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.60 CFG0_EMMC2_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.61 CFG0_FSS_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.62 CFG0_DCC_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.63 CFG0_LOCK1_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.64 CFG0_LOCK1_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.65 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.66 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.67 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.68 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.69 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.70 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.71 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.72 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.73 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.74 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R9_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.75 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R10_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.76 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R11_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.77 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R12_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.78 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R13_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.79 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R14_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.80 CFG0_ENET1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.81 CFG0_ENET2_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.82 CFG0_ICSSM0_CTRL0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.83 CFG0_EPWM_TB_CLKEN_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.84 CFG0_EPWM0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.85 CFG0_EPWM1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.86 CFG0_EPWM2_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.87 CFG0_SOCA_SEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.88 CFG0_SOCB_SEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.89 CFG0_EQEP0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.90 CFG0_EQEP1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.91 CFG0_EQEP2_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.92 CFG0_EQEP_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.93 CFG0_TIMER1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.94 CFG0_TIMER3_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.95 CFG0_TIMER5_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.96 CFG0_TIMER7_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.97 CFG0_EMMC0_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.98 CFG0_EMMC1_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.99 CFG0_EMMC2_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.100 CFG0_FSS_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.101 CFG0_DCC_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.102 CFG0_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.103 CFG0_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.104 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.105 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.106 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.107 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.108 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.109 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.110 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.111 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.112 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.113 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R9 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.114 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R10 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.115 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R11 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.116 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R12 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.117 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R13 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.118 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R14 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.119 CFG0_OBSCLK0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.120 CFG0_CLKOUT_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.121 CFG0_ICSSM0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.122 CFG0_MAIN_PLL0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.123 CFG0_MAIN_PLL1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.124 CFG0_MAIN_PLL2_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.125 CFG0_MAIN_PLL8_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.126 CFG0_MAIN_PLL12_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.127 CFG0_MAIN_PLL16_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.128 CFG0_MAIN_PLL17_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.129 CFG0_CPSW_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.130 CFG0_EMMC0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.131 CFG0_EMMC1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.132 CFG0_EMMC2_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.133 CFG0_GPMC_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.134 CFG0_TIMER0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.135 CFG0_TIMER1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.136 CFG0_TIMER2_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.137 CFG0_TIMER3_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.138 CFG0_TIMER4_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.139 CFG0_TIMER5_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.140 CFG0_TIMER6_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.141 CFG0_TIMER7_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.142 CFG0_SPI0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.143 CFG0_SPI1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.144 CFG0_SPI2_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.145 CFG0_USART0_CLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.146 CFG0_USART1_CLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.147 CFG0_USART2_CLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.148 CFG0_USART3_CLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.149 CFG0_USART4_CLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.150 CFG0_USART5_CLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.151 CFG0_USART6_CLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.152 CFG0_USART0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.153 CFG0_USART1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.154 CFG0_USART2_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.155 CFG0_USART3_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.156 CFG0_USART4_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.157 CFG0_USART5_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.158 CFG0_USART6_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.159 CFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.160 CFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.161 CFG0_DPI0_CLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.162 CFG0_DSS_DISPC0_CLKSEL1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.163 CFG0_MCASP0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.164 CFG0_MCASP1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.165 CFG0_MCASP2_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.166 CFG0_MCASP0_AHCLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.167 CFG0_MCASP1_AHCLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.168 CFG0_MCASP2_AHCLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.169 CFG0_WWD0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.170 CFG0_WWD1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.171 CFG0_WWD2_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.172 CFG0_WWD3_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.173 CFG0_WWD15_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.174 CFG0_MCAN0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.175 CFG0_OSPI0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.176 CFG0_OLDI0_DAT0_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.177 CFG0_OLDI0_DAT1_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.178 CFG0_OLDI0_DAT2_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.179 CFG0_OLDI0_DAT3_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.180 CFG0_OLDI0_CLK_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.181 CFG0_OLDI1_DAT0_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.182 CFG0_OLDI1_DAT1_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.183 CFG0_OLDI1_DAT2_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.184 CFG0_OLDI1_DAT3_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.185 CFG0_OLDI1_CLK_IO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.186 CFG0_OLDI_PD_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.187 CFG0_OLDI_LB_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.188 CFG0_LOCK2_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.189 CFG0_LOCK2_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.190 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.191 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.192 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.193 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.194 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.195 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.196 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.197 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.198 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.199 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R9_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.200 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R10_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.201 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R11_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.202 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R12_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.203 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R13_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.204 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R14_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.205 CFG0_OBSCLK0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.206 CFG0_CLKOUT_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.207 CFG0_ICSSM0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.208 CFG0_MAIN_PLL0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.209 CFG0_MAIN_PLL1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.210 CFG0_MAIN_PLL2_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.211 CFG0_MAIN_PLL8_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.212 CFG0_MAIN_PLL12_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.213 CFG0_MAIN_PLL16_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.214 CFG0_MAIN_PLL17_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.215 CFG0_CPSW_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.216 CFG0_EMMC0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.217 CFG0_EMMC1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.218 CFG0_EMMC2_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.219 CFG0_GPMC_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.220 CFG0_TIMER0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.221 CFG0_TIMER1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.222 CFG0_TIMER2_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.223 CFG0_TIMER3_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.224 CFG0_TIMER4_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.225 CFG0_TIMER5_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.226 CFG0_TIMER6_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.227 CFG0_TIMER7_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.228 CFG0_SPI0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.229 CFG0_SPI1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.230 CFG0_SPI2_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.231 CFG0_USART0_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.232 CFG0_USART1_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.233 CFG0_USART2_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.234 CFG0_USART3_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.235 CFG0_USART4_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.236 CFG0_USART5_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.237 CFG0_USART6_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.238 CFG0_USART0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.239 CFG0_USART1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.240 CFG0_USART2_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.241 CFG0_USART3_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.242 CFG0_USART4_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.243 CFG0_USART5_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.244 CFG0_USART6_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.245 CFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.246 CFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.247 CFG0_DPI0_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.248 CFG0_DSS_DISPC0_CLKSEL1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.249 CFG0_MCASP0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.250 CFG0_MCASP1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.251 CFG0_MCASP2_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.252 CFG0_MCASP0_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.253 CFG0_MCASP1_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.254 CFG0_MCASP2_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.255 CFG0_WWD0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.256 CFG0_WWD1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.257 CFG0_WWD2_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.258 CFG0_WWD3_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.259 CFG0_WWD15_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.260 CFG0_MCAN0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.261 CFG0_OSPI0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.262 CFG0_OLDI0_DAT0_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.263 CFG0_OLDI0_DAT1_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.264 CFG0_OLDI0_DAT2_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.265 CFG0_OLDI0_DAT3_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.266 CFG0_OLDI0_CLK_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.267 CFG0_OLDI1_DAT0_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.268 CFG0_OLDI1_DAT1_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.269 CFG0_OLDI1_DAT2_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.270 CFG0_OLDI1_DAT3_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.271 CFG0_OLDI1_CLK_IO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.272 CFG0_OLDI_PD_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.273 CFG0_OLDI_LB_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.274 CFG0_LOCK2_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.275 CFG0_LOCK2_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.276 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.277 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.278 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.279 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.280 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.281 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.282 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.283 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.284 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.285 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R9 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.286 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R10 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.287 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R11 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.288 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R12 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.289 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R13 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.290 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R14 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.291 CFG0_MAIN_PLL_TEST_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.292 CFG0_LOCK4_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.293 CFG0_LOCK4_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.294 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.295 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.296 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.297 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.298 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.299 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.300 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.301 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.302 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.303 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R9_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.304 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R10_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.305 CFG0_MAIN_PLL_TEST_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.306 CFG0_LOCK4_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.307 CFG0_LOCK4_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.308 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.309 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.310 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.311 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.312 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.313 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.314 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.315 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.316 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.317 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R9 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.318 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R10 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.319 CFG0_LOCK6_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.320 CFG0_LOCK6_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.321 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.322 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.323 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.324 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.325 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.326 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.327 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.328 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.329 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.330 CFG0_LOCK6_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.331 CFG0_LOCK6_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.332 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.333 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.334 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.335 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.336 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.337 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.338 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.339 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.340 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.341 CFG0_IPC_SET0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.342 CFG0_IPC_CLR0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.343 CFG0_CBA_ERR_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.344 CFG0_ACCESS_ERR_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.345 CFG0_IPC_SET0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.346 CFG0_IPC_CLR0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.347 CFG0_CBA_ERR_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.348 CFG0_ACCESS_ERR_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.349 CFG0_MCU_GPIO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.350 CFG0_TEMP_DIODE_TRIM Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.351 CFG0_IO_VOLTAGE_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.352 CFG0_MCU_TIMER1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.353 CFG0_MCU_TIMER3_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.354 CFG0_MCU_I2C0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.355 CFG0_MAIN_MTOG_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.356 CFG0_WKUP_MTOG_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.357 CFG0_TOG_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.358 CFG0_MCU_GPIO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.359 CFG0_TEMP_DIODE_TRIM_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.360 CFG0_IO_VOLTAGE_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.361 CFG0_MCU_TIMER1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.362 CFG0_MCU_TIMER3_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.363 CFG0_MCU_I2C0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.364 CFG0_MAIN_MTOG_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.365 CFG0_WKUP_MTOG_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.366 CFG0_TOG_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.367 CFG0_MCU_OBSCLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.368 CFG0_HFOSC0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.369 CFG0_HFOSC0_TRIM Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.370 CFG0_HFOSC0_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.371 CFG0_RC12M_OSC_TRIM Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.372 CFG0_HFOSC0_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.373 CFG0_LFXOSC_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.374 CFG0_LFXOSC_TRIM Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.375 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.376 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS_SYSTICK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.377 CFG0_MCU_PLL_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.378 CFG0_DEVICE_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.379 CFG0_MCU_TIMER0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.380 CFG0_MCU_TIMER1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.381 CFG0_MCU_TIMER2_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.382 CFG0_MCU_TIMER3_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.383 CFG0_MCU_GPIO_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.384 CFG0_MCU_MCAN0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.385 CFG0_MCU_MCAN1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.386 CFG0_MCU_SPI0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.387 CFG0_MCU_SPI1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.388 CFG0_MCU_WWD0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.389 CFG0_MCU_OBSCLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.390 CFG0_HFOSC0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.391 CFG0_HFOSC0_TRIM_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.392 CFG0_HFOSC0_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.393 CFG0_RC12M_OSC_TRIM_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.394 CFG0_HFOSC0_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.395 CFG0_LFXOSC_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.396 CFG0_LFXOSC_TRIM_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.397 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.398 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS_SYSTICK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.399 CFG0_MCU_PLL_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.400 CFG0_DEVICE_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.401 CFG0_MCU_TIMER0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.402 CFG0_MCU_TIMER1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.403 CFG0_MCU_TIMER2_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.404 CFG0_MCU_TIMER3_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.405 CFG0_MCU_GPIO_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.406 CFG0_MCU_MCAN0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.407 CFG0_MCU_MCAN1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.408 CFG0_MCU_SPI0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.409 CFG0_MCU_SPI1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.410 CFG0_MCU_WWD0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.411 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.412 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_PATCOUNT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.413 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SEED0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.414 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SEED1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.415 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SPARE0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.416 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SPARE1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.417 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.418 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_MISR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.419 CFG0_LOCK3_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.420 CFG0_LOCK3_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.421 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.422 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.423 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_PATCOUNT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.424 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SEED0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.425 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SEED1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.426 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SPARE0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.427 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SPARE1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.428 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.429 CFG0_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_MISR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.430 CFG0_LOCK3_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.431 CFG0_LOCK3_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.432 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.433 CFG0_OLDI_PD_CTRL_TEST_REG Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.434 CFG0_PBIST_EN_TEST_REG Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.435 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R11_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.436 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R12_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.437 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R13_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.438 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R14_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.439 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R15_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.440 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R16_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.441 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R17_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.442 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R18_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.443 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R19_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.444 CFG0_OLDI_PD_CTRL_TEST_REG_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.445 CFG0_PBIST_EN_TEST_REG_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.446 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R11 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.447 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R12 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.448 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R13 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.449 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R14 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.450 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R15 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.451 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R16 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.452 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R17 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.453 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R18 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.454 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R19 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.455 CFG0_POR_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.456 CFG0_POR_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.457 CFG0_POR_BANDGAP_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.458 CFG0_POK_VDDA_MCU_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.459 CFG0_POK_VDDA_MCU_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.460 CFG0_POK_VDD_CORE_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.461 CFG0_POK_VDD_CORE_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.462 CFG0_POK_VDDR_CORE_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.463 CFG0_POK_VDDR_CORE_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.464 CFG0_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.465 CFG0_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.466 CFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.467 CFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.468 CFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.469 CFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.470 CFG0_POK_VDDS_DDRIO_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.471 CFG0_POK_VDDS_DDRIO_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.472 CFG0_POK_VDDA_PMIC_IN_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.473 CFG0_RST_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.474 CFG0_RST_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.475 CFG0_RST_SRC Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.476 CFG0_RST_MAGIC_WORD Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.477 CFG0_ISO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.478 CFG0_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.479 CFG0_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.480 CFG0_PRG_PP_0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.481 CFG0_PRG_PP_1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.482 CFG0_CLKGATE_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.483 CFG0_LVDS_BANDGAP_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.484 CFG0_POR_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.485 CFG0_POR_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.486 CFG0_POR_BANDGAP_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.487 CFG0_POK_VDDA_MCU_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.488 CFG0_POK_VDDA_MCU_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.489 CFG0_POK_VDD_CORE_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.490 CFG0_POK_VDD_CORE_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.491 CFG0_POK_VDDR_CORE_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.492 CFG0_POK_VDDR_CORE_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.493 CFG0_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.494 CFG0_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.495 CFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.496 CFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.497 CFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.498 CFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.499 CFG0_POK_VDDS_DDRIO_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.500 CFG0_POK_VDDS_DDRIO_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.501 CFG0_POK_VDDA_PMIC_IN_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.502 CFG0_RST_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.503 CFG0_RST_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.504 CFG0_RST_SRC_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.505 CFG0_RST_MAGIC_WORD_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.506 CFG0_ISO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.507 CFG0_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.508 CFG0_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.509 CFG0_PRG_PP_0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.510 CFG0_PRG_PP_1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.511 CFG0_CLKGATE_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.512 CFG0_LVDS_BANDGAP_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.513 CFG0_JTAGID Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.514 CFG0_JTAG_USER_ID Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.515 CFG0_MAIN_DEVSTAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.516 CFG0_MAIN_BOOTCFG Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.517 CFG0_BOOT_PROGRESS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.518 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.519 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.520 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.521 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.522 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.523 CFG0_MAC_ID0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.524 CFG0_MAC_ID1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.525 CFG0_USB_DEVICE_ID0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.526 CFG0_USB_DEVICE_ID1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.527 CFG0_GP_SW0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.528 CFG0_GP_SW1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.529 CFG0_GP_SW2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.530 CFG0_GP_SW3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.531 CFG0_JTAGID_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.532 CFG0_JTAG_USER_ID_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.533 CFG0_MAIN_DEVSTAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.534 CFG0_MAIN_BOOTCFG_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.535 CFG0_BOOT_PROGRESS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.536 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.537 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.538 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE2_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.539 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE3_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.540 CFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE6_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.541 CFG0_MAC_ID0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.542 CFG0_MAC_ID1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.543 CFG0_USB_DEVICE_ID0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.544 CFG0_USB_DEVICE_ID1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.545 CFG0_GP_SW0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.546 CFG0_GP_SW1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.547 CFG0_GP_SW2_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.548 CFG0_GP_SW3_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.549 CFG0_USB0_PHY_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.550 CFG0_USB1_PHY_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.551 CFG0_SDIO0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.552 CFG0_SDIO1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.553 CFG0_SDIO2_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.554 CFG0_WKUP_TIMER1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.555 CFG0_WKUP_I2C0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.556 CFG0_USB0_PHY_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.557 CFG0_USB1_PHY_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.558 CFG0_SDIO0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.559 CFG0_SDIO1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.560 CFG0_SDIO2_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.561 CFG0_WKUP_TIMER1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.562 CFG0_WKUP_I2C0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.563 CFG0_WKUP_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.564 CFG0_WKUP_GTC_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.565 CFG0_EFUSE_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.566 CFG0_DDR16SS_PMCTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.567 CFG0_USB0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.568 CFG0_USB1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.569 CFG0_WKUP_TIMER0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.570 CFG0_WKUP_TIMER1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.571 CFG0_WKUP_WWD0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.572 CFG0_WKUP_WWD0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.573 CFG0_WKUP_RTC_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.574 CFG0_WKUP_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.575 CFG0_WKUP_GTC_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.576 CFG0_EFUSE_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.577 CFG0_DDR16SS_PMCTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.578 CFG0_USB0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.579 CFG0_USB1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.580 CFG0_WKUP_TIMER0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.581 CFG0_WKUP_TIMER1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.582 CFG0_WKUP_WWD0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.583 CFG0_WKUP_WWD0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.584 CFG0_WKUP_RTC_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.585 CFG0_FUSE_CRC_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.586 CFG0_CHAIN1_CRC_CALC Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.587 CFG0_CHAIN2_CRC_CALC Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.588 CFG0_CHAIN1_CRC_CALC_RO Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.589 CFG0_CHAIN2_CRC_CALC_RO Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.590 CFG0_PBIST_EN Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.591 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.592 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.593 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.594 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.595 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.596 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.597 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.598 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.599 CFG0_FUSE_CRC_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.600 CFG0_CHAIN1_CRC_CALC_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.601 CFG0_CHAIN2_CRC_CALC_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.602 CFG0_CHAIN1_CRC_CALC_RO_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.603 CFG0_CHAIN2_CRC_CALC_RO_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.604 CFG0_PBIST_EN_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.605 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.606 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.607 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.608 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.609 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.610 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.611 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.612 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.613 CFG0_DV_REG32 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.614 CFG0_DV_REG33 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.615 CFG0_DV_REG32_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.616 CFG0_DV_REG33_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.617 CFG0_CHNG_DDR4_FSP_REQ Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.618 CFG0_CHNG_DDR4_FSP_ACK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.619 CFG0_DDR4_FSP_CLKCHNG_REQ Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.620 CFG0_DDR4_FSP_CLKCHNG_ACK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.621 CFG0_LOCK5_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.622 CFG0_LOCK5_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.623 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P5_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.624 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P5_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.625 CFG0_CHNG_DDR4_FSP_REQ_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.626 CFG0_CHNG_DDR4_FSP_ACK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.627 CFG0_DDR4_FSP_CLKCHNG_REQ_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.628 CFG0_DDR4_FSP_CLKCHNG_ACK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.629 CFG0_LOCK5_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.630 CFG0_LOCK5_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.631 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P5_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.632 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P5_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.633 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.634 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT0_SET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.635 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT0_CLR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.636 CFG0_FW_STS_IN0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.637 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.638 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT1_SET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.639 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT1_CLR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.640 CFG0_FW_STS_IN1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.641 CFG0_PMCTRL_SYS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.642 CFG0_PMCTRL_IO_0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.643 CFG0_PMCTRL_IO_1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.644 CFG0_PMCTRL_MOSC Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.645 CFG0_PM_MISC_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.646 CFG0_PMCTRL_IO_GLB Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.647 CFG0_PM_PERMISSION Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.648 CFG0_DEEPSLEEP_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.649 CFG0_WKUP0_EN Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.650 CFG0_CANUART_WAKE_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.651 CFG0_CANUART_WAKE_STAT0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.652 CFG0_CANUART_WAKE_STAT1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.653 CFG0_WFI_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.654 CFG0_DS_MAGIC_WORD Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.655 CFG0_DS_MAIN Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.656 CFG0_DS_DM_RESET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.657 CFG0_DS_DDR0_RESET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.658 CFG0_DS_USB0_RESET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.659 CFG0_DS_USB1_RESET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.660 CFG0_DM_CLKSTOP_EN Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.661 CFG0_DM_CLKSTOP_ACK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.662 CFG0_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_REQ Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.663 CFG0_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_ACK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.664 CFG0_DEVICE_TYPE Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.665 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R9_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.666 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R10_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.667 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.668 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT0_SET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.669 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT0_CLR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.670 CFG0_FW_STS_IN0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.671 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.672 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT1_SET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.673 CFG0_FW_CTRL_OUT1_CLR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.674 CFG0_FW_STS_IN1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.675 CFG0_PMCTRL_SYS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.676 CFG0_PMCTRL_IO_0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.677 CFG0_PMCTRL_IO_1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.678 CFG0_PMCTRL_MOSC_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.679 CFG0_PM_MISC_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.680 CFG0_PMCTRL_IO_GLB_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.681 CFG0_PM_PERMISSION_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.682 CFG0_DEEPSLEEP_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.683 CFG0_WKUP0_EN_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.684 CFG0_CANUART_WAKE_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.685 CFG0_CANUART_WAKE_STAT0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.686 CFG0_CANUART_WAKE_STAT1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.687 CFG0_WFI_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.688 CFG0_DS_MAGIC_WORD_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.689 CFG0_DS_MAIN_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.690 CFG0_DS_DM_RESET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.691 CFG0_DS_DDR0_RESET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.692 CFG0_DS_USB0_RESET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.693 CFG0_DS_USB1_RESET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.694 CFG0_DM_CLKSTOP_EN_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.695 CFG0_DM_CLKSTOP_ACK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.696 CFG0_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_REQ_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.697 CFG0_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_ACK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.698 CFG0_DEVICE_TYPE_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.699 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R9 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.700 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R10 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.701 CFG0_BACKUP_REG_N Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.702 CFG0_LOCK7_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.703 CFG0_LOCK7_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.704 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.705 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.706 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.707 CFG0_BACKUP_REG_PROXY_N Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.708 CFG0_LOCK7_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.709 CFG0_LOCK7_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.710 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.711 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.712 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.713 Access Table
- 14.2.1.1.2
MCU_CTRL_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.1 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_PID Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.2 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MMR_CFG1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.3 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_IPC_SET0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.4 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_IPC_CLR0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.5 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CBA_ERR_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.6 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_ACCESS_ERR_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.7 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK0_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.8 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK0_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.9 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_INTR_RAW_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.10 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.11 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLE Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.12 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.13 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_EOI Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.14 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_ADDRESS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.15 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.16 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.17 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.18 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.19 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.20 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.21 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.22 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.23 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.24 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_PID_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.25 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.26 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_IPC_SET0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.27 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_IPC_CLR0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.28 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CBA_ERR_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.29 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_ACCESS_ERR_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.30 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.31 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.32 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.33 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.34 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.35 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.36 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_EOI_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.37 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.38 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.39 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.40 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.41 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.42 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.43 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.44 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.45 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.46 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.47 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_GPIO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.48 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.49 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.50 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.51 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.52 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.53 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.54 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_TEMP_DIODE_TRIM Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.55 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_IO_VOLTAGE_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.56 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.57 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER3_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.58 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_I2C0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.59 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MAIN_MTOG_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.60 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_MTOG_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.61 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_TOG_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.62 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK1_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.63 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK1_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.64 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.65 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.66 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.67 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.68 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.69 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.70 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.71 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.72 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.73 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R9_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.74 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R10_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.75 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R11_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.76 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R12_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.77 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_GPIO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.78 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.79 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG2_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.80 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG3_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.81 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG4_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.82 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG5_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.83 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DBOUNCE_CFG6_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.84 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_TEMP_DIODE_TRIM_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.85 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_IO_VOLTAGE_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.86 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.87 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER3_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.88 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_I2C0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.89 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MAIN_MTOG_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.90 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_MTOG_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.91 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_TOG_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.92 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.93 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.94 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.95 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.96 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.97 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.98 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.99 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.100 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.101 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.102 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.103 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R9 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.104 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R10 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.105 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R11 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.106 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R12 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.107 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_OBSCLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.108 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_HFOSC0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.109 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_HFOSC0_TRIM Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.110 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_HFOSC0_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.111 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RC12M_OSC_TRIM Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.112 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_HFOSC0_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.113 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LFXOSC_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.114 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LFXOSC_TRIM Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.115 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.116 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS_SYSTICK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.117 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_PLL_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.118 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.119 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.120 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.121 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER2_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.122 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER3_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.123 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_GPIO_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.124 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_MCAN0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.125 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_MCAN1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.126 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_SPI0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.127 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_SPI1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.128 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_WWD0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.129 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK2_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.130 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK2_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.131 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.132 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.133 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_OBSCLK_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.134 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_HFOSC0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.135 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_HFOSC0_TRIM_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.136 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_HFOSC0_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.137 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RC12M_OSC_TRIM_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.138 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_HFOSC0_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.139 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LFXOSC_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.140 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LFXOSC_TRIM_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.141 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.142 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS_SYSTICK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.143 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_PLL_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.144 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.145 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.146 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.147 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER2_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.148 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_TIMER3_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.149 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_GPIO_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.150 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_MCAN0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.151 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_MCAN1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.152 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_SPI0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.153 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_SPI1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.154 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_WWD0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.155 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK2_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.156 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK2_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.157 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.158 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.159 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.160 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_PATCOUNT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.161 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SEED0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.162 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SEED1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.163 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SPARE0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.164 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SPARE1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.165 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.166 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_MISR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.167 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK3_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.168 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK3_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.169 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.170 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.171 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_PATCOUNT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.172 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SEED0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.173 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SEED1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.174 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SPARE0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.175 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_SPARE1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.176 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.177 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_MCU_M4FSS0_LBIST_MISR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.178 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK3_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.179 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK3_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.180 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.181 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DV_REG4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.182 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DV_REG5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.183 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_OLDI_PD_CTRL_TEST_REG Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.184 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_PBIST_EN_TEST_REG Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.185 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK4_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.186 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK4_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.187 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.188 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.189 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.190 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.191 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.192 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.193 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.194 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.195 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.196 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R9_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.197 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R10_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.198 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R11_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.199 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R12_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.200 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R13_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.201 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R14_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.202 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R15_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.203 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R16_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.204 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R17_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.205 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R18_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.206 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R19_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.207 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DV_REG4_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.208 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_DV_REG5_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.209 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_OLDI_PD_CTRL_TEST_REG_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.210 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_PBIST_EN_TEST_REG_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.211 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK4_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.212 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK4_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.213 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.214 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.215 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.216 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.217 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.218 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.219 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.220 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.221 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.222 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R9 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.223 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R10 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.224 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R11 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.225 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R12 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.226 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R13 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.227 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R14 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.228 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R15 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.229 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R16 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.230 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R17 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.231 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R18 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.232 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R19 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.233 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POR_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.234 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POR_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.235 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POR_BANDGAP_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.236 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDA_MCU_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.237 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDA_MCU_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.238 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDD_CORE_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.239 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDD_CORE_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.240 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDR_CORE_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.241 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDR_CORE_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.242 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.243 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.244 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.245 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.246 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.247 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.248 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDS_DDRIO_UV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.249 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDS_DDRIO_OV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.250 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDA_PMIC_IN_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.251 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RST_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.252 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RST_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.253 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RST_SRC Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.254 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RST_MAGIC_WORD Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.255 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_ISO_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.256 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.257 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.258 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_PRG_PP_0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.259 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_PRG_PP_1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.260 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLKGATE_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.261 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LVDS_BANDGAP_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.262 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK6_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.263 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK6_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.264 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.265 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.266 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.267 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.268 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.269 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.270 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.271 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POR_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.272 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POR_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.273 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POR_BANDGAP_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.274 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDA_MCU_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.275 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDA_MCU_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.276 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDD_CORE_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.277 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDD_CORE_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.278 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDR_CORE_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.279 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDR_CORE_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.280 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.281 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.282 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.283 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.284 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.285 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.286 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDS_DDRIO_UV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.287 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDS_DDRIO_OV_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.288 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_POK_VDDA_PMIC_IN_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.289 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RST_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.290 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RST_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.291 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RST_SRC_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.292 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_RST_MAGIC_WORD_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.293 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_ISO_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.294 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.295 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.296 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_PRG_PP_0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.297 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_PRG_PP_1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.298 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLKGATE_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.299 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LVDS_BANDGAP_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.300 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK6_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.301 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_LOCK6_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.302 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.303 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.304 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.305 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.306 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.307 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.308 CFG0_MCU_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.2.309 Access Table
- 14.2.1.1.3
WKUP_CTRL_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.1 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PID Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.2 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MMR_CFG1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.3 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_JTAGID Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.4 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_JTAG_USER_ID Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.5 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MAIN_DEVSTAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.6 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MAIN_BOOTCFG Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.7 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_BOOT_PROGRESS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.8 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.9 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.10 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.11 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.12 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.13 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MAC_ID0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.14 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MAC_ID1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.15 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB_DEVICE_ID0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.16 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB_DEVICE_ID1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.17 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_GP_SW0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.18 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_GP_SW1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.19 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_GP_SW2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.20 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_GP_SW3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.21 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CBA_ERR_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.22 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_ACCESS_ERR_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.23 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK0_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.24 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK0_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.25 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_INTR_RAW_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.26 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.27 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLE Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.28 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.29 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_EOI Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.30 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_ADDRESS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.31 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.32 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.33 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.34 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.35 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.36 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.37 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.38 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.39 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.40 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.41 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PID_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.42 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.43 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_JTAGID_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.44 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_JTAG_USER_ID_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.45 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MAIN_DEVSTAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.46 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MAIN_BOOTCFG_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.47 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_BOOT_PROGRESS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.48 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.49 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.50 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE2_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.51 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE3_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.52 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_FEATURE6_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.53 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MAC_ID0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.54 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_MAC_ID1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.55 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB_DEVICE_ID0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.56 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB_DEVICE_ID1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.57 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_GP_SW0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.58 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_GP_SW1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.59 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_GP_SW2_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.60 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_GP_SW3_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.61 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CBA_ERR_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.62 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_ACCESS_ERR_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.63 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.64 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.65 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.66 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.67 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.68 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.69 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_EOI_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.70 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.71 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.72 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.73 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.74 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.75 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.76 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.77 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.78 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.79 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.80 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P0_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.81 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB0_PHY_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.82 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB1_PHY_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.83 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_SDIO0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.84 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_SDIO1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.85 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_SDIO2_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.86 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_TIMER1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.87 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_I2C0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.88 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_TOG_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.89 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK1_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.90 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK1_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.91 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.92 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.93 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.94 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.95 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.96 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.97 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.98 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.99 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.100 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R9_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.101 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R10_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.102 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R11_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.103 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R12_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.104 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB0_PHY_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.105 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB1_PHY_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.106 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_SDIO0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.107 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_SDIO1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.108 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_SDIO2_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.109 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_TIMER1_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.110 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_I2C0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.111 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_TOG_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.112 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.113 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.114 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.115 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.116 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.117 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.118 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.119 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.120 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.121 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.122 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.123 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R9 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.124 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R10 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.125 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R11 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.126 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P1_R12 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.127 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.128 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLKOUT_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.129 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_GTC_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.130 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_EFUSE_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.131 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DDR16SS_PMCTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.132 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.133 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.134 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_TIMER0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.135 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_TIMER1_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.136 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_WWD0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.137 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_WWD0_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.138 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_RTC_CLKSEL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.139 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK2_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.140 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK2_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.141 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.142 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.143 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.144 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.145 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.146 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.147 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.148 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.149 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.150 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R9_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.151 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R10_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.152 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R11_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.153 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R12_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.154 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.155 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLKOUT_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.156 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_GTC_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.157 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_EFUSE_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.158 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DDR16SS_PMCTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.159 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.160 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_USB1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.161 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_TIMER0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.162 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_TIMER1_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.163 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_WWD0_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.164 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_WWD0_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.165 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP_RTC_CLKSEL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.166 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK2_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.167 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK2_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.168 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.169 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.170 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.171 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.172 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.173 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.174 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.175 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.176 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.177 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R9 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.178 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R10 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.179 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R11 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.180 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P2_R12 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.181 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FUSE_CRC_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.182 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHAIN1_CRC_CALC Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.183 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHAIN2_CRC_CALC Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.184 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHAIN1_CRC_CALC_RO Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.185 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHAIN2_CRC_CALC_RO Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.186 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PBIST_EN Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.187 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK3_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.188 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK3_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.189 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.190 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.191 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.192 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.193 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.194 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.195 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.196 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.197 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.198 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FUSE_CRC_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.199 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHAIN1_CRC_CALC_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.200 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHAIN2_CRC_CALC_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.201 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHAIN1_CRC_CALC_RO_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.202 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHAIN2_CRC_CALC_RO_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.203 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PBIST_EN_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.204 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK3_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.205 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK3_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.206 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.207 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.208 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.209 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.210 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.211 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.212 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.213 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.214 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P3_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.215 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DV_REG32 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.216 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DV_REG33 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.217 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK4_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.218 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK4_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.219 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.220 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.221 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.222 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.223 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.224 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.225 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.226 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.227 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.228 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DV_REG32_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.229 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DV_REG33_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.230 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK4_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.231 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK4_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.232 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.233 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.234 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.235 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.236 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.237 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.238 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.239 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.240 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P4_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.241 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHNG_DDR4_FSP_REQ Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.242 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHNG_DDR4_FSP_ACK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.243 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DDR4_FSP_CLKCHNG_REQ Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.244 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DDR4_FSP_CLKCHNG_ACK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.245 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK5_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.246 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK5_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.247 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P5_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.248 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P5_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.249 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHNG_DDR4_FSP_REQ_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.250 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CHNG_DDR4_FSP_ACK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.251 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DDR4_FSP_CLKCHNG_REQ_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.252 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DDR4_FSP_CLKCHNG_ACK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.253 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK5_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.254 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK5_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.255 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P5_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.256 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P5_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.257 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.258 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT0_SET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.259 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT0_CLR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.260 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_STS_IN0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.261 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.262 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT1_SET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.263 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT1_CLR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.264 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_STS_IN1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.265 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_SYS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.266 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_IO_0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.267 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_IO_1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.268 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_MOSC Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.269 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PM_MISC_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.270 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_IO_GLB Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.271 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PM_PERMISSION Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.272 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEEPSLEEP_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.273 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_RST_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.274 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_RST_STAT Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.275 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_RST_SRC Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.276 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_RST_MAGIC_WORD Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.277 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP0_EN Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.278 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLKGATE_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.279 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CANUART_WAKE_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.280 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CANUART_WAKE_STAT0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.281 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CANUART_WAKE_STAT1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.282 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WFI_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.283 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_SLEEP_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.284 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_MAGIC_WORD Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.285 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_MAIN Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.286 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_DM_RESET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.287 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_DDR0_RESET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.288 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_USB0_RESET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.289 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_USB1_RESET Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.290 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DM_CLKSTOP_EN Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.291 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DM_CLKSTOP_ACK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.292 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_REQ Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.293 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_ACK Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.294 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_TYPE Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.295 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK6_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.296 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK6_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.297 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.298 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.299 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.300 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.301 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.302 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.303 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R6_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.304 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R7_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.305 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R8_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.306 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R9_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.307 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R10_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.308 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.309 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT0_SET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.310 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT0_CLR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.311 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_STS_IN0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.312 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.313 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT1_SET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.314 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_CTRL_OUT1_CLR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.315 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_FW_STS_IN1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.316 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_SYS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.317 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_IO_0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.318 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_IO_1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.319 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_MOSC_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.320 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PM_MISC_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.321 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PMCTRL_IO_GLB_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.322 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_PM_PERMISSION_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.323 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEEPSLEEP_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.324 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_RST_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.325 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_RST_STAT_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.326 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_RST_SRC_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.327 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_RST_MAGIC_WORD_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.328 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WKUP0_EN_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.329 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLKGATE_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.330 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CANUART_WAKE_CTRL_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.331 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CANUART_WAKE_STAT0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.332 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CANUART_WAKE_STAT1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.333 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_WFI_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.334 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_SLEEP_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.335 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_MAGIC_WORD_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.336 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_MAIN_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.337 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_DM_RESET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.338 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_DDR0_RESET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.339 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_USB0_RESET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.340 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DS_USB1_RESET_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.341 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DM_CLKSTOP_EN_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.342 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DM_CLKSTOP_ACK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.343 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_REQ_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.344 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_ACK_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.345 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_DEVICE_TYPE_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.346 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK6_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.347 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK6_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.348 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.349 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.350 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.351 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.352 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.353 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.354 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R6 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.355 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R7 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.356 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R8 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.357 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R9 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.358 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P6_R10 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.359 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_BACKUP_REG Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.360 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK7_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.361 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK7_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.362 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P7_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.363 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P7_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.364 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P7_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.365 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_BACKUP_REG_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.366 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK7_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.367 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_LOCK7_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.368 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P7_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.369 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P7_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.370 CFG0_WKUP_CTRL_MMR_CLAIMREG_P7_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.3.371 Access Table
- 14.2.1.1.1
CTRL_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.2
Pad Configuration Registers
- 14.2.1.2.1 Pad Configuration Register Functional Description
- 14.2.1.2.2 Pad Configuration PADCONFIG Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3
Pad Configuration Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1
PADCFG_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.1 CFG0_PID Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.2 CFG0_MMR_CFG0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.3 CFG0_MMR_CFG1 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.4 CFG0_LOCK0_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.5 CFG0_LOCK0_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.6 CFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.7 CFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.8 CFG0_INTR_ENABLE Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.9 CFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.10 CFG0_EOI Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.11 CFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.12 CFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.13 CFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.14 CFG0_FAULT_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.15 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.16 CFG0_PID_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.17 CFG0_MMR_CFG0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.18 CFG0_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.19 CFG0_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.20 CFG0_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.21 CFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.22 CFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.23 CFG0_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.24 CFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.25 CFG0_EOI_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.26 CFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.27 CFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.28 CFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.29 CFG0_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.30 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.31 CFG0_LOCK1_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.32 CFG0_LOCK1_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.33 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.34 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.35 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.36 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.37 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.38 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.39 CFG0_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.40 CFG0_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.41 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.42 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.43 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.44 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.45 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.46 CFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.1.47 Access Table
- 14.2.1.2.3.2
WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.1 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_PID Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.2 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_MMR_CFG0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.3 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_MMR_CFG1 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.4 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_LOCK0_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.5 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_LOCK0_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.6 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_INTR_RAW_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.7 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.8 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_INTR_ENABLE Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.9 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.10 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_EOI Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.11 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_FAULT_ADDRESS Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.12 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.13 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.14 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_FAULT_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.15 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.16 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_PID_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.17 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_MMR_CFG0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.18 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.19 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.20 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.21 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.22 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.23 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.24 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.25 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_EOI_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.26 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.27 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.28 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.29 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.30 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.31 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_LOCK1_KICK0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.32 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_LOCK1_KICK1 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.33 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.34 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_CLAIMREG_P1_R1_READONLY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.35 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.36 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.37 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.38 CFG0_WKUP_PADCFG_CTRL_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Registers
- 14.2.1.2.3.2.39 Access Table
- 14.2.1.2.3.1
PADCFG_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.3 Kick Protection Registers
- 14.2.1.4
Security Control Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1
MAIN_SEC_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.1 CFG2_CLSTR9_CORE0_DBG_CFG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.2 CFG2_CLSTR9_CORE1_DBG_CFG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.3 CFG2_CLSTR9_CORE2_DBG_CFG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.4 CFG2_CLSTR9_CORE3_DBG_CFG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.5 CFG2_CLSTR16_CORE0_DBG_CFG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.6 CFG0_PID Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.7 CFG0_CLSTR9_DEF Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.8 CFG0_CLSTR9_CFG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.9 CFG0_CLSTR9_PMCTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.10 CFG0_CLSTR9_PMSTAT Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.11 CFG0_CLSTR9_CORE0_BOOTVECT_LO Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.12 CFG0_CLSTR9_CORE0_BOOTVECT_HI Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.13 CFG0_CLSTR9_CORE1_BOOTVECT_LO Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.14 CFG0_CLSTR9_CORE1_BOOTVECT_HI Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.15 CFG0_CLSTR9_CORE2_BOOTVECT_LO Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.16 CFG0_CLSTR9_CORE2_BOOTVECT_HI Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.17 CFG0_CLSTR9_CORE3_BOOTVECT_LO Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.18 CFG0_CLSTR9_CORE3_BOOTVECT_HI Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.19 CFG0_CLSTR16_DEF Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.20 CFG0_CLSTR16_CORE0_PMSTAT Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.21 CFG0_GIC_CONFIG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.1.22 Access Table
- 14.2.1.4.2
WKUP_SEC_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.1 CFG2_CLSTR28_CORE0_DBG_CFG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.2 CFG0_PID Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.3 CFG0_CLSTR28_DEF Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.4 CFG0_CLSTR28_CFG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.5 CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_CFG Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.6 CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_BOOTVECT_LO Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.7 CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_BOOTVECT_HI Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.8 CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_PMCTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.9 CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_PMSTAT Registers
- 14.2.1.4.2.10 Access Table
- 14.2.1.4.1
MAIN_SEC_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.1
General Purpose Control Registers
- 14.2.2
Power Registers
- 14.2.2.1
PSC Registers
- 14.2.2.1.1 _PSC_PID Registers
- 14.2.2.1.2 _PSC_GBLCTL Registers
- 14.2.2.1.3 _PSC_GBLSTAT Registers
- 14.2.2.1.4 _PSC_INTEVAL Registers
- 14.2.2.1.5 _PSC_MERRPR_N Registers
- 14.2.2.1.6 _PSC_MERRCR_N Registers
- 14.2.2.1.7 _PSC_PERRPR Registers
- 14.2.2.1.8 _PSC_PERRCR Registers
- 14.2.2.1.9 _PSC_EPCPR Registers
- 14.2.2.1.10 _PSC_EPCCR Registers
- 14.2.2.1.11 _PSC_RAILSTAT Registers
- 14.2.2.1.12 _PSC_RAILCTL Registers
- 14.2.2.1.13 _PSC_RAILSEL Registers
- 14.2.2.1.14 _PSC_PTCMD Registers
- 14.2.2.1.15 _PSC_PTSTAT Registers
- 14.2.2.1.16 _PSC_PDSTAT_N Registers
- 14.2.2.1.17 _PSC_PDCTL_N Registers
- 14.2.2.1.18 _PSC_PDCFG_N Registers
- 14.2.2.1.19 _PSC_MDCFG_N Registers
- 14.2.2.1.20 _PSC_MDSTAT_N Registers
- 14.2.2.1.21 _PSC_MDCTL_N Registers
- 14.2.2.1.22 Access Table
- 14.2.2.2
PSC_FW_0 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.1 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_0_CH_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.2.2.2.2 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_0_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.3 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_0_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.4 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_0_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.5 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_1_CH_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.2.2.2.6 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_1_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.7 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_1_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.8 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_1_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.9 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_2_CH_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.2.2.2.10 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_2_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.11 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_2_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.12 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_2_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.13 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_3_CH_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.2.2.2.14 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_3_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.15 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_3_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.16 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_3_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.17 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_4_CH_0_CONTROL Registers
- 14.2.2.2.18 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_4_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.19 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_4_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.20 FW_DST_FWCH_REGION_4_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.21 GLB_PID Registers
- 14.2.2.2.22 GLB_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.2.2.2.23 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Registers
- 14.2.2.2.24 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.25 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.26 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.27 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.28 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.29 GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.2.2.2.30 GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Registers
- 14.2.2.2.31 GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Registers
- 14.2.2.2.32 Access Table
- 14.2.2.3
VTM Registers
- 14.2.2.3.1 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_PID Registers
- 14.2.2.3.2 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_DEVINFO_PWR0 Registers
- 14.2.2.3.3 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_GT_TH1_INT_RAW_STAT_SET Registers
- 14.2.2.3.4 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_GT_TH1_INT_EN_STAT_CLR Registers
- 14.2.2.3.5 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_GT_TH1_INT_EN_SET Registers
- 14.2.2.3.6 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_GT_TH1_INT_EN_CLR Registers
- 14.2.2.3.7 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_GT_TH2_INT_RAW_STAT_SET Registers
- 14.2.2.3.8 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_GT_TH2_INT_EN_STAT_CLR Registers
- 14.2.2.3.9 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_GT_TH2_INT_EN_SET Registers
- 14.2.2.3.10 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_GT_TH2_INT_EN_CLR Registers
- 14.2.2.3.11 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_LT_TH0_INT_RAW_STAT_SET Registers
- 14.2.2.3.12 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_LT_TH0_INT_EN_STAT_CLR Registers
- 14.2.2.3.13 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_LT_TH0_INT_EN_SET Registers
- 14.2.2.3.14 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_LT_TH0_INT_EN_CLR Registers
- 14.2.2.3.15 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_VD_VTM_VD_DEVINFO_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.16 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_VD_VTM_VD_OPPVID_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.17 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_VD_VTM_VD_EVT_STAT_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.18 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_VD_VTM_VD_EVT_SEL_SET_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.19 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_VD_VTM_VD_EVT_SEL_CLR_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.20 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_TMPSENS_VTM_TMPSENS_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.21 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_TMPSENS_VTM_TMPSENS_STAT_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.22 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_TMPSENS_VTM_TMPSENS_TH_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.23 MMR_VBUSP_CFG1_VTM_TMPSENS_VTM_TMPSENS_TH2_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.24 MMR_VBUSP_CFG2_VTM_CLK_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.2.3.25 MMR_VBUSP_CFG2_VTM_MISC_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.2.3.26 MMR_VBUSP_CFG2_VTM_MISC_CTRL2 Registers
- 14.2.2.3.27 MMR_VBUSP_CFG2_VTM_SAMPLE_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.2.3.28 MMR_VBUSP_CFG2_VTM_TMPSENS_VTM_TMPSENS_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.29 MMR_VBUSP_CFG2_VTM_TMPSENS_VTM_TMPSENS_TRIM_J_J Registers
- 14.2.2.3.30 ECCAGGR_CFG_REV Registers
- 14.2.2.3.31 ECCAGGR_CFG_VECTOR Registers
- 14.2.2.3.32 ECCAGGR_CFG_STAT Registers
- 14.2.2.3.33 ECCAGGR_CFG_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.2.2.3.34 ECCAGGR_CFG_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.2.2.3.35 ECCAGGR_CFG_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.2.2.3.36 ECCAGGR_CFG_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.2.2.3.37 ECCAGGR_CFG_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.2.2.3.38 ECCAGGR_CFG_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.2.2.3.39 ECCAGGR_CFG_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.2.2.3.40 ECCAGGR_CFG_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.2.2.3.41 ECCAGGR_CFG_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.2.2.3.42 ECCAGGR_CFG_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.2.2.3.43 ECCAGGR_CFG_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.2.2.3.44 ECCAGGR_CFG_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.2.2.3.45 ECCAGGR_CFG_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.2.2.3.46 Access Table
- 14.2.2.1
PSC Registers
- 14.2.3
Clocking Registers
- 14.2.3.1
PLL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.1 CFG_PLL0_PID Registers
- 14.2.3.1.2 CFG_PLL0_CFG Registers
- 14.2.3.1.3 CFG_PLL0_LOCKKEY0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.4 CFG_PLL0_LOCKKEY1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.5 CFG_PLL0_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.6 CFG_PLL0_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.7 CFG_PLL0_FREQ_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.8 CFG_PLL0_FREQ_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.9 CFG_PLL0_DIV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.10 CFG_PLL0_SS_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.11 CFG_PLL0_SS_SPREAD Registers
- 14.2.3.1.12 CFG_PLL0_CAL_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.13 CFG_PLL0_CAL_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.14 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.15 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.16 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL2 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.17 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL3 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.18 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL4 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.19 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL5 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.20 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL6 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.21 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL7 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.22 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL8 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.23 CFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL9 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.24 CFG_PLL1_PID Registers
- 14.2.3.1.25 CFG_PLL1_CFG Registers
- 14.2.3.1.26 CFG_PLL1_LOCKKEY0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.27 CFG_PLL1_LOCKKEY1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.28 CFG_PLL1_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.29 CFG_PLL1_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.30 CFG_PLL1_FREQ_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.31 CFG_PLL1_FREQ_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.32 CFG_PLL1_DIV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.33 CFG_PLL1_SS_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.34 CFG_PLL1_SS_SPREAD Registers
- 14.2.3.1.35 CFG_PLL1_CAL_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.36 CFG_PLL1_CAL_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.37 CFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.38 CFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.39 CFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL2 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.40 CFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL3 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.41 CFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL4 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.42 CFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL5 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.43 CFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL6 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.44 CFG_PLL2_PID Registers
- 14.2.3.1.45 CFG_PLL2_CFG Registers
- 14.2.3.1.46 CFG_PLL2_LOCKKEY0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.47 CFG_PLL2_LOCKKEY1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.48 CFG_PLL2_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.49 CFG_PLL2_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.50 CFG_PLL2_FREQ_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.51 CFG_PLL2_FREQ_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.52 CFG_PLL2_DIV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.53 CFG_PLL2_SS_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.54 CFG_PLL2_SS_SPREAD Registers
- 14.2.3.1.55 CFG_PLL2_CAL_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.56 CFG_PLL2_CAL_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.57 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.58 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.59 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL2 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.60 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL3 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.61 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL4 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.62 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL5 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.63 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL6 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.64 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL7 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.65 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL8 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.66 CFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL9 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.67 CFG_PLL8_PID Registers
- 14.2.3.1.68 CFG_PLL8_CFG Registers
- 14.2.3.1.69 CFG_PLL8_LOCKKEY0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.70 CFG_PLL8_LOCKKEY1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.71 CFG_PLL8_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.72 CFG_PLL8_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.73 CFG_PLL8_FREQ_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.74 CFG_PLL8_FREQ_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.75 CFG_PLL8_DIV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.76 CFG_PLL8_SS_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.77 CFG_PLL8_SS_SPREAD Registers
- 14.2.3.1.78 CFG_PLL8_CAL_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.79 CFG_PLL8_CAL_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.80 CFG_PLL8_HSDIV_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.81 CFG_PLL12_PID Registers
- 14.2.3.1.82 CFG_PLL12_CFG Registers
- 14.2.3.1.83 CFG_PLL12_LOCKKEY0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.84 CFG_PLL12_LOCKKEY1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.85 CFG_PLL12_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.86 CFG_PLL12_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.87 CFG_PLL12_FREQ_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.88 CFG_PLL12_FREQ_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.89 CFG_PLL12_DIV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.90 CFG_PLL12_SS_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.91 CFG_PLL12_SS_SPREAD Registers
- 14.2.3.1.92 CFG_PLL12_CAL_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.93 CFG_PLL12_CAL_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.94 CFG_PLL12_HSDIV_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.95 CFG_PLL15_PID Registers
- 14.2.3.1.96 CFG_PLL15_CFG Registers
- 14.2.3.1.97 CFG_PLL15_LOCKKEY0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.98 CFG_PLL15_LOCKKEY1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.99 CFG_PLL15_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.100 CFG_PLL15_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.101 CFG_PLL15_FREQ_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.102 CFG_PLL15_FREQ_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.103 CFG_PLL15_DIV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.104 CFG_PLL15_SS_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.105 CFG_PLL15_SS_SPREAD Registers
- 14.2.3.1.106 CFG_PLL15_CAL_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.107 CFG_PLL15_CAL_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.108 CFG_PLL15_HSDIV_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.109 CFG_PLL15_HSDIV_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.110 CFG_PLL16_PID Registers
- 14.2.3.1.111 CFG_PLL16_CFG Registers
- 14.2.3.1.112 CFG_PLL16_LOCKKEY0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.113 CFG_PLL16_LOCKKEY1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.114 CFG_PLL16_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.115 CFG_PLL16_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.116 CFG_PLL16_FREQ_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.117 CFG_PLL16_FREQ_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.118 CFG_PLL16_DIV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.119 CFG_PLL16_SS_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.120 CFG_PLL16_SS_SPREAD Registers
- 14.2.3.1.121 CFG_PLL16_CAL_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.122 CFG_PLL16_CAL_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.123 CFG_PLL16_HSDIV_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.124 CFG_PLL17_PID Registers
- 14.2.3.1.125 CFG_PLL17_CFG Registers
- 14.2.3.1.126 CFG_PLL17_LOCKKEY0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.127 CFG_PLL17_LOCKKEY1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.128 CFG_PLL17_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.129 CFG_PLL17_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.130 CFG_PLL17_FREQ_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.131 CFG_PLL17_FREQ_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.132 CFG_PLL17_DIV_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.133 CFG_PLL17_SS_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.134 CFG_PLL17_SS_SPREAD Registers
- 14.2.3.1.135 CFG_PLL17_CAL_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.136 CFG_PLL17_CAL_STAT Registers
- 14.2.3.1.137 CFG_PLL17_HSDIV_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.2.3.1.138 Access Table
- 14.2.3.1
PLL Registers
- 14.2.1
CTRL_MMR Registers
- 14.3
Processors and Accelerators Registers
- 14.3.1
A53SS Registers
- 14.3.1.1
A53SS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1 SS_ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.3.1.1.2 SS_ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.3 SS_ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.3.1.1.4 SS_ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.3.1.1.5 SS_ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.6 SS_ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.7 SS_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.8 SS_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.9 SS_ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.10 SS_ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.11 SS_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.12 SS_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.13 SS_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.14 SS_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.15 SS_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.16 SS_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.17 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.3.1.1.18 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.19 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.3.1.1.20 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.3.1.1.21 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.22 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.23 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.24 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.25 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.26 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.27 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.28 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.29 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.30 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.31 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.32 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.33 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.3.1.1.34 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.35 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.3.1.1.36 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.3.1.1.37 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.38 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.39 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.40 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.41 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.42 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.43 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.44 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.45 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.46 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.47 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.48 CORE1_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.49 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.3.1.1.50 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.51 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.3.1.1.52 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.3.1.1.53 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.54 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.55 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.56 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.57 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.58 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.59 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.60 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.61 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.62 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.63 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.64 CORE2_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.65 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.3.1.1.66 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.67 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.3.1.1.68 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.3.1.1.69 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.70 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.71 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.72 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.73 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.1.1.74 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.75 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.76 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.77 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.78 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.79 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.80 CORE3_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.81 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.82 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.83 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.84 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.85 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.86 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.87 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.88 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.89 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY8 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.90 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY9 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.91 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY10 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.92 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY11 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.93 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY12 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.94 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY13 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.95 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY14 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.96 SS_ROM_ROMENTRY15 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.97 SS_ROM_ROM_PERIPHID4_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.98 SS_ROM_ROM_PERIPHID5_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.99 SS_ROM_ROM_PERIPHID6_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.100 SS_ROM_ROM_PERIPHID7_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.101 SS_ROM_ROM_PERIPHID0_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.102 SS_ROM_ROM_PERIPHID1_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.103 SS_ROM_ROM_PERIPHID2_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.104 SS_ROM_ROM_PERIPHID3_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.105 SS_ROM_ROM_COMPONID0_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.106 SS_ROM_ROM_COMPONID1_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.107 SS_ROM_ROM_COMPONID2_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.108 SS_ROM_ROM_COMPONID3_VAL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.109 CORE0_DBG_EDESR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.110 CORE0_DBG_EDECR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.111 CORE0_DBG_EDWAR_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.112 CORE0_DBG_EDWAR_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.113 CORE0_DBG_DBGDTRRX_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.114 CORE0_DBG_EDITR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.115 CORE0_DBG_EDSCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.116 CORE0_DBG_DBGDTRTX_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.117 CORE0_DBG_EDRCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.118 CORE0_DBG_EDACR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.119 CORE0_DBG_EDECCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.120 CORE0_DBG_EDPCSR_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.121 CORE0_DBG_EDCIDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.122 CORE0_DBG_EDVIDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.123 CORE0_DBG_EDPCSR_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.124 CORE0_DBG_OSLAR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.125 CORE0_DBG_EDPRCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.126 CORE0_DBG_EDPRSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.127 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.128 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.129 CORE0_DBG_DBGBCR0_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.130 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.131 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.132 CORE0_DBG_DBGBCR1_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.133 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR2_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.134 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR2_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.135 CORE0_DBG_DBGBCR2_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.136 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR3_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.137 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR3_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.138 CORE0_DBG_DBGBCR3_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.139 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR4_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.140 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR4_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.141 CORE0_DBG_DBGBCR4_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.142 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR5_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.143 CORE0_DBG_DBGBVR5_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.144 CORE0_DBG_DBGBCR5_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.145 CORE0_DBG_DBGWVR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.146 CORE0_DBG_DBGWVR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.147 CORE0_DBG_DBGWCR0_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.148 CORE0_DBG_DBGWVR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.149 CORE0_DBG_DBGWVR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.150 CORE0_DBG_DBGWCR1_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.151 CORE0_DBG_DBGWVR2_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.152 CORE0_DBG_DBGWVR2_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.153 CORE0_DBG_DBGWCR2_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.154 CORE0_DBG_DBGWVR3_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.155 CORE0_DBG_DBGWVR3_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.156 CORE0_DBG_DBGWCR3_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.157 CORE0_DBG_MIDR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.158 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64PFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.159 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64PFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.160 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64DFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.161 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64DFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.162 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.163 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.164 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.165 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.166 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64PFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.167 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64PFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.168 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64DFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.169 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64DFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.170 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.171 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.172 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.173 CORE0_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.174 CORE0_DBG_EDITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.175 CORE0_DBG_DBGCLAIMSET_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.176 CORE0_DBG_DBGCLAIMCLR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.177 CORE0_DBG_EDDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.178 CORE0_DBG_EDDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.179 CORE0_DBG_EDLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.180 CORE0_DBG_EDLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.181 CORE0_DBG_DBGAUTHSTATUS_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.182 CORE0_DBG_EDDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.183 CORE0_DBG_EDDEVID2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.184 CORE0_DBG_EDDEVID1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.185 CORE0_DBG_EDDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.186 CORE0_DBG_EDDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.187 CORE0_DBG_EDPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.188 CORE0_DBG_EDPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.189 CORE0_DBG_EDPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.190 CORE0_DBG_EDPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.191 CORE0_DBG_EDPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.192 CORE0_DBG_EDCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.193 CORE0_DBG_EDCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.194 CORE0_DBG_EDCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.195 CORE0_DBG_EDCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.196 CORE0_CTI_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.197 CORE0_CTI_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.3.1.1.198 CORE0_CTI_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.199 CORE0_CTI_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.200 CORE0_CTI_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.201 CORE0_CTI_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.202 CORE0_CTI_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.203 CORE0_CTI_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.204 CORE0_CTI_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.205 CORE0_CTI_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.206 CORE0_CTI_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.207 CORE0_CTI_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.208 CORE0_CTI_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.209 CORE0_CTI_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.210 CORE0_CTI_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.211 CORE0_CTI_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.212 CORE0_CTI_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.213 CORE0_CTI_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.214 CORE0_CTI_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.215 CORE0_CTI_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.216 CORE0_CTI_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.217 CORE0_CTI_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.218 CORE0_CTI_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.219 CORE0_CTI_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.220 CORE0_CTI_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.221 CORE0_CTI_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.222 CORE0_CTI_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.223 CORE0_CTI_CTIITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.224 CORE0_CTI_CTICLAIMSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.225 CORE0_CTI_CTICLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.226 CORE0_CTI_CTIDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.227 CORE0_CTI_CTIDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.228 CORE0_CTI_CTILAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.229 CORE0_CTI_CTILSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.230 CORE0_CTI_CTIAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.231 CORE0_CTI_CTIDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.232 CORE0_CTI_CTIDEVID2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.233 CORE0_CTI_CTIDEVID1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.234 CORE0_CTI_CTIDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.235 CORE0_CTI_CTIDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.236 CORE0_CTI_CTIPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.237 CORE0_CTI_CTIPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.238 CORE0_CTI_CTIPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.239 CORE0_CTI_CTIPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.240 CORE0_CTI_CTIPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.241 CORE0_CTI_CTIPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.242 CORE0_CTI_CTIPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.243 CORE0_CTI_CTIPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.244 CORE0_CTI_CTICIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.245 CORE0_CTI_CTICIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.246 CORE0_CTI_CTICIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.247 CORE0_CTI_CTICIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.248 CORE0_PMU_PMEVCNTR0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.249 CORE0_PMU_PMEVCNTR1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.250 CORE0_PMU_PMEVCNTR2_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.251 CORE0_PMU_PMEVCNTR3_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.252 CORE0_PMU_PMEVCNTR4_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.253 CORE0_PMU_PMEVCNTR5_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.254 CORE0_PMU_PMCCNTR_EL0_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.255 CORE0_PMU_PMCCNTR_EL0_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.256 CORE0_PMU_PMEVTYPER0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.257 CORE0_PMU_PMEVTYPER1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.258 CORE0_PMU_PMEVTYPER2_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.259 CORE0_PMU_PMEVTYPER3_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.260 CORE0_PMU_PMEVTYPER4_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.261 CORE0_PMU_PMEVTYPER5_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.262 CORE0_PMU_PMCCFILTR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.263 CORE0_PMU_PMCNTENSET_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.264 CORE0_PMU_PMCNTENCLR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.265 CORE0_PMU_PMINTENSET_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.266 CORE0_PMU_PMINTENCLR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.267 CORE0_PMU_PMOVSCLR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.268 CORE0_PMU_PMSWINC_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.269 CORE0_PMU_PMOVSSET_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.270 CORE0_PMU_PMCFGR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.271 CORE0_PMU_PMCR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.272 CORE0_PMU_PMCEID0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.273 CORE0_PMU_PMCEID1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.274 CORE0_PMU_PMITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.275 CORE0_PMU_PMDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.276 CORE0_PMU_PMDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.277 CORE0_PMU_PMLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.278 CORE0_PMU_PMLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.279 CORE0_PMU_PMAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.280 CORE0_PMU_PMDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.281 CORE0_PMU_PMDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.282 CORE0_PMU_PMPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.283 CORE0_PMU_PMPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.284 CORE0_PMU_PMPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.285 CORE0_PMU_PMPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.286 CORE0_PMU_PMPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.287 CORE0_PMU_PMPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.288 CORE0_PMU_PMPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.289 CORE0_PMU_PMPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.290 CORE0_PMU_PMCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.291 CORE0_PMU_PMCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.292 CORE0_PMU_PMCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.293 CORE0_PMU_PMCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.294 CORE0_ETM_TRCPRGCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.295 CORE0_ETM_TRCSTATR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.296 CORE0_ETM_TRCCONFIGR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.297 CORE0_ETM_TRCAUXCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.298 CORE0_ETM_TRCEVENTCTL0R Registers
- 14.3.1.1.299 CORE0_ETM_TRCEVENTCTL1R Registers
- 14.3.1.1.300 CORE0_ETM_TRCSTALLCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.301 CORE0_ETM_TRCTSCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.302 CORE0_ETM_TRCSYNCPR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.303 CORE0_ETM_TRCCCCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.304 CORE0_ETM_TRCBBCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.305 CORE0_ETM_TRCTRACEIDR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.306 CORE0_ETM_TRCVICTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.307 CORE0_ETM_TRCVIIECTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.308 CORE0_ETM_TRCVISSCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.309 CORE0_ETM_TRCSEQEVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.310 CORE0_ETM_TRCSEQEVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.311 CORE0_ETM_TRCSEQEVR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.312 CORE0_ETM_TRCSEQRSTEVR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.313 CORE0_ETM_TRCSEQSTR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.314 CORE0_ETM_TRCEXTINSELR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.315 CORE0_ETM_TRCCNTRLDVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.316 CORE0_ETM_TRCCNTRLDVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.317 CORE0_ETM_TRCCNTCTLR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.318 CORE0_ETM_TRCCNTCTLR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.319 CORE0_ETM_TRCCNTVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.320 CORE0_ETM_TRCCNTVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.321 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR8 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.322 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR9 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.323 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR10 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.324 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR11 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.325 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR12 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.326 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR13 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.327 CORE0_ETM_TRCIMSPEC0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.328 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.329 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.330 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.331 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.332 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.333 CORE0_ETM_TRCIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.334 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.335 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.336 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.337 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.338 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.339 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.340 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR8 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.341 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR9 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.342 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR10 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.343 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR11 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.344 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR12 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.345 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR13 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.346 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR14 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.347 CORE0_ETM_TRCRSCTLR15 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.348 CORE0_ETM_TRCSSCCR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.349 CORE0_ETM_TRCSSCSR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.350 CORE0_ETM_TRCOSLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.351 CORE0_ETM_TRCOSLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.352 CORE0_ETM_TRCPDCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.353 CORE0_ETM_TRCPDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.354 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR0_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.355 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR0_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.356 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.357 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.358 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR2_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.359 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR2_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.360 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR3_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.361 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR3_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.362 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR4_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.363 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR4_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.364 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR5_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.365 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR5_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.366 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR6_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.367 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR6_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.368 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR7_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.369 CORE0_ETM_TRCACVR7_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.370 CORE0_ETM_TRCACATR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.371 CORE0_ETM_TRCACATR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.372 CORE0_ETM_TRCACATR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.373 CORE0_ETM_TRCACATR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.374 CORE0_ETM_TRCACATR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.375 CORE0_ETM_TRCACATR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.376 CORE0_ETM_TRCACATR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.377 CORE0_ETM_TRCACATR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.378 CORE0_ETM_TRCCIDCVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.379 CORE0_ETM_TRCVMIDCVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.380 CORE0_ETM_TRCCIDCCTLR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.381 CORE0_ETM_TRCITATBIDR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.382 CORE0_ETM_TRCITIDATAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.383 CORE0_ETM_TRCITIATBINR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.384 CORE0_ETM_TRCITIATBOUTR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.385 CORE0_ETM_TRCITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.386 CORE0_ETM_TRCCLAIMSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.387 CORE0_ETM_TRCCLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.388 CORE0_ETM_TRCDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.389 CORE0_ETM_TRCDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.390 CORE0_ETM_TRCLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.391 CORE0_ETM_TRCLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.392 CORE0_ETM_TRCAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.393 CORE0_ETM_TRCDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.394 CORE0_ETM_TRCDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.395 CORE0_ETM_TRCDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.396 CORE0_ETM_TRCPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.397 CORE0_ETM_TRCPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.398 CORE0_ETM_TRCPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.399 CORE0_ETM_TRCPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.400 CORE0_ETM_TRCPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.401 CORE0_ETM_TRCPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.402 CORE0_ETM_TRCPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.403 CORE0_ETM_TRCPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.404 CORE0_ETM_TRCCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.405 CORE0_ETM_TRCCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.406 CORE0_ETM_TRCCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.407 CORE0_ETM_TRCCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.408 CORE1_DBG_EDESR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.409 CORE1_DBG_EDECR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.410 CORE1_DBG_EDWAR_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.411 CORE1_DBG_EDWAR_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.412 CORE1_DBG_DBGDTRRX_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.413 CORE1_DBG_EDITR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.414 CORE1_DBG_EDSCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.415 CORE1_DBG_DBGDTRTX_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.416 CORE1_DBG_EDRCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.417 CORE1_DBG_EDACR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.418 CORE1_DBG_EDECCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.419 CORE1_DBG_EDPCSR_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.420 CORE1_DBG_EDCIDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.421 CORE1_DBG_EDVIDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.422 CORE1_DBG_EDPCSR_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.423 CORE1_DBG_OSLAR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.424 CORE1_DBG_EDPRCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.425 CORE1_DBG_EDPRSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.426 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.427 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.428 CORE1_DBG_DBGBCR0_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.429 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.430 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.431 CORE1_DBG_DBGBCR1_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.432 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR2_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.433 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR2_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.434 CORE1_DBG_DBGBCR2_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.435 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR3_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.436 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR3_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.437 CORE1_DBG_DBGBCR3_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.438 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR4_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.439 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR4_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.440 CORE1_DBG_DBGBCR4_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.441 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR5_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.442 CORE1_DBG_DBGBVR5_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.443 CORE1_DBG_DBGBCR5_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.444 CORE1_DBG_DBGWVR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.445 CORE1_DBG_DBGWVR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.446 CORE1_DBG_DBGWCR0_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.447 CORE1_DBG_DBGWVR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.448 CORE1_DBG_DBGWVR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.449 CORE1_DBG_DBGWCR1_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.450 CORE1_DBG_DBGWVR2_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.451 CORE1_DBG_DBGWVR2_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.452 CORE1_DBG_DBGWCR2_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.453 CORE1_DBG_DBGWVR3_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.454 CORE1_DBG_DBGWVR3_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.455 CORE1_DBG_DBGWCR3_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.456 CORE1_DBG_MIDR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.457 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64PFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.458 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64PFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.459 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64DFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.460 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64DFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.461 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.462 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.463 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.464 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.465 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64PFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.466 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64PFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.467 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64DFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.468 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64DFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.469 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.470 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.471 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.472 CORE1_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.473 CORE1_DBG_EDITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.474 CORE1_DBG_DBGCLAIMSET_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.475 CORE1_DBG_DBGCLAIMCLR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.476 CORE1_DBG_EDDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.477 CORE1_DBG_EDDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.478 CORE1_DBG_EDLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.479 CORE1_DBG_EDLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.480 CORE1_DBG_DBGAUTHSTATUS_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.481 CORE1_DBG_EDDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.482 CORE1_DBG_EDDEVID2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.483 CORE1_DBG_EDDEVID1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.484 CORE1_DBG_EDDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.485 CORE1_DBG_EDDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.486 CORE1_DBG_EDPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.487 CORE1_DBG_EDPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.488 CORE1_DBG_EDPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.489 CORE1_DBG_EDPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.490 CORE1_DBG_EDPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.491 CORE1_DBG_EDCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.492 CORE1_DBG_EDCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.493 CORE1_DBG_EDCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.494 CORE1_DBG_EDCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.495 CORE1_PMU_PMEVCNTR0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.496 CORE1_PMU_PMEVCNTR1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.497 CORE1_PMU_PMEVCNTR2_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.498 CORE1_PMU_PMEVCNTR3_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.499 CORE1_PMU_PMEVCNTR4_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.500 CORE1_PMU_PMEVCNTR5_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.501 CORE1_PMU_PMCCNTR_EL0_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.502 CORE1_PMU_PMCCNTR_EL0_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.503 CORE1_PMU_PMEVTYPER0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.504 CORE1_PMU_PMEVTYPER1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.505 CORE1_PMU_PMEVTYPER2_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.506 CORE1_PMU_PMEVTYPER3_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.507 CORE1_PMU_PMEVTYPER4_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.508 CORE1_PMU_PMEVTYPER5_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.509 CORE1_PMU_PMCCFILTR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.510 CORE1_PMU_PMCNTENSET_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.511 CORE1_PMU_PMCNTENCLR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.512 CORE1_PMU_PMINTENSET_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.513 CORE1_PMU_PMINTENCLR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.514 CORE1_PMU_PMOVSCLR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.515 CORE1_PMU_PMSWINC_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.516 CORE1_PMU_PMOVSSET_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.517 CORE1_PMU_PMCFGR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.518 CORE1_PMU_PMCR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.519 CORE1_PMU_PMCEID0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.520 CORE1_PMU_PMCEID1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.521 CORE1_PMU_PMITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.522 CORE1_PMU_PMDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.523 CORE1_PMU_PMDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.524 CORE1_PMU_PMLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.525 CORE1_PMU_PMLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.526 CORE1_PMU_PMAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.527 CORE1_PMU_PMDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.528 CORE1_PMU_PMDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.529 CORE1_PMU_PMPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.530 CORE1_PMU_PMPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.531 CORE1_PMU_PMPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.532 CORE1_PMU_PMPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.533 CORE1_PMU_PMPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.534 CORE1_PMU_PMPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.535 CORE1_PMU_PMPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.536 CORE1_PMU_PMPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.537 CORE1_PMU_PMCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.538 CORE1_PMU_PMCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.539 CORE1_PMU_PMCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.540 CORE1_PMU_PMCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.541 CORE1_ETM_TRCPRGCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.542 CORE1_ETM_TRCSTATR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.543 CORE1_ETM_TRCCONFIGR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.544 CORE1_ETM_TRCAUXCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.545 CORE1_ETM_TRCEVENTCTL0R Registers
- 14.3.1.1.546 CORE1_ETM_TRCEVENTCTL1R Registers
- 14.3.1.1.547 CORE1_ETM_TRCSTALLCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.548 CORE1_ETM_TRCTSCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.549 CORE1_ETM_TRCSYNCPR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.550 CORE1_ETM_TRCCCCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.551 CORE1_ETM_TRCBBCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.552 CORE1_ETM_TRCTRACEIDR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.553 CORE1_ETM_TRCVICTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.554 CORE1_ETM_TRCVIIECTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.555 CORE1_ETM_TRCVISSCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.556 CORE1_ETM_TRCSEQEVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.557 CORE1_ETM_TRCSEQEVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.558 CORE1_ETM_TRCSEQEVR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.559 CORE1_ETM_TRCSEQRSTEVR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.560 CORE1_ETM_TRCSEQSTR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.561 CORE1_ETM_TRCEXTINSELR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.562 CORE1_ETM_TRCCNTRLDVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.563 CORE1_ETM_TRCCNTRLDVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.564 CORE1_ETM_TRCCNTCTLR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.565 CORE1_ETM_TRCCNTCTLR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.566 CORE1_ETM_TRCCNTVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.567 CORE1_ETM_TRCCNTVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.568 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR8 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.569 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR9 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.570 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR10 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.571 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR11 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.572 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR12 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.573 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR13 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.574 CORE1_ETM_TRCIMSPEC0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.575 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.576 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.577 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.578 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.579 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.580 CORE1_ETM_TRCIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.581 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.582 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.583 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.584 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.585 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.586 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.587 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR8 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.588 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR9 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.589 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR10 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.590 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR11 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.591 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR12 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.592 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR13 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.593 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR14 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.594 CORE1_ETM_TRCRSCTLR15 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.595 CORE1_ETM_TRCSSCCR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.596 CORE1_ETM_TRCSSCSR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.597 CORE1_ETM_TRCOSLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.598 CORE1_ETM_TRCOSLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.599 CORE1_ETM_TRCPDCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.600 CORE1_ETM_TRCPDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.601 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR0_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.602 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR0_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.603 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.604 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.605 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR2_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.606 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR2_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.607 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR3_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.608 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR3_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.609 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR4_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.610 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR4_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.611 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR5_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.612 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR5_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.613 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR6_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.614 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR6_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.615 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR7_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.616 CORE1_ETM_TRCACVR7_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.617 CORE1_ETM_TRCACATR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.618 CORE1_ETM_TRCACATR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.619 CORE1_ETM_TRCACATR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.620 CORE1_ETM_TRCACATR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.621 CORE1_ETM_TRCACATR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.622 CORE1_ETM_TRCACATR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.623 CORE1_ETM_TRCACATR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.624 CORE1_ETM_TRCACATR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.625 CORE1_ETM_TRCCIDCVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.626 CORE1_ETM_TRCVMIDCVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.627 CORE1_ETM_TRCCIDCCTLR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.628 CORE1_ETM_TRCITATBIDR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.629 CORE1_ETM_TRCITIDATAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.630 CORE1_ETM_TRCITIATBINR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.631 CORE1_ETM_TRCITIATBOUTR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.632 CORE1_ETM_TRCITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.633 CORE1_ETM_TRCCLAIMSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.634 CORE1_ETM_TRCCLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.635 CORE1_ETM_TRCDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.636 CORE1_ETM_TRCDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.637 CORE1_ETM_TRCLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.638 CORE1_ETM_TRCLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.639 CORE1_ETM_TRCAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.640 CORE1_ETM_TRCDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.641 CORE1_ETM_TRCDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.642 CORE1_ETM_TRCDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.643 CORE1_ETM_TRCPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.644 CORE1_ETM_TRCPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.645 CORE1_ETM_TRCPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.646 CORE1_ETM_TRCPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.647 CORE1_ETM_TRCPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.648 CORE1_ETM_TRCPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.649 CORE1_ETM_TRCPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.650 CORE1_ETM_TRCPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.651 CORE1_ETM_TRCCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.652 CORE1_ETM_TRCCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.653 CORE1_ETM_TRCCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.654 CORE1_ETM_TRCCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.655 CORE1_CTI_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.656 CORE1_CTI_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.3.1.1.657 CORE1_CTI_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.658 CORE1_CTI_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.659 CORE1_CTI_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.660 CORE1_CTI_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.661 CORE1_CTI_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.662 CORE1_CTI_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.663 CORE1_CTI_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.664 CORE1_CTI_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.665 CORE1_CTI_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.666 CORE1_CTI_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.667 CORE1_CTI_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.668 CORE1_CTI_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.669 CORE1_CTI_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.670 CORE1_CTI_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.671 CORE1_CTI_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.672 CORE1_CTI_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.673 CORE1_CTI_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.674 CORE1_CTI_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.675 CORE1_CTI_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.676 CORE1_CTI_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.677 CORE1_CTI_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.678 CORE1_CTI_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.679 CORE1_CTI_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.680 CORE1_CTI_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.681 CORE1_CTI_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.682 CORE1_CTI_CTIITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.683 CORE1_CTI_CTICLAIMSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.684 CORE1_CTI_CTICLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.685 CORE1_CTI_CTIDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.686 CORE1_CTI_CTIDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.687 CORE1_CTI_CTILAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.688 CORE1_CTI_CTILSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.689 CORE1_CTI_CTIAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.690 CORE1_CTI_CTIDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.691 CORE1_CTI_CTIDEVID2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.692 CORE1_CTI_CTIDEVID1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.693 CORE1_CTI_CTIDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.694 CORE1_CTI_CTIDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.695 CORE1_CTI_CTIPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.696 CORE1_CTI_CTIPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.697 CORE1_CTI_CTIPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.698 CORE1_CTI_CTIPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.699 CORE1_CTI_CTIPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.700 CORE1_CTI_CTIPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.701 CORE1_CTI_CTIPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.702 CORE1_CTI_CTIPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.703 CORE1_CTI_CTICIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.704 CORE1_CTI_CTICIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.705 CORE1_CTI_CTICIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.706 CORE1_CTI_CTICIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.707 CORE2_DBG_EDESR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.708 CORE2_DBG_EDECR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.709 CORE2_DBG_EDWAR_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.710 CORE2_DBG_EDWAR_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.711 CORE2_DBG_DBGDTRRX_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.712 CORE2_DBG_EDITR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.713 CORE2_DBG_EDSCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.714 CORE2_DBG_DBGDTRTX_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.715 CORE2_DBG_EDRCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.716 CORE2_DBG_EDACR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.717 CORE2_DBG_EDECCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.718 CORE2_DBG_EDPCSR_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.719 CORE2_DBG_EDCIDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.720 CORE2_DBG_EDVIDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.721 CORE2_DBG_EDPCSR_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.722 CORE2_DBG_OSLAR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.723 CORE2_DBG_EDPRCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.724 CORE2_DBG_EDPRSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.725 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.726 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.727 CORE2_DBG_DBGBCR0_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.728 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.729 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.730 CORE2_DBG_DBGBCR1_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.731 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR2_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.732 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR2_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.733 CORE2_DBG_DBGBCR2_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.734 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR3_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.735 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR3_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.736 CORE2_DBG_DBGBCR3_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.737 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR4_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.738 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR4_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.739 CORE2_DBG_DBGBCR4_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.740 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR5_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.741 CORE2_DBG_DBGBVR5_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.742 CORE2_DBG_DBGBCR5_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.743 CORE2_DBG_DBGWVR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.744 CORE2_DBG_DBGWVR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.745 CORE2_DBG_DBGWCR0_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.746 CORE2_DBG_DBGWVR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.747 CORE2_DBG_DBGWVR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.748 CORE2_DBG_DBGWCR1_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.749 CORE2_DBG_DBGWVR2_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.750 CORE2_DBG_DBGWVR2_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.751 CORE2_DBG_DBGWCR2_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.752 CORE2_DBG_DBGWVR3_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.753 CORE2_DBG_DBGWVR3_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.754 CORE2_DBG_DBGWCR3_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.755 CORE2_DBG_MIDR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.756 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64PFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.757 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64PFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.758 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64DFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.759 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64DFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.760 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.761 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.762 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.763 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.764 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64PFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.765 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64PFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.766 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64DFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.767 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64DFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.768 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.769 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.770 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.771 CORE2_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.772 CORE2_DBG_EDITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.773 CORE2_DBG_DBGCLAIMSET_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.774 CORE2_DBG_DBGCLAIMCLR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.775 CORE2_DBG_EDDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.776 CORE2_DBG_EDDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.777 CORE2_DBG_EDLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.778 CORE2_DBG_EDLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.779 CORE2_DBG_DBGAUTHSTATUS_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.780 CORE2_DBG_EDDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.781 CORE2_DBG_EDDEVID2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.782 CORE2_DBG_EDDEVID1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.783 CORE2_DBG_EDDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.784 CORE2_DBG_EDDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.785 CORE2_DBG_EDPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.786 CORE2_DBG_EDPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.787 CORE2_DBG_EDPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.788 CORE2_DBG_EDPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.789 CORE2_DBG_EDPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.790 CORE2_DBG_EDCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.791 CORE2_DBG_EDCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.792 CORE2_DBG_EDCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.793 CORE2_DBG_EDCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.794 CORE2_PMU_PMEVCNTR0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.795 CORE2_PMU_PMEVCNTR1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.796 CORE2_PMU_PMEVCNTR2_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.797 CORE2_PMU_PMEVCNTR3_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.798 CORE2_PMU_PMEVCNTR4_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.799 CORE2_PMU_PMEVCNTR5_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.800 CORE2_PMU_PMCCNTR_EL0_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.801 CORE2_PMU_PMCCNTR_EL0_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.802 CORE2_PMU_PMEVTYPER0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.803 CORE2_PMU_PMEVTYPER1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.804 CORE2_PMU_PMEVTYPER2_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.805 CORE2_PMU_PMEVTYPER3_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.806 CORE2_PMU_PMEVTYPER4_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.807 CORE2_PMU_PMEVTYPER5_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.808 CORE2_PMU_PMCCFILTR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.809 CORE2_PMU_PMCNTENSET_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.810 CORE2_PMU_PMCNTENCLR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.811 CORE2_PMU_PMINTENSET_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.812 CORE2_PMU_PMINTENCLR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.813 CORE2_PMU_PMOVSCLR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.814 CORE2_PMU_PMSWINC_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.815 CORE2_PMU_PMOVSSET_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.816 CORE2_PMU_PMCFGR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.817 CORE2_PMU_PMCR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.818 CORE2_PMU_PMCEID0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.819 CORE2_PMU_PMCEID1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.820 CORE2_PMU_PMITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.821 CORE2_PMU_PMDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.822 CORE2_PMU_PMDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.823 CORE2_PMU_PMLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.824 CORE2_PMU_PMLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.825 CORE2_PMU_PMAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.826 CORE2_PMU_PMDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.827 CORE2_PMU_PMDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.828 CORE2_PMU_PMPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.829 CORE2_PMU_PMPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.830 CORE2_PMU_PMPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.831 CORE2_PMU_PMPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.832 CORE2_PMU_PMPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.833 CORE2_PMU_PMPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.834 CORE2_PMU_PMPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.835 CORE2_PMU_PMPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.836 CORE2_PMU_PMCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.837 CORE2_PMU_PMCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.838 CORE2_PMU_PMCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.839 CORE2_PMU_PMCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.840 CORE2_ETM_TRCPRGCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.841 CORE2_ETM_TRCSTATR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.842 CORE2_ETM_TRCCONFIGR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.843 CORE2_ETM_TRCAUXCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.844 CORE2_ETM_TRCEVENTCTL0R Registers
- 14.3.1.1.845 CORE2_ETM_TRCEVENTCTL1R Registers
- 14.3.1.1.846 CORE2_ETM_TRCSTALLCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.847 CORE2_ETM_TRCTSCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.848 CORE2_ETM_TRCSYNCPR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.849 CORE2_ETM_TRCCCCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.850 CORE2_ETM_TRCBBCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.851 CORE2_ETM_TRCTRACEIDR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.852 CORE2_ETM_TRCVICTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.853 CORE2_ETM_TRCVIIECTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.854 CORE2_ETM_TRCVISSCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.855 CORE2_ETM_TRCSEQEVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.856 CORE2_ETM_TRCSEQEVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.857 CORE2_ETM_TRCSEQEVR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.858 CORE2_ETM_TRCSEQRSTEVR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.859 CORE2_ETM_TRCSEQSTR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.860 CORE2_ETM_TRCEXTINSELR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.861 CORE2_ETM_TRCCNTRLDVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.862 CORE2_ETM_TRCCNTRLDVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.863 CORE2_ETM_TRCCNTCTLR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.864 CORE2_ETM_TRCCNTCTLR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.865 CORE2_ETM_TRCCNTVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.866 CORE2_ETM_TRCCNTVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.867 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR8 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.868 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR9 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.869 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR10 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.870 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR11 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.871 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR12 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.872 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR13 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.873 CORE2_ETM_TRCIMSPEC0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.874 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.875 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.876 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.877 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.878 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.879 CORE2_ETM_TRCIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.880 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.881 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.882 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.883 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.884 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.885 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.886 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR8 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.887 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR9 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.888 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR10 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.889 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR11 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.890 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR12 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.891 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR13 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.892 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR14 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.893 CORE2_ETM_TRCRSCTLR15 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.894 CORE2_ETM_TRCSSCCR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.895 CORE2_ETM_TRCSSCSR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.896 CORE2_ETM_TRCOSLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.897 CORE2_ETM_TRCOSLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.898 CORE2_ETM_TRCPDCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.899 CORE2_ETM_TRCPDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.900 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR0_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.901 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR0_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.902 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.903 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.904 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR2_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.905 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR2_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.906 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR3_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.907 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR3_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.908 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR4_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.909 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR4_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.910 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR5_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.911 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR5_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.912 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR6_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.913 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR6_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.914 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR7_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.915 CORE2_ETM_TRCACVR7_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.916 CORE2_ETM_TRCACATR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.917 CORE2_ETM_TRCACATR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.918 CORE2_ETM_TRCACATR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.919 CORE2_ETM_TRCACATR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.920 CORE2_ETM_TRCACATR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.921 CORE2_ETM_TRCACATR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.922 CORE2_ETM_TRCACATR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.923 CORE2_ETM_TRCACATR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.924 CORE2_ETM_TRCCIDCVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.925 CORE2_ETM_TRCVMIDCVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.926 CORE2_ETM_TRCCIDCCTLR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.927 CORE2_ETM_TRCITATBIDR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.928 CORE2_ETM_TRCITIDATAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.929 CORE2_ETM_TRCITIATBINR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.930 CORE2_ETM_TRCITIATBOUTR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.931 CORE2_ETM_TRCITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.932 CORE2_ETM_TRCCLAIMSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.933 CORE2_ETM_TRCCLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.934 CORE2_ETM_TRCDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.935 CORE2_ETM_TRCDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.936 CORE2_ETM_TRCLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.937 CORE2_ETM_TRCLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.938 CORE2_ETM_TRCAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.939 CORE2_ETM_TRCDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.940 CORE2_ETM_TRCDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.941 CORE2_ETM_TRCDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.942 CORE2_ETM_TRCPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.943 CORE2_ETM_TRCPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.944 CORE2_ETM_TRCPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.945 CORE2_ETM_TRCPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.946 CORE2_ETM_TRCPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.947 CORE2_ETM_TRCPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.948 CORE2_ETM_TRCPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.949 CORE2_ETM_TRCPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.950 CORE2_ETM_TRCCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.951 CORE2_ETM_TRCCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.952 CORE2_ETM_TRCCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.953 CORE2_ETM_TRCCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.954 CORE2_CTI_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.955 CORE2_CTI_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.3.1.1.956 CORE2_CTI_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.957 CORE2_CTI_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.958 CORE2_CTI_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.959 CORE2_CTI_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.960 CORE2_CTI_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.961 CORE2_CTI_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.962 CORE2_CTI_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.963 CORE2_CTI_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.964 CORE2_CTI_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.965 CORE2_CTI_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.966 CORE2_CTI_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.967 CORE2_CTI_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.968 CORE2_CTI_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.969 CORE2_CTI_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.970 CORE2_CTI_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.971 CORE2_CTI_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.972 CORE2_CTI_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.973 CORE2_CTI_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.974 CORE2_CTI_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.975 CORE2_CTI_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.976 CORE2_CTI_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.977 CORE2_CTI_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.978 CORE2_CTI_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.979 CORE2_CTI_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.980 CORE2_CTI_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.981 CORE2_CTI_CTIITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.982 CORE2_CTI_CTICLAIMSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.983 CORE2_CTI_CTICLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.984 CORE2_CTI_CTIDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.985 CORE2_CTI_CTIDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.986 CORE2_CTI_CTILAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.987 CORE2_CTI_CTILSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.988 CORE2_CTI_CTIAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.989 CORE2_CTI_CTIDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.990 CORE2_CTI_CTIDEVID2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.991 CORE2_CTI_CTIDEVID1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.992 CORE2_CTI_CTIDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.993 CORE2_CTI_CTIDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.994 CORE2_CTI_CTIPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.995 CORE2_CTI_CTIPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.996 CORE2_CTI_CTIPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.997 CORE2_CTI_CTIPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.998 CORE2_CTI_CTIPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.999 CORE2_CTI_CTIPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1000 CORE2_CTI_CTIPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1001 CORE2_CTI_CTIPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1002 CORE2_CTI_CTICIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1003 CORE2_CTI_CTICIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1004 CORE2_CTI_CTICIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1005 CORE2_CTI_CTICIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1006 CORE3_DBG_EDESR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1007 CORE3_DBG_EDECR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1008 CORE3_DBG_EDWAR_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1009 CORE3_DBG_EDWAR_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1010 CORE3_DBG_DBGDTRRX_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1011 CORE3_DBG_EDITR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1012 CORE3_DBG_EDSCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1013 CORE3_DBG_DBGDTRTX_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1014 CORE3_DBG_EDRCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1015 CORE3_DBG_EDACR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1016 CORE3_DBG_EDECCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1017 CORE3_DBG_EDPCSR_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1018 CORE3_DBG_EDCIDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1019 CORE3_DBG_EDVIDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1020 CORE3_DBG_EDPCSR_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1021 CORE3_DBG_OSLAR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1022 CORE3_DBG_EDPRCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1023 CORE3_DBG_EDPRSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1024 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1025 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1026 CORE3_DBG_DBGBCR0_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1027 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1028 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1029 CORE3_DBG_DBGBCR1_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1030 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR2_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1031 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR2_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1032 CORE3_DBG_DBGBCR2_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1033 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR3_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1034 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR3_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1035 CORE3_DBG_DBGBCR3_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1036 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR4_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1037 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR4_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1038 CORE3_DBG_DBGBCR4_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1039 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR5_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1040 CORE3_DBG_DBGBVR5_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1041 CORE3_DBG_DBGBCR5_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1042 CORE3_DBG_DBGWVR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1043 CORE3_DBG_DBGWVR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1044 CORE3_DBG_DBGWCR0_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1045 CORE3_DBG_DBGWVR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1046 CORE3_DBG_DBGWVR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1047 CORE3_DBG_DBGWCR1_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1048 CORE3_DBG_DBGWVR2_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1049 CORE3_DBG_DBGWVR2_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1050 CORE3_DBG_DBGWCR2_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1051 CORE3_DBG_DBGWVR3_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1052 CORE3_DBG_DBGWVR3_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1053 CORE3_DBG_DBGWCR3_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1054 CORE3_DBG_MIDR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1055 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64PFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1056 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64PFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1057 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64DFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1058 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64DFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1059 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1060 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1061 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1062 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR0_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1063 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64PFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1064 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64PFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1065 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64DFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1066 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64DFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1067 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1068 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64ISAR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1069 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR1_EL1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1070 CORE3_DBG_ID_AA64MMFR1_EL1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1071 CORE3_DBG_EDITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1072 CORE3_DBG_DBGCLAIMSET_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1073 CORE3_DBG_DBGCLAIMCLR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1074 CORE3_DBG_EDDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1075 CORE3_DBG_EDDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1076 CORE3_DBG_EDLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1077 CORE3_DBG_EDLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1078 CORE3_DBG_DBGAUTHSTATUS_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1079 CORE3_DBG_EDDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1080 CORE3_DBG_EDDEVID2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1081 CORE3_DBG_EDDEVID1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1082 CORE3_DBG_EDDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1083 CORE3_DBG_EDDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1084 CORE3_DBG_EDPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1085 CORE3_DBG_EDPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1086 CORE3_DBG_EDPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1087 CORE3_DBG_EDPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1088 CORE3_DBG_EDPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1089 CORE3_DBG_EDCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1090 CORE3_DBG_EDCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1091 CORE3_DBG_EDCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1092 CORE3_DBG_EDCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1093 CORE3_PMU_PMEVCNTR0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1094 CORE3_PMU_PMEVCNTR1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1095 CORE3_PMU_PMEVCNTR2_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1096 CORE3_PMU_PMEVCNTR3_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1097 CORE3_PMU_PMEVCNTR4_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1098 CORE3_PMU_PMEVCNTR5_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1099 CORE3_PMU_PMCCNTR_EL0_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1100 CORE3_PMU_PMCCNTR_EL0_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1101 CORE3_PMU_PMEVTYPER0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1102 CORE3_PMU_PMEVTYPER1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1103 CORE3_PMU_PMEVTYPER2_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1104 CORE3_PMU_PMEVTYPER3_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1105 CORE3_PMU_PMEVTYPER4_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1106 CORE3_PMU_PMEVTYPER5_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1107 CORE3_PMU_PMCCFILTR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1108 CORE3_PMU_PMCNTENSET_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1109 CORE3_PMU_PMCNTENCLR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1110 CORE3_PMU_PMINTENSET_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1111 CORE3_PMU_PMINTENCLR_EL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1112 CORE3_PMU_PMOVSCLR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1113 CORE3_PMU_PMSWINC_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1114 CORE3_PMU_PMOVSSET_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1115 CORE3_PMU_PMCFGR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1116 CORE3_PMU_PMCR_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1117 CORE3_PMU_PMCEID0_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1118 CORE3_PMU_PMCEID1_EL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1119 CORE3_PMU_PMITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1120 CORE3_PMU_PMDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1121 CORE3_PMU_PMDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1122 CORE3_PMU_PMLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1123 CORE3_PMU_PMLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1124 CORE3_PMU_PMAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1125 CORE3_PMU_PMDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1126 CORE3_PMU_PMDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1127 CORE3_PMU_PMPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1128 CORE3_PMU_PMPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1129 CORE3_PMU_PMPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1130 CORE3_PMU_PMPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1131 CORE3_PMU_PMPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1132 CORE3_PMU_PMPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1133 CORE3_PMU_PMPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1134 CORE3_PMU_PMPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1135 CORE3_PMU_PMCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1136 CORE3_PMU_PMCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1137 CORE3_PMU_PMCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1138 CORE3_PMU_PMCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1139 CORE3_ETM_TRCPRGCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1140 CORE3_ETM_TRCSTATR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1141 CORE3_ETM_TRCCONFIGR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1142 CORE3_ETM_TRCAUXCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1143 CORE3_ETM_TRCEVENTCTL0R Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1144 CORE3_ETM_TRCEVENTCTL1R Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1145 CORE3_ETM_TRCSTALLCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1146 CORE3_ETM_TRCTSCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1147 CORE3_ETM_TRCSYNCPR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1148 CORE3_ETM_TRCCCCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1149 CORE3_ETM_TRCBBCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1150 CORE3_ETM_TRCTRACEIDR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1151 CORE3_ETM_TRCVICTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1152 CORE3_ETM_TRCVIIECTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1153 CORE3_ETM_TRCVISSCTLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1154 CORE3_ETM_TRCSEQEVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1155 CORE3_ETM_TRCSEQEVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1156 CORE3_ETM_TRCSEQEVR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1157 CORE3_ETM_TRCSEQRSTEVR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1158 CORE3_ETM_TRCSEQSTR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1159 CORE3_ETM_TRCEXTINSELR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1160 CORE3_ETM_TRCCNTRLDVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1161 CORE3_ETM_TRCCNTRLDVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1162 CORE3_ETM_TRCCNTCTLR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1163 CORE3_ETM_TRCCNTCTLR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1164 CORE3_ETM_TRCCNTVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1165 CORE3_ETM_TRCCNTVR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1166 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR8 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1167 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR9 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1168 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR10 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1169 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR11 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1170 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR12 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1171 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR13 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1172 CORE3_ETM_TRCIMSPEC0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1173 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1174 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1175 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1176 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1177 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1178 CORE3_ETM_TRCIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1179 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1180 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1181 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1182 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1183 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1184 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1185 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR8 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1186 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR9 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1187 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR10 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1188 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR11 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1189 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR12 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1190 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR13 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1191 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR14 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1192 CORE3_ETM_TRCRSCTLR15 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1193 CORE3_ETM_TRCSSCCR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1194 CORE3_ETM_TRCSSCSR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1195 CORE3_ETM_TRCOSLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1196 CORE3_ETM_TRCOSLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1197 CORE3_ETM_TRCPDCR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1198 CORE3_ETM_TRCPDSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1199 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR0_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1200 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR0_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1201 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR1_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1202 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR1_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1203 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR2_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1204 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR2_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1205 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR3_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1206 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR3_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1207 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR4_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1208 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR4_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1209 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR5_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1210 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR5_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1211 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR6_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1212 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR6_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1213 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR7_31_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1214 CORE3_ETM_TRCACVR7_63_32 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1215 CORE3_ETM_TRCACATR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1216 CORE3_ETM_TRCACATR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1217 CORE3_ETM_TRCACATR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1218 CORE3_ETM_TRCACATR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1219 CORE3_ETM_TRCACATR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1220 CORE3_ETM_TRCACATR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1221 CORE3_ETM_TRCACATR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1222 CORE3_ETM_TRCACATR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1223 CORE3_ETM_TRCCIDCVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1224 CORE3_ETM_TRCVMIDCVR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1225 CORE3_ETM_TRCCIDCCTLR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1226 CORE3_ETM_TRCITATBIDR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1227 CORE3_ETM_TRCITIDATAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1228 CORE3_ETM_TRCITIATBINR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1229 CORE3_ETM_TRCITIATBOUTR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1230 CORE3_ETM_TRCITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1231 CORE3_ETM_TRCCLAIMSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1232 CORE3_ETM_TRCCLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1233 CORE3_ETM_TRCDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1234 CORE3_ETM_TRCDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1235 CORE3_ETM_TRCLAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1236 CORE3_ETM_TRCLSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1237 CORE3_ETM_TRCAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1238 CORE3_ETM_TRCDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1239 CORE3_ETM_TRCDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1240 CORE3_ETM_TRCDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1241 CORE3_ETM_TRCPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1242 CORE3_ETM_TRCPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1243 CORE3_ETM_TRCPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1244 CORE3_ETM_TRCPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1245 CORE3_ETM_TRCPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1246 CORE3_ETM_TRCPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1247 CORE3_ETM_TRCPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1248 CORE3_ETM_TRCPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1249 CORE3_ETM_TRCCIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1250 CORE3_ETM_TRCCIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1251 CORE3_ETM_TRCCIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1252 CORE3_ETM_TRCCIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1253 CORE3_CTI_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1254 CORE3_CTI_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1255 CORE3_CTI_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1256 CORE3_CTI_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1257 CORE3_CTI_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1258 CORE3_CTI_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1259 CORE3_CTI_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1260 CORE3_CTI_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1261 CORE3_CTI_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1262 CORE3_CTI_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1263 CORE3_CTI_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1264 CORE3_CTI_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1265 CORE3_CTI_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1266 CORE3_CTI_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1267 CORE3_CTI_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1268 CORE3_CTI_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1269 CORE3_CTI_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1270 CORE3_CTI_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1271 CORE3_CTI_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1272 CORE3_CTI_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1273 CORE3_CTI_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1274 CORE3_CTI_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1275 CORE3_CTI_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1276 CORE3_CTI_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1277 CORE3_CTI_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1278 CORE3_CTI_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1279 CORE3_CTI_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1280 CORE3_CTI_CTIITCTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1281 CORE3_CTI_CTICLAIMSET Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1282 CORE3_CTI_CTICLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1283 CORE3_CTI_CTIDEVAFF0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1284 CORE3_CTI_CTIDEVAFF1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1285 CORE3_CTI_CTILAR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1286 CORE3_CTI_CTILSR Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1287 CORE3_CTI_CTIAUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1288 CORE3_CTI_CTIDEVARCH Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1289 CORE3_CTI_CTIDEVID2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1290 CORE3_CTI_CTIDEVID1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1291 CORE3_CTI_CTIDEVID Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1292 CORE3_CTI_CTIDEVTYPE Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1293 CORE3_CTI_CTIPIDR4 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1294 CORE3_CTI_CTIPIDR5 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1295 CORE3_CTI_CTIPIDR6 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1296 CORE3_CTI_CTIPIDR7 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1297 CORE3_CTI_CTIPIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1298 CORE3_CTI_CTIPIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1299 CORE3_CTI_CTIPIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1300 CORE3_CTI_CTIPIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1301 CORE3_CTI_CTICIDR0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1302 CORE3_CTI_CTICIDR1 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1303 CORE3_CTI_CTICIDR2 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1304 CORE3_CTI_CTICIDR3 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.1305 Access Table
- 14.3.1.2
A53_RS_BW_LIMITER Registers
- 14.3.1.2.1 REGS_PID Registers
- 14.3.1.2.2 REGS_CTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.2.3 REGS_RD_BW_CIR Registers
- 14.3.1.2.4 REGS_RD_BW_PIR Registers
- 14.3.1.2.5 REGS_RD_BW_BURST_OFFSET Registers
- 14.3.1.2.6 REGS_RD_BW_INFO Registers
- 14.3.1.2.7 REGS_RD_BW_STATS Registers
- 14.3.1.2.8 REGS_RD_BW_STATS_THRSHLD Registers
- 14.3.1.2.9 REGS_RD_BW_WINDOWS_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.2.10 REGS_RD_BW_STATS_CIR Registers
- 14.3.1.2.11 REGS_RD_BW_STATS_PIR Registers
- 14.3.1.2.12 REGS_RD_BW_THRSHLD_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.2.13 REGS_RD_BYTES_MAX Registers
- 14.3.1.2.14 REGS_RD_TXN Registers
- 14.3.1.2.15 REGS_RD_TXN_INFO Registers
- 14.3.1.2.16 REGS_RD_TXN_STATS Registers
- 14.3.1.2.17 REGS_RD_TXN_STATS_THRSHLD Registers
- 14.3.1.2.18 REGS_RD_TXN_WINDOWS_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.2.19 REGS_RD_TXN_LIMIT_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.2.20 REGS_RD_TXN_THRESHOLD_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.2.21 REGS_RD_TXN_LIMIT_TOTAL Registers
- 14.3.1.2.22 REGS_RD_TXN_THRESHOLD_TOTAL Registers
- 14.3.1.2.23 REGS_RD_TXN_MAX Registers
- 14.3.1.2.24 Access Table
- 14.3.1.3
A53_WS_BW_LIMITER Registers
- 14.3.1.3.1 REGS_PID Registers
- 14.3.1.3.2 REGS_CTRL Registers
- 14.3.1.3.3 REGS_WR_BW_CIR Registers
- 14.3.1.3.4 REGS_WR_BW_PIR Registers
- 14.3.1.3.5 REGS_WR_BW_BURST_OFFSET Registers
- 14.3.1.3.6 REGS_WR_BW_INFO Registers
- 14.3.1.3.7 REGS_WR_BW_STATS Registers
- 14.3.1.3.8 REGS_WR_BW_STATS_THRSHLD Registers
- 14.3.1.3.9 REGS_WR_BW_WINDOWS_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.3.10 REGS_WR_BW_STATS_CIR Registers
- 14.3.1.3.11 REGS_WR_BW_STATS_PIR Registers
- 14.3.1.3.12 REGS_WR_BW_THRSHLD_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.3.13 REGS_WR_BYTES_MAX Registers
- 14.3.1.3.14 REGS_WR_TXN Registers
- 14.3.1.3.15 REGS_WR_TXN_INFO Registers
- 14.3.1.3.16 REGS_WR_TXN_STATS Registers
- 14.3.1.3.17 REGS_WR_TXN_STATS_THRSHLD Registers
- 14.3.1.3.18 REGS_WR_TXN_WINDOWS_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.3.19 REGS_WR_TXN_LIMIT_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.3.20 REGS_WR_TXN_THRESHOLD_CNT Registers
- 14.3.1.3.21 REGS_WR_TXN_LIMIT_TOTAL Registers
- 14.3.1.3.22 REGS_WR_TXN_THRESHOLD_TOTAL Registers
- 14.3.1.3.23 REGS_WR_TXN_MAX Registers
- 14.3.1.3.24 Access Table
- 14.3.1.4
COMPUTE_CLUSTER_PBIST_0 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.1 PBIST_RF0L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.2 PBIST_RF1L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.3 PBIST_RF2L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.4 PBIST_RF3L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.5 PBIST_RF4L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.6 PBIST_RF5L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.7 PBIST_RF6L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.8 PBIST_RF7L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.9 PBIST_RF8L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.10 PBIST_RF9L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.11 PBIST_RF10L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.12 PBIST_RF11L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.13 PBIST_RF12L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.14 PBIST_RF13L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.15 PBIST_RF14L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.16 PBIST_RF15L Registers
- 14.3.1.4.17 PBIST_RF0U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.18 PBIST_RF1U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.19 PBIST_RF2U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.20 PBIST_RF3U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.21 PBIST_RF4U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.22 PBIST_RF5U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.23 PBIST_RF6U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.24 PBIST_RF7U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.25 PBIST_RF8U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.26 PBIST_RF9U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.27 PBIST_RF10U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.28 PBIST_RF11U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.29 PBIST_RF12U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.30 PBIST_RF13U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.31 PBIST_RF14U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.32 PBIST_RF15U Registers
- 14.3.1.4.33 PBIST_A0 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.34 PBIST_A1 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.35 PBIST_A2 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.36 PBIST_A3 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.37 PBIST_L0 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.38 PBIST_L1 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.39 PBIST_L2 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.40 PBIST_L3 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.41 PBIST_D Registers
- 14.3.1.4.42 PBIST_E Registers
- 14.3.1.4.43 PBIST_CA0 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.44 PBIST_CA1 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.45 PBIST_CA2 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.46 PBIST_CA3 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.47 PBIST_CL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.48 PBIST_CL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.49 PBIST_CL2 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.50 PBIST_CL3 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.51 PBIST_I0 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.52 PBIST_I1 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.53 PBIST_I2 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.54 PBIST_I3 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.55 PBIST_RAMT Registers
- 14.3.1.4.56 PBIST_DLR Registers
- 14.3.1.4.57 PBIST_CMS Registers
- 14.3.1.4.58 PBIST_STR Registers
- 14.3.1.4.59 PBIST_SCR Registers
- 14.3.1.4.60 PBIST_CSR Registers
- 14.3.1.4.61 PBIST_FDLY Registers
- 14.3.1.4.62 PBIST_PACT Registers
- 14.3.1.4.63 PBIST_PID Registers
- 14.3.1.4.64 PBIST_OVER Registers
- 14.3.1.4.65 PBIST_FSRF Registers
- 14.3.1.4.66 PBIST_FSRC Registers
- 14.3.1.4.67 PBIST_FSRA Registers
- 14.3.1.4.68 PBIST_FSRDL0 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.69 PBIST_FSRDL1 Registers
- 14.3.1.4.70 PBIST_MARGIN_MODE Registers
- 14.3.1.4.71 PBIST_WRENZ Registers
- 14.3.1.4.72 PBIST_PAGE_PGS Registers
- 14.3.1.4.73 PBIST_ROM Registers
- 14.3.1.4.74 PBIST_ALGO Registers
- 14.3.1.4.75 PBIST_RINFO Registers
- 14.3.1.4.76 Access Table
- 14.3.1.1
A53SS Registers
- 14.3.2
M4FSS Registers
- 14.3.2.1 M4FSS_DRAM_0 Registers
- 14.3.2.2 M4FSS_IRAM_0 Registers
- 14.3.2.3
M4FSS_RAT_0 Registers
- 14.3.2.3.1 RAT_PID Registers
- 14.3.2.3.2 RAT_CONFIG Registers
- 14.3.2.3.3 RAT_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.3.2.3.4 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Registers
- 14.3.2.3.5 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.3.2.3.6 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.3.2.3.7 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.3.2.3.8 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.3.2.3.9 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.3.2.3.10 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.3.2.3.11 RAT_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Registers
- 14.3.2.3.12 RAT_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Registers
- 14.3.2.3.13 RAT_EXCEPTION_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.2.3.14 RAT_EXCEPTION_ENABLE_CLEAR Registers
- 14.3.2.3.15 RAT_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.2.3.16 RAT_REGION_REGION_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.3.2.3.17 RAT_REGION_REGION_BASE_J_J Registers
- 14.3.2.3.18 RAT_REGION_REGION_TRANS_L_J_J Registers
- 14.3.2.3.19 RAT_REGION_REGION_TRANS_U_J_J Registers
- 14.3.2.3.20 Access Table
- 14.3.3
R5FSS Registers
- 14.3.3.1
R5FSS_COMMON0 Registers
- 14.3.3.1.1 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_DISABLE_CR Registers
- 14.3.3.1.2 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_CPU0_EVNT_BUS_SB_ERR_CNT_STATUS Registers
- 14.3.3.1.3 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_CPU1_EVNT_BUS_SB_ERR_CNT_STATUS Registers
- 14.3.3.1.4 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_CPU0_EVNT_BUS_MB_ERR_CNT_STATUS Registers
- 14.3.3.1.5 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_CPU1_EVNT_BUS_MB_ERR_CNT_STATUS Registers
- 14.3.3.1.6 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_ESM_STATUS Registers
- 14.3.3.1.7 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_ESM_SET Registers
- 14.3.3.1.8 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_ESM_CLR Registers
- 14.3.3.1.9 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_MASK_ESM_SET Registers
- 14.3.3.1.10 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_MASK_ESM_CLR Registers
- 14.3.3.1.11 EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVT_BUS_REVID Registers
- 14.3.3.1.12 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.3.3.1.13 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.3.3.1.14 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.3.3.1.15 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.3.3.1.16 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.3.1.17 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.3.1.18 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.3.1.19 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.3.1.20 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.3.1.21 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.3.1.22 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.3.1.23 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.3.1.24 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.3.1.25 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.3.3.1.26 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.3.3.1.27 CORE0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.3.3.1.28 Access Table
- 14.3.3.1
R5FSS_COMMON0 Registers
- 14.3.4
VIM Registers
- 14.3.4.1 Revision Register (Base Address + 0x00)
- 14.3.4.2 Info Register (Base Address + 0x04)
- 14.3.4.3 Prioritized IRQ (Base Address + 0x08)
- 14.3.4.4 Prioritized FIQ (Base Address + 0x0C)
- 14.3.4.5 IRQ Group Status (Base Address + 0x10)
- 14.3.4.6 FIQ Group Status (Base Address + 0x14)
- 14.3.4.7 IRQ Vector Address (Base Address + 0x18)
- 14.3.4.8 FIQ Vector Address (Base Address + 0x1C)
- 14.3.4.9 Active IRQ (Base Address + 0x20)
- 14.3.4.10 Active FIQ (Base Address + 0x24)
- 14.3.4.11 IRQ Priority Mask Register (Base Address + 0x28)
- 14.3.4.12 FIQ Priority Mask Register (Base Address + 0x2C)
- 14.3.4.13 DED Vector Address (Base Address + 0x30)
- 14.3.4.14 Group M Interrupt Raw Status/Set Register (Base Address + 0x400 + M*0x20 + 0x00)
- 14.3.4.15 Group M Interrupt Enabled Status/Clear Register (Base Address + 0x400 + M*0x20 + 0x04)
- 14.3.4.16 Group M Interrupt Enabled Set Register (Base Address + 0x400 + M*0x20 + 0x08)
- 14.3.4.17 Group M Interrupt Enabled Clear Register (Base Address + 0x400 + M*0x20 + 0x0C)
- 14.3.4.18 Group M Interrupt IRQ Enabled Status/Clear Register (Base Address + 0x400 + M*0x20 + 0x10)
- 14.3.4.19 Group M Interrupt FIQ Enabled Status/Clear Register (Base Address + 0x400 + M*0x20 + 0x14)
- 14.3.4.20 Group M Interrupt Map Register (Base Address + 0x400 + M*0x20 + 0x18)
- 14.3.4.21 Group M Type Map Register (Base Address + 0x400 + M*0x20 + 0x1C)
- 14.3.4.22 Interrupt Q Priority Register (Base Address + 0x1000 + Q*0x4)
- 14.3.4.23 Interrupt Q Vector Register (Base Address + 0x2000 + Q*0x4)
- 14.3.5
PRUSS
Registers
- 14.3.5.1
ICSSM Registers
- 14.3.5.1.1 DRAM0_SLV_RAM_RAM_REG_N Registers
- 14.3.5.1.2 DRAM1_SLV_RAM_RAM_REG_N Registers
- 14.3.5.1.3 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_PID Registers
- 14.3.5.1.4 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_CONFIG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.5 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.3.5.1.6 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Registers
- 14.3.5.1.7 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.8 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.9 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.10 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.11 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.12 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.13 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Registers
- 14.3.5.1.14 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.15 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.5.1.16 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EXCEPTION_ENABLE_CLEAR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.17 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.18 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_REGION_REGION_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.19 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_REGION_REGION_BASE_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.20 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_REGION_REGION_TRANS_L_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.21 RAT_SLICE0_CFG_REGION_REGION_TRANS_U_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.22 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_PID Registers
- 14.3.5.1.23 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_CONFIG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.24 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_DESTINATION_ID Registers
- 14.3.5.1.25 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Registers
- 14.3.5.1.26 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.27 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.28 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.29 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.30 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.31 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.32 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Registers
- 14.3.5.1.33 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.34 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.5.1.35 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EXCEPTION_ENABLE_CLEAR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.36 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.37 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_REGION_REGION_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.38 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_REGION_REGION_BASE_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.39 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_REGION_REGION_TRANS_L_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.40 RAT_SLICE1_CFG_REGION_REGION_TRANS_U_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.41 RAM_SLV_RAM_RAM_REG_N Registers
- 14.3.5.1.42 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_REVISION_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.43 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.44 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_GLOBAL_ENABLE_HINT_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.45 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_GLB_NEST_LEVEL_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.46 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_STATUS_SET_INDEX_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.47 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_STATUS_CLR_INDEX_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.48 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_ENABLE_SET_INDEX_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.49 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_ENABLE_CLR_INDEX_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.50 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_HINT_ENABLE_SET_INDEX_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.51 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_HINT_ENABLE_CLR_INDEX_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.52 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_GLB_PRI_INTR_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.53 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_RAW_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.54 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_RAW_STATUS_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.55 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_ENA_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.56 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_ENA_STATUS_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.57 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_ENABLE_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.58 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_ENABLE_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.59 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.60 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_ENABLE_CLR_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.61 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.62 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.63 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.64 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.65 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.66 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.67 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.68 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.69 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.70 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG9 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.71 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG10 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.72 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG11 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.73 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG12 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.74 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG13 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.75 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG14 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.76 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_CH_MAP_REG15 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.77 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_HINT_MAP_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.78 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_HINT_MAP_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.79 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_HINT_MAP_REG2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.80 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.81 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.82 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.83 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.84 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.85 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.86 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.87 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.88 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.89 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_PRI_HINT_REG9 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.90 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_POLARITY_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.91 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_POLARITY_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.92 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_TYPE_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.93 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_TYPE_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.94 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.95 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.96 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.97 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.98 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.99 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.100 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.101 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.102 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.103 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_NEST_LEVEL_REG9 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.104 PR1_ICSS_INTC_INTC_SLV_ENABLE_HINT_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.105 PR1_PROT_SLV_UNLOCK_KEY Registers
- 14.3.5.1.106 PR1_PROT_SLV_CFG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.107 PR1_CFG_SLV_PID_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.108 PR1_CFG_SLV_HWDIS_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.109 PR1_CFG_SLV_GPCFG0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.110 PR1_CFG_SLV_GPCFG1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.111 PR1_CFG_SLV_CGR_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.112 PR1_CFG_SLV_GPECFG0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.113 PR1_CFG_SLV_GPECFG1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.114 PR1_CFG_SLV_RESET_ISO_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.115 PR1_CFG_SLV_MII_RT_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.116 PR1_CFG_SLV_IEPCLK_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.117 PR1_CFG_SLV_SPP_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.118 PR1_CFG_SLV_SPIN_CFG_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.119 PR1_CFG_SLV_CORE_SYNC_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.120 PR1_CFG_SLV_SA_MX_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.121 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_DIV_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.122 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_SEL_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.123 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.124 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_SEL_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.125 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.126 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_SEL_REG2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.127 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.128 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_SEL_REG3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.129 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.130 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_SEL_REG4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.131 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.132 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_SEL_REG5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.133 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.134 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_SEL_REG6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.135 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.136 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_SEL_REG7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.137 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.138 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_CLK_SEL_REG8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.139 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.140 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_DIV_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.141 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_SEL_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.142 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.143 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_SEL_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.144 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.145 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_SEL_REG2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.146 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.147 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_SEL_REG3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.148 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.149 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_SEL_REG4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.150 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.151 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_SEL_REG5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.152 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.153 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_SEL_REG6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.154 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.155 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_SEL_REG7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.156 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.157 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_CLK_SEL_REG8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.158 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_SD_SAMPLE_SIZE_REG8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.159 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_ED_RX_CFG_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.160 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_ED_TX_CFG_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.161 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_ED_CH0_CFG0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.162 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_ED_CH0_CFG1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.163 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_ED_CH1_CFG0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.164 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_ED_CH1_CFG1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.165 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_ED_CH2_CFG0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.166 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU0_ED_CH2_CFG1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.167 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_ED_RX_CFG_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.168 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_ED_TX_CFG_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.169 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_ED_CH0_CFG0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.170 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_ED_CH0_CFG1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.171 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_ED_CH1_CFG0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.172 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_ED_CH1_CFG1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.173 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_ED_CH2_CFG0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.174 PR1_CFG_SLV_PRU1_ED_CH2_CFG1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.175 PR1_CFG_SLV_RTU0_POKE_EN0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.176 PR1_CFG_SLV_RTU1_POKE_EN0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.177 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.178 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.179 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.180 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.181 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM0_0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.182 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM0_1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.183 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM0_2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.184 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM1_0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.185 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM1_1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.186 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM1_2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.187 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM2_0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.188 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM2_1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.189 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM2_2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.190 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM3_0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.191 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM3_1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.192 PR1_CFG_SLV_PWM3_2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.193 PR1_CFG_SLV_SPIN_LOCK0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.194 PR1_CFG_SLV_SPIN_LOCK1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.195 PR1_CFG_SLV_PA_STAT_PDSP_CFG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.196 PR1_CFG_SLV_PA_STAT_PDSP_STAT0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.197 PR1_CFG_SLV_PA_STAT_PDSP_CFG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.198 PR1_CFG_SLV_PA_STAT_PDSP_STAT1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.199 PR1_CFG_SLV_PA_STAT_PDSP_CFG2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.200 PR1_CFG_SLV_PA_STAT_PDSP_STAT2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.201 PR1_CFG_SLV_PA_STAT_PDSP_CFG3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.202 PR1_CFG_SLV_PA_STAT_PDSP_STAT3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.203 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_RBR_TBR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.204 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_INT_EN Registers
- 14.3.5.1.205 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_INT_FIFO Registers
- 14.3.5.1.206 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_LCTR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.207 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_MCTR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.208 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_LSR1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.209 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_MSR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.210 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_SCRATCH Registers
- 14.3.5.1.211 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_DIVLSB Registers
- 14.3.5.1.212 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_DIVMSB Registers
- 14.3.5.1.213 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_PID Registers
- 14.3.5.1.214 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_PWR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.215 PR1_ICSS_UART_UART_SLV_MODE Registers
- 14.3.5.1.216 IEP0_GLOBAL_CFG_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.217 IEP0_GLOBAL_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.218 IEP0_COMPEN_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.219 IEP0_SLOW_COMPEN_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.220 IEP0_COUNT_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.221 IEP0_COUNT_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.222 IEP0_CAP_CFG_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.223 IEP0_CAP_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.224 IEP0_CAPR0_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.225 IEP0_CAPR0_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.226 IEP0_CAPR1_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.227 IEP0_CAPR1_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.228 IEP0_CAPR2_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.229 IEP0_CAPR2_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.230 IEP0_CAPR3_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.231 IEP0_CAPR3_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.232 IEP0_CAPR4_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.233 IEP0_CAPR4_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.234 IEP0_CAPR5_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.235 IEP0_CAPR5_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.236 IEP0_CAPR6_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.237 IEP0_CAPR6_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.238 IEP0_CAPF6_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.239 IEP0_CAPF6_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.240 IEP0_CAPR7_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.241 IEP0_CAPR7_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.242 IEP0_CAPF7_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.243 IEP0_CAPF7_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.244 IEP0_CMP_CFG_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.245 IEP0_CMP_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.246 IEP0_CMP0_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.247 IEP0_CMP0_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.248 IEP0_CMP1_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.249 IEP0_CMP1_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.250 IEP0_CMP2_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.251 IEP0_CMP2_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.252 IEP0_CMP3_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.253 IEP0_CMP3_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.254 IEP0_CMP4_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.255 IEP0_CMP4_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.256 IEP0_CMP5_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.257 IEP0_CMP5_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.258 IEP0_CMP6_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.259 IEP0_CMP6_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.260 IEP0_CMP7_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.261 IEP0_CMP7_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.262 IEP0_RXIPG0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.263 IEP0_RXIPG1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.264 IEP0_CMP8_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.265 IEP0_CMP8_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.266 IEP0_CMP9_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.267 IEP0_CMP9_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.268 IEP0_CMP10_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.269 IEP0_CMP10_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.270 IEP0_CMP11_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.271 IEP0_CMP11_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.272 IEP0_CMP12_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.273 IEP0_CMP12_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.274 IEP0_CMP13_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.275 IEP0_CMP13_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.276 IEP0_CMP14_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.277 IEP0_CMP14_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.278 IEP0_CMP15_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.279 IEP0_CMP15_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.280 IEP0_COUNT_RESET_VAL_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.281 IEP0_COUNT_RESET_VAL_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.282 IEP0_PWM_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.283 IEP0_CAPR0_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.284 IEP0_CAPR0_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.285 IEP0_CAPR1_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.286 IEP0_CAPR1_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.287 IEP0_CAPR2_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.288 IEP0_CAPR2_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.289 IEP0_CAPR3_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.290 IEP0_CAPR3_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.291 IEP0_CAPR4_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.292 IEP0_CAPR4_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.293 IEP0_CAPR5_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.294 IEP0_CAPR5_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.295 IEP0_CAPR6_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.296 IEP0_CAPR6_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.297 IEP0_CAPF6_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.298 IEP0_CAPF6_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.299 IEP0_CAPR7_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.300 IEP0_CAPR7_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.301 IEP0_CAPF7_BI_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.302 IEP0_CAPF7_BI_REG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.303 IEP0_SYNC_CTRL_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.304 IEP0_SYNC_FIRST_STAT_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.305 IEP0_SYNC0_STAT_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.306 IEP0_SYNC1_STAT_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.307 IEP0_SYNC_PWIDTH_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.308 IEP0_SYNC0_PERIOD_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.309 IEP0_SYNC1_DELAY_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.310 IEP0_SYNC_START_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.311 IEP0_WD_PREDIV_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.312 IEP0_PDI_WD_TIM_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.313 IEP0_PD_WD_TIM_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.314 IEP0_WD_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.315 IEP0_WD_EXP_CNT_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.316 IEP0_WD_CTRL_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.317 IEP0_DIGIO_CTRL_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.318 IEP0_DIGIO_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.319 IEP0_DIGIO_DATA_IN_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.320 IEP0_DIGIO_DATA_IN_RAW_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.321 IEP0_DIGIO_DATA_OUT_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.322 IEP0_DIGIO_DATA_OUT_EN_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.323 IEP0_DIGIO_EXP_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.324 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_TSCNT Registers
- 14.3.5.1.325 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_CNTPHS Registers
- 14.3.5.1.326 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_CAP1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.327 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_CAP2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.328 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_CAP3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.329 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_CAP4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.330 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_ECCTL2_ECCTL1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.331 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_ECFLG_ECEINT Registers
- 14.3.5.1.332 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_ECCLR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.333 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_ECFRC Registers
- 14.3.5.1.334 PR1_ICSS_ECAP0_ECAP_SLV_PID Registers
- 14.3.5.1.335 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RXCFG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.336 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RXCFG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.337 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_TXCFG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.338 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_TXCFG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.339 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_TX_CRC0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.340 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_TX_CRC1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.341 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_TX_IPG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.342 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_TX_IPG1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.343 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_PRS0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.344 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_PRS1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.345 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RX_FRMS0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.346 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RX_FRMS1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.347 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RX_PCNT0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.348 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RX_PCNT1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.349 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RX_ERR0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.350 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RX_ERR1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.351 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RX_FIFO_LEVEL0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.352 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_RX_FIFO_LEVEL1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.353 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_TX_FIFO_LEVEL0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.354 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_CFG_TX_FIFO_LEVEL1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.355 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_MDIO_VERSION_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.356 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.357 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_ALIVE_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.358 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_LINK_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.359 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_LINK_INT_RAW_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.360 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_LINK_INT_MASKED_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.361 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_LINK_INT_MASK_SET_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.362 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_LINK_INT_MASK_CLEAR_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.363 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_USER_INT_RAW_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.364 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_USER_INT_MASKED_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.365 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_USER_INT_MASK_SET_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.366 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_USER_INT_MASK_CLEAR_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.367 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_MANUAL_IF_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.368 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_POLL_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.369 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_POLL_EN_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.370 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_CLAUS45_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.371 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_USER_ADDR0_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.372 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_USER_ADDR1_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.373 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_USER_GROUP_USER_GROUP_USER_ACCESS_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.374 PR1_MDIO_V1P7_MDIO_USER_GROUP_USER_GROUP_USER_PHY_SEL_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.3.5.1.375 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_ICSS_G_CFG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.376 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_PREEMPT_CFG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.377 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_SMDT1S_CFG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.378 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_SMDT1C_CFG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.379 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_POOL_PTR_CFG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.380 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_TX_EARLY_EOF Registers
- 14.3.5.1.381 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_FRAG_CNT_CFG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.382 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.383 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.384 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.385 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.386 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.387 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.388 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.389 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.390 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.391 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE9 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.392 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE10 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.393 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE11 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.394 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE12 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.395 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE13 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.396 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE14 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.397 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE15 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.398 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE16 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.399 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE17 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.400 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE18 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.401 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE19 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.402 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE20 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.403 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE21 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.404 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE22 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.405 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE23 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.406 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE24 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.407 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE25 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.408 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE26 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.409 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE27 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.410 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE28 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.411 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE29 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.412 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE30 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.413 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE31 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.414 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.415 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.416 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.417 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.418 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.419 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.420 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.421 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.422 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.423 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK9 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.424 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK10 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.425 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK11 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.426 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK12 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.427 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK13 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.428 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK14 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.429 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_PEEK15 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.430 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.431 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT1 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.432 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT2 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.433 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT3 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.434 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT4 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.435 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT5 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.436 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT6 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.437 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT7 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.438 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT8 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.439 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT9 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.440 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT10 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.441 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT11 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.442 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT12 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.443 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT13 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.444 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT14 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.445 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT15 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.446 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT16 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.447 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT17 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.448 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT18 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.449 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT19 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.450 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT20 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.451 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT21 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.452 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT22 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.453 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT23 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.454 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT24 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.455 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT25 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.456 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT26 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.457 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT27 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.458 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT28 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.459 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT29 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.460 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT30 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.461 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_CNT31 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.462 PR1_MII_RT_PR1_MII_RT_G_CFG_REGS_G_QUEUE_RESET Registers
- 14.3.5.1.463 ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.3.5.1.464 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.465 ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.3.5.1.466 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.3.5.1.467 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.468 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.469 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.470 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.471 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.3.5.1.472 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.473 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.474 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.3.5.1.475 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.3.5.1.476 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.477 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.3.5.1.478 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.3.5.1.479 Access Table
- 14.3.5.1
ICSSM Registers
- 14.3.6
GPU Registers
- 14.3.6.1 Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
- 14.3.6.2
GPU_WS_BW_LIMITER Registers
- 14.3.6.2.1 REGS_PID Registers
- 14.3.6.2.2 REGS_CTRL Registers
- 14.3.6.2.3 REGS_WR_BW_CIR Registers
- 14.3.6.2.4 REGS_WR_BW_PIR Registers
- 14.3.6.2.5 REGS_WR_BW_BURST_OFFSET Registers
- 14.3.6.2.6 REGS_WR_BW_INFO Registers
- 14.3.6.2.7 REGS_WR_BW_STATS Registers
- 14.3.6.2.8 REGS_WR_BW_STATS_THRSHLD Registers
- 14.3.6.2.9 REGS_WR_BW_WINDOWS_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.2.10 REGS_WR_BW_STATS_CIR Registers
- 14.3.6.2.11 REGS_WR_BW_STATS_PIR Registers
- 14.3.6.2.12 REGS_WR_BW_THRSHLD_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.2.13 REGS_WR_BYTES_MAX Registers
- 14.3.6.2.14 REGS_WR_TXN Registers
- 14.3.6.2.15 REGS_WR_TXN_INFO Registers
- 14.3.6.2.16 REGS_WR_TXN_STATS Registers
- 14.3.6.2.17 REGS_WR_TXN_STATS_THRSHLD Registers
- 14.3.6.2.18 REGS_WR_TXN_WINDOWS_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.2.19 REGS_WR_TXN_LIMIT_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.2.20 REGS_WR_TXN_THRESHOLD_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.2.21 REGS_WR_TXN_LIMIT_TOTAL Registers
- 14.3.6.2.22 REGS_WR_TXN_THRESHOLD_TOTAL Registers
- 14.3.6.2.23 REGS_WR_TXN_MAX Registers
- 14.3.6.2.24 Access Table
- 14.3.6.3
GPU_RS_BW_LIMITER Registers
- 14.3.6.3.1 REGS_PID Registers
- 14.3.6.3.2 REGS_CTRL Registers
- 14.3.6.3.3 REGS_RD_BW_CIR Registers
- 14.3.6.3.4 REGS_RD_BW_PIR Registers
- 14.3.6.3.5 REGS_RD_BW_BURST_OFFSET Registers
- 14.3.6.3.6 REGS_RD_BW_INFO Registers
- 14.3.6.3.7 REGS_RD_BW_STATS Registers
- 14.3.6.3.8 REGS_RD_BW_STATS_THRSHLD Registers
- 14.3.6.3.9 REGS_RD_BW_WINDOWS_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.3.10 REGS_RD_BW_STATS_CIR Registers
- 14.3.6.3.11 REGS_RD_BW_STATS_PIR Registers
- 14.3.6.3.12 REGS_RD_BW_THRSHLD_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.3.13 REGS_RD_BYTES_MAX Registers
- 14.3.6.3.14 REGS_RD_TXN Registers
- 14.3.6.3.15 REGS_RD_TXN_INFO Registers
- 14.3.6.3.16 REGS_RD_TXN_STATS Registers
- 14.3.6.3.17 REGS_RD_TXN_STATS_THRSHLD Registers
- 14.3.6.3.18 REGS_RD_TXN_WINDOWS_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.3.19 REGS_RD_TXN_LIMIT_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.3.20 REGS_RD_TXN_THRESHOLD_CNT Registers
- 14.3.6.3.21 REGS_RD_TXN_LIMIT_TOTAL Registers
- 14.3.6.3.22 REGS_RD_TXN_THRESHOLD_TOTAL Registers
- 14.3.6.3.23 REGS_RD_TXN_MAX Registers
- 14.3.6.3.24 Access Table
- 14.3.1
A53SS Registers
- 14.4
Interprocessor Communication Registers
- 14.4.1
MAILBOX_CLUSTER_0 Registers
- 14.4.1.1 REGS0_REVISION Registers
- 14.4.1.2 REGS0_SYSCONFIG Registers
- 14.4.1.3 REGS0_MESSAGE_N Registers
- 14.4.1.4 REGS0_FIFO_STATUS_N Registers
- 14.4.1.5 REGS0_MSG_STATUS_N Registers
- 14.4.1.6 REGS0_IRQ_EOI Registers
- 14.4.1.7 REGS0_USERS_USERS_IRQ_STATUS_RAW_J_J Registers
- 14.4.1.8 REGS0_USERS_USERS_IRQ_STATUS_CLR_J_J Registers
- 14.4.1.9 REGS0_USERS_USERS_IRQ_ENABLE_SET_J_J Registers
- 14.4.1.10 REGS0_USERS_USERS_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR_J_J Registers
- 14.4.1.11 Access Table
- 14.4.2 SPINLOCK Registers
- 14.4.1
MAILBOX_CLUSTER_0 Registers
- 14.5
Memory Controller Registers
- 14.5.1 ROM Registers
- 14.5.2
PSRAMECC Registers
- 14.5.2.1 RAM_RAM_REG_N Registers
- 14.5.2.2 ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.5.2.3 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.5.2.4 ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.5.2.5 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.5.2.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.5.2.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.2.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.2.9 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.2.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.5.2.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.2.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.2.13 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.2.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.5.2.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.5.2.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.5.2.17 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.5.2.18 Access Table
- 14.5.3
PSRAMECC_16K Registers
- 14.5.3.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.5.3.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.5.3.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.5.3.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.5.3.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.5.3.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.3.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.3.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.3.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.5.3.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.3.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.3.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.5.3.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.5.3.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.5.3.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.5.3.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.5.3.17 RAM_RAM_REG_N Registers
- 14.5.3.18 Access Table
- 14.5.4
DDR16SS Registers
- 14.5.4.1 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_SS_ID_REV_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.2 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_SS_CTL_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.3 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_CTL_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.4 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_R1_MAT_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.5 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_R2_MAT_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.6 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_R3_MAT_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.7 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_DEF_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.8 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_R1_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.9 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_R2_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.10 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_R3_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.11 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_OLD_CMD_PR_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.12 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_AERR_LOG1_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.13 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_AERR_LOG2_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.14 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_BUS_TO Registers
- 14.5.4.15 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_INT_RAW_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.16 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_INT_STAT_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.17 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_INT_SET_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.18 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_INT_CLR_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.19 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_V2A_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.20 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PERF_CNT_SEL_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.21 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PERF_CNT1_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.22 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PERF_CNT2_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.23 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PERF_CNT3_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.24 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PERF_CNT4_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.25 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_CTRL_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.26 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_RID_INDX_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.27 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_RID_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.28 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_R0_STR_ADDR_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.29 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_R0_END_ADDR_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.30 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_R1_STR_ADDR_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.31 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_R1_END_ADDR_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.32 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_R2_STR_ADDR_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.33 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_R2_END_ADDR_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.34 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_1B_ERR_CNT_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.35 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_1B_ERR_THRSH_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.36 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_1B_ERR_ADR_LOG_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.37 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_1B_ERR_MSK_LOG_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.38 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_2B_ERR_ADR_LOG_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.39 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_ECC_2B_ERR_MSK_LOG_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.40 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL1_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.41 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL2_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.42 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL3_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.43 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL4_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.44 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL5_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.45 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL6_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.46 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL7_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.47 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL8_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.48 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL9_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.49 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_CTRL10_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.50 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_STAT1_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.51 REGS_SS_CFG_SSCFG_PHY_TEST_STAT2_REG Registers
- 14.5.4.52 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_0 Registers
- 14.5.4.53 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_1 Registers
- 14.5.4.54 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_2 Registers
- 14.5.4.55 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_3 Registers
- 14.5.4.56 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_4 Registers
- 14.5.4.57 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_5 Registers
- 14.5.4.58 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_6 Registers
- 14.5.4.59 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_7 Registers
- 14.5.4.60 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_8 Registers
- 14.5.4.61 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_9 Registers
- 14.5.4.62 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_10 Registers
- 14.5.4.63 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_11 Registers
- 14.5.4.64 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_12 Registers
- 14.5.4.65 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_13 Registers
- 14.5.4.66 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_14 Registers
- 14.5.4.67 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_15 Registers
- 14.5.4.68 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_16 Registers
- 14.5.4.69 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_17 Registers
- 14.5.4.70 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_18 Registers
- 14.5.4.71 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_19 Registers
- 14.5.4.72 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_20 Registers
- 14.5.4.73 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_21 Registers
- 14.5.4.74 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_22 Registers
- 14.5.4.75 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_23 Registers
- 14.5.4.76 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_24 Registers
- 14.5.4.77 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_25 Registers
- 14.5.4.78 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_26 Registers
- 14.5.4.79 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_27 Registers
- 14.5.4.80 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_28 Registers
- 14.5.4.81 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_29 Registers
- 14.5.4.82 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_30 Registers
- 14.5.4.83 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_31 Registers
- 14.5.4.84 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_32 Registers
- 14.5.4.85 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_33 Registers
- 14.5.4.86 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_34 Registers
- 14.5.4.87 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_35 Registers
- 14.5.4.88 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_36 Registers
- 14.5.4.89 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_37 Registers
- 14.5.4.90 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_38 Registers
- 14.5.4.91 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_39 Registers
- 14.5.4.92 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_40 Registers
- 14.5.4.93 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_41 Registers
- 14.5.4.94 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_42 Registers
- 14.5.4.95 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_43 Registers
- 14.5.4.96 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_44 Registers
- 14.5.4.97 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_45 Registers
- 14.5.4.98 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_46 Registers
- 14.5.4.99 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_47 Registers
- 14.5.4.100 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_48 Registers
- 14.5.4.101 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_49 Registers
- 14.5.4.102 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_50 Registers
- 14.5.4.103 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_51 Registers
- 14.5.4.104 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_52 Registers
- 14.5.4.105 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_53 Registers
- 14.5.4.106 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_54 Registers
- 14.5.4.107 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_55 Registers
- 14.5.4.108 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_56 Registers
- 14.5.4.109 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_57 Registers
- 14.5.4.110 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_58 Registers
- 14.5.4.111 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_59 Registers
- 14.5.4.112 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_60 Registers
- 14.5.4.113 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_61 Registers
- 14.5.4.114 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_62 Registers
- 14.5.4.115 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_63 Registers
- 14.5.4.116 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_64 Registers
- 14.5.4.117 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_65 Registers
- 14.5.4.118 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_66 Registers
- 14.5.4.119 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_67 Registers
- 14.5.4.120 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_68 Registers
- 14.5.4.121 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_69 Registers
- 14.5.4.122 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_70 Registers
- 14.5.4.123 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_71 Registers
- 14.5.4.124 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_72 Registers
- 14.5.4.125 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_73 Registers
- 14.5.4.126 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_74 Registers
- 14.5.4.127 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_75 Registers
- 14.5.4.128 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_76 Registers
- 14.5.4.129 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_77 Registers
- 14.5.4.130 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_78 Registers
- 14.5.4.131 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_79 Registers
- 14.5.4.132 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_80 Registers
- 14.5.4.133 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_81 Registers
- 14.5.4.134 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_82 Registers
- 14.5.4.135 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_83 Registers
- 14.5.4.136 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_84 Registers
- 14.5.4.137 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_85 Registers
- 14.5.4.138 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_86 Registers
- 14.5.4.139 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_87 Registers
- 14.5.4.140 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_88 Registers
- 14.5.4.141 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_89 Registers
- 14.5.4.142 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_90 Registers
- 14.5.4.143 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_91 Registers
- 14.5.4.144 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_92 Registers
- 14.5.4.145 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_93 Registers
- 14.5.4.146 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_94 Registers
- 14.5.4.147 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_95 Registers
- 14.5.4.148 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_96 Registers
- 14.5.4.149 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_97 Registers
- 14.5.4.150 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_98 Registers
- 14.5.4.151 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_99 Registers
- 14.5.4.152 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_100 Registers
- 14.5.4.153 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_101 Registers
- 14.5.4.154 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_102 Registers
- 14.5.4.155 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_103 Registers
- 14.5.4.156 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_104 Registers
- 14.5.4.157 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_105 Registers
- 14.5.4.158 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_106 Registers
- 14.5.4.159 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_107 Registers
- 14.5.4.160 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_108 Registers
- 14.5.4.161 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_109 Registers
- 14.5.4.162 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_110 Registers
- 14.5.4.163 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_111 Registers
- 14.5.4.164 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_112 Registers
- 14.5.4.165 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_113 Registers
- 14.5.4.166 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_114 Registers
- 14.5.4.167 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_115 Registers
- 14.5.4.168 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_116 Registers
- 14.5.4.169 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_117 Registers
- 14.5.4.170 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_118 Registers
- 14.5.4.171 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_119 Registers
- 14.5.4.172 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_120 Registers
- 14.5.4.173 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_121 Registers
- 14.5.4.174 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_122 Registers
- 14.5.4.175 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_123 Registers
- 14.5.4.176 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_124 Registers
- 14.5.4.177 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_125 Registers
- 14.5.4.178 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_126 Registers
- 14.5.4.179 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_127 Registers
- 14.5.4.180 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_128 Registers
- 14.5.4.181 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_129 Registers
- 14.5.4.182 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_130 Registers
- 14.5.4.183 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_131 Registers
- 14.5.4.184 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_132 Registers
- 14.5.4.185 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_133 Registers
- 14.5.4.186 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_134 Registers
- 14.5.4.187 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_135 Registers
- 14.5.4.188 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_136 Registers
- 14.5.4.189 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_137 Registers
- 14.5.4.190 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_138 Registers
- 14.5.4.191 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_139 Registers
- 14.5.4.192 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_140 Registers
- 14.5.4.193 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_141 Registers
- 14.5.4.194 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_142 Registers
- 14.5.4.195 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_143 Registers
- 14.5.4.196 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_144 Registers
- 14.5.4.197 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_145 Registers
- 14.5.4.198 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_146 Registers
- 14.5.4.199 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_147 Registers
- 14.5.4.200 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_148 Registers
- 14.5.4.201 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_149 Registers
- 14.5.4.202 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_150 Registers
- 14.5.4.203 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_151 Registers
- 14.5.4.204 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_152 Registers
- 14.5.4.205 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_153 Registers
- 14.5.4.206 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_154 Registers
- 14.5.4.207 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_155 Registers
- 14.5.4.208 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_156 Registers
- 14.5.4.209 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_157 Registers
- 14.5.4.210 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_158 Registers
- 14.5.4.211 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_159 Registers
- 14.5.4.212 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_160 Registers
- 14.5.4.213 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_161 Registers
- 14.5.4.214 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_162 Registers
- 14.5.4.215 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_163 Registers
- 14.5.4.216 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_164 Registers
- 14.5.4.217 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_165 Registers
- 14.5.4.218 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_166 Registers
- 14.5.4.219 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_167 Registers
- 14.5.4.220 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_168 Registers
- 14.5.4.221 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_169 Registers
- 14.5.4.222 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_170 Registers
- 14.5.4.223 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_171 Registers
- 14.5.4.224 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_172 Registers
- 14.5.4.225 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_173 Registers
- 14.5.4.226 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_174 Registers
- 14.5.4.227 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_175 Registers
- 14.5.4.228 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_176 Registers
- 14.5.4.229 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_177 Registers
- 14.5.4.230 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_178 Registers
- 14.5.4.231 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_179 Registers
- 14.5.4.232 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_180 Registers
- 14.5.4.233 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_181 Registers
- 14.5.4.234 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_182 Registers
- 14.5.4.235 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_183 Registers
- 14.5.4.236 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_184 Registers
- 14.5.4.237 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_185 Registers
- 14.5.4.238 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_186 Registers
- 14.5.4.239 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_187 Registers
- 14.5.4.240 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_188 Registers
- 14.5.4.241 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_189 Registers
- 14.5.4.242 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_190 Registers
- 14.5.4.243 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_191 Registers
- 14.5.4.244 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_192 Registers
- 14.5.4.245 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_193 Registers
- 14.5.4.246 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_194 Registers
- 14.5.4.247 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_195 Registers
- 14.5.4.248 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_196 Registers
- 14.5.4.249 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_197 Registers
- 14.5.4.250 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_198 Registers
- 14.5.4.251 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_199 Registers
- 14.5.4.252 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_200 Registers
- 14.5.4.253 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_201 Registers
- 14.5.4.254 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_202 Registers
- 14.5.4.255 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_203 Registers
- 14.5.4.256 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_204 Registers
- 14.5.4.257 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_205 Registers
- 14.5.4.258 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_206 Registers
- 14.5.4.259 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_207 Registers
- 14.5.4.260 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_208 Registers
- 14.5.4.261 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_209 Registers
- 14.5.4.262 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_210 Registers
- 14.5.4.263 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_211 Registers
- 14.5.4.264 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_212 Registers
- 14.5.4.265 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_213 Registers
- 14.5.4.266 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_214 Registers
- 14.5.4.267 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_215 Registers
- 14.5.4.268 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_216 Registers
- 14.5.4.269 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_217 Registers
- 14.5.4.270 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_218 Registers
- 14.5.4.271 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_219 Registers
- 14.5.4.272 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_220 Registers
- 14.5.4.273 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_221 Registers
- 14.5.4.274 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_222 Registers
- 14.5.4.275 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_223 Registers
- 14.5.4.276 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_224 Registers
- 14.5.4.277 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_225 Registers
- 14.5.4.278 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_226 Registers
- 14.5.4.279 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_227 Registers
- 14.5.4.280 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_228 Registers
- 14.5.4.281 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_229 Registers
- 14.5.4.282 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_230 Registers
- 14.5.4.283 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_231 Registers
- 14.5.4.284 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_232 Registers
- 14.5.4.285 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_233 Registers
- 14.5.4.286 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_234 Registers
- 14.5.4.287 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_235 Registers
- 14.5.4.288 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_236 Registers
- 14.5.4.289 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_237 Registers
- 14.5.4.290 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_238 Registers
- 14.5.4.291 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_239 Registers
- 14.5.4.292 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_240 Registers
- 14.5.4.293 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_241 Registers
- 14.5.4.294 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_242 Registers
- 14.5.4.295 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_243 Registers
- 14.5.4.296 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_244 Registers
- 14.5.4.297 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_245 Registers
- 14.5.4.298 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_246 Registers
- 14.5.4.299 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_247 Registers
- 14.5.4.300 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_248 Registers
- 14.5.4.301 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_249 Registers
- 14.5.4.302 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_250 Registers
- 14.5.4.303 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_251 Registers
- 14.5.4.304 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_252 Registers
- 14.5.4.305 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_253 Registers
- 14.5.4.306 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_254 Registers
- 14.5.4.307 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_255 Registers
- 14.5.4.308 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_256 Registers
- 14.5.4.309 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_257 Registers
- 14.5.4.310 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_258 Registers
- 14.5.4.311 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_259 Registers
- 14.5.4.312 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_260 Registers
- 14.5.4.313 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_261 Registers
- 14.5.4.314 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_262 Registers
- 14.5.4.315 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_263 Registers
- 14.5.4.316 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_264 Registers
- 14.5.4.317 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_265 Registers
- 14.5.4.318 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_266 Registers
- 14.5.4.319 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_267 Registers
- 14.5.4.320 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_268 Registers
- 14.5.4.321 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_269 Registers
- 14.5.4.322 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_270 Registers
- 14.5.4.323 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_271 Registers
- 14.5.4.324 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_272 Registers
- 14.5.4.325 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_273 Registers
- 14.5.4.326 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_274 Registers
- 14.5.4.327 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_275 Registers
- 14.5.4.328 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_276 Registers
- 14.5.4.329 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_277 Registers
- 14.5.4.330 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_278 Registers
- 14.5.4.331 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_279 Registers
- 14.5.4.332 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_280 Registers
- 14.5.4.333 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_281 Registers
- 14.5.4.334 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_282 Registers
- 14.5.4.335 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_283 Registers
- 14.5.4.336 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_284 Registers
- 14.5.4.337 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_285 Registers
- 14.5.4.338 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_286 Registers
- 14.5.4.339 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_287 Registers
- 14.5.4.340 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_288 Registers
- 14.5.4.341 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_289 Registers
- 14.5.4.342 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_290 Registers
- 14.5.4.343 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_291 Registers
- 14.5.4.344 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_292 Registers
- 14.5.4.345 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_293 Registers
- 14.5.4.346 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_294 Registers
- 14.5.4.347 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_295 Registers
- 14.5.4.348 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_296 Registers
- 14.5.4.349 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_297 Registers
- 14.5.4.350 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_298 Registers
- 14.5.4.351 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_299 Registers
- 14.5.4.352 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_300 Registers
- 14.5.4.353 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_301 Registers
- 14.5.4.354 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_302 Registers
- 14.5.4.355 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_303 Registers
- 14.5.4.356 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_304 Registers
- 14.5.4.357 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_305 Registers
- 14.5.4.358 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_306 Registers
- 14.5.4.359 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_307 Registers
- 14.5.4.360 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_308 Registers
- 14.5.4.361 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_309 Registers
- 14.5.4.362 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_310 Registers
- 14.5.4.363 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_311 Registers
- 14.5.4.364 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_312 Registers
- 14.5.4.365 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_313 Registers
- 14.5.4.366 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_314 Registers
- 14.5.4.367 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_315 Registers
- 14.5.4.368 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_316 Registers
- 14.5.4.369 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_317 Registers
- 14.5.4.370 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_318 Registers
- 14.5.4.371 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_319 Registers
- 14.5.4.372 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_320 Registers
- 14.5.4.373 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_321 Registers
- 14.5.4.374 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_322 Registers
- 14.5.4.375 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_323 Registers
- 14.5.4.376 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_324 Registers
- 14.5.4.377 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_325 Registers
- 14.5.4.378 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_326 Registers
- 14.5.4.379 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_327 Registers
- 14.5.4.380 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_328 Registers
- 14.5.4.381 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_329 Registers
- 14.5.4.382 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_330 Registers
- 14.5.4.383 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_331 Registers
- 14.5.4.384 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_332 Registers
- 14.5.4.385 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_333 Registers
- 14.5.4.386 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_334 Registers
- 14.5.4.387 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_335 Registers
- 14.5.4.388 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_336 Registers
- 14.5.4.389 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_337 Registers
- 14.5.4.390 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_338 Registers
- 14.5.4.391 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_339 Registers
- 14.5.4.392 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_340 Registers
- 14.5.4.393 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_341 Registers
- 14.5.4.394 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_342 Registers
- 14.5.4.395 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_343 Registers
- 14.5.4.396 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_344 Registers
- 14.5.4.397 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_345 Registers
- 14.5.4.398 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_346 Registers
- 14.5.4.399 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_347 Registers
- 14.5.4.400 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_348 Registers
- 14.5.4.401 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_349 Registers
- 14.5.4.402 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_350 Registers
- 14.5.4.403 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_351 Registers
- 14.5.4.404 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_352 Registers
- 14.5.4.405 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_353 Registers
- 14.5.4.406 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_354 Registers
- 14.5.4.407 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_355 Registers
- 14.5.4.408 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_356 Registers
- 14.5.4.409 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_357 Registers
- 14.5.4.410 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_358 Registers
- 14.5.4.411 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_359 Registers
- 14.5.4.412 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_360 Registers
- 14.5.4.413 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_361 Registers
- 14.5.4.414 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_362 Registers
- 14.5.4.415 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_363 Registers
- 14.5.4.416 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_364 Registers
- 14.5.4.417 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_365 Registers
- 14.5.4.418 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_366 Registers
- 14.5.4.419 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_367 Registers
- 14.5.4.420 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_368 Registers
- 14.5.4.421 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_369 Registers
- 14.5.4.422 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_370 Registers
- 14.5.4.423 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_371 Registers
- 14.5.4.424 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_372 Registers
- 14.5.4.425 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_373 Registers
- 14.5.4.426 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_374 Registers
- 14.5.4.427 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_375 Registers
- 14.5.4.428 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_376 Registers
- 14.5.4.429 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_377 Registers
- 14.5.4.430 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_378 Registers
- 14.5.4.431 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_379 Registers
- 14.5.4.432 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_380 Registers
- 14.5.4.433 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_381 Registers
- 14.5.4.434 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_382 Registers
- 14.5.4.435 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_383 Registers
- 14.5.4.436 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_384 Registers
- 14.5.4.437 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_385 Registers
- 14.5.4.438 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_386 Registers
- 14.5.4.439 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_387 Registers
- 14.5.4.440 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_388 Registers
- 14.5.4.441 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_389 Registers
- 14.5.4.442 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_390 Registers
- 14.5.4.443 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_391 Registers
- 14.5.4.444 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_392 Registers
- 14.5.4.445 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_393 Registers
- 14.5.4.446 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_394 Registers
- 14.5.4.447 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_395 Registers
- 14.5.4.448 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_396 Registers
- 14.5.4.449 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_397 Registers
- 14.5.4.450 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_398 Registers
- 14.5.4.451 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_399 Registers
- 14.5.4.452 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_400 Registers
- 14.5.4.453 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_401 Registers
- 14.5.4.454 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_402 Registers
- 14.5.4.455 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_403 Registers
- 14.5.4.456 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_404 Registers
- 14.5.4.457 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_405 Registers
- 14.5.4.458 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_406 Registers
- 14.5.4.459 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_407 Registers
- 14.5.4.460 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_408 Registers
- 14.5.4.461 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_409 Registers
- 14.5.4.462 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_410 Registers
- 14.5.4.463 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_411 Registers
- 14.5.4.464 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_412 Registers
- 14.5.4.465 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_413 Registers
- 14.5.4.466 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_414 Registers
- 14.5.4.467 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_415 Registers
- 14.5.4.468 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_416 Registers
- 14.5.4.469 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_417 Registers
- 14.5.4.470 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_418 Registers
- 14.5.4.471 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_419 Registers
- 14.5.4.472 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_420 Registers
- 14.5.4.473 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_421 Registers
- 14.5.4.474 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_CTL_422 Registers
- 14.5.4.475 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_0 Registers
- 14.5.4.476 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_1 Registers
- 14.5.4.477 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_2 Registers
- 14.5.4.478 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_3 Registers
- 14.5.4.479 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_4 Registers
- 14.5.4.480 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_5 Registers
- 14.5.4.481 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_6 Registers
- 14.5.4.482 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_7 Registers
- 14.5.4.483 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_8 Registers
- 14.5.4.484 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_9 Registers
- 14.5.4.485 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_10 Registers
- 14.5.4.486 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_11 Registers
- 14.5.4.487 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_12 Registers
- 14.5.4.488 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_13 Registers
- 14.5.4.489 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_14 Registers
- 14.5.4.490 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_15 Registers
- 14.5.4.491 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_16 Registers
- 14.5.4.492 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_17 Registers
- 14.5.4.493 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_18 Registers
- 14.5.4.494 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_19 Registers
- 14.5.4.495 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_20 Registers
- 14.5.4.496 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_21 Registers
- 14.5.4.497 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_22 Registers
- 14.5.4.498 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_23 Registers
- 14.5.4.499 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_24 Registers
- 14.5.4.500 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_25 Registers
- 14.5.4.501 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_26 Registers
- 14.5.4.502 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_27 Registers
- 14.5.4.503 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_28 Registers
- 14.5.4.504 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_29 Registers
- 14.5.4.505 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_30 Registers
- 14.5.4.506 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_31 Registers
- 14.5.4.507 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_32 Registers
- 14.5.4.508 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_33 Registers
- 14.5.4.509 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_34 Registers
- 14.5.4.510 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_35 Registers
- 14.5.4.511 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_36 Registers
- 14.5.4.512 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_37 Registers
- 14.5.4.513 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_38 Registers
- 14.5.4.514 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_39 Registers
- 14.5.4.515 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_40 Registers
- 14.5.4.516 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_41 Registers
- 14.5.4.517 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_42 Registers
- 14.5.4.518 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_43 Registers
- 14.5.4.519 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_44 Registers
- 14.5.4.520 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_45 Registers
- 14.5.4.521 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_46 Registers
- 14.5.4.522 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_47 Registers
- 14.5.4.523 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_48 Registers
- 14.5.4.524 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_49 Registers
- 14.5.4.525 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_50 Registers
- 14.5.4.526 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_51 Registers
- 14.5.4.527 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_52 Registers
- 14.5.4.528 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_53 Registers
- 14.5.4.529 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_54 Registers
- 14.5.4.530 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_55 Registers
- 14.5.4.531 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_56 Registers
- 14.5.4.532 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_57 Registers
- 14.5.4.533 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_58 Registers
- 14.5.4.534 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_59 Registers
- 14.5.4.535 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_60 Registers
- 14.5.4.536 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_61 Registers
- 14.5.4.537 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_62 Registers
- 14.5.4.538 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_63 Registers
- 14.5.4.539 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_64 Registers
- 14.5.4.540 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_65 Registers
- 14.5.4.541 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_66 Registers
- 14.5.4.542 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_67 Registers
- 14.5.4.543 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_68 Registers
- 14.5.4.544 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_69 Registers
- 14.5.4.545 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_70 Registers
- 14.5.4.546 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_71 Registers
- 14.5.4.547 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_72 Registers
- 14.5.4.548 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_73 Registers
- 14.5.4.549 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_74 Registers
- 14.5.4.550 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_75 Registers
- 14.5.4.551 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_76 Registers
- 14.5.4.552 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_77 Registers
- 14.5.4.553 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_78 Registers
- 14.5.4.554 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_79 Registers
- 14.5.4.555 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_80 Registers
- 14.5.4.556 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_81 Registers
- 14.5.4.557 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_82 Registers
- 14.5.4.558 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_83 Registers
- 14.5.4.559 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_84 Registers
- 14.5.4.560 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_85 Registers
- 14.5.4.561 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_86 Registers
- 14.5.4.562 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_87 Registers
- 14.5.4.563 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_88 Registers
- 14.5.4.564 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_89 Registers
- 14.5.4.565 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_90 Registers
- 14.5.4.566 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_91 Registers
- 14.5.4.567 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_92 Registers
- 14.5.4.568 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_93 Registers
- 14.5.4.569 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_94 Registers
- 14.5.4.570 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_95 Registers
- 14.5.4.571 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_96 Registers
- 14.5.4.572 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_97 Registers
- 14.5.4.573 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_98 Registers
- 14.5.4.574 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_99 Registers
- 14.5.4.575 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_100 Registers
- 14.5.4.576 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_101 Registers
- 14.5.4.577 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_102 Registers
- 14.5.4.578 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_103 Registers
- 14.5.4.579 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_104 Registers
- 14.5.4.580 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_105 Registers
- 14.5.4.581 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_106 Registers
- 14.5.4.582 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_107 Registers
- 14.5.4.583 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_108 Registers
- 14.5.4.584 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_109 Registers
- 14.5.4.585 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_110 Registers
- 14.5.4.586 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_111 Registers
- 14.5.4.587 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_112 Registers
- 14.5.4.588 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_113 Registers
- 14.5.4.589 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_114 Registers
- 14.5.4.590 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_115 Registers
- 14.5.4.591 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_116 Registers
- 14.5.4.592 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_117 Registers
- 14.5.4.593 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_118 Registers
- 14.5.4.594 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_119 Registers
- 14.5.4.595 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_120 Registers
- 14.5.4.596 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_121 Registers
- 14.5.4.597 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_122 Registers
- 14.5.4.598 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_123 Registers
- 14.5.4.599 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_124 Registers
- 14.5.4.600 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_125 Registers
- 14.5.4.601 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_126 Registers
- 14.5.4.602 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_127 Registers
- 14.5.4.603 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_128 Registers
- 14.5.4.604 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_129 Registers
- 14.5.4.605 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_130 Registers
- 14.5.4.606 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_131 Registers
- 14.5.4.607 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_132 Registers
- 14.5.4.608 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_133 Registers
- 14.5.4.609 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_134 Registers
- 14.5.4.610 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_135 Registers
- 14.5.4.611 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_136 Registers
- 14.5.4.612 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_137 Registers
- 14.5.4.613 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_138 Registers
- 14.5.4.614 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_139 Registers
- 14.5.4.615 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_140 Registers
- 14.5.4.616 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_141 Registers
- 14.5.4.617 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_142 Registers
- 14.5.4.618 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_143 Registers
- 14.5.4.619 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_144 Registers
- 14.5.4.620 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_145 Registers
- 14.5.4.621 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_146 Registers
- 14.5.4.622 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_147 Registers
- 14.5.4.623 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_148 Registers
- 14.5.4.624 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_149 Registers
- 14.5.4.625 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_150 Registers
- 14.5.4.626 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_151 Registers
- 14.5.4.627 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_152 Registers
- 14.5.4.628 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_153 Registers
- 14.5.4.629 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_154 Registers
- 14.5.4.630 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_155 Registers
- 14.5.4.631 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_156 Registers
- 14.5.4.632 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_157 Registers
- 14.5.4.633 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_158 Registers
- 14.5.4.634 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_159 Registers
- 14.5.4.635 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_160 Registers
- 14.5.4.636 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_161 Registers
- 14.5.4.637 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_162 Registers
- 14.5.4.638 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_163 Registers
- 14.5.4.639 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_164 Registers
- 14.5.4.640 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_165 Registers
- 14.5.4.641 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_166 Registers
- 14.5.4.642 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_167 Registers
- 14.5.4.643 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_168 Registers
- 14.5.4.644 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_169 Registers
- 14.5.4.645 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_170 Registers
- 14.5.4.646 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_171 Registers
- 14.5.4.647 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_172 Registers
- 14.5.4.648 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_173 Registers
- 14.5.4.649 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_174 Registers
- 14.5.4.650 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_175 Registers
- 14.5.4.651 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_176 Registers
- 14.5.4.652 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_177 Registers
- 14.5.4.653 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_178 Registers
- 14.5.4.654 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_179 Registers
- 14.5.4.655 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_180 Registers
- 14.5.4.656 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_181 Registers
- 14.5.4.657 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_182 Registers
- 14.5.4.658 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_183 Registers
- 14.5.4.659 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_184 Registers
- 14.5.4.660 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_185 Registers
- 14.5.4.661 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_186 Registers
- 14.5.4.662 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_187 Registers
- 14.5.4.663 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_188 Registers
- 14.5.4.664 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_189 Registers
- 14.5.4.665 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_190 Registers
- 14.5.4.666 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_191 Registers
- 14.5.4.667 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_192 Registers
- 14.5.4.668 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_193 Registers
- 14.5.4.669 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_194 Registers
- 14.5.4.670 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_195 Registers
- 14.5.4.671 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_196 Registers
- 14.5.4.672 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_197 Registers
- 14.5.4.673 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_198 Registers
- 14.5.4.674 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_199 Registers
- 14.5.4.675 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_200 Registers
- 14.5.4.676 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_201 Registers
- 14.5.4.677 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_202 Registers
- 14.5.4.678 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_203 Registers
- 14.5.4.679 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_204 Registers
- 14.5.4.680 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_205 Registers
- 14.5.4.681 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_206 Registers
- 14.5.4.682 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_207 Registers
- 14.5.4.683 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_208 Registers
- 14.5.4.684 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_209 Registers
- 14.5.4.685 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_210 Registers
- 14.5.4.686 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_211 Registers
- 14.5.4.687 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_212 Registers
- 14.5.4.688 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_213 Registers
- 14.5.4.689 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_214 Registers
- 14.5.4.690 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_215 Registers
- 14.5.4.691 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_216 Registers
- 14.5.4.692 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_217 Registers
- 14.5.4.693 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_218 Registers
- 14.5.4.694 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_219 Registers
- 14.5.4.695 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_220 Registers
- 14.5.4.696 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_221 Registers
- 14.5.4.697 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_222 Registers
- 14.5.4.698 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_223 Registers
- 14.5.4.699 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_224 Registers
- 14.5.4.700 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_225 Registers
- 14.5.4.701 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_226 Registers
- 14.5.4.702 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_227 Registers
- 14.5.4.703 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_228 Registers
- 14.5.4.704 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_229 Registers
- 14.5.4.705 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_230 Registers
- 14.5.4.706 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_231 Registers
- 14.5.4.707 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_232 Registers
- 14.5.4.708 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_233 Registers
- 14.5.4.709 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_234 Registers
- 14.5.4.710 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_235 Registers
- 14.5.4.711 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_236 Registers
- 14.5.4.712 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_237 Registers
- 14.5.4.713 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_238 Registers
- 14.5.4.714 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_239 Registers
- 14.5.4.715 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_240 Registers
- 14.5.4.716 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_241 Registers
- 14.5.4.717 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_242 Registers
- 14.5.4.718 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_243 Registers
- 14.5.4.719 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_244 Registers
- 14.5.4.720 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_245 Registers
- 14.5.4.721 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_246 Registers
- 14.5.4.722 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_247 Registers
- 14.5.4.723 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_248 Registers
- 14.5.4.724 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_249 Registers
- 14.5.4.725 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_250 Registers
- 14.5.4.726 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_251 Registers
- 14.5.4.727 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_252 Registers
- 14.5.4.728 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_253 Registers
- 14.5.4.729 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_254 Registers
- 14.5.4.730 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_255 Registers
- 14.5.4.731 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_256 Registers
- 14.5.4.732 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_257 Registers
- 14.5.4.733 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_258 Registers
- 14.5.4.734 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_259 Registers
- 14.5.4.735 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_260 Registers
- 14.5.4.736 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_261 Registers
- 14.5.4.737 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_262 Registers
- 14.5.4.738 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_263 Registers
- 14.5.4.739 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_264 Registers
- 14.5.4.740 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_265 Registers
- 14.5.4.741 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_266 Registers
- 14.5.4.742 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_267 Registers
- 14.5.4.743 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_268 Registers
- 14.5.4.744 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_269 Registers
- 14.5.4.745 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_270 Registers
- 14.5.4.746 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_271 Registers
- 14.5.4.747 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_272 Registers
- 14.5.4.748 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_273 Registers
- 14.5.4.749 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_274 Registers
- 14.5.4.750 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_275 Registers
- 14.5.4.751 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_276 Registers
- 14.5.4.752 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_277 Registers
- 14.5.4.753 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_278 Registers
- 14.5.4.754 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_279 Registers
- 14.5.4.755 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_280 Registers
- 14.5.4.756 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_281 Registers
- 14.5.4.757 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_282 Registers
- 14.5.4.758 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_283 Registers
- 14.5.4.759 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_284 Registers
- 14.5.4.760 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_285 Registers
- 14.5.4.761 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_286 Registers
- 14.5.4.762 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_287 Registers
- 14.5.4.763 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_288 Registers
- 14.5.4.764 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_289 Registers
- 14.5.4.765 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_290 Registers
- 14.5.4.766 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_291 Registers
- 14.5.4.767 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_292 Registers
- 14.5.4.768 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_293 Registers
- 14.5.4.769 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_294 Registers
- 14.5.4.770 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_295 Registers
- 14.5.4.771 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_296 Registers
- 14.5.4.772 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_297 Registers
- 14.5.4.773 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_298 Registers
- 14.5.4.774 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_299 Registers
- 14.5.4.775 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_300 Registers
- 14.5.4.776 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_301 Registers
- 14.5.4.777 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_302 Registers
- 14.5.4.778 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_303 Registers
- 14.5.4.779 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_304 Registers
- 14.5.4.780 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_305 Registers
- 14.5.4.781 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_306 Registers
- 14.5.4.782 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_307 Registers
- 14.5.4.783 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_308 Registers
- 14.5.4.784 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_309 Registers
- 14.5.4.785 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_310 Registers
- 14.5.4.786 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_311 Registers
- 14.5.4.787 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_312 Registers
- 14.5.4.788 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_313 Registers
- 14.5.4.789 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_314 Registers
- 14.5.4.790 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_315 Registers
- 14.5.4.791 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_316 Registers
- 14.5.4.792 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_317 Registers
- 14.5.4.793 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_318 Registers
- 14.5.4.794 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_319 Registers
- 14.5.4.795 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_320 Registers
- 14.5.4.796 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_321 Registers
- 14.5.4.797 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_322 Registers
- 14.5.4.798 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_323 Registers
- 14.5.4.799 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_324 Registers
- 14.5.4.800 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_325 Registers
- 14.5.4.801 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_326 Registers
- 14.5.4.802 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_327 Registers
- 14.5.4.803 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_328 Registers
- 14.5.4.804 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_329 Registers
- 14.5.4.805 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_330 Registers
- 14.5.4.806 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_331 Registers
- 14.5.4.807 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_332 Registers
- 14.5.4.808 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_333 Registers
- 14.5.4.809 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_334 Registers
- 14.5.4.810 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_335 Registers
- 14.5.4.811 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_336 Registers
- 14.5.4.812 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_337 Registers
- 14.5.4.813 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_338 Registers
- 14.5.4.814 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_339 Registers
- 14.5.4.815 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_340 Registers
- 14.5.4.816 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_341 Registers
- 14.5.4.817 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_342 Registers
- 14.5.4.818 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_343 Registers
- 14.5.4.819 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PI_344 Registers
- 14.5.4.820 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_0 Registers
- 14.5.4.821 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1 Registers
- 14.5.4.822 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_2 Registers
- 14.5.4.823 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_3 Registers
- 14.5.4.824 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_4 Registers
- 14.5.4.825 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_5 Registers
- 14.5.4.826 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_6 Registers
- 14.5.4.827 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_7 Registers
- 14.5.4.828 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_8 Registers
- 14.5.4.829 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_9 Registers
- 14.5.4.830 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_10 Registers
- 14.5.4.831 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_11 Registers
- 14.5.4.832 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_12 Registers
- 14.5.4.833 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_13 Registers
- 14.5.4.834 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_14 Registers
- 14.5.4.835 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_15 Registers
- 14.5.4.836 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_16 Registers
- 14.5.4.837 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_17 Registers
- 14.5.4.838 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_18 Registers
- 14.5.4.839 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_19 Registers
- 14.5.4.840 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_20 Registers
- 14.5.4.841 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_21 Registers
- 14.5.4.842 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_22 Registers
- 14.5.4.843 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_23 Registers
- 14.5.4.844 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_24 Registers
- 14.5.4.845 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_25 Registers
- 14.5.4.846 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_26 Registers
- 14.5.4.847 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_27 Registers
- 14.5.4.848 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_28 Registers
- 14.5.4.849 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_29 Registers
- 14.5.4.850 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_30 Registers
- 14.5.4.851 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_31 Registers
- 14.5.4.852 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_32 Registers
- 14.5.4.853 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_33 Registers
- 14.5.4.854 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_34 Registers
- 14.5.4.855 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_35 Registers
- 14.5.4.856 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_36 Registers
- 14.5.4.857 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_37 Registers
- 14.5.4.858 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_38 Registers
- 14.5.4.859 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_39 Registers
- 14.5.4.860 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_40 Registers
- 14.5.4.861 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_41 Registers
- 14.5.4.862 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_42 Registers
- 14.5.4.863 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_43 Registers
- 14.5.4.864 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_44 Registers
- 14.5.4.865 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_45 Registers
- 14.5.4.866 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_46 Registers
- 14.5.4.867 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_47 Registers
- 14.5.4.868 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_48 Registers
- 14.5.4.869 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_49 Registers
- 14.5.4.870 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_50 Registers
- 14.5.4.871 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_51 Registers
- 14.5.4.872 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_52 Registers
- 14.5.4.873 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_53 Registers
- 14.5.4.874 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_54 Registers
- 14.5.4.875 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_55 Registers
- 14.5.4.876 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_56 Registers
- 14.5.4.877 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_57 Registers
- 14.5.4.878 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_58 Registers
- 14.5.4.879 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_59 Registers
- 14.5.4.880 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_60 Registers
- 14.5.4.881 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_61 Registers
- 14.5.4.882 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_62 Registers
- 14.5.4.883 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_63 Registers
- 14.5.4.884 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_64 Registers
- 14.5.4.885 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_65 Registers
- 14.5.4.886 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_66 Registers
- 14.5.4.887 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_67 Registers
- 14.5.4.888 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_68 Registers
- 14.5.4.889 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_69 Registers
- 14.5.4.890 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_70 Registers
- 14.5.4.891 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_71 Registers
- 14.5.4.892 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_72 Registers
- 14.5.4.893 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_73 Registers
- 14.5.4.894 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_74 Registers
- 14.5.4.895 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_75 Registers
- 14.5.4.896 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_76 Registers
- 14.5.4.897 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_77 Registers
- 14.5.4.898 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_78 Registers
- 14.5.4.899 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_79 Registers
- 14.5.4.900 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_80 Registers
- 14.5.4.901 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_81 Registers
- 14.5.4.902 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_82 Registers
- 14.5.4.903 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_83 Registers
- 14.5.4.904 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_84 Registers
- 14.5.4.905 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_85 Registers
- 14.5.4.906 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_86 Registers
- 14.5.4.907 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_87 Registers
- 14.5.4.908 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_88 Registers
- 14.5.4.909 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_89 Registers
- 14.5.4.910 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_90 Registers
- 14.5.4.911 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_91 Registers
- 14.5.4.912 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_92 Registers
- 14.5.4.913 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_93 Registers
- 14.5.4.914 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_94 Registers
- 14.5.4.915 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_95 Registers
- 14.5.4.916 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_96 Registers
- 14.5.4.917 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_97 Registers
- 14.5.4.918 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_98 Registers
- 14.5.4.919 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_99 Registers
- 14.5.4.920 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_100 Registers
- 14.5.4.921 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_101 Registers
- 14.5.4.922 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_102 Registers
- 14.5.4.923 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_103 Registers
- 14.5.4.924 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_104 Registers
- 14.5.4.925 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_105 Registers
- 14.5.4.926 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_106 Registers
- 14.5.4.927 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_107 Registers
- 14.5.4.928 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_108 Registers
- 14.5.4.929 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_109 Registers
- 14.5.4.930 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_110 Registers
- 14.5.4.931 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_111 Registers
- 14.5.4.932 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_112 Registers
- 14.5.4.933 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_113 Registers
- 14.5.4.934 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_114 Registers
- 14.5.4.935 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_115 Registers
- 14.5.4.936 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_116 Registers
- 14.5.4.937 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_117 Registers
- 14.5.4.938 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_118 Registers
- 14.5.4.939 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_119 Registers
- 14.5.4.940 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_120 Registers
- 14.5.4.941 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_121 Registers
- 14.5.4.942 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_122 Registers
- 14.5.4.943 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_123 Registers
- 14.5.4.944 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_124 Registers
- 14.5.4.945 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_125 Registers
- 14.5.4.946 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_256 Registers
- 14.5.4.947 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_257 Registers
- 14.5.4.948 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_258 Registers
- 14.5.4.949 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_259 Registers
- 14.5.4.950 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_260 Registers
- 14.5.4.951 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_261 Registers
- 14.5.4.952 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_262 Registers
- 14.5.4.953 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_263 Registers
- 14.5.4.954 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_264 Registers
- 14.5.4.955 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_265 Registers
- 14.5.4.956 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_266 Registers
- 14.5.4.957 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_267 Registers
- 14.5.4.958 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_268 Registers
- 14.5.4.959 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_269 Registers
- 14.5.4.960 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_270 Registers
- 14.5.4.961 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_271 Registers
- 14.5.4.962 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_272 Registers
- 14.5.4.963 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_273 Registers
- 14.5.4.964 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_274 Registers
- 14.5.4.965 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_275 Registers
- 14.5.4.966 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_276 Registers
- 14.5.4.967 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_277 Registers
- 14.5.4.968 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_278 Registers
- 14.5.4.969 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_279 Registers
- 14.5.4.970 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_280 Registers
- 14.5.4.971 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_281 Registers
- 14.5.4.972 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_282 Registers
- 14.5.4.973 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_283 Registers
- 14.5.4.974 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_284 Registers
- 14.5.4.975 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_285 Registers
- 14.5.4.976 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_286 Registers
- 14.5.4.977 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_287 Registers
- 14.5.4.978 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_288 Registers
- 14.5.4.979 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_289 Registers
- 14.5.4.980 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_290 Registers
- 14.5.4.981 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_291 Registers
- 14.5.4.982 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_292 Registers
- 14.5.4.983 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_293 Registers
- 14.5.4.984 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_294 Registers
- 14.5.4.985 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_295 Registers
- 14.5.4.986 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_296 Registers
- 14.5.4.987 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_297 Registers
- 14.5.4.988 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_298 Registers
- 14.5.4.989 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_299 Registers
- 14.5.4.990 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_300 Registers
- 14.5.4.991 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_301 Registers
- 14.5.4.992 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_302 Registers
- 14.5.4.993 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_303 Registers
- 14.5.4.994 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_304 Registers
- 14.5.4.995 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_305 Registers
- 14.5.4.996 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_306 Registers
- 14.5.4.997 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_307 Registers
- 14.5.4.998 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_308 Registers
- 14.5.4.999 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_309 Registers
- 14.5.4.1000 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_310 Registers
- 14.5.4.1001 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_311 Registers
- 14.5.4.1002 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_312 Registers
- 14.5.4.1003 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_313 Registers
- 14.5.4.1004 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_314 Registers
- 14.5.4.1005 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_315 Registers
- 14.5.4.1006 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_316 Registers
- 14.5.4.1007 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_317 Registers
- 14.5.4.1008 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_318 Registers
- 14.5.4.1009 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_319 Registers
- 14.5.4.1010 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_320 Registers
- 14.5.4.1011 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_321 Registers
- 14.5.4.1012 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_322 Registers
- 14.5.4.1013 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_323 Registers
- 14.5.4.1014 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_324 Registers
- 14.5.4.1015 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_325 Registers
- 14.5.4.1016 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_326 Registers
- 14.5.4.1017 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_327 Registers
- 14.5.4.1018 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_328 Registers
- 14.5.4.1019 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_329 Registers
- 14.5.4.1020 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_330 Registers
- 14.5.4.1021 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_331 Registers
- 14.5.4.1022 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_332 Registers
- 14.5.4.1023 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_333 Registers
- 14.5.4.1024 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_334 Registers
- 14.5.4.1025 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_335 Registers
- 14.5.4.1026 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_336 Registers
- 14.5.4.1027 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_337 Registers
- 14.5.4.1028 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_338 Registers
- 14.5.4.1029 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_339 Registers
- 14.5.4.1030 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_340 Registers
- 14.5.4.1031 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_341 Registers
- 14.5.4.1032 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_342 Registers
- 14.5.4.1033 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_343 Registers
- 14.5.4.1034 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_344 Registers
- 14.5.4.1035 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_345 Registers
- 14.5.4.1036 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_346 Registers
- 14.5.4.1037 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_347 Registers
- 14.5.4.1038 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_348 Registers
- 14.5.4.1039 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_349 Registers
- 14.5.4.1040 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_350 Registers
- 14.5.4.1041 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_351 Registers
- 14.5.4.1042 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_352 Registers
- 14.5.4.1043 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_353 Registers
- 14.5.4.1044 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_354 Registers
- 14.5.4.1045 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_355 Registers
- 14.5.4.1046 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_356 Registers
- 14.5.4.1047 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_357 Registers
- 14.5.4.1048 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_358 Registers
- 14.5.4.1049 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_359 Registers
- 14.5.4.1050 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_360 Registers
- 14.5.4.1051 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_361 Registers
- 14.5.4.1052 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_362 Registers
- 14.5.4.1053 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_363 Registers
- 14.5.4.1054 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_364 Registers
- 14.5.4.1055 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_365 Registers
- 14.5.4.1056 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_366 Registers
- 14.5.4.1057 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_367 Registers
- 14.5.4.1058 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_368 Registers
- 14.5.4.1059 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_369 Registers
- 14.5.4.1060 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_370 Registers
- 14.5.4.1061 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_371 Registers
- 14.5.4.1062 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_372 Registers
- 14.5.4.1063 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_373 Registers
- 14.5.4.1064 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_374 Registers
- 14.5.4.1065 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_375 Registers
- 14.5.4.1066 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_376 Registers
- 14.5.4.1067 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_377 Registers
- 14.5.4.1068 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_378 Registers
- 14.5.4.1069 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_379 Registers
- 14.5.4.1070 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_380 Registers
- 14.5.4.1071 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_381 Registers
- 14.5.4.1072 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_512 Registers
- 14.5.4.1073 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_513 Registers
- 14.5.4.1074 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_514 Registers
- 14.5.4.1075 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_515 Registers
- 14.5.4.1076 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_516 Registers
- 14.5.4.1077 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_517 Registers
- 14.5.4.1078 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_518 Registers
- 14.5.4.1079 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_519 Registers
- 14.5.4.1080 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_520 Registers
- 14.5.4.1081 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_521 Registers
- 14.5.4.1082 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_522 Registers
- 14.5.4.1083 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_523 Registers
- 14.5.4.1084 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_524 Registers
- 14.5.4.1085 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_525 Registers
- 14.5.4.1086 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_526 Registers
- 14.5.4.1087 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_527 Registers
- 14.5.4.1088 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_528 Registers
- 14.5.4.1089 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_529 Registers
- 14.5.4.1090 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_530 Registers
- 14.5.4.1091 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_531 Registers
- 14.5.4.1092 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_532 Registers
- 14.5.4.1093 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_533 Registers
- 14.5.4.1094 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_534 Registers
- 14.5.4.1095 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_535 Registers
- 14.5.4.1096 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_536 Registers
- 14.5.4.1097 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_537 Registers
- 14.5.4.1098 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_538 Registers
- 14.5.4.1099 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_539 Registers
- 14.5.4.1100 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_540 Registers
- 14.5.4.1101 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_541 Registers
- 14.5.4.1102 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_542 Registers
- 14.5.4.1103 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_543 Registers
- 14.5.4.1104 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_544 Registers
- 14.5.4.1105 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_545 Registers
- 14.5.4.1106 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_546 Registers
- 14.5.4.1107 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_547 Registers
- 14.5.4.1108 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_548 Registers
- 14.5.4.1109 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_549 Registers
- 14.5.4.1110 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_550 Registers
- 14.5.4.1111 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_551 Registers
- 14.5.4.1112 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_552 Registers
- 14.5.4.1113 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_553 Registers
- 14.5.4.1114 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_554 Registers
- 14.5.4.1115 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_768 Registers
- 14.5.4.1116 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_769 Registers
- 14.5.4.1117 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_770 Registers
- 14.5.4.1118 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_771 Registers
- 14.5.4.1119 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_772 Registers
- 14.5.4.1120 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_773 Registers
- 14.5.4.1121 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_774 Registers
- 14.5.4.1122 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_775 Registers
- 14.5.4.1123 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_776 Registers
- 14.5.4.1124 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_777 Registers
- 14.5.4.1125 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_778 Registers
- 14.5.4.1126 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_779 Registers
- 14.5.4.1127 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_780 Registers
- 14.5.4.1128 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_781 Registers
- 14.5.4.1129 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_782 Registers
- 14.5.4.1130 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_783 Registers
- 14.5.4.1131 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_784 Registers
- 14.5.4.1132 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_785 Registers
- 14.5.4.1133 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_786 Registers
- 14.5.4.1134 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_787 Registers
- 14.5.4.1135 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_788 Registers
- 14.5.4.1136 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_789 Registers
- 14.5.4.1137 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_790 Registers
- 14.5.4.1138 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_791 Registers
- 14.5.4.1139 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_792 Registers
- 14.5.4.1140 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_793 Registers
- 14.5.4.1141 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_794 Registers
- 14.5.4.1142 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_795 Registers
- 14.5.4.1143 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_796 Registers
- 14.5.4.1144 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_797 Registers
- 14.5.4.1145 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_798 Registers
- 14.5.4.1146 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_799 Registers
- 14.5.4.1147 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_800 Registers
- 14.5.4.1148 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_801 Registers
- 14.5.4.1149 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_802 Registers
- 14.5.4.1150 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_803 Registers
- 14.5.4.1151 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_804 Registers
- 14.5.4.1152 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_805 Registers
- 14.5.4.1153 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_806 Registers
- 14.5.4.1154 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_807 Registers
- 14.5.4.1155 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_808 Registers
- 14.5.4.1156 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_809 Registers
- 14.5.4.1157 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_810 Registers
- 14.5.4.1158 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1024 Registers
- 14.5.4.1159 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1025 Registers
- 14.5.4.1160 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1026 Registers
- 14.5.4.1161 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1027 Registers
- 14.5.4.1162 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1028 Registers
- 14.5.4.1163 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1029 Registers
- 14.5.4.1164 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1030 Registers
- 14.5.4.1165 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1031 Registers
- 14.5.4.1166 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1032 Registers
- 14.5.4.1167 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1033 Registers
- 14.5.4.1168 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1034 Registers
- 14.5.4.1169 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1035 Registers
- 14.5.4.1170 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1036 Registers
- 14.5.4.1171 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1037 Registers
- 14.5.4.1172 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1038 Registers
- 14.5.4.1173 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1039 Registers
- 14.5.4.1174 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1040 Registers
- 14.5.4.1175 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1041 Registers
- 14.5.4.1176 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1042 Registers
- 14.5.4.1177 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1043 Registers
- 14.5.4.1178 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1044 Registers
- 14.5.4.1179 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1045 Registers
- 14.5.4.1180 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1046 Registers
- 14.5.4.1181 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1047 Registers
- 14.5.4.1182 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1048 Registers
- 14.5.4.1183 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1049 Registers
- 14.5.4.1184 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1050 Registers
- 14.5.4.1185 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1051 Registers
- 14.5.4.1186 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1052 Registers
- 14.5.4.1187 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1053 Registers
- 14.5.4.1188 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1054 Registers
- 14.5.4.1189 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1055 Registers
- 14.5.4.1190 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1056 Registers
- 14.5.4.1191 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1057 Registers
- 14.5.4.1192 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1058 Registers
- 14.5.4.1193 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1059 Registers
- 14.5.4.1194 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1060 Registers
- 14.5.4.1195 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1061 Registers
- 14.5.4.1196 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1062 Registers
- 14.5.4.1197 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1063 Registers
- 14.5.4.1198 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1064 Registers
- 14.5.4.1199 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1065 Registers
- 14.5.4.1200 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1066 Registers
- 14.5.4.1201 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1280 Registers
- 14.5.4.1202 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1281 Registers
- 14.5.4.1203 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1282 Registers
- 14.5.4.1204 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1283 Registers
- 14.5.4.1205 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1284 Registers
- 14.5.4.1206 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1285 Registers
- 14.5.4.1207 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1286 Registers
- 14.5.4.1208 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1287 Registers
- 14.5.4.1209 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1288 Registers
- 14.5.4.1210 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1289 Registers
- 14.5.4.1211 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1290 Registers
- 14.5.4.1212 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1291 Registers
- 14.5.4.1213 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1292 Registers
- 14.5.4.1214 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1293 Registers
- 14.5.4.1215 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1294 Registers
- 14.5.4.1216 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1295 Registers
- 14.5.4.1217 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1296 Registers
- 14.5.4.1218 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1297 Registers
- 14.5.4.1219 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1298 Registers
- 14.5.4.1220 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1299 Registers
- 14.5.4.1221 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1300 Registers
- 14.5.4.1222 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1301 Registers
- 14.5.4.1223 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1302 Registers
- 14.5.4.1224 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1303 Registers
- 14.5.4.1225 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1304 Registers
- 14.5.4.1226 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1305 Registers
- 14.5.4.1227 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1306 Registers
- 14.5.4.1228 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1307 Registers
- 14.5.4.1229 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1308 Registers
- 14.5.4.1230 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1309 Registers
- 14.5.4.1231 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1310 Registers
- 14.5.4.1232 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1311 Registers
- 14.5.4.1233 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1312 Registers
- 14.5.4.1234 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1313 Registers
- 14.5.4.1235 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1314 Registers
- 14.5.4.1236 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1315 Registers
- 14.5.4.1237 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1316 Registers
- 14.5.4.1238 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1317 Registers
- 14.5.4.1239 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1318 Registers
- 14.5.4.1240 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1319 Registers
- 14.5.4.1241 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1320 Registers
- 14.5.4.1242 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1321 Registers
- 14.5.4.1243 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1322 Registers
- 14.5.4.1244 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1323 Registers
- 14.5.4.1245 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1324 Registers
- 14.5.4.1246 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1325 Registers
- 14.5.4.1247 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1326 Registers
- 14.5.4.1248 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1327 Registers
- 14.5.4.1249 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1328 Registers
- 14.5.4.1250 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1329 Registers
- 14.5.4.1251 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1330 Registers
- 14.5.4.1252 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1331 Registers
- 14.5.4.1253 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1332 Registers
- 14.5.4.1254 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1333 Registers
- 14.5.4.1255 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1334 Registers
- 14.5.4.1256 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1335 Registers
- 14.5.4.1257 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1336 Registers
- 14.5.4.1258 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1337 Registers
- 14.5.4.1259 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1338 Registers
- 14.5.4.1260 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1339 Registers
- 14.5.4.1261 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1340 Registers
- 14.5.4.1262 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1341 Registers
- 14.5.4.1263 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1342 Registers
- 14.5.4.1264 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1343 Registers
- 14.5.4.1265 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1344 Registers
- 14.5.4.1266 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1345 Registers
- 14.5.4.1267 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1346 Registers
- 14.5.4.1268 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1347 Registers
- 14.5.4.1269 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1348 Registers
- 14.5.4.1270 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1349 Registers
- 14.5.4.1271 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1350 Registers
- 14.5.4.1272 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1351 Registers
- 14.5.4.1273 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1352 Registers
- 14.5.4.1274 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1353 Registers
- 14.5.4.1275 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1354 Registers
- 14.5.4.1276 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1355 Registers
- 14.5.4.1277 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1356 Registers
- 14.5.4.1278 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1357 Registers
- 14.5.4.1279 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1358 Registers
- 14.5.4.1280 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1359 Registers
- 14.5.4.1281 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1360 Registers
- 14.5.4.1282 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1361 Registers
- 14.5.4.1283 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1362 Registers
- 14.5.4.1284 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1363 Registers
- 14.5.4.1285 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1364 Registers
- 14.5.4.1286 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1365 Registers
- 14.5.4.1287 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1366 Registers
- 14.5.4.1288 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1367 Registers
- 14.5.4.1289 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1368 Registers
- 14.5.4.1290 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1369 Registers
- 14.5.4.1291 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1370 Registers
- 14.5.4.1292 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1371 Registers
- 14.5.4.1293 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1372 Registers
- 14.5.4.1294 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1373 Registers
- 14.5.4.1295 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1374 Registers
- 14.5.4.1296 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1375 Registers
- 14.5.4.1297 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1376 Registers
- 14.5.4.1298 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1377 Registers
- 14.5.4.1299 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1378 Registers
- 14.5.4.1300 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1379 Registers
- 14.5.4.1301 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1380 Registers
- 14.5.4.1302 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1381 Registers
- 14.5.4.1303 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1382 Registers
- 14.5.4.1304 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1383 Registers
- 14.5.4.1305 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1384 Registers
- 14.5.4.1306 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1385 Registers
- 14.5.4.1307 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1386 Registers
- 14.5.4.1308 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1387 Registers
- 14.5.4.1309 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1388 Registers
- 14.5.4.1310 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1389 Registers
- 14.5.4.1311 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1390 Registers
- 14.5.4.1312 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1391 Registers
- 14.5.4.1313 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1392 Registers
- 14.5.4.1314 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1393 Registers
- 14.5.4.1315 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1394 Registers
- 14.5.4.1316 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1395 Registers
- 14.5.4.1317 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1396 Registers
- 14.5.4.1318 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1397 Registers
- 14.5.4.1319 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1398 Registers
- 14.5.4.1320 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1399 Registers
- 14.5.4.1321 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1400 Registers
- 14.5.4.1322 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1401 Registers
- 14.5.4.1323 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1402 Registers
- 14.5.4.1324 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1403 Registers
- 14.5.4.1325 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1404 Registers
- 14.5.4.1326 CTLPHY_WRAP_CTL_CFG_CTLCFG_DENALI_PHY_1405 Registers
- 14.5.4.1327 Access Table
- 14.6
Interrupt Router Registers
- 14.6.1
GICSS Registers
- 14.6.1.1 GIC_TRANSLATER_TRANSLATER__1_GITS_TRANSLATER Registers
- 14.6.1.2 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__1_GICD_CTLR Registers
- 14.6.1.3 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__3_GICD_TYPER Registers
- 14.6.1.4 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__4_GICD_IIDR Registers
- 14.6.1.5 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__5_GICD_SETSPI_NSR Registers
- 14.6.1.6 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__6_GICD_CLRSPI_NSR Registers
- 14.6.1.7 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__7_GICD_SETSPI_SR Registers
- 14.6.1.8 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__8_GICD_CLRSPI_SR Registers
- 14.6.1.9 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__9_GICD_IGROUPR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.10 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__10_GICD_IGROUPR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.11 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__10_GICD_IGROUPR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.12 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__10_GICD_IGROUPR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.13 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__10_GICD_IGROUPR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.14 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__10_GICD_IGROUPR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.15 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__10_GICD_IGROUPR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.16 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__10_GICD_IGROUPR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.17 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__10_GICD_IGROUPR8 Registers
- 14.6.1.18 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__12_GICD_ISENABLER1 Registers
- 14.6.1.19 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__12_GICD_ISENABLER2 Registers
- 14.6.1.20 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__12_GICD_ISENABLER3 Registers
- 14.6.1.21 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__12_GICD_ISENABLER4 Registers
- 14.6.1.22 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__12_GICD_ISENABLER5 Registers
- 14.6.1.23 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__12_GICD_ISENABLER6 Registers
- 14.6.1.24 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__12_GICD_ISENABLER7 Registers
- 14.6.1.25 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__12_GICD_ISENABLER8 Registers
- 14.6.1.26 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__14_GICD_ICENABLER1 Registers
- 14.6.1.27 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__14_GICD_ICENABLER2 Registers
- 14.6.1.28 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__14_GICD_ICENABLER3 Registers
- 14.6.1.29 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__14_GICD_ICENABLER4 Registers
- 14.6.1.30 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__14_GICD_ICENABLER5 Registers
- 14.6.1.31 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__14_GICD_ICENABLER6 Registers
- 14.6.1.32 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__14_GICD_ICENABLER7 Registers
- 14.6.1.33 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__14_GICD_ICENABLER8 Registers
- 14.6.1.34 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__16_GICD_ISPENDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.35 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__16_GICD_ISPENDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.36 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__16_GICD_ISPENDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.37 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__16_GICD_ISPENDR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.38 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__16_GICD_ISPENDR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.39 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__16_GICD_ISPENDR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.40 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__16_GICD_ISPENDR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.41 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__16_GICD_ISPENDR8 Registers
- 14.6.1.42 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__18_GICD_ICPENDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.43 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__18_GICD_ICPENDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.44 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__18_GICD_ICPENDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.45 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__18_GICD_ICPENDR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.46 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__18_GICD_ICPENDR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.47 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__18_GICD_ICPENDR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.48 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__18_GICD_ICPENDR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.49 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__18_GICD_ICPENDR8 Registers
- 14.6.1.50 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__20_GICD_ISACTIVER1 Registers
- 14.6.1.51 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__20_GICD_ISACTIVER2 Registers
- 14.6.1.52 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__20_GICD_ISACTIVER3 Registers
- 14.6.1.53 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__20_GICD_ISACTIVER4 Registers
- 14.6.1.54 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__20_GICD_ISACTIVER5 Registers
- 14.6.1.55 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__20_GICD_ISACTIVER6 Registers
- 14.6.1.56 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__20_GICD_ISACTIVER7 Registers
- 14.6.1.57 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__20_GICD_ISACTIVER8 Registers
- 14.6.1.58 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__22_GICD_ICACTIVER1 Registers
- 14.6.1.59 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__22_GICD_ICACTIVER2 Registers
- 14.6.1.60 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__22_GICD_ICACTIVER3 Registers
- 14.6.1.61 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__22_GICD_ICACTIVER4 Registers
- 14.6.1.62 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__22_GICD_ICACTIVER5 Registers
- 14.6.1.63 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__22_GICD_ICACTIVER6 Registers
- 14.6.1.64 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__22_GICD_ICACTIVER7 Registers
- 14.6.1.65 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__22_GICD_ICACTIVER8 Registers
- 14.6.1.66 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR8 Registers
- 14.6.1.67 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR9 Registers
- 14.6.1.68 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR10 Registers
- 14.6.1.69 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR11 Registers
- 14.6.1.70 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR12 Registers
- 14.6.1.71 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR13 Registers
- 14.6.1.72 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR14 Registers
- 14.6.1.73 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR15 Registers
- 14.6.1.74 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR16 Registers
- 14.6.1.75 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR17 Registers
- 14.6.1.76 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR18 Registers
- 14.6.1.77 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR19 Registers
- 14.6.1.78 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR20 Registers
- 14.6.1.79 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR21 Registers
- 14.6.1.80 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR22 Registers
- 14.6.1.81 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR23 Registers
- 14.6.1.82 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR24 Registers
- 14.6.1.83 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR25 Registers
- 14.6.1.84 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR26 Registers
- 14.6.1.85 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR27 Registers
- 14.6.1.86 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR28 Registers
- 14.6.1.87 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR29 Registers
- 14.6.1.88 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR30 Registers
- 14.6.1.89 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR31 Registers
- 14.6.1.90 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR32 Registers
- 14.6.1.91 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR33 Registers
- 14.6.1.92 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR34 Registers
- 14.6.1.93 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR35 Registers
- 14.6.1.94 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR36 Registers
- 14.6.1.95 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR37 Registers
- 14.6.1.96 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR38 Registers
- 14.6.1.97 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR39 Registers
- 14.6.1.98 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR40 Registers
- 14.6.1.99 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR41 Registers
- 14.6.1.100 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR42 Registers
- 14.6.1.101 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR43 Registers
- 14.6.1.102 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR44 Registers
- 14.6.1.103 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR45 Registers
- 14.6.1.104 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR46 Registers
- 14.6.1.105 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR47 Registers
- 14.6.1.106 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR48 Registers
- 14.6.1.107 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR49 Registers
- 14.6.1.108 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR50 Registers
- 14.6.1.109 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR51 Registers
- 14.6.1.110 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR52 Registers
- 14.6.1.111 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR53 Registers
- 14.6.1.112 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR54 Registers
- 14.6.1.113 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR55 Registers
- 14.6.1.114 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR56 Registers
- 14.6.1.115 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR57 Registers
- 14.6.1.116 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR58 Registers
- 14.6.1.117 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR59 Registers
- 14.6.1.118 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR60 Registers
- 14.6.1.119 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR61 Registers
- 14.6.1.120 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR62 Registers
- 14.6.1.121 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR63 Registers
- 14.6.1.122 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR64 Registers
- 14.6.1.123 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR65 Registers
- 14.6.1.124 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR66 Registers
- 14.6.1.125 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR67 Registers
- 14.6.1.126 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR68 Registers
- 14.6.1.127 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR69 Registers
- 14.6.1.128 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR70 Registers
- 14.6.1.129 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__24_GICD_IPRIORITYR71 Registers
- 14.6.1.130 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR8 Registers
- 14.6.1.131 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR9 Registers
- 14.6.1.132 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR10 Registers
- 14.6.1.133 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR11 Registers
- 14.6.1.134 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR12 Registers
- 14.6.1.135 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR13 Registers
- 14.6.1.136 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR14 Registers
- 14.6.1.137 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR15 Registers
- 14.6.1.138 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR16 Registers
- 14.6.1.139 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR17 Registers
- 14.6.1.140 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR18 Registers
- 14.6.1.141 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR19 Registers
- 14.6.1.142 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR20 Registers
- 14.6.1.143 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR21 Registers
- 14.6.1.144 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR22 Registers
- 14.6.1.145 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR23 Registers
- 14.6.1.146 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR24 Registers
- 14.6.1.147 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR25 Registers
- 14.6.1.148 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR26 Registers
- 14.6.1.149 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR27 Registers
- 14.6.1.150 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR28 Registers
- 14.6.1.151 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR29 Registers
- 14.6.1.152 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR30 Registers
- 14.6.1.153 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR31 Registers
- 14.6.1.154 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR32 Registers
- 14.6.1.155 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR33 Registers
- 14.6.1.156 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR34 Registers
- 14.6.1.157 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR35 Registers
- 14.6.1.158 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR36 Registers
- 14.6.1.159 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR37 Registers
- 14.6.1.160 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR38 Registers
- 14.6.1.161 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR39 Registers
- 14.6.1.162 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR40 Registers
- 14.6.1.163 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR41 Registers
- 14.6.1.164 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR42 Registers
- 14.6.1.165 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR43 Registers
- 14.6.1.166 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR44 Registers
- 14.6.1.167 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR45 Registers
- 14.6.1.168 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR46 Registers
- 14.6.1.169 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR47 Registers
- 14.6.1.170 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR48 Registers
- 14.6.1.171 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR49 Registers
- 14.6.1.172 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR50 Registers
- 14.6.1.173 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR51 Registers
- 14.6.1.174 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR52 Registers
- 14.6.1.175 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR53 Registers
- 14.6.1.176 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR54 Registers
- 14.6.1.177 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR55 Registers
- 14.6.1.178 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR56 Registers
- 14.6.1.179 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR57 Registers
- 14.6.1.180 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR58 Registers
- 14.6.1.181 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR59 Registers
- 14.6.1.182 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR60 Registers
- 14.6.1.183 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR61 Registers
- 14.6.1.184 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR62 Registers
- 14.6.1.185 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR63 Registers
- 14.6.1.186 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR64 Registers
- 14.6.1.187 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR65 Registers
- 14.6.1.188 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR66 Registers
- 14.6.1.189 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR67 Registers
- 14.6.1.190 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR68 Registers
- 14.6.1.191 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR69 Registers
- 14.6.1.192 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR70 Registers
- 14.6.1.193 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__26_GICD_ITARGETSR71 Registers
- 14.6.1.194 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.195 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.196 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.197 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.198 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.199 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.200 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR8 Registers
- 14.6.1.201 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR9 Registers
- 14.6.1.202 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR10 Registers
- 14.6.1.203 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR11 Registers
- 14.6.1.204 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR12 Registers
- 14.6.1.205 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR13 Registers
- 14.6.1.206 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR14 Registers
- 14.6.1.207 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR15 Registers
- 14.6.1.208 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR16 Registers
- 14.6.1.209 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__29_GICD_ICFGR17 Registers
- 14.6.1.210 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__30_GICD_IGRPMODR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.211 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__31_GICD_IGRPMODR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.212 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__31_GICD_IGRPMODR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.213 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__31_GICD_IGRPMODR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.214 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__31_GICD_IGRPMODR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.215 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__31_GICD_IGRPMODR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.216 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__31_GICD_IGRPMODR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.217 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__31_GICD_IGRPMODR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.218 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__31_GICD_IGRPMODR8 Registers
- 14.6.1.219 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__32_GICD_NSACR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.220 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__32_GICD_NSACR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.221 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.222 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.223 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.224 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.225 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.226 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.227 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR8 Registers
- 14.6.1.228 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR9 Registers
- 14.6.1.229 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR10 Registers
- 14.6.1.230 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR11 Registers
- 14.6.1.231 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR12 Registers
- 14.6.1.232 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR13 Registers
- 14.6.1.233 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR14 Registers
- 14.6.1.234 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR15 Registers
- 14.6.1.235 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR16 Registers
- 14.6.1.236 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__33_GICD_NSACR17 Registers
- 14.6.1.237 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER32_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.238 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER32_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.239 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER33_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.240 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER33_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.241 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER34_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.242 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER34_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.243 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER35_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.244 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER35_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.245 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER36_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.246 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER36_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.247 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER37_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.248 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER37_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.249 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER38_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.250 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER38_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.251 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER39_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.252 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER39_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.253 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER40_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.254 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER40_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.255 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER41_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.256 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER41_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.257 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER42_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.258 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER42_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.259 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER43_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.260 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER43_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.261 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER44_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.262 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER44_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.263 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER45_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.264 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER45_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.265 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER46_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.266 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER46_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.267 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER47_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.268 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER47_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.269 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER48_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.270 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER48_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.271 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER49_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.272 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER49_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.273 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER50_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.274 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER50_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.275 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER51_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.276 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER51_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.277 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER52_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.278 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER52_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.279 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER53_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.280 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER53_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.281 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER54_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.282 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER54_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.283 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER55_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.284 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER55_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.285 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER56_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.286 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER56_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.287 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER57_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.288 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER57_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.289 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER58_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.290 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER58_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.291 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER59_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.292 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER59_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.293 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER60_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.294 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER60_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.295 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER61_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.296 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER61_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.297 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER62_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.298 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER62_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.299 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER63_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.300 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER63_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.301 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER64_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.302 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER64_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.303 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER65_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.304 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER65_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.305 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER66_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.306 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER66_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.307 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER67_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.308 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER67_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.309 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER68_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.310 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER68_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.311 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER69_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.312 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER69_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.313 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER70_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.314 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER70_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.315 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER71_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.316 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER71_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.317 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER72_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.318 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER72_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.319 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER73_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.320 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER73_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.321 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER74_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.322 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER74_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.323 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER75_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.324 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER75_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.325 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER76_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.326 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER76_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.327 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER77_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.328 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER77_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.329 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER78_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.330 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER78_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.331 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER79_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.332 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER79_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.333 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER80_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.334 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER80_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.335 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER81_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.336 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER81_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.337 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER82_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.338 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER82_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.339 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER83_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.340 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER83_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.341 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER84_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.342 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER84_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.343 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER85_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.344 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER85_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.345 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER86_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.346 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER86_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.347 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER87_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.348 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER87_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.349 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER88_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.350 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER88_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.351 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER89_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.352 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER89_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.353 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER90_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.354 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER90_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.355 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER91_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.356 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER91_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.357 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER92_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.358 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER92_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.359 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER93_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.360 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER93_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.361 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER94_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.362 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER94_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.363 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER95_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.364 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER95_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.365 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER96_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.366 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER96_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.367 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER97_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.368 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER97_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.369 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER98_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.370 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER98_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.371 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER99_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.372 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER99_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.373 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER100_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.374 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER100_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.375 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER101_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.376 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER101_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.377 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER102_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.378 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER102_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.379 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER103_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.380 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER103_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.381 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER104_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.382 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER104_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.383 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER105_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.384 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER105_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.385 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER106_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.386 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER106_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.387 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER107_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.388 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER107_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.389 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER108_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.390 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER108_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.391 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER109_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.392 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER109_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.393 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER110_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.394 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER110_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.395 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER111_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.396 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER111_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.397 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER112_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.398 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER112_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.399 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER113_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.400 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER113_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.401 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER114_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.402 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER114_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.403 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER115_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.404 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER115_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.405 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER116_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.406 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER116_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.407 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER117_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.408 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER117_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.409 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER118_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.410 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER118_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.411 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER119_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.412 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER119_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.413 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER120_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.414 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER120_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.415 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER121_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.416 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER121_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.417 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER122_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.418 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER122_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.419 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER123_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.420 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER123_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.421 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER124_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.422 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER124_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.423 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER125_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.424 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER125_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.425 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER126_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.426 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER126_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.427 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER127_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.428 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER127_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.429 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER128_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.430 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER128_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.431 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER129_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.432 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER129_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.433 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER130_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.434 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER130_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.435 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER131_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.436 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER131_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.437 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER132_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.438 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER132_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.439 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER133_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.440 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER133_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.441 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER134_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.442 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER134_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.443 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER135_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.444 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER135_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.445 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER136_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.446 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER136_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.447 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER137_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.448 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER137_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.449 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER138_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.450 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER138_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.451 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER139_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.452 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER139_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.453 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER140_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.454 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER140_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.455 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER141_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.456 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER141_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.457 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER142_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.458 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER142_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.459 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER143_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.460 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER143_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.461 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER144_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.462 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER144_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.463 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER145_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.464 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER145_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.465 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER146_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.466 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER146_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.467 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER147_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.468 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER147_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.469 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER148_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.470 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER148_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.471 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER149_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.472 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER149_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.473 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER150_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.474 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER150_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.475 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER151_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.476 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER151_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.477 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER152_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.478 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER152_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.479 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER153_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.480 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER153_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.481 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER154_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.482 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER154_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.483 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER155_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.484 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER155_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.485 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER156_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.486 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER156_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.487 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER157_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.488 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER157_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.489 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER158_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.490 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER158_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.491 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER159_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.492 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER159_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.493 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER160_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.494 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER160_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.495 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER161_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.496 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER161_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.497 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER162_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.498 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER162_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.499 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER163_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.500 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER163_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.501 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER164_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.502 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER164_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.503 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER165_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.504 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER165_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.505 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER166_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.506 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER166_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.507 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER167_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.508 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER167_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.509 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER168_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.510 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER168_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.511 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER169_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.512 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER169_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.513 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER170_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.514 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER170_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.515 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER171_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.516 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER171_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.517 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER172_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.518 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER172_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.519 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER173_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.520 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER173_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.521 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER174_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.522 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER174_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.523 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER175_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.524 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER175_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.525 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER176_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.526 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER176_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.527 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER177_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.528 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER177_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.529 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER178_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.530 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER178_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.531 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER179_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.532 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER179_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.533 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER180_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.534 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER180_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.535 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER181_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.536 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER181_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.537 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER182_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.538 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER182_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.539 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER183_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.540 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER183_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.541 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER184_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.542 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER184_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.543 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER185_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.544 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER185_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.545 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER186_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.546 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER186_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.547 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER187_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.548 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER187_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.549 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER188_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.550 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER188_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.551 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER189_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.552 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER189_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.553 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER190_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.554 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER190_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.555 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER191_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.556 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER191_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.557 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER192_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.558 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER192_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.559 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER193_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.560 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER193_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.561 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER194_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.562 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER194_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.563 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER195_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.564 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER195_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.565 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER196_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.566 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER196_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.567 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER197_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.568 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER197_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.569 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER198_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.570 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER198_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.571 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER199_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.572 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER199_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.573 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER200_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.574 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER200_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.575 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER201_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.576 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER201_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.577 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER202_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.578 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER202_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.579 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER203_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.580 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER203_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.581 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER204_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.582 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER204_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.583 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER205_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.584 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER205_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.585 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER206_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.586 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER206_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.587 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER207_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.588 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER207_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.589 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER208_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.590 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER208_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.591 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER209_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.592 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER209_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.593 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER210_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.594 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER210_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.595 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER211_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.596 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER211_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.597 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER212_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.598 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER212_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.599 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER213_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.600 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER213_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.601 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER214_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.602 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER214_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.603 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER215_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.604 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER215_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.605 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER216_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.606 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER216_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.607 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER217_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.608 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER217_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.609 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER218_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.610 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER218_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.611 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER219_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.612 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER219_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.613 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER220_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.614 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER220_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.615 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER221_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.616 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER221_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.617 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER222_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.618 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER222_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.619 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER223_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.620 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER223_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.621 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER224_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.622 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER224_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.623 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER225_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.624 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER225_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.625 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER226_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.626 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER226_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.627 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER227_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.628 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER227_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.629 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER228_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.630 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER228_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.631 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER229_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.632 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER229_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.633 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER230_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.634 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER230_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.635 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER231_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.636 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER231_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.637 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER232_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.638 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER232_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.639 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER233_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.640 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER233_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.641 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER234_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.642 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER234_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.643 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER235_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.644 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER235_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.645 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER236_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.646 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER236_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.647 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER237_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.648 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER237_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.649 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER238_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.650 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER238_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.651 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER239_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.652 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER239_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.653 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER240_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.654 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER240_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.655 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER241_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.656 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER241_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.657 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER242_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.658 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER242_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.659 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER243_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.660 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER243_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.661 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER244_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.662 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER244_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.663 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER245_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.664 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER245_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.665 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER246_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.666 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER246_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.667 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER247_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.668 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER247_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.669 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER248_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.670 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER248_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.671 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER249_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.672 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER249_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.673 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER250_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.674 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER250_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.675 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER251_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.676 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER251_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.677 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER252_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.678 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER252_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.679 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER253_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.680 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER253_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.681 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER254_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.682 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER254_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.683 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER255_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.684 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER255_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.685 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER256_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.686 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER256_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.687 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER257_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.688 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER257_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.689 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER258_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.690 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER258_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.691 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER259_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.692 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER259_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.693 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER260_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.694 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER260_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.695 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER261_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.696 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER261_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.697 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER262_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.698 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER262_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.699 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER263_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.700 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER263_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.701 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER264_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.702 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER264_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.703 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER265_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.704 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER265_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.705 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER266_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.706 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER266_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.707 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER267_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.708 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER267_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.709 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER268_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.710 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER268_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.711 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER269_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.712 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER269_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.713 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER270_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.714 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER270_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.715 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER271_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.716 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER271_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.717 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER272_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.718 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER272_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.719 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER273_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.720 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER273_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.721 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER274_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.722 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER274_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.723 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER275_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.724 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER275_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.725 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER276_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.726 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER276_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.727 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER277_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.728 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER277_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.729 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER278_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.730 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER278_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.731 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER279_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.732 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER279_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.733 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER280_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.734 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER280_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.735 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER281_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.736 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER281_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.737 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER282_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.738 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER282_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.739 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER283_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.740 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER283_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.741 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER284_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.742 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER284_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.743 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER285_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.744 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER285_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.745 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER286_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.746 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER286_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.747 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER287_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.748 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__37_GICD_IROUTER287_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.749 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__38_GICD_ESTATUSR Registers
- 14.6.1.750 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__39_GICD_ERRTESTR Registers
- 14.6.1.751 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__40_GICD_SPISR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.752 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__40_GICD_SPISR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.753 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__40_GICD_SPISR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.754 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__40_GICD_SPISR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.755 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__40_GICD_SPISR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.756 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__40_GICD_SPISR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.757 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__40_GICD_SPISR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.758 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__40_GICD_SPISR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.759 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__41_GICD_PIDR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.760 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__42_GICD_PIDR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.761 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__43_GICD_PIDR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.762 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__44_GICD_PIDR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.763 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__45_GICD_PIDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.764 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__46_GICD_PIDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.765 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__47_GICD_PIDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.766 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__48_GICD_PIDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.767 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__49_GICD_CIDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.768 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__50_GICD_CIDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.769 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__51_GICD_CIDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.770 GIC_DISTRIBUTOR__52_GICD_CIDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.771 GIC_MESSAGE_BASED_SPIS__1_GICD_SETSPI_NSR Registers
- 14.6.1.772 GIC_MESSAGE_BASED_SPIS__2_GICD_CLRSPI_NSR Registers
- 14.6.1.773 GIC_MESSAGE_BASED_SPIS__3_GICD_SETSPI_SR Registers
- 14.6.1.774 GIC_MESSAGE_BASED_SPIS__4_GICD_CLRSPI_SR Registers
- 14.6.1.775 GIC_ITS__1_GITS_CTLR Registers
- 14.6.1.776 GIC_ITS__2_GITS_IIDR Registers
- 14.6.1.777 GIC_ITS__3_GITS_TYPER_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.778 GIC_ITS__4_GITS_TYPER_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.779 GIC_ITS__5_GITS_CBASER_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.780 GIC_ITS__6_GITS_CBASER_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.781 GIC_ITS__7_GITS_CWRITER_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.782 GIC_ITS__8_GITS_CWRITER_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.783 GIC_ITS__9_GITS_CREADR_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.784 GIC_ITS__10_GITS_CREADR_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.785 GIC_ITS__11_GITS_BASER0_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.786 GIC_ITS__12_GITS_BASER0_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.787 GIC_ITS__13_GITS_TRKCTLR Registers
- 14.6.1.788 GIC_ITS__14_GITS_TRKR Registers
- 14.6.1.789 GIC_ITS__15_GITS_TRKDIDR Registers
- 14.6.1.790 GIC_ITS__16_GITS_TRKPIDR Registers
- 14.6.1.791 GIC_ITS__17_GITS_TRKVIDR Registers
- 14.6.1.792 GIC_ITS__18_GITS_TRKTGTR Registers
- 14.6.1.793 GIC_ITS__19_GITS_TRKICR Registers
- 14.6.1.794 GIC_ITS__20_GITS_TRKLCR Registers
- 14.6.1.795 GIC_ITS__21_GITS_PIDR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.796 GIC_ITS__22_GITS_PIDR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.797 GIC_ITS__23_GITS_PIDR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.798 GIC_ITS__24_GITS_PIDR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.799 GIC_ITS__25_GITS_PIDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.800 GIC_ITS__26_GITS_PIDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.801 GIC_ITS__27_GITS_PIDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.802 GIC_ITS__28_GITS_PIDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.803 GIC_ITS__29_GITS_CIDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.804 GIC_ITS__30_GITS_CIDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.805 GIC_ITS__31_GITS_CIDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.806 GIC_ITS__32_GITS_CIDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.807 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__2_GICR_CTLR Registers
- 14.6.1.808 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__3_GICR_IIDR Registers
- 14.6.1.809 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__4_GICR_TYPER_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.810 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__5_GICR_TYPER_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.811 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__6_GICR_WAKER Registers
- 14.6.1.812 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__7_GICR_PROPBASER_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.813 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__8_GICR_PROPBASER_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.814 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__9_GICR_PENDBASER_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.815 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__10_GICR_PENDBASER_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.816 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__11_GICR_PIDR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.817 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__12_GICR_PIDR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.818 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__13_GICR_PIDR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.819 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__14_GICR_PIDR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.820 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__15_GICR_PIDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.821 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__16_GICR_PIDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.822 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__17_GICR_PIDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.823 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__18_GICR_PIDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.824 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__19_GICR_CIDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.825 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__20_GICR_CIDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.826 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__21_GICR_CIDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.827 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_0__22_GICR_CIDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.828 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__1_GICR_IGROUPR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.829 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__2_GICR_ISENABLER0 Registers
- 14.6.1.830 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__3_GICR_ICENABLER0 Registers
- 14.6.1.831 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__4_GICR_ISPENDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.832 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__5_GICR_ICPENDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.833 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__6_GICR_ISACTIVER0 Registers
- 14.6.1.834 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__7_GICR_ICACTIVER0 Registers
- 14.6.1.835 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.836 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.837 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.838 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.839 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.840 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.841 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.842 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.843 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__9_GICR_ICFGR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.844 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__10_GICR_ICFGR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.845 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__11_GICR_IGRPMODR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.846 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__12_GICR_NSACR Registers
- 14.6.1.847 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__13_GICR_MISCSTATUSR Registers
- 14.6.1.848 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_0__14_GICR_PPISR Registers
- 14.6.1.849 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__2_GICR_CTLR Registers
- 14.6.1.850 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__3_GICR_IIDR Registers
- 14.6.1.851 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__4_GICR_TYPER_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.852 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__5_GICR_TYPER_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.853 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__6_GICR_WAKER Registers
- 14.6.1.854 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__7_GICR_PROPBASER_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.855 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__8_GICR_PROPBASER_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.856 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__9_GICR_PENDBASER_LOWER Registers
- 14.6.1.857 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__10_GICR_PENDBASER_UPPER Registers
- 14.6.1.858 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__11_GICR_PIDR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.859 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__12_GICR_PIDR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.860 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__13_GICR_PIDR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.861 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__14_GICR_PIDR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.862 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__15_GICR_PIDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.863 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__16_GICR_PIDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.864 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__17_GICR_PIDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.865 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__18_GICR_PIDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.866 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__19_GICR_CIDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.867 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__20_GICR_CIDR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.868 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__21_GICR_CIDR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.869 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_CONTROL_LPI_1__22_GICR_CIDR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.870 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__1_GICR_IGROUPR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.871 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__2_GICR_ISENABLER0 Registers
- 14.6.1.872 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__3_GICR_ICENABLER0 Registers
- 14.6.1.873 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__4_GICR_ISPENDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.874 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__5_GICR_ICPENDR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.875 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__6_GICR_ISACTIVER0 Registers
- 14.6.1.876 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__7_GICR_ICACTIVER0 Registers
- 14.6.1.877 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.878 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.879 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR2 Registers
- 14.6.1.880 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR3 Registers
- 14.6.1.881 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR4 Registers
- 14.6.1.882 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR5 Registers
- 14.6.1.883 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR6 Registers
- 14.6.1.884 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__8_GICR_IPRIORITYR7 Registers
- 14.6.1.885 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__9_GICR_ICFGR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.886 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__10_GICR_ICFGR1 Registers
- 14.6.1.887 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__11_GICR_IGRPMODR0 Registers
- 14.6.1.888 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__12_GICR_NSACR Registers
- 14.6.1.889 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__13_GICR_MISCSTATUSR Registers
- 14.6.1.890 GIC_REDISTRIBUTOR_SGI_PPI_1__14_GICR_PPISR Registers
- 14.6.1.891 REGS_REV Registers
- 14.6.1.892 REGS_VECTOR Registers
- 14.6.1.893 REGS_STAT Registers
- 14.6.1.894 REGS_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.6.1.895 REGS_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.6.1.896 REGS_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.6.1.897 REGS_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.6.1.898 REGS_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.6.1.899 REGS_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.6.1.900 REGS_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.6.1.901 REGS_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.6.1.902 REGS_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.6.1.903 REGS_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.6.1.904 REGS_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.6.1.905 REGS_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.6.1.906 REGS_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.6.1.907 Access Table
- 14.6.2 MAIN_GPIOMUX_INTROUTER Registers
- 14.6.3 MCU_GPIOMUX_INTROUTER Registers
- 14.6.4 CMP_EVENT_INTROUTER Registers
- 14.6.5 TIMESYNC_EVENT_ROUTER Registers
- 14.6.1
GICSS Registers
- 14.7
DMA Controller Registers
- 14.7.1
DMASS_BCDMA_0 Registers
- 14.7.1.1 BCDMA_CRED_CRED_CRED_CRED_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.2 BCDMA_BCHAN_BCHAN_BCHAN_CFG_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.3 BCDMA_BCHAN_BCHAN_BCHAN_PRI_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.4 BCDMA_BCHAN_BCHAN_BCHAN_TST_SCHED_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.5 BCDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCFG_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.6 BCDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_TPRI_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.7 BCDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_THREAD_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.8 BCDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_TFIFO_DEPTH_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.9 BCDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_TST_SCHED_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.10 BCDMA_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCFG_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.11 BCDMA_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCHAN_RPRI_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.12 BCDMA_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCHAN_THREAD_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.13 BCDMA_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCHAN_RST_SCHED_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.14 BCDMA_GCFG_REVISION Registers
- 14.7.1.15 BCDMA_GCFG_PERF_CTRL Registers
- 14.7.1.16 BCDMA_GCFG_EMU_CTRL Registers
- 14.7.1.17 BCDMA_GCFG_PSIL_TO Registers
- 14.7.1.18 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP0 Registers
- 14.7.1.19 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP1 Registers
- 14.7.1.20 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP2 Registers
- 14.7.1.21 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP3 Registers
- 14.7.1.22 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP4 Registers
- 14.7.1.23 BCDMA_GCFG_PM0 Registers
- 14.7.1.24 BCDMA_GCFG_PM1 Registers
- 14.7.1.25 BCDMA_GCFG_DBGADDR Registers
- 14.7.1.26 BCDMA_GCFG_DBGDATA Registers
- 14.7.1.27 BCDMA_RING_RING_RING_BA_LO_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.28 BCDMA_RING_RING_RING_BA_HI_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.29 BCDMA_RING_RING_RING_SIZE_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.30 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_CTL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.31 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_SWTRIG_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.32 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_STATUS0_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.33 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_STATUS1_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.34 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_STDATA_J_J_N Registers
- 14.7.1.35 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER0_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.36 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER1_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.37 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER2_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.38 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER3_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.39 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER4_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.40 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER5_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.41 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER6_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.42 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER7_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.43 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER8_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.44 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER9_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.45 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER10_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.46 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER11_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.47 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER12_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.48 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER13_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.49 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER14_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.50 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER15_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.51 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.52 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_BCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.53 BCDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_SBCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.54 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_CTL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.55 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_SWTRIG_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.56 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_STATUS0_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.57 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_STATUS1_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.58 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_STDATA_J_J_N Registers
- 14.7.1.59 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER0_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.60 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER1_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.61 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER2_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.62 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER3_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.63 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER4_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.64 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER5_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.65 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER6_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.66 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER7_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.67 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER8_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.68 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER9_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.69 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER10_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.70 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER11_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.71 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER12_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.72 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER13_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.73 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER14_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.74 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER15_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.75 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.76 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_BCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.77 BCDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_SBCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.78 BCDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_RINGRT_FDB_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.79 BCDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_RINGRT_FOCC_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.80 BCDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_RINGRT_RDB_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.81 BCDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_RINGRT_ROCC_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.82 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_CTL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.83 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_SWTRIG_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.84 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_STATUS0_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.85 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_STATUS1_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.86 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_STATUS2_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.87 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_STATUS3_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.88 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_STDATA_J_J_N Registers
- 14.7.1.89 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_STDATAW_J_J_N Registers
- 14.7.1.90 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_PCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.91 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_BCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.92 BCDMA_BCHANRT_CHANRT_CHANRT_SBCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.1.93 Access Table
- 14.7.2
DMASS_INTAGGR_0 Registers
- 14.7.2.1 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_VINT_ENABLE_SET_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.2 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_VINT_ENABLE_CLEAR_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.3 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_VINT_STATUS_SET_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.4 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_VINT_STATUS_CLEAR_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.5 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_VINT_STATUSM_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.6 INTAGGR_IMAP_ENTRY_ENTRY_IMAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.7 INTAGGR_CFG_REVISION Registers
- 14.7.2.8 INTAGGR_CFG_INTCAP Registers
- 14.7.2.9 INTAGGR_CFG_AUXCAP Registers
- 14.7.2.10 INTAGGR_L2G_LEVI_LEVI_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.11 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY0_UENTRY0_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.12 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY1_UENTRY1_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.13 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY2_UENTRY2_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.14 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY3_UENTRY3_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.15 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY4_UENTRY4_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.16 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY5_UENTRY5_MAP Registers
- 14.7.2.17 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY6_UENTRY6_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.18 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY7_UENTRY7_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.19 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY8_UENTRY8_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.20 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY9_UENTRY9_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.21 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY10_UENTRY10_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.22 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY11_UENTRY11_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.23 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY12_UENTRY12_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.24 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY13_UENTRY13_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.25 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UENTRY14_UENTRY14_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.26 INTAGGR_MCAST_GEVI_GEVI_MCMAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.27 INTAGGR_GCNTCFG_GEVI_GEVI_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.28 INTAGGR_GCNTRTI_GEVI_GEVI_COUNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.2.29 Access Table
- 14.7.3
DMASS_PKTDMA_0 Registers
- 14.7.3.1 PKTDMA_CRED_CRED_CRED_CRED_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.2 PKTDMA_RFLOW_RFLOW_RFLOW_RFA_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.3 PKTDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCFG_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.4 PKTDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_TPRI_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.5 PKTDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_THREAD_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.6 PKTDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_TFIFO_DEPTH_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.7 PKTDMA_TCHAN_TCHAN_TCHAN_TST_SCHED_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.8 PKTDMA_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCFG_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.9 PKTDMA_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCHAN_RPRI_CTRL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.10 PKTDMA_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCHAN_THREAD_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.11 PKTDMA_RCHAN_RCHAN_RCHAN_RST_SCHED_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.12 PKTDMA_GCFG_REVISION Registers
- 14.7.3.13 PKTDMA_GCFG_PERF_CTRL Registers
- 14.7.3.14 PKTDMA_GCFG_EMU_CTRL Registers
- 14.7.3.15 PKTDMA_GCFG_PSIL_TO Registers
- 14.7.3.16 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP0 Registers
- 14.7.3.17 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP1 Registers
- 14.7.3.18 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP2 Registers
- 14.7.3.19 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP3 Registers
- 14.7.3.20 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP4 Registers
- 14.7.3.21 PKTDMA_GCFG_PM0 Registers
- 14.7.3.22 PKTDMA_GCFG_PM1 Registers
- 14.7.3.23 PKTDMA_GCFG_DBGADDR Registers
- 14.7.3.24 PKTDMA_GCFG_DBGDATA Registers
- 14.7.3.25 PKTDMA_GCFG_RFLOWFWSTAT Registers
- 14.7.3.26 PKTDMA_RING_RING_RING_BA_LO_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.27 PKTDMA_RING_RING_RING_BA_HI_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.28 PKTDMA_RING_RING_RING_SIZE_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.29 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_CTL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.30 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_STATUS0_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.31 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_STATUS1_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.32 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_STDATA_J_J_N Registers
- 14.7.3.33 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER0_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.34 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER1_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.35 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER2_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.36 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER3_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.37 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER4_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.38 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER5_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.39 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER6_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.40 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER7_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.41 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER8_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.42 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER9_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.43 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER10_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.44 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER11_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.45 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER12_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.46 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER13_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.47 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER14_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.48 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PEER15_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.49 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_PCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.50 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_DCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.51 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_BCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.52 PKTDMA_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_RCHANRT_SBCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.53 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_CTL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.54 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_STATUS0_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.55 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_STATUS1_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.56 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_STDATA_J_J_N Registers
- 14.7.3.57 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER0_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.58 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER1_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.59 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER2_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.60 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER3_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.61 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER4_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.62 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER5_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.63 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER6_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.64 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER7_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.65 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER8_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.66 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER9_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.67 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER10_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.68 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER11_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.69 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER12_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.70 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER13_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.71 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER14_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.72 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PEER15_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.73 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_PCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.74 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_BCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.75 PKTDMA_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_TCHANRT_SBCNT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.76 PKTDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_RINGRT_FDB_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.77 PKTDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_RINGRT_FOCC_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.78 PKTDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_RINGRT_RDB_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.79 PKTDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_RINGRT_ROCC_J_J Registers
- 14.7.3.80 Access Table
- 14.7.4 DMASS_PSILCFG_0 Registers
- 14.7.5
DMASS_PSILSS_0 Registers
- 14.7.5.1 PSILSS_MMRS_PID Registers
- 14.7.5.2 PSILSS_MMRS_CONFIG Registers
- 14.7.5.3 PSILSS_MMRS_EVENT Registers
- 14.7.5.4 PSILSS_MMRS_LINK Registers
- 14.7.5.5 PSILSS_MMRS_DOWN Registers
- 14.7.5.6 ETLSW_MMRS_PID Registers
- 14.7.5.7 ETLSW_MMRS_CONFIG Registers
- 14.7.5.8 ETLSW_MMRS_EVENT Registers
- 14.7.5.9 ETLSW_MMRS_LINK Registers
- 14.7.5.10 ETLSW_MMRS_DOWN Registers
- 14.7.5.11 Access Table
- 14.7.6
DMASS_RINGACC_0 Registers
- 14.7.6.1 RINGACC_GCFG_REVISION Registers
- 14.7.6.2 RINGACC_GCFG_TRACE_CTL Registers
- 14.7.6.3 RINGACC_GCFG_OVRFLOW Registers
- 14.7.6.4 RINGACC_GCFG_ERROR_EVT Registers
- 14.7.6.5 RINGACC_GCFG_ERROR_LOG Registers
- 14.7.6.6 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_RINGRT_DB_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.7 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_RINGRT_OCC_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.8 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_RINGRT_INDX_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.9 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_RINGRT_HWOCC_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.10 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_RINGRT_HWINDX_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.11 RINGACC_CFG_RING_RING_BA_LO_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.12 RINGACC_CFG_RING_RING_BA_HI_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.13 RINGACC_CFG_RING_RING_SIZE_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.14 RINGACC_CFG_RING_RING_EVENT_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.15 RINGACC_CFG_RING_RING_ORDERID_J_J Registers
- 14.7.6.16 Access Table
- 14.7.7
DMASS_SEC_PROXY_0 Registers
- 14.7.7.1 SEC_PROXY_MMRS_PID Registers
- 14.7.7.2 SEC_PROXY_MMRS_CONFIG Registers
- 14.7.7.3 SEC_PROXY_MMRS_GLB_EVT Registers
- 14.7.7.4 SEC_PROXY_SCFG_BUFFER_L Registers
- 14.7.7.5 SEC_PROXY_SCFG_BUFFER_H Registers
- 14.7.7.6 SEC_PROXY_SCFG_TARGET_L Registers
- 14.7.7.7 SEC_PROXY_SCFG_TARGET_H Registers
- 14.7.7.8 SEC_PROXY_SCFG_ORDERID Registers
- 14.7.7.9 SEC_PROXY_SCFG_THREAD_THREAD_CTL_J_J Registers
- 14.7.7.10 SEC_PROXY_SCFG_THREAD_THREAD_EVT_MAP_J_J Registers
- 14.7.7.11 SEC_PROXY_SCFG_THREAD_THREAD_DST_J_J Registers
- 14.7.7.12 SEC_PROXY_RT_THREAD_THREAD_STATUS_J_J Registers
- 14.7.7.13 SEC_PROXY_RT_THREAD_THREAD_THR_J_J Registers
- 14.7.7.14 SEC_PROXY_SRC_TARGET_DATA_THREAD_THREAD_DATA_J_J Registers
- 14.7.7.15 SEC_PROXY_SRC_TARGET_DATA_THREAD_THREAD_MESSAGE_J_J_N Registers
- 14.7.7.16 Access Table
- 14.7.8
PDMA Registers
- 14.7.8.1 _PDMA_REV Registers
- 14.7.8.2 _PDMA_VECTOR Registers
- 14.7.8.3 _PDMA_STAT Registers
- 14.7.8.4 _PDMA_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.7.8.5 _PDMA_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.7.8.6 _PDMA_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.7.8.7 _PDMA_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.7.8.8 _PDMA_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.7.8.9 _PDMA_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.7.8.10 _PDMA_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.7.8.11 _PDMA_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.7.8.12 _PDMA_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.7.8.13 _PDMA_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.7.8.14 _PDMA_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.7.8.15 _PDMA_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.7.8.16 _PDMA_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.7.8.17 Access Table
- 14.7.1
DMASS_BCDMA_0 Registers
- 14.8
Peripherals Registers
- 14.8.1
Audio Registers
- 14.8.1.1
MCASP Registers
- 14.8.1.1.1 CFG_PID Registers
- 14.8.1.1.2 CFG_PWRIDLESYSCONFIG Registers
- 14.8.1.1.3 CFG_PFUNC Registers
- 14.8.1.1.4 CFG_PDIR Registers
- 14.8.1.1.5 CFG_PDOUT Registers
- 14.8.1.1.6 CFG_PDIN Registers
- 14.8.1.1.7 CFG_PDCLR Registers
- 14.8.1.1.8 CFG_GBLCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.9 CFG_AMUTE Registers
- 14.8.1.1.10 CFG_DLBCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.11 CFG_DITCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.12 CFG_RGBLCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.13 CFG_RMASK Registers
- 14.8.1.1.14 CFG_RFMT Registers
- 14.8.1.1.15 CFG_AFSRCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.16 CFG_ACLKRCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.17 CFG_AHCLKRCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.18 CFG_RTDM Registers
- 14.8.1.1.19 CFG_RINTCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.20 CFG_RSTAT Registers
- 14.8.1.1.21 CFG_RSLOT Registers
- 14.8.1.1.22 CFG_RCLKCHK Registers
- 14.8.1.1.23 CFG_PIDTCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.24 CFG_XGBLCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.25 CFG_XMASK Registers
- 14.8.1.1.26 CFG_XFMT Registers
- 14.8.1.1.27 CFG_AFSXCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.28 CFG_ACLKXCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.29 CFG_AHCLKXCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.30 CFG_XTDM Registers
- 14.8.1.1.31 CFG_XINTCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.32 CFG_XSTAT Registers
- 14.8.1.1.33 CFG_XSLOT Registers
- 14.8.1.1.34 CFG_XCLKCHK Registers
- 14.8.1.1.35 CFG_XEVTCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.36 CFG_DITCSRA0 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.37 CFG_DITCSRA1 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.38 CFG_DITCSRA2 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.39 CFG_DITCSRA3 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.40 CFG_DITCSRA4 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.41 CFG_DITCSRA5 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.42 CFG_DITCSRB0 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.43 CFG_DITCSRB1 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.44 CFG_DITCSRB2 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.45 CFG_DITCSRB3 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.46 CFG_DITCSRB4 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.47 CFG_DITCSRB5 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.48 CFG_DITUDRA0 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.49 CFG_DITUDRA1 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.50 CFG_DITUDRA2 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.51 CFG_DITUDRA3 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.52 CFG_DITUDRA4 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.53 CFG_DITUDRA5 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.54 CFG_DITUDRB0 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.55 CFG_DITUDRB1 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.56 CFG_DITUDRB2 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.57 CFG_DITUDRB3 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.58 CFG_DITUDRB4 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.59 CFG_DITUDRB5 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.60 CFG_SRCTL0 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.61 CFG_SRCTL1 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.62 CFG_SRCTL2 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.63 CFG_SRCTL3 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.64 CFG_SRCTL4 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.65 CFG_SRCTL5 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.66 CFG_SRCTL6 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.67 CFG_SRCTL7 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.68 CFG_SRCTL8 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.69 CFG_SRCTL9 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.70 CFG_SRCTL10 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.71 CFG_SRCTL11 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.72 CFG_SRCTL12 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.73 CFG_SRCTL13 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.74 CFG_SRCTL14 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.75 CFG_SRCTL15 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.76 CFG_XBUF0 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.77 CFG_XBUF1 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.78 CFG_XBUF2 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.79 CFG_XBUF3 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.80 CFG_XBUF4 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.81 CFG_XBUF5 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.82 CFG_XBUF6 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.83 CFG_XBUF7 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.84 CFG_XBUF8 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.85 CFG_XBUF9 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.86 CFG_XBUF10 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.87 CFG_XBUF11 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.88 CFG_XBUF12 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.89 CFG_XBUF13 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.90 CFG_XBUF14 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.91 CFG_XBUF15 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.92 CFG_RBUF0 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.93 CFG_RBUF1 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.94 CFG_RBUF2 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.95 CFG_RBUF3 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.96 CFG_RBUF4 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.97 CFG_RBUF5 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.98 CFG_RBUF6 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.99 CFG_RBUF7 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.100 CFG_RBUF8 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.101 CFG_RBUF9 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.102 CFG_RBUF10 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.103 CFG_RBUF11 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.104 CFG_RBUF12 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.105 CFG_RBUF13 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.106 CFG_RBUF14 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.107 CFG_RBUF15 Registers
- 14.8.1.1.108 CFG_WFIFOCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.109 CFG_WFIFOSTS Registers
- 14.8.1.1.110 CFG_RFIFOCTL Registers
- 14.8.1.1.111 CFG_RFIFOSTS Registers
- 14.8.1.1.112 Access Table
- 14.8.1.1
MCASP Registers
- 14.8.2
General Connectivity Registers
- 14.8.2.1
GPIO Registers
- 14.8.2.1.1 _GPIO_PID Registers
- 14.8.2.1.2 _GPIO_PCR Registers
- 14.8.2.1.3 _GPIO_BINTEN Registers
- 14.8.2.1.4 _GPIO_DIR01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.5 _GPIO_OUT_DATA01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.6 _GPIO_SET_DATA01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.7 _GPIO_CLR_DATA01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.8 _GPIO_IN_DATA01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.9 _GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.10 _GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.11 _GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.12 _GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.13 _GPIO_INTSTAT01 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.14 _GPIO_DIR23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.15 _GPIO_OUT_DATA23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.16 _GPIO_SET_DATA23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.17 _GPIO_CLR_DATA23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.18 _GPIO_IN_DATA23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.19 _GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.20 _GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.21 _GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.22 _GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.23 _GPIO_INTSTAT23 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.24 _GPIO_DIR45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.25 _GPIO_OUT_DATA45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.26 _GPIO_SET_DATA45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.27 _GPIO_CLR_DATA45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.28 _GPIO_IN_DATA45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.29 _GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.30 _GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.31 _GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.32 _GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.33 _GPIO_INTSTAT45 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.34 _GPIO_DIR67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.35 _GPIO_OUT_DATA67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.36 _GPIO_SET_DATA67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.37 _GPIO_CLR_DATA67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.38 _GPIO_IN_DATA67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.39 _GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.40 _GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.41 _GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.42 _GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.43 _GPIO_INTSTAT67 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.44 _GPIO_DIR8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.45 _GPIO_OUT_DATA8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.46 _GPIO_SET_DATA8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.47 _GPIO_CLR_DATA8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.48 _GPIO_IN_DATA8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.49 _GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.50 _GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.51 _GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.52 _GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.53 _GPIO_INTSTAT8 Registers
- 14.8.2.1.54 Access Table
- 14.8.2.2
I2C Registers
- 14.8.2.2.1 CFG_I2C_REVNB_LO Registers
- 14.8.2.2.2 CFG_I2C_REVNB_HI Registers
- 14.8.2.2.3 CFG_I2C_SYSC Registers
- 14.8.2.2.4 CFG_I2C_EOI Registers
- 14.8.2.2.5 CFG_I2C_IRQSTATUS_RAW Registers
- 14.8.2.2.6 CFG_I2C_IRQSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.2.2.7 CFG_I2C_IRQENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.2.2.8 CFG_I2C_IRQENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.2.2.9 CFG_I2C_WE Registers
- 14.8.2.2.10 CFG_I2C_DMARXENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.2.2.11 CFG_I2C_DMATXENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.2.2.12 CFG_I2C_DMARXENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.2.2.13 CFG_I2C_DMATXENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.2.2.14 CFG_I2C_DMARXWAKE_EN Registers
- 14.8.2.2.15 CFG_I2C_DMATXWAKE_EN Registers
- 14.8.2.2.16 CFG_I2C_IE Registers
- 14.8.2.2.17 CFG_I2C_STAT Registers
- 14.8.2.2.18 CFG_I2C_SYSS Registers
- 14.8.2.2.19 CFG_I2C_BUF Registers
- 14.8.2.2.20 CFG_I2C_CNT Registers
- 14.8.2.2.21 CFG_I2C_DATA Registers
- 14.8.2.2.22 CFG_I2C_CON Registers
- 14.8.2.2.23 CFG_I2C_OA Registers
- 14.8.2.2.24 CFG_I2C_SA Registers
- 14.8.2.2.25 CFG_I2C_PSC Registers
- 14.8.2.2.26 CFG_I2C_SCLL Registers
- 14.8.2.2.27 CFG_I2C_SCLH Registers
- 14.8.2.2.28 CFG_I2C_SYSTEST Registers
- 14.8.2.2.29 CFG_I2C_BUFSTAT Registers
- 14.8.2.2.30 CFG_I2C_OA1 Registers
- 14.8.2.2.31 CFG_I2C_OA2 Registers
- 14.8.2.2.32 CFG_I2C_OA3 Registers
- 14.8.2.2.33 CFG_I2C_ACTOA Registers
- 14.8.2.2.34 CFG_I2C_SBLOCK Registers
- 14.8.2.2.35 Access Table
- 14.8.2.3
MCSPI Registers
- 14.8.2.3.1 CFG_HL_REV Registers
- 14.8.2.3.2 CFG_HL_HWINFO Registers
- 14.8.2.3.3 CFG_HL_SYSCONFIG Registers
- 14.8.2.3.4 CFG_REVISION Registers
- 14.8.2.3.5 CFG_SYSCONFIG Registers
- 14.8.2.3.6 CFG_SYSSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.2.3.7 CFG_IRQSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.2.3.8 CFG_IRQENABLE Registers
- 14.8.2.3.9 CFG_WAKEUPENABLE Registers
- 14.8.2.3.10 CFG_SYST Registers
- 14.8.2.3.11 CFG_MODULCTRL Registers
- 14.8.2.3.12 CFG_CH0CONF Registers
- 14.8.2.3.13 CFG_CH0STAT Registers
- 14.8.2.3.14 CFG_CH0CTRL Registers
- 14.8.2.3.15 CFG_TX0 Registers
- 14.8.2.3.16 CFG_RX0 Registers
- 14.8.2.3.17 CFG_CH1CONF Registers
- 14.8.2.3.18 CFG_CH1STAT Registers
- 14.8.2.3.19 CFG_CH1CTRL Registers
- 14.8.2.3.20 CFG_TX1 Registers
- 14.8.2.3.21 CFG_RX1 Registers
- 14.8.2.3.22 CFG_CH2CONF Registers
- 14.8.2.3.23 CFG_CH2STAT Registers
- 14.8.2.3.24 CFG_CH2CTRL Registers
- 14.8.2.3.25 CFG_TX2 Registers
- 14.8.2.3.26 CFG_RX2 Registers
- 14.8.2.3.27 CFG_CH3CONF Registers
- 14.8.2.3.28 CFG_CH3STAT Registers
- 14.8.2.3.29 CFG_CH3CTRL Registers
- 14.8.2.3.30 CFG_TX3 Registers
- 14.8.2.3.31 CFG_RX3 Registers
- 14.8.2.3.32 CFG_XFERLEVEL Registers
- 14.8.2.3.33 CFG_DAFTX Registers
- 14.8.2.3.34 CFG_DAFRX Registers
- 14.8.2.3.35 Access Table
- 14.8.2.4
UART Registers
- 14.8.2.4.1 _UART_DLL Registers
- 14.8.2.4.2 _UART_RHR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.3 _UART_THR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.4 _UART_DLH Registers
- 14.8.2.4.5 _UART_IER_CIR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.6 _UART_IER_IRDA Registers
- 14.8.2.4.7 _UART_IER_UART Registers
- 14.8.2.4.8 _UART_EFR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.9 _UART_FCR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.10 _UART_IIR_CIR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.11 _UART_IIR_IRDA Registers
- 14.8.2.4.12 _UART_IIR_UART Registers
- 14.8.2.4.13 _UART_LCR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.14 _UART_MCR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.15 _UART_XON1_ADDR1 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.16 _UART_LSR_CIR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.17 _UART_LSR_IRDA Registers
- 14.8.2.4.18 _UART_LSR_UART Registers
- 14.8.2.4.19 _UART_XON2_ADDR2 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.20 _UART_MSR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.21 _UART_TCR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.22 _UART_XOFF1 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.23 _UART_SPR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.24 _UART_TLR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.25 _UART_XOFF2 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.26 _UART_MDR1 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.27 _UART_MDR2 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.28 _UART_SFLSR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.29 _UART_TXFLL Registers
- 14.8.2.4.30 _UART_RESUME Registers
- 14.8.2.4.31 _UART_TXFLH Registers
- 14.8.2.4.32 _UART_RXFLL Registers
- 14.8.2.4.33 _UART_SFREGL Registers
- 14.8.2.4.34 _UART_RXFLH Registers
- 14.8.2.4.35 _UART_SFREGH Registers
- 14.8.2.4.36 _UART_BLR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.37 _UART_UASR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.38 _UART_ACREG Registers
- 14.8.2.4.39 _UART_SCR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.40 _UART_SSR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.41 _UART_EBLR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.42 _UART_MVR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.43 _UART_SYSC Registers
- 14.8.2.4.44 _UART_SYSS Registers
- 14.8.2.4.45 _UART_WER Registers
- 14.8.2.4.46 _UART_CFPS Registers
- 14.8.2.4.47 _UART_RXFIFO_LVL Registers
- 14.8.2.4.48 _UART_TXFIFO_LVL Registers
- 14.8.2.4.49 _UART_IER2 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.50 _UART_ISR2 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.51 _UART_FREQ_SEL Registers
- 14.8.2.4.52 _UART_ABAUD_1ST_CHAR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.53 _UART_BAUD_2ND_CHAR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.54 _UART_MDR3 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.55 _UART_TX_DMA_THRESHOLD Registers
- 14.8.2.4.56 _UART_MDR4 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.57 _UART_EFR2 Registers
- 14.8.2.4.58 _UART_ECR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.59 _UART_TIMEGUARD Registers
- 14.8.2.4.60 _UART_TIMEOUTL Registers
- 14.8.2.4.61 _UART_TIMEOUTH Registers
- 14.8.2.4.62 _UART_SCCR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.63 _UART_ERHR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.64 _UART_ETHR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.65 _UART_MAR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.66 _UART_MMR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.67 _UART_MBR Registers
- 14.8.2.4.68 Access Table
- 14.8.2.1
GPIO Registers
- 14.8.3
High-speed Serial Interfaces Registers
- 14.8.3.1
CPSW Registers
- 14.8.3.1.1 ECC_ECC_ECC_REV Registers
- 14.8.3.1.2 ECC_ECC_ECC_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.3.1.3 ECC_ECC_ECC_STAT Registers
- 14.8.3.1.4 ECC_ECC_ECC_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.5 ECC_ECC_ECC_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.6 ECC_ECC_ECC_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.7 ECC_ECC_ECC_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.8 ECC_ECC_ECC_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.9 ECC_ECC_ECC_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.10 ECC_ECC_ECC_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.11 ECC_ECC_ECC_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.12 ECC_ECC_ECC_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.13 ECC_ECC_ECC_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.3.1.14 ECC_ECC_ECC_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.3.1.15 ECC_ECC_ECC_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.3.1.16 ECC_ECC_ECC_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.3.1.17 NUSS_CPSW_NUSS_IDVER_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.18 NUSS_SYNCE_COUNT_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.19 NUSS_SYNCE_MUX_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.20 NUSS_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.21 NUSS_SGMII_NON_FIBER_MODE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.22 NUSS_SERDES_RESET_ISO_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.23 NUSS_SUBSSYSTEM_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.24 NUSS_SUBSYSTEM_CONFIG_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.25 NUSS_RGMII1_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.26 NUSS_RGMII2_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.27 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_SGMII_IDVER_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.28 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_SOFT_RESET_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.29 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_CONTROL_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.30 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_STATUS_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.31 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_MR_ADV_ABILITY_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.32 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_MR_NP_TX_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.33 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_MR_LP_ADV_ABILITY_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.34 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_MR_LP_NP_RX_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.35 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_DIAG_CLEAR_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.36 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_DIAG_CONTROL_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.37 NUSS_CPSGMII_CPSGMII_DIAG_STATUS_REG_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.38 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_MDIO_VERSION_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.39 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.40 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_ALIVE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.41 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_LINK_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.42 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_LINK_INT_RAW_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.43 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_LINK_INT_MASKED_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.44 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_LINK_INT_MASK_SET_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.45 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_LINK_INT_MASK_CLEAR_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.46 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_USER_INT_RAW_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.47 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_USER_INT_MASKED_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.48 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_USER_INT_MASK_SET_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.49 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_USER_INT_MASK_CLEAR_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.50 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_MANUAL_IF_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.51 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_POLL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.52 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_POLL_EN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.53 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_CLAUS45_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.54 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_USER_ADDR0_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.55 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_USER_ADDR1_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.56 NUSS_INTD_INTD_REVISION Registers
- 14.8.3.1.57 NUSS_INTD_INTD_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.58 NUSS_INTD_INTD_INTR_VECTOR_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.59 NUSS_INTD_INTD_ENABLE_REG_OUT_PULSE_0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.60 NUSS_INTD_INTD_ENABLE_CLR_REG_OUT_PULSE_0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.61 NUSS_INTD_INTD_STATUS_REG_OUT_PULSE_0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.62 NUSS_INTD_INTD_INTR_VECTOR_REG_OUT_PULSE Registers
- 14.8.3.1.63 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_ID_VER_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.64 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.65 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_EM_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.66 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_PORT_EN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.67 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_PTYPE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.68 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_SOFT_IDLE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.69 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_THRU_RATE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.70 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_GAP_THRESH_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.71 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_EEE_PRESCALE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.72 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_G_OFLOW_THRESH_SET_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.73 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_G_OFLOW_THRESH_CLR_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.74 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.75 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.76 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.77 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.78 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_VLAN_LTYPE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.79 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_EST_TS_DOMAIN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.80 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CUT_THRESHOLD_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.81 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_FREQUENCY_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.82 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_IET_HOLD_CNT_LD_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.83 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI0_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.84 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI1_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.85 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI2_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.86 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI3_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.87 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI4_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.88 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI5_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.89 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI6_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.90 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI7_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.91 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_USER_GROUP_USER_ACCESS_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.92 NUSS_MDIO_MDIO_USER_GROUP_USER_PHY_SEL_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.93 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.94 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_FLOW_ID_OFFSET_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.95 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_BLK_CNT_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.96 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_PORT_VLAN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.97 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.98 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_PRI_CTL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.99 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_RX_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.100 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_RX_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.101 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_BLKS_PRI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.102 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_IDLE2LPI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.103 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_LPI2WAKE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.104 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_EEE_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.105 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_FIFO_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.106 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_RX_DSCP_MAP_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.107 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_PRI_CIR_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.108 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_PRI_EIR_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.109 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_D_THRESH_SET_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.110 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_D_THRESH_SET_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.111 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.112 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.113 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.114 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.115 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.116 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.117 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_SRC_ID_A_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.118 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_SRC_ID_B_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.119 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_HOST_BLKS_PRI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.120 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_RESERVED_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.121 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.122 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAX_BLKS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.123 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_BLK_CNT_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.124 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PORT_VLAN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.125 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.126 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PRI_CTL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.127 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_RX_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.128 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_RX_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.129 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_BLKS_PRI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.130 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_IDLE2LPI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.131 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_LPI2WAKE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.132 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_EEE_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.133 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_IET_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.134 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_IET_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.135 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_IET_VERIFY_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.136 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_FIFO_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.137 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_EST_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.138 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_RX_DSCP_MAP_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.139 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PRI_CIR_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.140 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PRI_EIR_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.141 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_THRESH_SET_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.142 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_THRESH_SET_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.143 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.144 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.145 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.146 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.147 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.148 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.149 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_OFLOW_ADDVAL_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.150 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_OFLOW_ADDVAL_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.151 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_SA_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.152 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_SA_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.153 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_CTL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.154 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_SEQ_LTYPE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.155 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_VLAN_LTYPE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.156 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_CTL_LTYPE2_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.157 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_CTL2_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.158 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.159 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.160 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_SOFT_RESET_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.161 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_BOFFTEST_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.162 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_RX_PAUSETIMER_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.163 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_RXN_PAUSETIMER_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.164 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_TX_PAUSETIMER_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.165 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_TXN_PAUSETIMER_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.166 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_EMCONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.167 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_TX_GAP_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.168 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_PORT_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.169 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_POINTER_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.170 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_A_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.171 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_B_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.172 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_C_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.173 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_D_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.174 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_CUT_THRU_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.175 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PORT_SPEED_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.176 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_RESERVED_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.177 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.178 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAX_BLKS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.179 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_BLK_CNT_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.180 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PORT_VLAN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.181 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.182 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PRI_CTL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.183 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_RX_PRI_MAP_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.184 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_RX_MAXLEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.185 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_BLKS_PRI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.186 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_IDLE2LPI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.187 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_LPI2WAKE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.188 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_EEE_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.189 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_IET_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.190 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_IET_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.191 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_IET_VERIFY_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.192 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_FIFO_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.193 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_EST_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.194 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_RX_DSCP_MAP_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.195 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PRI_CIR_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.196 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PRI_EIR_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.197 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_THRESH_SET_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.198 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_THRESH_SET_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.199 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.200 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.201 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.202 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.203 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.204 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.205 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_OFLOW_ADDVAL_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.206 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_OFLOW_ADDVAL_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.207 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_SA_L_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.208 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_SA_H_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.209 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_CTL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.210 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_SEQ_LTYPE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.211 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_VLAN_LTYPE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.212 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_CTL_LTYPE2_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.213 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_CTL2_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.214 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.215 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.216 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_SOFT_RESET_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.217 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_BOFFTEST_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.218 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_RX_PAUSETIMER_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.219 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_RXN_PAUSETIMER_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.220 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_TX_PAUSETIMER_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.221 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_TXN_PAUSETIMER_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.222 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_EMCONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.223 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_TX_GAP_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.224 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_PORT_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.225 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_POINTER_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.226 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_A_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.227 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_B_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.228 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_C_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.229 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_D_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.230 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_CUT_THRU_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.231 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PORT_SPEED_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.232 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_EST_FETCH_LOC_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.233 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXGOODFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.234 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXBROADCASTFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.235 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXMULTICASTFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.236 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXPAUSEFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.237 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXCRCERRORS_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.238 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXALIGNCODEERRORS_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.239 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXOVERSIZEDFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.240 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXJABBERFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.241 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXUNDERSIZEDFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.242 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXFRAGMENTS_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.243 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.244 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_OVERRUN_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.245 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXOCTETS_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.246 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXGOODFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.247 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXBROADCASTFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.248 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXMULTICASTFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.249 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXPAUSEFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.250 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXDEFERREDFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.251 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXCOLLISIONFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.252 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXSINGLECOLLFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.253 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXMULTCOLLFRAMES_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.254 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXEXCESSIVECOLLISIONS_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.255 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXLATECOLLISIONS_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.256 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXIPGERROR_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.257 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXCARRIERSENSEERRORS_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.258 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXOCTETS_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.259 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES64_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.260 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES65T127_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.261 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES128T255_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.262 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES256T511_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.263 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES512T1023_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.264 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES1024TUP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.265 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_NETOCTETS_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.266 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RX_BOTTOM_OF_FIFO_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.267 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_PORTMASK_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.268 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RX_TOP_OF_FIFO_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.269 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_RATE_LIMIT_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.270 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_VID_INGRESS_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.271 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_DA_EQ_SA_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.272 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_BLOCK_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.273 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_SECURE_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.274 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_AUTH_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.275 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_UNI_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.276 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_UNI_BCNT_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.277 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_MLT_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.278 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_MLT_BCNT_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.279 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_BRD_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.280 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_BRD_BCNT_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.281 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_POL_MATCH_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.282 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_POL_MATCH_RED_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.283 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_POL_MATCH_YELLOW_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.284 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_MULT_SA_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.285 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_DUAL_VLAN_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.286 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_LEN_ERROR_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.287 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_IP_NEXT_HDR_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.288 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_IPV4_FRAG_DROP_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.289 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_RX_ASSEMBLY_ERROR_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.290 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_RX_ASSEMBLY_OK_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.291 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_RX_SMD_ERROR_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.292 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_RX_FRAG_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.293 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_TX_HOLD_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.294 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_TX_FRAG_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.295 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TX_MEMORY_PROTECT_ERROR_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.296 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ENET_PN_TX_PRI_REG_J_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.297 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ENET_PN_TX_PRI_BCNT_REG_J_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.298 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ENET_PN_TX_PRI_DROP_REG_J_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.299 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ENET_PN_TX_PRI_DROP_BCNT_REG_J_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.300 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_IDVER_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.301 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.302 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_RFTCLK_SEL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.303 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_PUSH_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.304 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_LOAD_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.305 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_LOAD_EN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.306 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_COMP_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.307 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_COMP_LEN_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.308 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_INTSTAT_RAW_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.309 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_INTSTAT_MASKED_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.310 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_INT_ENABLE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.311 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_COMP_NUDGE_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.312 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_POP_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.313 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_0_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.314 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_1_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.315 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_2_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.316 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_3_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.317 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_LOAD_HIGH_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.318 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_COMP_HIGH_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.319 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ADD_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.320 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_PPM_LOW_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.321 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_PPM_HIGH_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.322 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_NUDGE_VAL_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.323 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.324 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_MOD_VER Registers
- 14.8.3.1.325 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.3.1.326 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.3.1.327 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_CTRL2 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.328 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_PRESCALE Registers
- 14.8.3.1.329 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_AGING_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.3.1.330 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_NXT_HDR Registers
- 14.8.3.1.331 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_TBLCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.1.332 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_TBLW2 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.333 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_TBLW1 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.334 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_TBLW0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.335 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_I0_ALE_PORTCTL0_N Registers
- 14.8.3.1.336 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_UVLAN_MEMBER Registers
- 14.8.3.1.337 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_UVLAN_URCAST Registers
- 14.8.3.1.338 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_UVLAN_RMCAST Registers
- 14.8.3.1.339 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_UVLAN_UNTAG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.340 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_FAST_LUT Registers
- 14.8.3.1.341 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_STAT_DIAG Registers
- 14.8.3.1.342 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_OAM_LB_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.3.1.343 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_EGRESSOP Registers
- 14.8.3.1.344 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.345 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.346 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.347 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.348 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.349 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.350 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.1.351 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICETBLCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.1.352 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECONTROL Registers
- 14.8.3.1.353 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICETESTCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.1.354 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICEHSTAT Registers
- 14.8.3.1.355 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_THREADMAPDEF Registers
- 14.8.3.1.356 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_THREADMAPCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.1.357 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ALE_THREADMAPVAL Registers
- 14.8.3.1.358 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_COMP_LOW_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.359 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_COMP_HIGH_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.360 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_CONTROL_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.361 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_LENGTH_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.362 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_PPM_LOW_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.363 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_PPM_HIGH_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.364 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_NUDGE_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.365 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_COMP_LOW_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.366 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_COMP_HIGH_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.367 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_CONTROL_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.368 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_LENGTH_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.369 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_PPM_LOW_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.370 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_PPM_HIGH_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.371 NUSS_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_NUDGE_REG_J Registers
- 14.8.3.1.372 Access Table
- 14.8.3.2
USB Registers
- 14.8.3.2.1 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_TRACE_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.2 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB0_W0_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.3 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB0_W1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.4 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB0_W2_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.5 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB0_W3_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.6 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB1_W0_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.7 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB1_W1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.8 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB1_W2_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.9 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB1_W3_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.10 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB2_W0_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.11 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB2_W1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.12 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB2_W2_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.13 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB2_W3_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.14 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB3_W0_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.15 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB3_W1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.16 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB3_W2_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.17 DEBUG_TRACE_MMR_TRACE_VBUSP_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_EP_TRB3_W3_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.18 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_REVISION Registers
- 14.8.3.2.19 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_OVERCURRENT_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.20 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_PHY_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.21 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_PHY_TEST Registers
- 14.8.3.2.22 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_CORE_STAT Registers
- 14.8.3.2.23 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_HOST_VBUS_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.24 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_MODE_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.25 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_WAKEUP_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.26 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_WAKEUP_STAT Registers
- 14.8.3.2.27 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_OVERRIDE_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.28 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_STATUS_RAW Registers
- 14.8.3.2.29 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.3.2.30 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.3.2.31 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.3.2.32 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_EOI Registers
- 14.8.3.2.33 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_INTR_TEST Registers
- 14.8.3.2.34 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_VBUS_FILTER Registers
- 14.8.3.2.35 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_VBUS_STAT Registers
- 14.8.3.2.36 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_DEBUG_CFG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.37 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_DEBUG_DATA Registers
- 14.8.3.2.38 MMR_MMRVBP_USB2SS_CFG_HOST_HUB_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.39 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.40 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.41 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.42 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.43 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.44 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.45 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.46 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.47 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG8 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.48 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG9 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.49 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG10 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.50 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG11 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.51 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG12 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.52 PHY2_AFE_RX_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.53 PHY2_AFE_RX_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.54 PHY2_AFE_RX_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.55 PHY2_AFE_RX_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.56 PHY2_AFE_RX_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.57 PHY2_AFE_RX_REG5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.58 PHY2_AFE_RX_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.59 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG13 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.60 PHY2_AFE_TX_REG14 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.61 PHY2_AFE_RX_REG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.62 PHY2_AFE_RX_REG8 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.63 PHY2_AFE_UNUSED_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.64 PHY2_AFE_UNUSED_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.65 PHY2_AFE_BG_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.66 PHY2_AFE_BG_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.67 PHY2_AFE_BG_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.68 PHY2_AFE_BG_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.69 PHY2_AFE_CALIB_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.70 PHY2_AFE_BC_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.71 PHY2_AFE_BC_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.72 PHY2_AFE_BC_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.73 PHY2_AFE_BC_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.74 PHY2_AFE_BC_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.75 PHY2_AFE_BC_REG5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.76 PHY2_AFE_BC_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.77 PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.78 PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.79 PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.80 PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.81 PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.82 PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.83 PHY2_AFE_BG_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.84 PHY2_AFE_CALIB_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.85 PHY2_AFE_BC_REG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.86 PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.87 PHY2_AFE_UNUSED_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.88 PHY2_AFE_UNUSED_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.89 PHY2_PLL_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.90 PHY2_PLL_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.91 PHY2_PLL_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.92 PHY2_PLL_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.93 PHY2_PLL_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.94 PHY2_PLL_REG5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.95 PHY2_PLL_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.96 PHY2_PLL_REG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.97 PHY2_PLL_REG8 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.98 PHY2_PLL_REG9 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.99 PHY2_PLL_REG10 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.100 PHY2_PLL_REG11 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.101 PHY2_PLL_REG12 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.102 PHY2_PLL_REG13 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.103 PHY2_PLL_REG14 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.104 PHY2_PLL_UNUSED_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.105 PHY2_PLL_UNUSED_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.106 PHY2_PLL_REG15 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.107 PHY2_PLL_REG16 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.108 PHY2_PLL_UNUSED_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.109 PHY2_CALIB_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.110 PHY2_CALIB_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.111 PHY2_BC_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.112 PHY2_BC_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.113 PHY2_BC_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.114 PHY2_BC_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.115 PHY2_BC_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.116 PHY2_BC_REG5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.117 PHY2_BC_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.118 PHY2_BC_REG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.119 PHY2_TED_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.120 PHY2_TED_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.121 PHY2_TED_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.122 PHY2_CALIB_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.123 PHY2_CALIB_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.124 PHY2_BC_REG8 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.125 PHY2_BC_REG9 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.126 PHY2_BC_REG10 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.127 PHY2_BC_REG11 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.128 PHY2_BC_REG12 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.129 PHY2_TED_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.130 PHY2_TED_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.131 PHY2_DIG_UNUSED_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.132 PHY2_DIG_UNUSED_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.133 PHY2_DIG_UNUSED_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.134 PHY2_DIG_UNUSED_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.135 PHY2_INTERRUPT_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.136 PHY2_INTERRUPT_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.137 PHY2_RX_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.138 PHY2_RX_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.139 PHY2_TX_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.140 PHY2_TX_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.141 PHY2_CDR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.142 PHY2_CDR_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.143 PHY2_CDR_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.144 PHY2_CDR_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.145 PHY2_CDR_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.146 PHY2_CDR_REG5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.147 PHY2_CDR_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.148 PHY2_CDR_REG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.149 PHY2_CDR_REG8 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.150 PHY2_RX_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.151 PHY2_RX_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.152 PHY2_RX_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.153 PHY2_RX_REG5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.154 PHY2_RX_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.155 PHY2_RX_REG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.156 PHY2_TX_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.157 PHY2_TX_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.158 PHY2_TX_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.159 PHY2_CDR_REG9 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.160 PHY2_CDR_REG10 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.161 PHY2_CDR_REG11 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.162 PHY2_CDR_RE12 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.163 PHY2_DIG_TXRX_UNUSED_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.164 PHY2_DIG_TXRX_UNUSED_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.165 PHY2_DIG_TXRX_UNUSED_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.166 PHY2_DIG_TXRX_UNUSED_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.167 PHY2_UTMI_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.168 PHY2_UTMI_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.169 PHY2_UTMI_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.170 PHY2_UTMI_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.171 PHY2_UTMI_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.172 PHY2_UTMI_REG5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.173 PHY2_UTMI_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.174 PHY2_UTMI_REG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.175 PHY2_UTMI_REG8 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.176 PHY2_UTMI_REG9 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.177 PHY2_UTMI_REG10 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.178 PHY2_UTMI_REG11 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.179 PHY2_UTMI_REG12 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.180 PHY2_UTMI_REG13 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.181 PHY2_UTMI_REG14 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.182 PHY2_UTMI_REG15 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.183 PHY2_UTMI_REG16 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.184 PHY2_UTMI_REG17 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.185 PHY2_UTMI_REG18 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.186 PHY2_UTMI_REG19 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.187 PHY2_UTMI_REG20 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.188 PHY2_UTMI_REG21 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.189 PHY2_UTMI_REG22 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.190 PHY2_UTMI_REG23 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.191 PHY2_UTMI_REG24 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.192 PHY2_UTMI_REG25 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.193 PHY2_UTMI_REG26 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.194 PHY2_UTMI_REG27 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.195 PHY2_UTMI_REG28 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.196 PHY2_UTMI_REG29 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.197 PHY2_UTMI_REG30 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.198 PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.199 PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.200 PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.201 PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.202 PHY2_UTMI_REG31 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.203 PHY2_UTMI_REG32 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.204 PHY2_UTMI_REG33 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.205 PHY2_UTMI_REG34 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.206 PHY2_UTMI_REG35 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.207 PHY2_UTMI_REG36 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.208 PHY2_UTMI_REG37 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.209 PHY2_UTMI_REG38 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.210 PHY2_UTMI_REG39 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.211 PHY2_UTMI_REG40 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.212 PHY2_UTMI_REG41 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.213 PHY2_UTMI_REG42 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.214 PHY2_UTMI_REG43 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.215 PHY2_UTMI_REG44 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.216 PHY2_UTMI_REG45 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.217 PHY2_UTMI_REG46 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.218 PHY2_UTMI_REG47 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.219 PHY2_UTMI_REG48 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.220 PHY2_UTMI_REG49 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.221 PHY2_UTMI_REG50 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.222 PHY2_UTMI_REG51 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.223 PHY2_UTMI_REG52 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.224 PHY2_UTMI_REG53 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.225 PHY2_UTMI_REG54 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.226 PHY2_UTMI_REG55 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.227 PHY2_UTMI_REG56 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.228 PHY2_UTMI_REG57 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.229 PHY2_UTMI_REG58 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.230 PHY2_UTMI_REG59 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.231 PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.232 PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.233 ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.8.3.2.234 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.3.2.235 ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.8.3.2.236 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.3.2.237 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.238 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.239 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.240 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.241 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.242 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.243 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.244 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.245 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.3.2.246 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.3.2.247 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.3.2.248 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.3.2.249 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_CAP_CAPLENGTH Registers
- 14.8.3.2.250 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_CAP_HCSPARAMS1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.251 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_CAP_HCSPARAMS2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.252 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_CAP_HCSPARAMS3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.253 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_CAP_HCCPARAMS1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.254 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_CAP_DBOFF Registers
- 14.8.3.2.255 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_CAP_RTSOFF Registers
- 14.8.3.2.256 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_CAP_HCCPARAMS2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.257 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_OPER_USBCMD Registers
- 14.8.3.2.258 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_OPER_USBSTS Registers
- 14.8.3.2.259 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_OPER_PAGESIZE Registers
- 14.8.3.2.260 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_OPER_DNCTRL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.261 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_OPER_CRCR_LO Registers
- 14.8.3.2.262 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_OPER_CRCR_HI Registers
- 14.8.3.2.263 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_OPER_DCBAAP_LO Registers
- 14.8.3.2.264 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_OPER_DCBAAP_HI Registers
- 14.8.3.2.265 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_OPER_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.266 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_PORT_XHCI_PORT_20_XHCI_PORT_20_PORTSC_20 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.267 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_PORT_XHCI_PORT_20_XHCI_PORT_20_PORTPMSC_20 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.268 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_PORT_XHCI_PORT_20_XHCI_PORT_20_PORTLI_20 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.269 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_PORT_XHCI_PORT_20_XHCI_PORT_20_PORTHLPMC_20 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.270 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_PORT_XHCI_PORT_30_XHCI_PORT_30_PORTPMSC_30 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.271 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_PORT_XHCI_PORT_30_XHCI_PORT_30_PORTLI_30 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.272 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_PORT_XHCI_PORT_30_XHCI_PORT_30_PORTHLPMC_30 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.273 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_RUNTIME_MFINDEX Registers
- 14.8.3.2.274 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_RUNTIME_RSVDZ Registers
- 14.8.3.2.275 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_INTR_XHCI_INTR_XHCI_INTR_IMAN_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.276 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_INTR_XHCI_INTR_XHCI_INTR_IMOD_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.277 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_INTR_XHCI_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERSTSZ_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.278 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_INTR_XHCI_INTR_XHCI_INTR_RSVDP_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.279 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_INTR_XHCI_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERSTBA_LO_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.280 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_INTR_XHCI_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERSTBA_HI_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.281 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_INTR_XHCI_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERDP_LO_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.282 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_INTR_XHCI_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERDP_HI_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.283 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DB_XHCI_DB_XHCI_DB_DB_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.284 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_EXTCAP_USBLEGSUP Registers
- 14.8.3.2.285 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_EXTCAP_USBLEGCTLSTS Registers
- 14.8.3.2.286 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_SUPPRTCAP2_SUPTPRT2_DW0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.287 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_SUPPRTCAP2_SUPTPRT2_DW1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.288 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_SUPPRTCAP2_SUPTPRT2_DW2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.289 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_SUPPRTCAP2_SUPTPRT2_DW3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.290 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_SUPPRTCAP3_SUPTPRT3_DW0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.291 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_SUPPRTCAP3_SUPTPRT3_DW1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.292 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_SUPPRTCAP3_SUPTPRT3_DW2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.293 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_SUPPRTCAP3_SUPTPRT3_DW3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.294 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GSBUSCFG0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.295 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GSBUSCFG1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.296 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXTHRCFG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.297 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GRXTHRCFG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.298 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.299 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GPMSTS Registers
- 14.8.3.2.300 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GSTS Registers
- 14.8.3.2.301 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GUCTL1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.302 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GSNPSID Registers
- 14.8.3.2.303 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GGPIO Registers
- 14.8.3.2.304 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GUID Registers
- 14.8.3.2.305 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GUCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.306 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GBUSERRADDRLO Registers
- 14.8.3.2.307 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GBUSERRADDRHI Registers
- 14.8.3.2.308 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GPRTBIMAPLO Registers
- 14.8.3.2.309 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GPRTBIMAPHI Registers
- 14.8.3.2.310 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GHWPARAMS0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.311 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GHWPARAMS1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.312 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GHWPARAMS2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.313 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GHWPARAMS3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.314 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GHWPARAMS4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.315 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GHWPARAMS5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.316 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GHWPARAMS6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.317 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GHWPARAMS7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.318 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GDBGFIFOSPACE Registers
- 14.8.3.2.319 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GDBGLTSSM Registers
- 14.8.3.2.320 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GDBGLNMCC Registers
- 14.8.3.2.321 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GDBGBMU Registers
- 14.8.3.2.322 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GDBGLSPMUX_HST Registers
- 14.8.3.2.323 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GDBGLSP Registers
- 14.8.3.2.324 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GDBGEPINFO0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.325 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GDBGEPINFO1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.326 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GPRTBIMAP_HSLO Registers
- 14.8.3.2.327 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GPRTBIMAP_HSHI Registers
- 14.8.3.2.328 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GPRTBIMAP_FSLO Registers
- 14.8.3.2.329 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GPRTBIMAP_FSHI Registers
- 14.8.3.2.330 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_RESERVED Registers
- 14.8.3.2.331 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GUCTL2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.332 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GHWPARAMS8 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.333 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GUCTL3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.334 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFOPRIDEV Registers
- 14.8.3.2.335 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFOPRIHST Registers
- 14.8.3.2.336 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GRXFIFOPRIHST Registers
- 14.8.3.2.337 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GDMAHLRATIO Registers
- 14.8.3.2.338 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GFLADJ Registers
- 14.8.3.2.339 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GPHY_GPHY_GUSB2PHYCFG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.340 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GI2C_GI2C_GUSB2I2CCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.341 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GULPI_GULPI_GUSB2PHYACC_ULPI Registers
- 14.8.3.2.342 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GPIPE_GPIPE_GUSB3PIPECTL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.343 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.344 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.345 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.346 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ3 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.347 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ4 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.348 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ5 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.349 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ6 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.350 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ7 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.351 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ8 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.352 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ9 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.353 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ10 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.354 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ11 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.355 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ12 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.356 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ13 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.357 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ14 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.358 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ15 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.359 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GRXFIFO_GRXFIFO_GRXFIFOSIZ0 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.360 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GRXFIFO_GRXFIFO_GRXFIFOSIZ1 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.361 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GRXFIFO_GRXFIFO_GRXFIFOSIZ2 Registers
- 14.8.3.2.362 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GEVNT_GEVNT_GEVNTADRLO_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.363 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GEVNT_GEVNT_GEVNTADRHI_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.364 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GEVNT_GEVNT_GEVNTSIZ_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.365 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GEVNT_GEVNT_GEVNTCOUNT_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.366 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_GBL_GRHB_GRHB_GUSB2RHBCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.367 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DCFG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.368 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.369 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DEVTEN Registers
- 14.8.3.2.370 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DSTS Registers
- 14.8.3.2.371 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DGCMDPAR Registers
- 14.8.3.2.372 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DGCMD Registers
- 14.8.3.2.373 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DALEPENA Registers
- 14.8.3.2.374 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DEV_RESERVED_DEV_RESERVED_RSVD_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.375 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR2_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.376 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.377 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR0_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.378 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMD_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.379 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEV_DEV_INTR_DEV_INTR_DEV_IMOD_J_J Registers
- 14.8.3.2.380 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_LINK_LINK_LINK_LU1LFPSRXTIM Registers
- 14.8.3.2.381 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_LINK_LINK_LINK_LINK_SETTINGS Registers
- 14.8.3.2.382 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_LINK_LINK_LINK_LLUCTL Registers
- 14.8.3.2.383 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_LINK_LINK_LINK_LPTMDPDELAY Registers
- 14.8.3.2.384 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEBUG_DEBUG_DEBUG_U3RHBDBG Registers
- 14.8.3.2.385 VBP2AHB_WRAP_CONTROLLER_VBP_USB3_CORE_DEBUG_RAM0_RAM0_N Registers
- 14.8.3.2.386 Access Table
- 14.8.3.1
CPSW Registers
- 14.8.4
Memory Interfaces Registers
- 14.8.4.1 FSS Registers
- 14.8.4.2
FSS_FSAS_0 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.1 FSAS_CFG_REVISION Registers
- 14.8.4.2.2 FSAS_CFG_SYSCONFIG Registers
- 14.8.4.2.3 FSAS_CFG_FRAG_ADR Registers
- 14.8.4.2.4 FSAS_CFG_FRAG_CTL Registers
- 14.8.4.2.5 FSAS_CFG_IRQ_IRQ_EOI Registers
- 14.8.4.2.6 FSAS_CFG_IRQ_IRQ_STATUS_RAW Registers
- 14.8.4.2.7 FSAS_CFG_IRQ_IRQ_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.2.8 FSAS_CFG_IRQ_IRQ_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.4.2.9 FSAS_CFG_IRQ_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.4.2.10 FSAS_CFG_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_RGSTRT_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.2.11 FSAS_CFG_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_RGSIZ_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.2.12 FSAS_CFG_ERR_ERR_ECC_BLOCK_ADR Registers
- 14.8.4.2.13 FSAS_CFG_ERR_ERR_ECC_TYPE Registers
- 14.8.4.2.14 FSAS_CFG_ERR_ERR_WRT_TYPE Registers
- 14.8.4.2.15 OTFA_CFG_REVID Registers
- 14.8.4.2.16 OTFA_CFG_SCFG Registers
- 14.8.4.2.17 OTFA_CFG_ISR Registers
- 14.8.4.2.18 OTFA_CFG_IS Registers
- 14.8.4.2.19 OTFA_CFG_IES Registers
- 14.8.4.2.20 OTFA_CFG_IEC Registers
- 14.8.4.2.21 OTFA_CFG_CCFG Registers
- 14.8.4.2.22 OTFA_CFG_CSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.2.23 OTFA_CFG_RGCFG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.24 OTFA_CFG_RGMACST0 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.25 OTFA_CFG_RGST0 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.26 OTFA_CFG_RGSI0 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.27 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE00 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.28 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE01 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.29 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE02 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.30 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE03 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.31 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE04 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.32 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE05 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.33 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE06 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.34 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE07 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.35 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP00 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.36 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP01 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.37 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP02 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.38 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP03 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.39 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP04 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.40 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP05 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.41 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP06 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.42 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP07 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.43 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA00 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.44 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA01 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.45 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA02 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.46 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA03 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.47 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP00 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.48 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP01 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.49 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP02 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.50 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP03 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.51 OTFA_CFG_RIV00 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.52 OTFA_CFG_RIV01 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.53 OTFA_CFG_RIV02 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.54 OTFA_CFG_RIV03 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.55 OTFA_CFG_RGCFG1 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.56 OTFA_CFG_RGMACST1 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.57 OTFA_CFG_RGST1 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.58 OTFA_CFG_RGSI1 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.59 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE10 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.60 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE11 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.61 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE12 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.62 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE13 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.63 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE14 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.64 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE15 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.65 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE16 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.66 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE17 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.67 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP10 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.68 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP11 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.69 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP12 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.70 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP13 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.71 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP14 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.72 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP15 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.73 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP16 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.74 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP17 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.75 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA10 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.76 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA11 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.77 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA12 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.78 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA13 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.79 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP10 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.80 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP11 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.81 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP12 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.82 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP13 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.83 OTFA_CFG_RIV10 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.84 OTFA_CFG_RIV11 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.85 OTFA_CFG_RIV12 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.86 OTFA_CFG_RIV13 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.87 OTFA_CFG_RGCFG2 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.88 OTFA_CFG_RGMACST2 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.89 OTFA_CFG_RGST2 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.90 OTFA_CFG_RGSI2 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.91 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE20 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.92 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE21 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.93 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE22 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.94 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE23 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.95 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE24 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.96 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE25 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.97 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE26 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.98 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE27 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.99 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP20 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.100 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP21 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.101 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP22 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.102 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP23 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.103 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP24 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.104 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP25 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.105 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP26 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.106 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP27 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.107 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA20 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.108 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA21 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.109 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA22 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.110 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA23 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.111 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP20 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.112 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP21 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.113 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP22 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.114 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP23 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.115 OTFA_CFG_RIV20 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.116 OTFA_CFG_RIV21 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.117 OTFA_CFG_RIV22 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.118 OTFA_CFG_RIV23 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.119 OTFA_CFG_RGCFG3 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.120 OTFA_CFG_RGMACST3 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.121 OTFA_CFG_RGST3 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.122 OTFA_CFG_RGSI3 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.123 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE30 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.124 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE31 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.125 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE32 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.126 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE33 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.127 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE34 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.128 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE35 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.129 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE36 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.130 OTFA_CFG_RKEYE37 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.131 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP30 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.132 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP31 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.133 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP32 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.134 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP33 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.135 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP34 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.136 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP35 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.137 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP36 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.138 OTFA_CFG_RKEYEP37 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.139 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA30 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.140 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA31 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.141 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA32 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.142 OTFA_CFG_RKEYA33 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.143 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP30 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.144 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP31 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.145 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP32 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.146 OTFA_CFG_RKEYAP33 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.147 OTFA_CFG_RIV30 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.148 OTFA_CFG_RIV31 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.149 OTFA_CFG_RIV32 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.150 OTFA_CFG_RIV33 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.151 OTFA_CFG_IRQADDINFO0 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.152 OTFA_CFG_IRQADDINFO1 Registers
- 14.8.4.2.153 OTFA_CFG_MACCACHEINFO Registers
- 14.8.4.2.154 OTFA_CFG_RMWRMCNT Registers
- 14.8.4.2.155 DAT_REG1_HPB_DATA_MEM_N Registers
- 14.8.4.2.156 DAT_REG0_HPB_DATA_MEM_N Registers
- 14.8.4.2.157 DAT_REG3_HPB_DATA_MEM_N Registers
- 14.8.4.2.158 Access Table
- 14.8.4.3
FSS_OSPI_0 Registers
- 14.8.4.3.1 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.8.4.3.2 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.4.3.3 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.8.4.3.4 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.4.3.5 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.6 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.3.7 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.3.8 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.3.9 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.10 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.3.11 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.3.12 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.3.13 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.4.3.14 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.4.3.15 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.4.3.16 OSPI0_ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.4.3.17 OSPI0_CTRL_CONFIG_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.18 OSPI0_CTRL_DEV_INSTR_RD_CONFIG_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.19 OSPI0_CTRL_DEV_INSTR_WR_CONFIG_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.20 OSPI0_CTRL_DEV_DELAY_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.21 OSPI0_CTRL_RD_DATA_CAPTURE_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.22 OSPI0_CTRL_DEV_SIZE_CONFIG_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.23 OSPI0_CTRL_SRAM_PARTITION_CFG_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.24 OSPI0_CTRL_IND_AHB_ADDR_TRIGGER_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.25 OSPI0_CTRL_DMA_PERIPH_CONFIG_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.26 OSPI0_CTRL_REMAP_ADDR_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.27 OSPI0_CTRL_MODE_BIT_CONFIG_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.28 OSPI0_CTRL_SRAM_FILL_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.29 OSPI0_CTRL_TX_THRESH_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.30 OSPI0_CTRL_RX_THRESH_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.31 OSPI0_CTRL_WRITE_COMPLETION_CTRL_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.32 OSPI0_CTRL_NO_OF_POLLS_BEF_EXP_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.33 OSPI0_CTRL_IRQ_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.34 OSPI0_CTRL_IRQ_MASK_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.35 OSPI0_CTRL_LOWER_WR_PROT_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.36 OSPI0_CTRL_UPPER_WR_PROT_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.37 OSPI0_CTRL_WR_PROT_CTRL_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.38 OSPI0_CTRL_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_CTRL_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.39 OSPI0_CTRL_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_WATERMARK_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.40 OSPI0_CTRL_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_START_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.41 OSPI0_CTRL_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_NUM_BYTES_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.42 OSPI0_CTRL_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_CTRL_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.43 OSPI0_CTRL_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_WATERMARK_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.44 OSPI0_CTRL_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_START_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.45 OSPI0_CTRL_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_NUM_BYTES_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.46 OSPI0_CTRL_INDIRECT_TRIGGER_ADDR_RANGE_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.47 OSPI0_CTRL_FLASH_COMMAND_CTRL_MEM_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.48 OSPI0_CTRL_FLASH_CMD_CTRL_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.49 OSPI0_CTRL_FLASH_CMD_ADDR_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.50 OSPI0_CTRL_FLASH_RD_DATA_LOWER_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.51 OSPI0_CTRL_FLASH_RD_DATA_UPPER_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.52 OSPI0_CTRL_FLASH_WR_DATA_LOWER_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.53 OSPI0_CTRL_FLASH_WR_DATA_UPPER_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.54 OSPI0_CTRL_POLLING_FLASH_STATUS_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.55 OSPI0_CTRL_PHY_CONFIGURATION_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.56 OSPI0_CTRL_PHY_MASTER_CONTROL_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.57 OSPI0_CTRL_DLL_OBSERVABLE_LOWER_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.58 OSPI0_CTRL_DLL_OBSERVABLE_UPPER_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.59 OSPI0_CTRL_OPCODE_EXT_LOWER_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.60 OSPI0_CTRL_OPCODE_EXT_UPPER_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.61 OSPI0_CTRL_MODULE_ID_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.3.62 OSPI0_SS_CFG_PID Registers
- 14.8.4.3.63 OSPI0_SS_CFG_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.4.3.64 OSPI0_SS_CFG_STAT Registers
- 14.8.4.3.65 OSPI0_SS_CFG_EOI Registers
- 14.8.4.3.66 Access Table
- 14.8.4.4
GPMC Registers
- 14.8.4.4.1 CFG_GPMC_REVISION Registers
- 14.8.4.4.2 CFG_GPMC_SYSCONFIG Registers
- 14.8.4.4.3 CFG_GPMC_SYSSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.4.4 CFG_GPMC_IRQSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.4.5 CFG_GPMC_IRQENABLE Registers
- 14.8.4.4.6 CFG_GPMC_TIMEOUT_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.4.7 CFG_GPMC_ERR_ADDRESS Registers
- 14.8.4.4.8 CFG_GPMC_ERR_TYPE Registers
- 14.8.4.4.9 CFG_GPMC_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.4.4.10 CFG_GPMC_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.4.11 CFG_GPMC_PREFETCH_CONFIG1 Registers
- 14.8.4.4.12 CFG_GPMC_PREFETCH_CONFIG2 Registers
- 14.8.4.4.13 CFG_GPMC_PREFETCH_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.4.14 CFG_GPMC_PREFETCH_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.4.15 CFG_GPMC_ECC_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.4.4.16 CFG_GPMC_ECC_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.4.17 CFG_GPMC_ECC_SIZE_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.4.4.18 CFG_GPMC_ECC_RESULT_N Registers
- 14.8.4.4.19 CFG_GPMC_BCH_SWDATA Registers
- 14.8.4.4.20 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_CONFIG1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.21 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_CONFIG2_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.22 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_CONFIG3_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.23 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_CONFIG4_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.24 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_CONFIG5_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.25 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_CONFIG6_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.26 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_CONFIG7_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.27 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_NAND_COMMAND_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.28 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_NAND_ADDRESS_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.29 CFG_CS_CS_GPMC_NAND_DATA_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.30 CFG_CSEL_CSEL_GPMC_BCH_RESULT_0_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.31 CFG_CSEL_CSEL_GPMC_BCH_RESULT_1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.32 CFG_CSEL_CSEL_GPMC_BCH_RESULT_2_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.33 CFG_CSEL_CSEL_GPMC_BCH_RESULT_3_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.34 CFG_CHIPSEL_CHIPSEL_GPMC_BCH_RESULT_4_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.35 CFG_CHIPSEL_CHIPSEL_GPMC_BCH_RESULT_5_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.36 CFG_CHIPSEL_CHIPSEL_GPMC_BCH_RESULT_6_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.4.37 Access Table
- 14.8.4.5
ELM Registers
- 14.8.4.5.1 _ELM_ELM_REVISION Registers
- 14.8.4.5.2 _ELM_ELM_SYSCONFIG Registers
- 14.8.4.5.3 _ELM_ELM_SYSSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.5.4 _ELM_ELM_IRQSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.5.5 _ELM_ELM_IRQENABLE Registers
- 14.8.4.5.6 _ELM_ELM_LOCATION_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.4.5.7 _ELM_ELM_PAGE_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.4.5.8 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_SYNDROME_FRAGMENT_0_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.9 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_SYNDROME_FRAGMENT_1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.10 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_SYNDROME_FRAGMENT_2_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.11 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_SYNDROME_FRAGMENT_3_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.12 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_SYNDROME_FRAGMENT_4_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.13 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_SYNDROME_FRAGMENT_5_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.14 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_SYNDROME_FRAGMENT_6_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.15 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_LOCATION_STATUS_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.16 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_0_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.17 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.18 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_2_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.19 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_3_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.20 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_4_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.21 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_5_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.22 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_6_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.23 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_7_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.24 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_8_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.25 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_9_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.26 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_10_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.27 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_11_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.28 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_12_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.29 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_13_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.30 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_14_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.31 _ELM_POLY_POLY_ELM_ERROR_LOCATION_15_J_J Registers
- 14.8.4.5.32 Access Table
- 14.8.4.6
MMCSD Registers
- 14.8.4.6.1 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_REV Registers
- 14.8.4.6.2 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.3 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_STAT Registers
- 14.8.4.6.4 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.4.6.5 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.6 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.7 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.8 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.9 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.10 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.11 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.12 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.13 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.4.6.14 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.15 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.4.6.16 ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.17 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_REV Registers
- 14.8.4.6.18 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.19 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_STAT Registers
- 14.8.4.6.20 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.4.6.21 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.22 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.23 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.24 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.25 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.26 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.27 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.28 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.29 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.4.6.30 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.31 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.4.6.32 ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.33 CTL_CFG_SDMA_SYS_ADDR_LO Registers
- 14.8.4.6.34 CTL_CFG_SDMA_SYS_ADDR_HI Registers
- 14.8.4.6.35 CTL_CFG_BLOCK_SIZE Registers
- 14.8.4.6.36 CTL_CFG_BLOCK_COUNT Registers
- 14.8.4.6.37 CTL_CFG_ARGUMENT1_LO Registers
- 14.8.4.6.38 CTL_CFG_ARGUMENT1_HI Registers
- 14.8.4.6.39 CTL_CFG_TRANSFER_MODE Registers
- 14.8.4.6.40 CTL_CFG_COMMAND Registers
- 14.8.4.6.41 CTL_CFG_RESPONSE_N Registers
- 14.8.4.6.42 CTL_CFG_DATA_PORT Registers
- 14.8.4.6.43 CTL_CFG_PRESENTSTATE Registers
- 14.8.4.6.44 CTL_CFG_HOST_CONTROL1 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.45 CTL_CFG_POWER_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.6.46 CTL_CFG_BLOCK_GAP_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.6.47 CTL_CFG_WAKEUP_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.6.48 CTL_CFG_CLOCK_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.6.49 CTL_CFG_TIMEOUT_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.6.50 CTL_CFG_SOFTWARE_RESET Registers
- 14.8.4.6.51 CTL_CFG_NORMAL_INTR_STS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.52 CTL_CFG_ERROR_INTR_STS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.53 CTL_CFG_NORMAL_INTR_STS_ENA Registers
- 14.8.4.6.54 CTL_CFG_ERROR_INTR_STS_ENA Registers
- 14.8.4.6.55 CTL_CFG_NORMAL_INTR_SIG_ENA Registers
- 14.8.4.6.56 CTL_CFG_ERROR_INTR_SIG_ENA Registers
- 14.8.4.6.57 CTL_CFG_AUTOCMD_ERR_STS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.58 CTL_CFG_HOST_CONTROL2 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.59 CTL_CFG_CAPABILITIES Registers
- 14.8.4.6.60 CTL_CFG_MAX_CURRENT_CAP Registers
- 14.8.4.6.61 CTL_CFG_FORCE_EVNT_ACMD_ERR_STS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.62 CTL_CFG_FORCE_EVNT_ERR_INT_STS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.63 CTL_CFG_ADMA_ERR_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.64 CTL_CFG_ADMA_SYS_ADDRESS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.65 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE0 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.66 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE1 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.67 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE2 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.68 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE3 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.69 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE4 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.70 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE5 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.71 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE6 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.72 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE7 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.73 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE8 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.74 CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE10 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.75 CTL_CFG_ADMA3_DESC_ADDRESS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.76 CTL_CFG_UHS2_BLOCK_SIZE Registers
- 14.8.4.6.77 CTL_CFG_UHS2_BLOCK_COUNT Registers
- 14.8.4.6.78 CTL_CFG_UHS2_COMMAND_PKT_N Registers
- 14.8.4.6.79 CTL_CFG_UHS2_XFER_MODE Registers
- 14.8.4.6.80 CTL_CFG_UHS2_COMMAND Registers
- 14.8.4.6.81 CTL_CFG_UHS2_RESPONSE_N Registers
- 14.8.4.6.82 CTL_CFG_UHS2_MESSAGE_SELECT Registers
- 14.8.4.6.83 CTL_CFG_UHS2_MESSAGE Registers
- 14.8.4.6.84 CTL_CFG_UHS2_DEVICE_INTR_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.85 CTL_CFG_UHS2_DEVICE_SELECT Registers
- 14.8.4.6.86 CTL_CFG_UHS2_DEVICE_INT_CODE Registers
- 14.8.4.6.87 CTL_CFG_UHS2_SOFTWARE_RESET Registers
- 14.8.4.6.88 CTL_CFG_UHS2_TIMER_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.6.89 CTL_CFG_UHS2_ERR_INTR_STS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.90 CTL_CFG_UHS2_ERR_INTR_STS_ENA Registers
- 14.8.4.6.91 CTL_CFG_UHS2_ERR_INTR_SIG_ENA Registers
- 14.8.4.6.92 CTL_CFG_UHS2_SETTINGS_PTR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.93 CTL_CFG_UHS2_CAPABILITIES_PTR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.94 CTL_CFG_UHS2_TEST_PTR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.95 CTL_CFG_SHARED_BUS_CTRL_PTR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.96 CTL_CFG_VENDOR_SPECFIC_PTR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.97 CTL_CFG_BOOT_TIMEOUT_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.6.98 CTL_CFG_VENDOR_REGISTER Registers
- 14.8.4.6.99 CTL_CFG_SLOT_INT_STS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.100 CTL_CFG_HOST_CONTROLLER_VER Registers
- 14.8.4.6.101 CTL_CFG_UHS2_GEN_SETTINGS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.102 CTL_CFG_UHS2_PHY_SETTINGS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.103 CTL_CFG_UHS2_LNK_TRN_SETTINGS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.104 CTL_CFG_UHS2_GEN_CAP Registers
- 14.8.4.6.105 CTL_CFG_UHS2_PHY_CAP Registers
- 14.8.4.6.106 CTL_CFG_UHS2_LNK_TRN_CAP Registers
- 14.8.4.6.107 CTL_CFG_FORCE_UHSII_ERR_INT_STS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.108 CTL_CFG_CQ_VERSION Registers
- 14.8.4.6.109 CTL_CFG_CQ_CAPABILITIES Registers
- 14.8.4.6.110 CTL_CFG_CQ_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.111 CTL_CFG_CQ_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.4.6.112 CTL_CFG_CQ_INTR_STS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.113 CTL_CFG_CQ_INTR_STS_ENA Registers
- 14.8.4.6.114 CTL_CFG_CQ_INTR_SIG_ENA Registers
- 14.8.4.6.115 CTL_CFG_CQ_INTR_COALESCING Registers
- 14.8.4.6.116 CTL_CFG_CQ_TDL_BASE_ADDR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.117 CTL_CFG_CQ_TDL_BASE_ADDR_UPBITS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.118 CTL_CFG_CQ_TASK_DOOR_BELL Registers
- 14.8.4.6.119 CTL_CFG_CQ_TASK_COMP_NOTIF Registers
- 14.8.4.6.120 CTL_CFG_CQ_DEV_QUEUE_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.121 CTL_CFG_CQ_DEV_PENDING_TASKS Registers
- 14.8.4.6.122 CTL_CFG_CQ_TASK_CLEAR Registers
- 14.8.4.6.123 CTL_CFG_CQ_SEND_STS_CONFIG1 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.124 CTL_CFG_CQ_SEND_STS_CONFIG2 Registers
- 14.8.4.6.125 CTL_CFG_CQ_DCMD_RESPONSE Registers
- 14.8.4.6.126 CTL_CFG_CQ_RESP_ERR_MASK Registers
- 14.8.4.6.127 CTL_CFG_CQ_TASK_ERR_INFO Registers
- 14.8.4.6.128 CTL_CFG_CQ_CMD_RESP_INDEX Registers
- 14.8.4.6.129 CTL_CFG_CQ_CMD_RESP_ARG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.130 CTL_CFG_CQ_ERROR_TASK_ID Registers
- 14.8.4.6.131 SS_CFG_SS_ID_REV_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.132 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_1_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.133 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_2_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.134 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_3_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.135 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_4_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.136 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_5_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.137 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_6_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.138 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_7_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.139 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_8_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.140 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_9_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.141 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_10_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.142 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_11_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.143 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_12_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.144 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_13_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.145 SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_14_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.146 SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_1_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.147 SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_2_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.148 SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_3_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.149 SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_4_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.150 SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_5_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.151 SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_6_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.152 SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_1_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.153 SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_2_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.154 SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_3_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.155 SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_4_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.156 SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_5_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.157 SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_6_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.158 SS_CFG_PHY_STAT_1_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.159 SS_CFG_PHY_STAT_2_REG Registers
- 14.8.4.6.160 Access Table
- 14.8.5
Industrial and Control Interfaces Registers
- 14.8.5.1
MCAN Registers
- 14.8.5.1.1 SS_MCANSS_PID Registers
- 14.8.5.1.2 SS_MCANSS_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.5.1.3 SS_MCANSS_STAT Registers
- 14.8.5.1.4 SS_MCANSS_ICS Registers
- 14.8.5.1.5 SS_MCANSS_IRS Registers
- 14.8.5.1.6 SS_MCANSS_IECS Registers
- 14.8.5.1.7 SS_MCANSS_IE Registers
- 14.8.5.1.8 SS_MCANSS_IES Registers
- 14.8.5.1.9 SS_MCANSS_EOI Registers
- 14.8.5.1.10 SS_MCANSS_EXT_TS_PRESCALER Registers
- 14.8.5.1.11 SS_MCANSS_EXT_TS_UNSERVICED_INTR_CNTR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.12 CFG_CREL Registers
- 14.8.5.1.13 CFG_ENDN Registers
- 14.8.5.1.14 CFG_CUST Registers
- 14.8.5.1.15 CFG_DBTP Registers
- 14.8.5.1.16 CFG_TEST Registers
- 14.8.5.1.17 CFG_RWD Registers
- 14.8.5.1.18 CFG_CCCR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.19 CFG_NBTP Registers
- 14.8.5.1.20 CFG_TSCC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.21 CFG_TSCV Registers
- 14.8.5.1.22 CFG_TOCC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.23 CFG_TOCV Registers
- 14.8.5.1.24 CFG_RESERVED00 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.25 CFG_RESERVED11 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.26 CFG_RESERVED22 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.27 CFG_RESERVED33 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.28 CFG_ECR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.29 CFG_PSR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.30 CFG_TDCR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.31 CFG_RESERVED44 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.32 CFG_IR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.33 CFG_IE Registers
- 14.8.5.1.34 CFG_ILS Registers
- 14.8.5.1.35 CFG_ILE Registers
- 14.8.5.1.36 CFG_RESERVED55 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.37 CFG_RESERVED66 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.38 CFG_RESERVED77 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.39 CFG_RESERVED88 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.40 CFG_RESERVED99 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.41 CFG_RESERVED1010 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.42 CFG_RESERVED1111 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.43 CFG_RESERVED1212 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.44 CFG_GFC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.45 CFG_SIDFC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.46 CFG_XIDFC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.47 CFG_RESERVED1313 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.48 CFG_XIDAM Registers
- 14.8.5.1.49 CFG_HPMS Registers
- 14.8.5.1.50 CFG_NDAT1 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.51 CFG_NDAT2 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.52 CFG_RXF0C Registers
- 14.8.5.1.53 CFG_RXF0S Registers
- 14.8.5.1.54 CFG_RXF0A Registers
- 14.8.5.1.55 CFG_RXBC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.56 CFG_RXF1C Registers
- 14.8.5.1.57 CFG_RXF1S Registers
- 14.8.5.1.58 CFG_RXF1A Registers
- 14.8.5.1.59 CFG_RXESC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.60 CFG_TXBC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.61 CFG_TXFQS Registers
- 14.8.5.1.62 CFG_TXESC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.63 CFG_TXBRP Registers
- 14.8.5.1.64 CFG_TXBAR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.65 CFG_TXBCR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.66 CFG_TXBTO Registers
- 14.8.5.1.67 CFG_TXBCF Registers
- 14.8.5.1.68 CFG_TXBTIE Registers
- 14.8.5.1.69 CFG_TXBCIE Registers
- 14.8.5.1.70 CFG_RESERVED1414 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.71 CFG_RESERVED1515 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.72 CFG_TXEFC Registers
- 14.8.5.1.73 CFG_TXEFS Registers
- 14.8.5.1.74 CFG_TXEFA Registers
- 14.8.5.1.75 CFG_RESERVED1616 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.76 CFG_RESERVUPPER256_N Registers
- 14.8.5.1.77 MSGMEM_RAM_RAM_REG_N Registers
- 14.8.5.1.78 ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.8.5.1.79 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.80 ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.8.5.1.81 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.5.1.82 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.5.1.83 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.84 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.85 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.86 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.5.1.87 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.88 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.89 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.5.1.90 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.5.1.91 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.92 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.5.1.93 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.5.1.94 Access Table
- 14.8.5.2
ECAP Registers
- 14.8.5.2.1 CTL_STS_TSCNT Registers
- 14.8.5.2.2 CTL_STS_CNTPHS Registers
- 14.8.5.2.3 CTL_STS_CAP1 Registers
- 14.8.5.2.4 CTL_STS_CAP2 Registers
- 14.8.5.2.5 CTL_STS_CAP3 Registers
- 14.8.5.2.6 CTL_STS_CAP4 Registers
- 14.8.5.2.7 CTL_STS_ECCTL Registers
- 14.8.5.2.8 CTL_STS_ECINT_EN_FLG Registers
- 14.8.5.2.9 CTL_STS_ECINT_CLR_FRC Registers
- 14.8.5.2.10 CTL_STS_PID Registers
- 14.8.5.2.11 Access Table
- 14.8.5.3
EPWM Registers
- 14.8.5.3.1 EPWM_TBCTL Registers
- 14.8.5.3.2 EPWM_TBSTS Registers
- 14.8.5.3.3 EPWM_TBPHSHR Registers
- 14.8.5.3.4 EPWM_TBPHS Registers
- 14.8.5.3.5 EPWM_TBCNT Registers
- 14.8.5.3.6 EPWM_TBPRD Registers
- 14.8.5.3.7 EPWM_CMPCTL Registers
- 14.8.5.3.8 EPWM_CMPAHR Registers
- 14.8.5.3.9 EPWM_CMPA Registers
- 14.8.5.3.10 EPWM_CMPB Registers
- 14.8.5.3.11 EPWM_AQCTLA Registers
- 14.8.5.3.12 EPWM_AQCTLB Registers
- 14.8.5.3.13 EPWM_AQSFRC Registers
- 14.8.5.3.14 EPWM_AQCSFRC Registers
- 14.8.5.3.15 EPWM_DBCTL Registers
- 14.8.5.3.16 EPWM_DBRED Registers
- 14.8.5.3.17 EPWM_DBFED Registers
- 14.8.5.3.18 EPWM_TZSEL Registers
- 14.8.5.3.19 EPWM_TZCTL Registers
- 14.8.5.3.20 EPWM_TZEINT Registers
- 14.8.5.3.21 EPWM_TZFLG Registers
- 14.8.5.3.22 EPWM_TZCLR Registers
- 14.8.5.3.23 EPWM_TZFRC Registers
- 14.8.5.3.24 EPWM_ETSEL Registers
- 14.8.5.3.25 EPWM_ETPS Registers
- 14.8.5.3.26 EPWM_ETFLG Registers
- 14.8.5.3.27 EPWM_ETCLR Registers
- 14.8.5.3.28 EPWM_ETFRC Registers
- 14.8.5.3.29 EPWM_PCCTL Registers
- 14.8.5.3.30 EPWM_PID Registers
- 14.8.5.3.31 Access Table
- 14.8.5.4
EQEP Registers
- 14.8.5.4.1 REG_QPOSCNT Registers
- 14.8.5.4.2 REG_QPOSINIT Registers
- 14.8.5.4.3 REG_QPOSMAX Registers
- 14.8.5.4.4 REG_QPOSCMP Registers
- 14.8.5.4.5 REG_QPOSILAT Registers
- 14.8.5.4.6 REG_QPOSSLAT Registers
- 14.8.5.4.7 REG_QPOSLAT Registers
- 14.8.5.4.8 REG_QUTMR Registers
- 14.8.5.4.9 REG_QUPRD Registers
- 14.8.5.4.10 REG_QWDTMR Registers
- 14.8.5.4.11 REG_QWDPRD Registers
- 14.8.5.4.12 REG_QDECCTL_TYPE2 Registers
- 14.8.5.4.13 REG_QEPCTL Registers
- 14.8.5.4.14 REG_QCAPCTL Registers
- 14.8.5.4.15 REG_QPOSCTL Registers
- 14.8.5.4.16 REG_QEINT_TYPE1 Registers
- 14.8.5.4.17 REG_QFLG_TYPE1 Registers
- 14.8.5.4.18 REG_QCLR_TYPE1 Registers
- 14.8.5.4.19 REG_QFRC_TYPE1 Registers
- 14.8.5.4.20 REG_QEPSTS_TYPE1 Registers
- 14.8.5.4.21 REG_QCTMR Registers
- 14.8.5.4.22 REG_QCPRD Registers
- 14.8.5.4.23 REG_QCTMRLAT Registers
- 14.8.5.4.24 REG_QCPRDLAT Registers
- 14.8.5.4.25 REG_RESERVED_N Registers
- 14.8.5.4.26 REG_PID Registers
- 14.8.5.4.27 REG_REV_TYPE2 Registers
- 14.8.5.4.28 REG_QEPSTROBESEL Registers
- 14.8.5.4.29 REG_QMACTRL Registers
- 14.8.5.4.30 REG_QEPSRCSEL Registers
- 14.8.5.4.31 Access Table
- 14.8.5.1
MCAN Registers
- 14.8.6
Camera Subsystem Registers
- 14.8.6.1
csi_rx_if Registers
- 14.8.6.1.1 ECC_AGGR_CFG_REV Registers
- 14.8.6.1.2 ECC_AGGR_CFG_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.6.1.3 ECC_AGGR_CFG_STAT Registers
- 14.8.6.1.4 ECC_AGGR_CFG_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.6.1.5 ECC_AGGR_CFG_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.6 ECC_AGGR_CFG_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.7 ECC_AGGR_CFG_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.8 ECC_AGGR_CFG_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.9 ECC_AGGR_CFG_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.10 ECC_AGGR_CFG_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.11 ECC_AGGR_CFG_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.12 ECC_AGGR_CFG_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.13 ECC_AGGR_CFG_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.6.1.14 ECC_AGGR_CFG_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.6.1.15 ECC_AGGR_CFG_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.6.1.16 ECC_AGGR_CFG_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.6.1.17 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_REVISION Registers
- 14.8.6.1.18 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.19 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_INTR_VECTOR_REG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.20 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_ENABLE_REG_LEVEL_0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.21 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_ENABLE_REG_PULSE_0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.22 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_ENABLE_CLR_REG_LEVEL_0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.23 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_ENABLE_CLR_REG_PULSE_0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.24 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_STATUS_REG_LEVEL_0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.25 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_STATUS_REG_PULSE_0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.26 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_STATUS_CLR_REG_LEVEL_0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.27 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_STATUS_CLR_REG_PULSE_0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.28 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_INTR_VECTOR_REG_LEVEL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.29 CP_INTD_CFG_INTD_CFG_INTR_VECTOR_REG_PULSE Registers
- 14.8.6.1.30 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_DEVICE_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.31 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_SOFT_RESET Registers
- 14.8.6.1.32 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STATIC_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.33 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ERROR_BYPASS_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.34 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_MONITOR_IRQS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.35 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_MONITOR_IRQS_MASK_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.36 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_INFO_IRQS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.37 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_INFO_IRQS_MASK_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.38 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ERROR_IRQS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.39 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ERROR_IRQS_MASK_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.40 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_DPHY_LANE_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.41 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_DPHY_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.42 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_DPHY_ERR_STATUS_IRQ Registers
- 14.8.6.1.43 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_DPHY_ERR_IRQ_MASK_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.44 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_INTEGRATION_DEBUG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.45 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ERROR_DEBUG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.46 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_TEST_GENERIC Registers
- 14.8.6.1.47 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.48 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.49 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_DATA_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.50 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.51 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_MONITOR_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.52 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_MONITOR_FRAME Registers
- 14.8.6.1.53 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_MONITOR_LB Registers
- 14.8.6.1.54 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_TIMER Registers
- 14.8.6.1.55 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_FCC_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.56 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_FCC_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.57 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM0_FIFO_FILL_LVL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.58 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.59 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.60 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_DATA_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.61 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.62 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_MONITOR_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.63 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_MONITOR_FRAME Registers
- 14.8.6.1.64 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_MONITOR_LB Registers
- 14.8.6.1.65 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_TIMER Registers
- 14.8.6.1.66 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_FCC_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.67 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_FCC_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.68 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM1_FIFO_FILL_LVL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.69 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.70 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.71 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_DATA_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.72 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.73 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_MONITOR_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.74 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_MONITOR_FRAME Registers
- 14.8.6.1.75 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_MONITOR_LB Registers
- 14.8.6.1.76 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_TIMER Registers
- 14.8.6.1.77 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_FCC_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.78 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_FCC_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.79 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM2_FIFO_FILL_LVL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.80 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.81 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.82 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_DATA_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.83 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.84 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_MONITOR_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.85 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_MONITOR_FRAME Registers
- 14.8.6.1.86 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_MONITOR_LB Registers
- 14.8.6.1.87 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_TIMER Registers
- 14.8.6.1.88 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_FCC_CFG Registers
- 14.8.6.1.89 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_FCC_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.90 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_STREAM3_FIFO_FILL_LVL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.91 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_INT_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.92 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_INT_RAW_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.93 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_INT_MASK Registers
- 14.8.6.1.94 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_INT_TEST Registers
- 14.8.6.1.95 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_FATAL_NONFATAL_SELECT Registers
- 14.8.6.1.96 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_SRAM_CORR_FAULT_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.97 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_SRAM_UNCORR_FAULT_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.98 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_SRAM_FAULT_STATS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.99 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_TRANS_TO_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.100 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_TRANS_TO_FAULT_MASK Registers
- 14.8.6.1.101 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_TRANS_TO_FAULT_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.102 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_PROTOCOL_FAULT_MASK Registers
- 14.8.6.1.103 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ASF_PROTOCOL_FAULT_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.6.1.104 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_APB_CSI2RX_ID_PROD_VER Registers
- 14.8.6.1.105 RX_SHIM_VBUSP_MMR_CSI2RXIF_CSIRX_ID Registers
- 14.8.6.1.106 RX_SHIM_VBUSP_MMR_CSI2RXIF_VP0 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.107 RX_SHIM_VBUSP_MMR_CSI2RXIF_VP1 Registers
- 14.8.6.1.108 RX_SHIM_VBUSP_MMR_CSI2RXIF_CNTL Registers
- 14.8.6.1.109 RX_SHIM_VBUSP_MMR_CSI2RXIF_CNTX_CNTL_CNTX_CNTL_DMACNTX_J_J Registers
- 14.8.6.1.110 RX_SHIM_VBUSP_MMR_CSI2RXIF_CNTX_CNTL_CNTX_CNTL_PSI_CFG0_J_J Registers
- 14.8.6.1.111 RX_SHIM_VBUSP_MMR_CSI2RXIF_CNTX_CNTL_CNTX_CNTL_PSI_CFG1_J_J Registers
- 14.8.6.1.112 Access Table
- 14.8.6.2
DPHY_RX Registers
- 14.8.6.2.1 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_K3_DPHY_RX_CMN0_CMN_DIG_TBIT2 Registers
- 14.8.6.2.2 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_K3_DPHY_RX_CMN0_CMN_DIG_TBIT10 Registers
- 14.8.6.2.3 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_K3_DPHY_RX_CMN0_CMN_DIG_TBIT13 Registers
- 14.8.6.2.4 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_K3_DPHY_RX_CMN0_CMN_DIG_TBIT14 Registers
- 14.8.6.2.5 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_K3_DPHY_RX_PCS_TX_DIG_TBIT0 Registers
- 14.8.6.2.6 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_K3_DPHY_RX_PCS_TX_DIG_TBIT1 Registers
- 14.8.6.2.7 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_K3_DPHY_RX_PCS_TX_DIG_TBIT2 Registers
- 14.8.6.2.8 VBUS2APB_WRAP_VBUSP_K3_DPHY_RX_PCS_TX_DIG_TBIT3 Registers
- 14.8.6.2.9 MMR_SLV_K3_DPHY_WRAP_LANE Registers
- 14.8.6.2.10 Access Table
- 14.8.6.1
csi_rx_if Registers
- 14.8.7
Timer Modules Registers
- 14.8.7.1
GTC Registers
- 14.8.7.1.1 GTC_CFG0_PID Registers
- 14.8.7.1.2 GTC_CFG0_GTC_PID Registers
- 14.8.7.1.3 GTC_CFG0_PUSHEVT Registers
- 14.8.7.1.4 GTC_CFG1_CNTCR Registers
- 14.8.7.1.5 GTC_CFG1_CNTSR Registers
- 14.8.7.1.6 GTC_CFG1_CNTCV_LO Registers
- 14.8.7.1.7 GTC_CFG1_CNTCV_HI Registers
- 14.8.7.1.8 GTC_CFG1_CNTFID0 Registers
- 14.8.7.1.9 GTC_CFG1_CNTFID1 Registers
- 14.8.7.1.10 GTC_CFG2_CNTCVS_LO Registers
- 14.8.7.1.11 GTC_CFG2_CNTCVS_HI Registers
- 14.8.7.1.12 GTC_CFG3_CNTTIDR Registers
- 14.8.7.1.13 Access Table
- 14.8.7.2
RTI Registers
- 14.8.7.2.1 CFG_GCTRL Registers
- 14.8.7.2.2 CFG_TBCTRL Registers
- 14.8.7.2.3 CFG_CAPCTRL Registers
- 14.8.7.2.4 CFG_COMPCTRL Registers
- 14.8.7.2.5 CFG_FRC0 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.6 CFG_UC0 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.7 CFG_CPUC0 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.8 CFG_CAFRC0 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.9 CFG_CAUC0 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.10 CFG_FRC1 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.11 CFG_UC1 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.12 CFG_CPUC1 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.13 CFG_CAFRC1 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.14 CFG_CAUC1 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.15 CFG_COMP0 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.16 CFG_UDCP0 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.17 CFG_COMP1 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.18 CFG_UDCP1 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.19 CFG_COMP2 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.20 CFG_UDCP2 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.21 CFG_COMP3 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.22 CFG_UDCP3 Registers
- 14.8.7.2.23 CFG_TBLCOMP Registers
- 14.8.7.2.24 CFG_TBHCOMP Registers
- 14.8.7.2.25 CFG_SETINT Registers
- 14.8.7.2.26 CFG_CLEARINT Registers
- 14.8.7.2.27 CFG_INTFLAG Registers
- 14.8.7.2.28 CFG_DWDCTRL Registers
- 14.8.7.2.29 CFG_DWDPRLD Registers
- 14.8.7.2.30 CFG_WDSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.7.2.31 CFG_WDKEY Registers
- 14.8.7.2.32 CFG_DWDCNTR Registers
- 14.8.7.2.33 CFG_WWDRXNCTRL Registers
- 14.8.7.2.34 CFG_WWDSIZECTRL Registers
- 14.8.7.2.35 CFG_INTCLRENABLE Registers
- 14.8.7.2.36 CFG_COMP0CLR Registers
- 14.8.7.2.37 CFG_COMP1CLR Registers
- 14.8.7.2.38 CFG_COMP2CLR Registers
- 14.8.7.2.39 CFG_COMP3CLR Registers
- 14.8.7.2.40 Access Table
- 14.8.7.3
rtcss Registers
- 14.8.7.3.1 RTC_RTC_RTC_MOD_VER Registers
- 14.8.7.3.2 RTC_RTC_RTC_SUB_S_CNT Registers
- 14.8.7.3.3 RTC_RTC_RTC_S_CNT_LSW Registers
- 14.8.7.3.4 RTC_RTC_RTC_S_CNT_MSW Registers
- 14.8.7.3.5 RTC_RTC_RTC_COMP Registers
- 14.8.7.3.6 RTC_RTC_RTC_OFF_ON_S_CNT_LSW Registers
- 14.8.7.3.7 RTC_RTC_RTC_OFF_ON_S_CNT_MSW Registers
- 14.8.7.3.8 RTC_RTC_RTC_ON_OFF_S_CNT_LSW Registers
- 14.8.7.3.9 RTC_RTC_RTC_ON_OFF_S_CNT_MSW Registers
- 14.8.7.3.10 RTC_RTC_RTC_DEBOUNCE Registers
- 14.8.7.3.11 RTC_RTC_RTC_ANALOG Registers
- 14.8.7.3.12 RTC_RTC_RTC_SCRATCH0_N Registers
- 14.8.7.3.13 RTC_RTC_RTC_GENRAL_CTL Registers
- 14.8.7.3.14 RTC_RTC_RTC_IRQSTATUS_RAW_SYS Registers
- 14.8.7.3.15 RTC_RTC_RTC_IRQSTATUS_SYS Registers
- 14.8.7.3.16 RTC_RTC_RTC_IRQENABLE_SET_SYS Registers
- 14.8.7.3.17 RTC_RTC_RTC_IRQENABLE_CLR_SYS Registers
- 14.8.7.3.18 RTC_RTC_RTC_SYNCPEND Registers
- 14.8.7.3.19 RTC_RTC_RTC_KICK0 Registers
- 14.8.7.3.20 RTC_RTC_RTC_KICK1 Registers
- 14.8.7.3.21 Access Table
- 14.8.7.4
TIMER Registers
- 14.8.7.4.1 CFG_TIDR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.2 CFG_TIOCP_CFG Registers
- 14.8.7.4.3 CFG_IRQ_EOI Registers
- 14.8.7.4.4 CFG_IRQSTATUS_RAW Registers
- 14.8.7.4.5 CFG_IRQSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.7.4.6 CFG_IRQSTATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.7.4.7 CFG_IRQSTATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.8 CFG_IRQWAKEEN Registers
- 14.8.7.4.9 CFG_TCLR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.10 CFG_TCRR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.11 CFG_TLDR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.12 CFG_TTGR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.13 CFG_TWPS Registers
- 14.8.7.4.14 CFG_TMAR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.15 CFG_TCAR1 Registers
- 14.8.7.4.16 CFG_TSICR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.17 CFG_TCAR2 Registers
- 14.8.7.4.18 CFG_TPIR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.19 CFG_TNIR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.20 CFG_TCVR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.21 CFG_TOCR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.22 CFG_TOWR Registers
- 14.8.7.4.23 Access Table
- 14.8.7.1
GTC Registers
- 14.8.8
Internal Diagnostics Modules Registers
- 14.8.8.1
DCC Registers
- 14.8.8.1.1 _DCC_DCCGCTRL Registers
- 14.8.8.1.2 _DCC_DCCREV Registers
- 14.8.8.1.3 _DCC_DCCCNTSEED0 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.4 _DCC_DCCVALIDSEED0 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.5 _DCC_DCCCNTSEED1 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.6 _DCC_DCCSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.8.1.7 _DCC_DCCCNT0 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.8 _DCC_DCCVALID0 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.9 _DCC_DCCCNT1 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.10 _DCC_DCCCLKSRC1 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.11 _DCC_DCCCLKSRC0 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.12 _DCC_DCCGCTRL2 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.13 _DCC_DCCSTATUS2 Registers
- 14.8.8.1.14 _DCC_DCCERRCNT Registers
- 14.8.8.1.15 Access Table
- 14.8.8.2
ESM Registers
- 14.8.8.2.1 CFG_PID Registers
- 14.8.8.2.2 CFG_INFO Registers
- 14.8.8.2.3 CFG_EN Registers
- 14.8.8.2.4 CFG_SFT_RST Registers
- 14.8.8.2.5 CFG_ERR_RAW Registers
- 14.8.8.2.6 CFG_ERR_STS Registers
- 14.8.8.2.7 CFG_ERR_EN_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.2.8 CFG_ERR_EN_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.2.9 CFG_LOW_PRI Registers
- 14.8.8.2.10 CFG_HI_PRI Registers
- 14.8.8.2.11 CFG_LOW Registers
- 14.8.8.2.12 CFG_HI Registers
- 14.8.8.2.13 CFG_EOI Registers
- 14.8.8.2.14 CFG_PIN_CTRL Registers
- 14.8.8.2.15 CFG_PIN_STS Registers
- 14.8.8.2.16 CFG_PIN_CNTR Registers
- 14.8.8.2.17 CFG_PIN_CNTR_PRE Registers
- 14.8.8.2.18 CFG_PWMH_PIN_CNTR Registers
- 14.8.8.2.19 CFG_PWMH_PIN_CNTR_PRE Registers
- 14.8.8.2.20 CFG_PWML_PIN_CNTR Registers
- 14.8.8.2.21 CFG_PWML_PIN_CNTR_PRE Registers
- 14.8.8.2.22 CFG_ERR_GRP_ERR_GRP_RAW_J_J Registers
- 14.8.8.2.23 CFG_ERR_GRP_ERR_GRP_STS_J_J Registers
- 14.8.8.2.24 CFG_ERR_GRP_ERR_GRP_INTR_EN_SET_J_J Registers
- 14.8.8.2.25 CFG_ERR_GRP_ERR_GRP_INTR_EN_CLR_J_J Registers
- 14.8.8.2.26 CFG_ERR_GRP_ERR_GRP_INT_PRIO_J_J Registers
- 14.8.8.2.27 CFG_ERR_GRP_ERR_GRP_PIN_EN_SET_J_J Registers
- 14.8.8.2.28 CFG_ERR_GRP_ERR_GRP_PIN_EN_CLR_J_J Registers
- 14.8.8.2.29 Access Table
- 14.8.8.3
MCRC64 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.1 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_CTRL0 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.2 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_CTRL1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.3 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_CTRL2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.4 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_INTS Registers
- 14.8.8.3.5 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_INTR Registers
- 14.8.8.3.6 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.8.3.7 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_INT_OFFSET_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.3.8 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_BUSY Registers
- 14.8.8.3.9 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_PCOUNT_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.10 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_SCOUNT_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.11 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_CURSEC_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.12 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_WDTOPLD1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.13 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_BCTOPLD1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.14 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SIGREGL1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.15 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SIGREGH1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.16 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_REGL1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.17 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_REGH1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.18 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SECSIGREGL1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.19 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SECSIGREGH1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.20 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_RAW_DATAREGL1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.21 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_RAW_DATAREGH1 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.22 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_PCOUNT_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.23 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_SCOUNT_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.24 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_CURSEC_REG2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.25 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_WDTOPLD2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.26 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_BCTOPLD2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.27 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SIGREGL2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.28 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SIGREGH2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.29 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_REGL2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.30 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_REGH2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.31 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SECSIGREGL2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.32 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SECSIGREGH2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.33 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_RAW_DATAREGL2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.34 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_RAW_DATAREGH2 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.35 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_PCOUNT_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.36 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_SCOUNT_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.37 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_CURSEC_REG3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.38 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_WDTOPLD3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.39 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_BCTOPLD3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.40 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SIGREGL3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.41 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SIGREGH3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.42 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_REGL3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.43 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_REGH3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.44 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SECSIGREGL3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.45 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SECSIGREGH3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.46 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_RAW_DATAREGL3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.47 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_RAW_DATAREGH3 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.48 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_PCOUNT_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.49 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_SCOUNT_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.50 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_CURSEC_REG4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.51 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_WDTOPLD4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.52 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_BCTOPLD4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.53 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SIGREGL4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.54 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SIGREGH4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.55 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_REGL4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.56 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_CRC_REGH4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.57 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SECSIGREGL4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.58 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_PSA_SECSIGREGH4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.59 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_RAW_DATAREGL4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.60 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_RAW_DATAREGH4 Registers
- 14.8.8.3.61 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_MCRC_BUS_SEL Registers
- 14.8.8.3.62 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_I0_PSA_SIGREG1_CPY_N Registers
- 14.8.8.3.63 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_I0_PSA_SIGREG2_CPY_N Registers
- 14.8.8.3.64 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_I0_PSA_SIGREG3_CPY_N Registers
- 14.8.8.3.65 REGS_MCRC64_MCRC64_I0_PSA_SIGREG4_CPY_N Registers
- 14.8.8.3.66 Access Table
- 14.8.8.4
ECC Aggregator Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1
ECC_AGGR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.17 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.18 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.19 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.20 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.21 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.22 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG1 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.1.23 Access Table
- 14.8.8.4.2
DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.1 ECCAGGR_REV Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.2 ECCAGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.3 ECCAGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.4 ECCAGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.5 ECCAGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.6 ECCAGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.7 ECCAGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.8 ECCAGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.9 ECCAGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.10 ECCAGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.11 ECCAGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.12 ECCAGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.13 ECCAGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.14 ECCAGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.15 ECCAGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.16 ECCAGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.2.17 Access Table
- 14.8.8.4.3
M4FSS_ECC_AGGR_0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.3.17 Access Table
- 14.8.8.4.4
PSC_ECC_AGGR_0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.1 REGS_REV Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.2 REGS_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.3 REGS_STAT Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.4 REGS_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.5 REGS_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.6 REGS_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.7 REGS_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.8 REGS_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.9 REGS_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.10 REGS_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.11 REGS_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.12 REGS_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.13 REGS_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.14 REGS_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.15 REGS_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.16 REGS_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.4.17 Access Table
- 14.8.8.4.5
SAFE_ECC_AGGR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_N Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Registers
- 14.8.8.4.5.17 Access Table
- 14.8.8.4.1
ECC_AGGR Registers
- 14.8.8.1
DCC Registers
- 14.8.9
Display Subsystem Registers
- 14.8.9.1
DSS Registers
- 14.8.9.1.1 COMMON_DSS_REVISION Registers
- 14.8.9.1.2 COMMON_DSS_SYSCONFIG Registers
- 14.8.9.1.3 COMMON_DSS_SYSSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.9.1.4 COMMON_DISPC_IRQ_EOI Registers
- 14.8.9.1.5 COMMON_DISPC_IRQSTATUS_RAW Registers
- 14.8.9.1.6 COMMON_DISPC_IRQSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.9.1.7 COMMON_DISPC_IRQENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.9.1.8 COMMON_DISPC_IRQENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.9.1.9 COMMON_VID_IRQENABLE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.10 COMMON_VID_IRQENABLE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.11 COMMON_VID_IRQSTATUS_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.12 COMMON_VID_IRQSTATUS_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.13 COMMON_VP_IRQENABLE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.14 COMMON_VP_IRQENABLE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.15 COMMON_VP_IRQSTATUS_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.16 COMMON_VP_IRQSTATUS_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.17 COMMON_DISPC_GLOBAL_MFLAG_ATTRIBUTE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.18 COMMON_DISPC_GLOBAL_OUTPUT_ENABLE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.19 COMMON_DISPC_GLOBAL_BUFFER Registers
- 14.8.9.1.20 COMMON_DSS_CBA_CFG Registers
- 14.8.9.1.21 COMMON_DISPC_DBG_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.9.1.22 COMMON_DISPC_DBG_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.9.1.23 COMMON_DISPC_CLKGATING_DISABLE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.24 COMMON_DISPC_SECURE_DISABLE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.25 COMMON1_DISPC_IRQ_EOI Registers
- 14.8.9.1.26 COMMON1_DISPC_IRQSTATUS_RAW Registers
- 14.8.9.1.27 COMMON1_DISPC_IRQSTATUS Registers
- 14.8.9.1.28 COMMON1_DISPC_IRQENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.8.9.1.29 COMMON1_DISPC_IRQENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.8.9.1.30 COMMON1_VID_IRQENABLE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.31 COMMON1_VID_IRQENABLE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.32 COMMON1_DISPC_SECURE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.33 COMMON1_VID_IRQSTATUS_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.34 COMMON1_VID_IRQSTATUS_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.35 COMMON1_VP_IRQENABLE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.36 COMMON1_VP_IRQENABLE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.37 COMMON1_VP_IRQSTATUS_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.38 COMMON1_VP_IRQSTATUS_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.39 VIDL1_ATTRIBUTES Registers
- 14.8.9.1.40 VIDL1_ATTRIBUTES2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.41 VIDL1_BA_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.42 VIDL1_BA_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.43 VIDL1_BA_UV_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.44 VIDL1_BA_UV_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.45 VIDL1_BUF_SIZE_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.9.1.46 VIDL1_BUF_THRESHOLD Registers
- 14.8.9.1.47 VIDL1_CSC_COEF0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.48 VIDL1_CSC_COEF1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.49 VIDL1_CSC_COEF2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.50 VIDL1_CSC_COEF3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.51 VIDL1_CSC_COEF4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.52 VIDL1_CSC_COEF5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.53 VIDL1_CSC_COEF6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.54 VIDL1_GLOBAL_ALPHA Registers
- 14.8.9.1.55 VIDL1_MFLAG_THRESHOLD Registers
- 14.8.9.1.56 VIDL1_PICTURE_SIZE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.57 VIDL1_PIXEL_INC Registers
- 14.8.9.1.58 VIDL1_PRELOAD Registers
- 14.8.9.1.59 VIDL1_ROW_INC Registers
- 14.8.9.1.60 VIDL1_BA_EXT_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.61 VIDL1_BA_EXT_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.62 VIDL1_BA_UV_EXT_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.63 VIDL1_BA_UV_EXT_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.64 VIDL1_CSC_COEF7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.65 VIDL1_ROW_INC_UV Registers
- 14.8.9.1.66 VIDL1_CLUT_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.67 VIDL1_CLUT_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.68 VIDL1_CLUT_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.69 VIDL1_CLUT_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.70 VIDL1_CLUT_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.71 VIDL1_CLUT_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.72 VIDL1_CLUT_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.73 VIDL1_CLUT_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.74 VIDL1_CLUT_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.75 VIDL1_CLUT_9 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.76 VIDL1_CLUT_10 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.77 VIDL1_CLUT_11 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.78 VIDL1_CLUT_12 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.79 VIDL1_CLUT_13 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.80 VIDL1_CLUT_14 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.81 VIDL1_CLUT_15 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.82 VIDL1_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES Registers
- 14.8.9.1.83 VIDL1_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.84 VIDL1_SAFETY_POSITION Registers
- 14.8.9.1.85 VIDL1_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.86 VIDL1_SAFETY_SIZE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.87 VIDL1_SAFETY_LFSR_SEED Registers
- 14.8.9.1.88 VIDL1_LUMAKEY Registers
- 14.8.9.1.89 VID_ACCUH_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.90 VID_ACCUH_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.91 VID_ACCUH2_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.92 VID_ACCUH2_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.93 VID_ACCUV_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.94 VID_ACCUV_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.95 VID_ACCUV2_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.96 VID_ACCUV2_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.97 VID_ATTRIBUTES Registers
- 14.8.9.1.98 VID_ATTRIBUTES2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.99 VID_BA_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.100 VID_BA_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.101 VID_BA_UV_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.102 VID_BA_UV_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.103 VID_BUF_SIZE_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.9.1.104 VID_BUF_THRESHOLD Registers
- 14.8.9.1.105 VID_CSC_COEF0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.106 VID_CSC_COEF1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.107 VID_CSC_COEF2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.108 VID_CSC_COEF3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.109 VID_CSC_COEF4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.110 VID_CSC_COEF5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.111 VID_CSC_COEF6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.112 VID_FIRH Registers
- 14.8.9.1.113 VID_FIRH2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.114 VID_FIRV Registers
- 14.8.9.1.115 VID_FIRV2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.116 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.117 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.118 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.119 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.120 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.121 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.122 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.123 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.124 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.125 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_C_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.126 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_C_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.127 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_C_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.128 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_C_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.129 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_C_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.130 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_C_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.131 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_C_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.132 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_C_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.133 VID_FIR_COEF_H0_C_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.134 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.135 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.136 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.137 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.138 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.139 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.140 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.141 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.142 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.143 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_9 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.144 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_10 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.145 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_11 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.146 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_12 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.147 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_13 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.148 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_14 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.149 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_15 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.150 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.151 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.152 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.153 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.154 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.155 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.156 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.157 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.158 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.159 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_9 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.160 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_10 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.161 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_11 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.162 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_12 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.163 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_13 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.164 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_14 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.165 VID_FIR_COEF_H12_C_15 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.166 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.167 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.168 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.169 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.170 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.171 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.172 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.173 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.174 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.175 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_C_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.176 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_C_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.177 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_C_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.178 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_C_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.179 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_C_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.180 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_C_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.181 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_C_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.182 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_C_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.183 VID_FIR_COEF_V0_C_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.184 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.185 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.186 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.187 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.188 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.189 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.190 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.191 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.192 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.193 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_9 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.194 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_10 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.195 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_11 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.196 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_12 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.197 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_13 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.198 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_14 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.199 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_15 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.200 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.201 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.202 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.203 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.204 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.205 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.206 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.207 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.208 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.209 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_9 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.210 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_10 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.211 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_11 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.212 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_12 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.213 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_13 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.214 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_14 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.215 VID_FIR_COEF_V12_C_15 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.216 VID_GLOBAL_ALPHA Registers
- 14.8.9.1.217 VID_MFLAG_THRESHOLD Registers
- 14.8.9.1.218 VID_PICTURE_SIZE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.219 VID_PIXEL_INC Registers
- 14.8.9.1.220 VID_PRELOAD Registers
- 14.8.9.1.221 VID_ROW_INC Registers
- 14.8.9.1.222 VID_SIZE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.223 VID_BA_EXT_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.224 VID_BA_EXT_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.225 VID_BA_UV_EXT_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.226 VID_BA_UV_EXT_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.227 VID_CSC_COEF7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.228 VID_ROW_INC_UV Registers
- 14.8.9.1.229 VID_CLUT_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.230 VID_CLUT_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.231 VID_CLUT_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.232 VID_CLUT_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.233 VID_CLUT_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.234 VID_CLUT_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.235 VID_CLUT_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.236 VID_CLUT_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.237 VID_CLUT_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.238 VID_CLUT_9 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.239 VID_CLUT_10 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.240 VID_CLUT_11 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.241 VID_CLUT_12 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.242 VID_CLUT_13 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.243 VID_CLUT_14 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.244 VID_CLUT_15 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.245 VID_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES Registers
- 14.8.9.1.246 VID_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.247 VID_SAFETY_POSITION Registers
- 14.8.9.1.248 VID_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.249 VID_SAFETY_SIZE Registers
- 14.8.9.1.250 VID_SAFETY_LFSR_SEED Registers
- 14.8.9.1.251 VID_LUMAKEY Registers
- 14.8.9.1.252 OVR1_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.9.1.253 OVR1_DEFAULT_COLOR Registers
- 14.8.9.1.254 OVR1_DEFAULT_COLOR2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.255 OVR1_TRANS_COLOR_MAX Registers
- 14.8.9.1.256 OVR1_TRANS_COLOR_MAX2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.257 OVR1_TRANS_COLOR_MIN Registers
- 14.8.9.1.258 OVR1_TRANS_COLOR_MIN2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.259 OVR1_ATTRIBUTES_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.260 OVR1_ATTRIBUTES_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.261 OVR1_ATTRIBUTES_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.262 OVR1_ATTRIBUTES_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.263 OVR2_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.9.1.264 OVR2_DEFAULT_COLOR Registers
- 14.8.9.1.265 OVR2_DEFAULT_COLOR2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.266 OVR2_TRANS_COLOR_MAX Registers
- 14.8.9.1.267 OVR2_TRANS_COLOR_MAX2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.268 OVR2_TRANS_COLOR_MIN Registers
- 14.8.9.1.269 OVR2_TRANS_COLOR_MIN2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.270 OVR2_ATTRIBUTES_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.271 OVR2_ATTRIBUTES_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.272 OVR2_ATTRIBUTES_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.273 OVR2_ATTRIBUTES_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.274 VP1_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.9.1.275 VP1_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.9.1.276 VP1_CSC_COEF0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.277 VP1_CSC_COEF1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.278 VP1_CSC_COEF2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.279 VP1_DATA_CYCLE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.280 VP1_DATA_CYCLE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.281 VP1_DATA_CYCLE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.282 VP1_LINE_NUMBER Registers
- 14.8.9.1.283 VP1_POL_FREQ Registers
- 14.8.9.1.284 VP1_SIZE_SCREEN Registers
- 14.8.9.1.285 VP1_TIMING_H Registers
- 14.8.9.1.286 VP1_TIMING_V Registers
- 14.8.9.1.287 VP1_CSC_COEF3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.288 VP1_CSC_COEF4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.289 VP1_CSC_COEF5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.290 VP1_CSC_COEF6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.291 VP1_CSC_COEF7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.292 VP1_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.293 VP1_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.294 VP1_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.295 VP1_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.296 VP1_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.297 VP1_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.298 VP1_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.299 VP1_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.300 VP1_SAFETY_POSITION_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.301 VP1_SAFETY_POSITION_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.302 VP1_SAFETY_POSITION_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.303 VP1_SAFETY_POSITION_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.304 VP1_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.305 VP1_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.306 VP1_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.307 VP1_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.308 VP1_SAFETY_SIZE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.309 VP1_SAFETY_SIZE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.310 VP1_SAFETY_SIZE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.311 VP1_SAFETY_SIZE_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.312 VP1_SAFETY_LFSR_SEED Registers
- 14.8.9.1.313 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.314 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.315 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.316 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.317 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.318 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.319 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.320 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.321 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.322 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_9 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.323 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_10 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.324 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_11 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.325 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_12 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.326 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_13 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.327 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_14 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.328 VP1_GAMMA_TABLE_15 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.329 VP1_DSS_OLDI_CFG Registers
- 14.8.9.1.330 VP1_DSS_OLDI_STATUS Registers
- 14.8.9.1.331 VP1_DSS_OLDI_LB Registers
- 14.8.9.1.332 VP2_CONFIG Registers
- 14.8.9.1.333 VP2_CONTROL Registers
- 14.8.9.1.334 VP2_CSC_COEF0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.335 VP2_CSC_COEF1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.336 VP2_CSC_COEF2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.337 VP2_DATA_CYCLE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.338 VP2_DATA_CYCLE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.339 VP2_DATA_CYCLE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.340 VP2_LINE_NUMBER Registers
- 14.8.9.1.341 VP2_POL_FREQ Registers
- 14.8.9.1.342 VP2_SIZE_SCREEN Registers
- 14.8.9.1.343 VP2_TIMING_H Registers
- 14.8.9.1.344 VP2_TIMING_V Registers
- 14.8.9.1.345 VP2_CSC_COEF3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.346 VP2_CSC_COEF4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.347 VP2_CSC_COEF5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.348 VP2_CSC_COEF6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.349 VP2_CSC_COEF7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.350 VP2_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.351 VP2_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.352 VP2_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.353 VP2_SAFETY_ATTRIBUTES_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.354 VP2_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.355 VP2_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.356 VP2_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.357 VP2_SAFETY_CAPT_SIGNATURE_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.358 VP2_SAFETY_POSITION_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.359 VP2_SAFETY_POSITION_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.360 VP2_SAFETY_POSITION_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.361 VP2_SAFETY_POSITION_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.362 VP2_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.363 VP2_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.364 VP2_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.365 VP2_SAFETY_REF_SIGNATURE_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.366 VP2_SAFETY_SIZE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.367 VP2_SAFETY_SIZE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.368 VP2_SAFETY_SIZE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.369 VP2_SAFETY_SIZE_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.370 VP2_SAFETY_LFSR_SEED Registers
- 14.8.9.1.371 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_0 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.372 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_1 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.373 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_2 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.374 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_3 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.375 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_4 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.376 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_5 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.377 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_6 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.378 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_7 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.379 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_8 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.380 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_9 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.381 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_10 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.382 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_11 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.383 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_12 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.384 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_13 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.385 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_14 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.386 VP2_GAMMA_TABLE_15 Registers
- 14.8.9.1.387 Access Table
- 14.8.9.1
DSS Registers
- 14.8.1
Audio Registers
- 14.9
On-Chip Debug Registers
- 14.9.1
DEBUGSS Registers
- 14.9.1.1 SYS_TRACE Registers
- 14.9.1.2 ROM_ENTRY1 Registers
- 14.9.1.3 ROM_ENTRY2 Registers
- 14.9.1.4 ROM_ENTRY3 Registers
- 14.9.1.5 ROM_ENTRY4 Registers
- 14.9.1.6 ROM_ENTRY5 Registers
- 14.9.1.7 ROM_ENTRY6 Registers
- 14.9.1.8 ROM_ENTRY7 Registers
- 14.9.1.9 ROM_ENTRY8 Registers
- 14.9.1.10 ROM_ENTRY9 Registers
- 14.9.1.11 ROM_ENTRY10 Registers
- 14.9.1.12 ROM_ENTRY11 Registers
- 14.9.1.13 ROM_ENTRY12 Registers
- 14.9.1.14 ROM_ENTRY13 Registers
- 14.9.1.15 ROM_ENTRY14 Registers
- 14.9.1.16 ROM_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.17 ROM_PERIPHID5 Registers
- 14.9.1.18 ROM_PERIPHID6 Registers
- 14.9.1.19 ROM_PERIPHID7 Registers
- 14.9.1.20 ROM_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.21 ROM_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.22 ROM_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.23 ROM_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.24 ROM_COMPONENTID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.25 ROM_COMPONENTID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.26 ROM_COMPONENTID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.27 ROM_COMPONENTID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.28 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTSETID Registers
- 14.9.1.29 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTSETSYSCFG Registers
- 14.9.1.30 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETSTR Registers
- 14.9.1.31 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_DBGTIMELOW Registers
- 14.9.1.32 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_DBGTIMEHI Registers
- 14.9.1.33 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTSETCFG Registers
- 14.9.1.34 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETSPLREG Registers
- 14.9.1.35 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL1 Registers
- 14.9.1.36 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL2 Registers
- 14.9.1.37 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL3 Registers
- 14.9.1.38 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL4 Registers
- 14.9.1.39 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL5 Registers
- 14.9.1.40 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL6 Registers
- 14.9.1.41 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL7 Registers
- 14.9.1.42 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL8 Registers
- 14.9.1.43 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_SETMSTID Registers
- 14.9.1.44 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTL Registers
- 14.9.1.45 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTNUMDBG Registers
- 14.9.1.46 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTUSERACCCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.47 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMCNTL Registers
- 14.9.1.48 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMMSTID Registers
- 14.9.1.49 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMINTVL Registers
- 14.9.1.50 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMSEL0 Registers
- 14.9.1.51 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMSEL1 Registers
- 14.9.1.52 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR0 Registers
- 14.9.1.53 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR1 Registers
- 14.9.1.54 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR2 Registers
- 14.9.1.55 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR3 Registers
- 14.9.1.56 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR4 Registers
- 14.9.1.57 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR5 Registers
- 14.9.1.58 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR6 Registers
- 14.9.1.59 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR7 Registers
- 14.9.1.60 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR8 Registers
- 14.9.1.61 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR9 Registers
- 14.9.1.62 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR10 Registers
- 14.9.1.63 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR11 Registers
- 14.9.1.64 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR12 Registers
- 14.9.1.65 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR13 Registers
- 14.9.1.66 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR14 Registers
- 14.9.1.67 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTINTVLR15 Registers
- 14.9.1.68 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL0 Registers
- 14.9.1.69 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL1 Registers
- 14.9.1.70 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL2 Registers
- 14.9.1.71 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL3 Registers
- 14.9.1.72 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL4 Registers
- 14.9.1.73 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL5 Registers
- 14.9.1.74 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL6 Registers
- 14.9.1.75 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL7 Registers
- 14.9.1.76 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTGNBL0 Registers
- 14.9.1.77 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTGNBL1 Registers
- 14.9.1.78 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTGRST0 Registers
- 14.9.1.79 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTGRST1 Registers
- 14.9.1.80 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR0 Registers
- 14.9.1.81 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR1 Registers
- 14.9.1.82 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR2 Registers
- 14.9.1.83 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR3 Registers
- 14.9.1.84 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR4 Registers
- 14.9.1.85 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR5 Registers
- 14.9.1.86 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR6 Registers
- 14.9.1.87 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR7 Registers
- 14.9.1.88 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR8 Registers
- 14.9.1.89 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR9 Registers
- 14.9.1.90 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR10 Registers
- 14.9.1.91 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR11 Registers
- 14.9.1.92 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR12 Registers
- 14.9.1.93 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR13 Registers
- 14.9.1.94 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR14 Registers
- 14.9.1.95 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR15 Registers
- 14.9.1.96 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR16 Registers
- 14.9.1.97 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR17 Registers
- 14.9.1.98 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR18 Registers
- 14.9.1.99 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR19 Registers
- 14.9.1.100 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR20 Registers
- 14.9.1.101 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR21 Registers
- 14.9.1.102 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR22 Registers
- 14.9.1.103 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR23 Registers
- 14.9.1.104 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR24 Registers
- 14.9.1.105 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR25 Registers
- 14.9.1.106 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR26 Registers
- 14.9.1.107 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR27 Registers
- 14.9.1.108 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR28 Registers
- 14.9.1.109 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR29 Registers
- 14.9.1.110 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR30 Registers
- 14.9.1.111 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCR31 Registers
- 14.9.1.112 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.113 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.114 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.115 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.116 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.117 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.118 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.119 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.120 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN8 Registers
- 14.9.1.121 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN9 Registers
- 14.9.1.122 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN10 Registers
- 14.9.1.123 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN11 Registers
- 14.9.1.124 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN12 Registers
- 14.9.1.125 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN13 Registers
- 14.9.1.126 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN14 Registers
- 14.9.1.127 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN15 Registers
- 14.9.1.128 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN16 Registers
- 14.9.1.129 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN17 Registers
- 14.9.1.130 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN18 Registers
- 14.9.1.131 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN19 Registers
- 14.9.1.132 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN20 Registers
- 14.9.1.133 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN21 Registers
- 14.9.1.134 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN22 Registers
- 14.9.1.135 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN23 Registers
- 14.9.1.136 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN24 Registers
- 14.9.1.137 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN25 Registers
- 14.9.1.138 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN26 Registers
- 14.9.1.139 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN27 Registers
- 14.9.1.140 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN28 Registers
- 14.9.1.141 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN29 Registers
- 14.9.1.142 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN30 Registers
- 14.9.1.143 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN31 Registers
- 14.9.1.144 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT0 Registers
- 14.9.1.145 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT1 Registers
- 14.9.1.146 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT2 Registers
- 14.9.1.147 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT3 Registers
- 14.9.1.148 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT4 Registers
- 14.9.1.149 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT5 Registers
- 14.9.1.150 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT6 Registers
- 14.9.1.151 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT7 Registers
- 14.9.1.152 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT8 Registers
- 14.9.1.153 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT9 Registers
- 14.9.1.154 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT10 Registers
- 14.9.1.155 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT11 Registers
- 14.9.1.156 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT12 Registers
- 14.9.1.157 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT13 Registers
- 14.9.1.158 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT14 Registers
- 14.9.1.159 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT15 Registers
- 14.9.1.160 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT16 Registers
- 14.9.1.161 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT17 Registers
- 14.9.1.162 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT18 Registers
- 14.9.1.163 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT19 Registers
- 14.9.1.164 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT20 Registers
- 14.9.1.165 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT21 Registers
- 14.9.1.166 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT22 Registers
- 14.9.1.167 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT23 Registers
- 14.9.1.168 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT24 Registers
- 14.9.1.169 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT25 Registers
- 14.9.1.170 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT26 Registers
- 14.9.1.171 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT27 Registers
- 14.9.1.172 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT28 Registers
- 14.9.1.173 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT29 Registers
- 14.9.1.174 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT30 Registers
- 14.9.1.175 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT31 Registers
- 14.9.1.176 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR0 Registers
- 14.9.1.177 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR1 Registers
- 14.9.1.178 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR2 Registers
- 14.9.1.179 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR3 Registers
- 14.9.1.180 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR4 Registers
- 14.9.1.181 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR5 Registers
- 14.9.1.182 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR6 Registers
- 14.9.1.183 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR7 Registers
- 14.9.1.184 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR8 Registers
- 14.9.1.185 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR9 Registers
- 14.9.1.186 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR10 Registers
- 14.9.1.187 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR11 Registers
- 14.9.1.188 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR12 Registers
- 14.9.1.189 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR13 Registers
- 14.9.1.190 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR14 Registers
- 14.9.1.191 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR15 Registers
- 14.9.1.192 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR16 Registers
- 14.9.1.193 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR17 Registers
- 14.9.1.194 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR18 Registers
- 14.9.1.195 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR19 Registers
- 14.9.1.196 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR20 Registers
- 14.9.1.197 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR21 Registers
- 14.9.1.198 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR22 Registers
- 14.9.1.199 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR23 Registers
- 14.9.1.200 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR24 Registers
- 14.9.1.201 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR25 Registers
- 14.9.1.202 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR26 Registers
- 14.9.1.203 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR27 Registers
- 14.9.1.204 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR28 Registers
- 14.9.1.205 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR29 Registers
- 14.9.1.206 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR30 Registers
- 14.9.1.207 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR31 Registers
- 14.9.1.208 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CT_EOI Registers
- 14.9.1.209 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQSTAT_RAW Registers
- 14.9.1.210 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQSTAT Registers
- 14.9.1.211 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.9.1.212 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.9.1.213 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_STPTCR Registers
- 14.9.1.214 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_STPTID Registers
- 14.9.1.215 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_STPASYNC Registers
- 14.9.1.216 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_STPFFCR Registers
- 14.9.1.217 CTSET2_WRAP_CFG_CTSET2_CFG_STPFEAT1 Registers
- 14.9.1.218 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_IDFILTER0 Registers
- 14.9.1.219 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_IDFILTER1 Registers
- 14.9.1.220 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_ITATBCTR1 Registers
- 14.9.1.221 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_ITATBCTR0 Registers
- 14.9.1.222 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.223 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.224 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.225 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.226 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.227 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.228 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.229 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.230 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_PIDR4 Registers
- 14.9.1.231 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_PIDR0 Registers
- 14.9.1.232 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_PIDR1 Registers
- 14.9.1.233 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_PIDR2 Registers
- 14.9.1.234 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_PIDR3 Registers
- 14.9.1.235 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_CIDR0 Registers
- 14.9.1.236 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_CIDR1 Registers
- 14.9.1.237 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_CIDR2 Registers
- 14.9.1.238 ATB_REPLICATOR_CFG_CXATBREPLICATOR_CFG_CIDR3 Registers
- 14.9.1.239 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_CT_TBR_RAMSZ Registers
- 14.9.1.240 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_FIFOSZ Registers
- 14.9.1.241 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_STAT Registers
- 14.9.1.242 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_RAMRDAT Registers
- 14.9.1.243 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_RAMRPTR Registers
- 14.9.1.244 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_RAMWPTR Registers
- 14.9.1.245 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_TRGCNT Registers
- 14.9.1.246 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_TBR_CTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.247 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_RAMWDAT Registers
- 14.9.1.248 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_OUTLVL Registers
- 14.9.1.249 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_SICTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.250 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_IDPERIOD Registers
- 14.9.1.251 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_CT_TBR_SEQCNTL Registers
- 14.9.1.252 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_EOI Registers
- 14.9.1.253 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_IRQSTATUS_RAW Registers
- 14.9.1.254 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_IRQSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.255 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_IRQENABLE_SET Registers
- 14.9.1.256 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_IRQENABLE_CLR Registers
- 14.9.1.257 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_OPSTAT Registers
- 14.9.1.258 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_OPCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.259 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.260 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.261 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_LOCKACC Registers
- 14.9.1.262 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_LOCKSTAT Registers
- 14.9.1.263 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_AUTHSTAT Registers
- 14.9.1.264 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.265 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.266 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.267 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_PERIPHID5 Registers
- 14.9.1.268 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_PERIPHID6 Registers
- 14.9.1.269 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_PERIPHID7 Registers
- 14.9.1.270 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.271 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.272 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.273 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.274 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.275 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.276 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.277 TBR_VBUSP_WRAP_TBR_CFG_TBR_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.278 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.1.279 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.280 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.1.281 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.1.282 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.1.283 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.284 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.285 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.286 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.287 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.288 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.289 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.290 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.291 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.292 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.293 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.294 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.295 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.296 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.297 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.298 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.299 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.300 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.301 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.302 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.303 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.1.304 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.305 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.306 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.307 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.308 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.309 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.310 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.311 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.1.312 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.1.313 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.314 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.315 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.316 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.317 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.318 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.319 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.320 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.321 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.322 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.323 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.324 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.325 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.326 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.327 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.328 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.329 ARM_CTI_0_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.330 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.1.331 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.332 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.1.333 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.1.334 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.1.335 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.336 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.337 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.338 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.339 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.340 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.341 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.342 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.343 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.344 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.345 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.346 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.347 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.348 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.349 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.350 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.351 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.352 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.353 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.354 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.355 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.1.356 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.357 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.358 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.359 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.360 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.361 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.362 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.363 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.1.364 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.1.365 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.366 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.367 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.368 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.369 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.370 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.371 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.372 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.373 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.374 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.375 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.376 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.377 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.378 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.379 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.380 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.381 ARM_CTI_1_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.382 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.1.383 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.384 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.1.385 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.1.386 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.1.387 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.388 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.389 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.390 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.391 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.392 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.393 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.394 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.395 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.396 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.397 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.398 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.399 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.400 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.401 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.402 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.403 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.404 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.405 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.406 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.407 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.1.408 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.409 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.410 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.411 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.412 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.413 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.414 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.415 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.1.416 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.1.417 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.418 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.419 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.420 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.421 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.422 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.423 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.424 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.425 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.426 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.427 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.428 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.429 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.430 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.431 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.432 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.433 ARM_CTI_2_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.434 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.1.435 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.436 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.1.437 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.1.438 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.1.439 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.440 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.441 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.442 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.443 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.444 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.445 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.446 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.447 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.448 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.449 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.450 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.451 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.452 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.453 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.454 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.455 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.456 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.457 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.458 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.459 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.1.460 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.461 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.462 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.463 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.464 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.465 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.466 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.467 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.1.468 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.1.469 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.470 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.471 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.472 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.473 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.474 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.475 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.476 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.477 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.478 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.479 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.480 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.481 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.482 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.483 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.484 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.485 ARM_CTI_3_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.486 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.1.487 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.488 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.1.489 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.1.490 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.1.491 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.492 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.493 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.494 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.495 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.496 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.497 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.498 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.499 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.500 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.501 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.502 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.503 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.504 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.505 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.506 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.507 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.508 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.509 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.510 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.511 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.1.512 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.513 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.514 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.515 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.516 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.517 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.518 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.519 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.1.520 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.1.521 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.522 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.523 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.524 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.525 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.526 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.527 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.528 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.529 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.530 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.531 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.532 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.533 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.534 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.535 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.536 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.537 ARM_CTI_4_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.538 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.1.539 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.540 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.1.541 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.1.542 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.1.543 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.544 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.545 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.546 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.547 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.548 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.549 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.550 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.551 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.552 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.553 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.554 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.555 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.556 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.557 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.558 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.559 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.560 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.561 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.562 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.563 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.1.564 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.565 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.566 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.567 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.568 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.569 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.570 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.571 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.1.572 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.1.573 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.574 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.575 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.576 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.577 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.578 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.579 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.580 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.581 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.582 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.583 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.584 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.585 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.586 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.587 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.588 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.589 ARM_CTI_5_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.590 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.1.591 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.592 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.1.593 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.1.594 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.1.595 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.596 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.597 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.598 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.599 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.600 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.601 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.602 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.603 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.604 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.605 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.606 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.607 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.608 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.609 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.610 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.611 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.612 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.613 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.614 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.615 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.1.616 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.617 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.618 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.619 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.620 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.621 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.622 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.623 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.1.624 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.1.625 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.626 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.627 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.628 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.629 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.630 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.631 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.632 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.633 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.634 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.635 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.636 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.637 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.638 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.639 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.640 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.641 ARM_CTI_6_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.642 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.1.643 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.644 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.1.645 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.1.646 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.1.647 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.648 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.649 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.650 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.651 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.652 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.653 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.654 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.655 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.656 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.657 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.658 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.659 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.660 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.661 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.662 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.663 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.664 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.665 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.666 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.667 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.1.668 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.669 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.670 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.671 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.672 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.673 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.674 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.675 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.1.676 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.1.677 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.678 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.679 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.680 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.681 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.682 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.683 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.684 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.685 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.686 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.687 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.688 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.689 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.690 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.691 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.692 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.693 ARM_CTI_7_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.694 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.1.695 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.696 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.1.697 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.1.698 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.1.699 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.700 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.701 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.702 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.703 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.704 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.705 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.706 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.707 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.1.708 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.1.709 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.1.710 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.1.711 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.1.712 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.1.713 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.1.714 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.1.715 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.716 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.717 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.718 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.719 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.1.720 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.1.721 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.722 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.1.723 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.724 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.1.725 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.726 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.1.727 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.1.728 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.1.729 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.1.730 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMSET Registers
- 14.9.1.731 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_CLAIMCLR Registers
- 14.9.1.732 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LAR Registers
- 14.9.1.733 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_LSR Registers
- 14.9.1.734 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_AUTHSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.1.735 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.1.736 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_DEVTYPE Registers
- 14.9.1.737 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.1.738 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.739 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.740 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.741 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.742 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.1.743 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.1.744 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.1.745 ARM_CTI_8_CFG_CSCTI_CFG_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.1.746 Access Table
- 14.9.2
DEBUGSS_WRAP Registers
- 14.9.2.1 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_ENTRY0 Registers
- 14.9.2.2 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_ENTRY1 Registers
- 14.9.2.3 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_ENTRY2 Registers
- 14.9.2.4 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY0 Registers
- 14.9.2.5 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY1 Registers
- 14.9.2.6 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY2 Registers
- 14.9.2.7 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY3 Registers
- 14.9.2.8 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY4 Registers
- 14.9.2.9 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY5 Registers
- 14.9.2.10 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY6 Registers
- 14.9.2.11 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY7 Registers
- 14.9.2.12 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY8 Registers
- 14.9.2.13 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY9 Registers
- 14.9.2.14 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY10 Registers
- 14.9.2.15 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY11 Registers
- 14.9.2.16 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY12 Registers
- 14.9.2.17 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY13 Registers
- 14.9.2.18 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY14 Registers
- 14.9.2.19 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY15 Registers
- 14.9.2.20 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY16 Registers
- 14.9.2.21 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY17 Registers
- 14.9.2.22 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY18 Registers
- 14.9.2.23 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY19 Registers
- 14.9.2.24 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY20 Registers
- 14.9.2.25 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY21 Registers
- 14.9.2.26 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY22 Registers
- 14.9.2.27 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY23 Registers
- 14.9.2.28 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY24 Registers
- 14.9.2.29 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY25 Registers
- 14.9.2.30 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY26 Registers
- 14.9.2.31 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY27 Registers
- 14.9.2.32 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY28 Registers
- 14.9.2.33 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY29 Registers
- 14.9.2.34 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY30 Registers
- 14.9.2.35 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY31 Registers
- 14.9.2.36 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY32 Registers
- 14.9.2.37 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY33 Registers
- 14.9.2.38 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY34 Registers
- 14.9.2.39 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY35 Registers
- 14.9.2.40 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY36 Registers
- 14.9.2.41 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY37 Registers
- 14.9.2.42 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY38 Registers
- 14.9.2.43 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY39 Registers
- 14.9.2.44 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY40 Registers
- 14.9.2.45 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY41 Registers
- 14.9.2.46 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY42 Registers
- 14.9.2.47 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY43 Registers
- 14.9.2.48 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY44 Registers
- 14.9.2.49 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY45 Registers
- 14.9.2.50 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY46 Registers
- 14.9.2.51 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY47 Registers
- 14.9.2.52 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY48 Registers
- 14.9.2.53 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY49 Registers
- 14.9.2.54 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY50 Registers
- 14.9.2.55 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY51 Registers
- 14.9.2.56 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY52 Registers
- 14.9.2.57 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY53 Registers
- 14.9.2.58 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY54 Registers
- 14.9.2.59 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY55 Registers
- 14.9.2.60 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY56 Registers
- 14.9.2.61 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY57 Registers
- 14.9.2.62 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY58 Registers
- 14.9.2.63 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY59 Registers
- 14.9.2.64 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY60 Registers
- 14.9.2.65 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY61 Registers
- 14.9.2.66 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY62 Registers
- 14.9.2.67 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY63 Registers
- 14.9.2.68 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.69 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.70 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.71 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.72 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.2.73 ROM_TABLE_0_0_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.74 ROM_TABLE_0_0_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.75 ROM_TABLE_0_0_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.76 ROM_TABLE_0_0_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.77 CFGAP0_JTAGID_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.78 CFGAP0_USERID_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.79 CFGAP0_VERSION_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.80 CFGAP0_SYSTEMSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.81 CFGAP0_APID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.82 APBAP0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.83 APBAP0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.84 APBAP0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.85 APBAP0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.86 APBAP0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.87 APBAP0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.88 APBAP0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.89 APBAP0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.90 APBAP0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.91 AXIAP0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.92 AXIAP0_TAREGL Registers
- 14.9.2.93 AXIAP0_TAREGH Registers
- 14.9.2.94 AXIAP0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.95 AXIAP0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.96 AXIAP0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.97 AXIAP0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.98 AXIAP0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.99 AXIAP0_MBT_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.100 AXIAP0_ROM_HI_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.101 AXIAP0_CFG_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.102 AXIAP0_ROM_LO_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.103 AXIAP0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.104 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG0 Registers
- 14.9.2.105 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG1 Registers
- 14.9.2.106 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG2 Registers
- 14.9.2.107 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG3 Registers
- 14.9.2.108 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG4 Registers
- 14.9.2.109 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG5 Registers
- 14.9.2.110 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG6 Registers
- 14.9.2.111 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG7 Registers
- 14.9.2.112 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG8 Registers
- 14.9.2.113 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG9 Registers
- 14.9.2.114 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG10 Registers
- 14.9.2.115 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG11 Registers
- 14.9.2.116 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG12 Registers
- 14.9.2.117 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG13 Registers
- 14.9.2.118 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG14 Registers
- 14.9.2.119 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG15 Registers
- 14.9.2.120 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG16 Registers
- 14.9.2.121 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG17 Registers
- 14.9.2.122 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG18 Registers
- 14.9.2.123 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG19 Registers
- 14.9.2.124 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG20 Registers
- 14.9.2.125 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG21 Registers
- 14.9.2.126 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG22 Registers
- 14.9.2.127 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG23 Registers
- 14.9.2.128 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG24 Registers
- 14.9.2.129 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG25 Registers
- 14.9.2.130 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG26 Registers
- 14.9.2.131 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG27 Registers
- 14.9.2.132 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG28 Registers
- 14.9.2.133 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG29 Registers
- 14.9.2.134 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG30 Registers
- 14.9.2.135 PWRAP0_CORE_PRECREG31 Registers
- 14.9.2.136 PWRAP0_SYS_PRECREG Registers
- 14.9.2.137 PWRAP0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.138 PVIEW0_PVIEW_STATE0 Registers
- 14.9.2.139 PVIEW0_PVIEW_CAPABILITY Registers
- 14.9.2.140 PVIEW0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.141 JTAGAP0_CSW Registers
- 14.9.2.142 JTAGAP0_PSEL_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.143 JTAGAP0_PSTA_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.144 JTAGAP0_BYTEFIFO1 Registers
- 14.9.2.145 JTAGAP0_BYTEFIFO2 Registers
- 14.9.2.146 JTAGAP0_BYTEFIFO3 Registers
- 14.9.2.147 JTAGAP0_BYTEFIFO4 Registers
- 14.9.2.148 JTAGAP0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.149 SECAP0_TXDATA Registers
- 14.9.2.150 SECAP0_TXCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.151 SECAP0_RXDATA Registers
- 14.9.2.152 SECAP0_RXCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.153 CORTEX0_CFG0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.154 CORTEX0_CFG0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.155 CORTEX0_CFG0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.156 CORTEX0_CFG0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.157 CORTEX0_CFG0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.158 CORTEX0_CFG0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.159 CORTEX0_CFG0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.160 CORTEX0_CFG0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.161 CORTEX0_CFG0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.162 CORTEX1_CFG0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.163 CORTEX1_CFG0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.164 CORTEX1_CFG0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.165 CORTEX1_CFG0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.166 CORTEX1_CFG0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.167 CORTEX1_CFG0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.168 CORTEX1_CFG0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.169 CORTEX1_CFG0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.170 CORTEX1_CFG0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.171 CORTEX2_CFG0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.172 CORTEX2_CFG0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.173 CORTEX2_CFG0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.174 CORTEX2_CFG0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.175 CORTEX2_CFG0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.176 CORTEX2_CFG0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.177 CORTEX2_CFG0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.178 CORTEX2_CFG0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.179 CORTEX2_CFG0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.180 CORTEX3_CFG0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.181 CORTEX3_CFG0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.182 CORTEX3_CFG0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.183 CORTEX3_CFG0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.184 CORTEX3_CFG0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.185 CORTEX3_CFG0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.186 CORTEX3_CFG0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.187 CORTEX3_CFG0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.188 CORTEX3_CFG0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.189 CORTEX4_CFG0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.190 CORTEX4_CFG0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.191 CORTEX4_CFG0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.192 CORTEX4_CFG0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.193 CORTEX4_CFG0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.194 CORTEX4_CFG0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.195 CORTEX4_CFG0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.196 CORTEX4_CFG0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.197 CORTEX4_CFG0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.198 CORTEX5_CFG0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.199 CORTEX5_CFG0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.200 CORTEX5_CFG0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.201 CORTEX5_CFG0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.202 CORTEX5_CFG0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.203 CORTEX5_CFG0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.204 CORTEX5_CFG0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.205 CORTEX5_CFG0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.206 CORTEX5_CFG0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.207 CORTEX6_CFG0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.208 CORTEX6_CFG0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.209 CORTEX6_CFG0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.210 CORTEX6_CFG0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.211 CORTEX6_CFG0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.212 CORTEX6_CFG0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.213 CORTEX6_CFG0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.214 CORTEX6_CFG0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.215 CORTEX6_CFG0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.216 CORTEX7_CFG0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.217 CORTEX7_CFG0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.218 CORTEX7_CFG0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.219 CORTEX7_CFG0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.220 CORTEX7_CFG0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.221 CORTEX7_CFG0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.222 CORTEX7_CFG0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.223 CORTEX7_CFG0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.224 CORTEX7_CFG0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.225 CORTEX8_CFG0_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.226 CORTEX8_CFG0_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.227 CORTEX8_CFG0_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.228 CORTEX8_CFG0_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.229 CORTEX8_CFG0_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.230 CORTEX8_CFG0_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.231 CORTEX8_CFG0_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.232 CORTEX8_CFG0_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.233 CORTEX8_CFG0_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.234 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY0 Registers
- 14.9.2.235 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY1 Registers
- 14.9.2.236 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY2 Registers
- 14.9.2.237 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY3 Registers
- 14.9.2.238 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY4 Registers
- 14.9.2.239 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY5 Registers
- 14.9.2.240 ROM_TABLE_1_0_COMPUTE_CLUSTER0 Registers
- 14.9.2.241 ROM_TABLE_1_0_COMPUTE_CLUSTER1 Registers
- 14.9.2.242 ROM_TABLE_1_0_COMPUTE_CLUSTER2 Registers
- 14.9.2.243 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL0 Registers
- 14.9.2.244 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL1 Registers
- 14.9.2.245 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL2 Registers
- 14.9.2.246 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL3 Registers
- 14.9.2.247 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL4 Registers
- 14.9.2.248 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL5 Registers
- 14.9.2.249 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL6 Registers
- 14.9.2.250 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL7 Registers
- 14.9.2.251 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL8 Registers
- 14.9.2.252 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL9 Registers
- 14.9.2.253 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL10 Registers
- 14.9.2.254 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL11 Registers
- 14.9.2.255 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP0 Registers
- 14.9.2.256 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP1 Registers
- 14.9.2.257 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP2 Registers
- 14.9.2.258 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP3 Registers
- 14.9.2.259 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP4 Registers
- 14.9.2.260 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP5 Registers
- 14.9.2.261 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP6 Registers
- 14.9.2.262 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP7 Registers
- 14.9.2.263 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP8 Registers
- 14.9.2.264 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP9 Registers
- 14.9.2.265 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP10 Registers
- 14.9.2.266 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP11 Registers
- 14.9.2.267 CSCTI0_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.2.268 CSCTI0_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.2.269 CSCTI0_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.2.270 CSCTI0_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.2.271 CSCTI0_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.2.272 CSCTI0_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.2.273 CSCTI0_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.2.274 CSCTI0_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.2.275 CSCTI0_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.2.276 CSCTI0_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.2.277 CSCTI0_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.2.278 CSCTI0_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.2.279 CSCTI0_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.2.280 CSCTI0_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.2.281 CSCTI0_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.2.282 CSCTI0_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.2.283 CSCTI0_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.2.284 CSCTI0_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.2.285 CSCTI0_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.2.286 CSCTI0_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.2.287 CSCTI0_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.2.288 CSCTI0_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.289 CSCTI0_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.290 CSCTI0_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.291 CSCTI0_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.292 CSCTI0_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.2.293 CSCTI0_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.2.294 CSCTI0_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.2.295 CSCTI0_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.2.296 CSCTI0_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.2.297 CSCTI0_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.2.298 CSCTI0_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.2.299 CSCTI0_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.2.300 CSCTI0_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.2.301 CSCTI0_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.2.302 CSCTI0_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.303 CSCTI0_CTSET Registers
- 14.9.2.304 CSCTI0_CTCLR Registers
- 14.9.2.305 CSCTI0_LAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.306 CSCTI0_LSREG Registers
- 14.9.2.307 CSCTI0_AUTHST Registers
- 14.9.2.308 CSCTI0_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.2.309 CSCTI0_DEVTYPEID Registers
- 14.9.2.310 CSCTI0_PERID4 Registers
- 14.9.2.311 CSCTI0_PERID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.312 CSCTI0_PERID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.313 CSCTI0_PERID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.314 CSCTI0_PERID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.315 CSCTI0_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.316 CSCTI0_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.317 CSCTI0_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.318 CSCTI0_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.319 DRM0_PERIPH_ID Registers
- 14.9.2.320 DRM0_VERSION Registers
- 14.9.2.321 DRM0_CAPABILITY Registers
- 14.9.2.322 DRM0_TRACE_CTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.323 DRM0_VBUSM_CTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.324 DRM0_DAP_TIMEOUT Registers
- 14.9.2.325 DRM0_CONFIG Registers
- 14.9.2.326 DRM0_EMUTRIGEN Registers
- 14.9.2.327 DRM0_BINVALLO Registers
- 14.9.2.328 DRM0_BINVALHI Registers
- 14.9.2.329 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG0 Registers
- 14.9.2.330 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG1 Registers
- 14.9.2.331 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG2 Registers
- 14.9.2.332 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG3 Registers
- 14.9.2.333 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG4 Registers
- 14.9.2.334 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG5 Registers
- 14.9.2.335 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG6 Registers
- 14.9.2.336 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG7 Registers
- 14.9.2.337 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG8 Registers
- 14.9.2.338 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG9 Registers
- 14.9.2.339 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG10 Registers
- 14.9.2.340 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG11 Registers
- 14.9.2.341 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG12 Registers
- 14.9.2.342 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG13 Registers
- 14.9.2.343 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG14 Registers
- 14.9.2.344 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG15 Registers
- 14.9.2.345 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG16 Registers
- 14.9.2.346 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG17 Registers
- 14.9.2.347 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG18 Registers
- 14.9.2.348 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG19 Registers
- 14.9.2.349 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG20 Registers
- 14.9.2.350 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG21 Registers
- 14.9.2.351 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG22 Registers
- 14.9.2.352 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG23 Registers
- 14.9.2.353 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG24 Registers
- 14.9.2.354 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG25 Registers
- 14.9.2.355 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG26 Registers
- 14.9.2.356 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG27 Registers
- 14.9.2.357 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG28 Registers
- 14.9.2.358 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG29 Registers
- 14.9.2.359 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG30 Registers
- 14.9.2.360 DRM0_SUSPEND_REG31 Registers
- 14.9.2.361 CSTPIU0_SUPPORTSIZE Registers
- 14.9.2.362 CSTPIU0_CURPORTSIZE Registers
- 14.9.2.363 CSTPIU0_TRIGMODEREG Registers
- 14.9.2.364 CSTPIU0_TRIGCTRREG Registers
- 14.9.2.365 CSTPIU0_TRIGMPYREG Registers
- 14.9.2.366 CSTPIU0_SUPTESTPAT Registers
- 14.9.2.367 CSTPIU0_CURTESTPAT Registers
- 14.9.2.368 CSTPIU0_TESTPATCNT Registers
- 14.9.2.369 CSTPIU0_FORMFLUSHSTAT Registers
- 14.9.2.370 CSTPIU0_FORMFLUSHCTL Registers
- 14.9.2.371 CSTPIU0_FORMSYNCCTR Registers
- 14.9.2.372 CSTPIU0_EXTCTLIN Registers
- 14.9.2.373 CSTPIU0_EXTCTLOUT Registers
- 14.9.2.374 CSTPIU0_ITTRFLINACK Registers
- 14.9.2.375 CSTPIU0_ITTRFLIN Registers
- 14.9.2.376 CSTPIU0_ITATBDATA0 Registers
- 14.9.2.377 CSTPIU0_ITATBCTR2 Registers
- 14.9.2.378 CSTPIU0_ITATBCTR1 Registers
- 14.9.2.379 CSTPIU0_ITATBCTR0 Registers
- 14.9.2.380 CSTPIU0_INTCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.381 CSTPIU0_CTSET Registers
- 14.9.2.382 CSTPIU0_CTCLR Registers
- 14.9.2.383 CSTPIU0_LAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.384 CSTPIU0_LSREG Registers
- 14.9.2.385 CSTPIU0_AUTHST Registers
- 14.9.2.386 CSTPIU0_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.2.387 CSTPIU0_DEVTYPEID Registers
- 14.9.2.388 CSTPIU0_PERID4 Registers
- 14.9.2.389 CSTPIU0_PERID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.390 CSTPIU0_PERID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.391 CSTPIU0_PERID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.392 CSTPIU0_PERID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.393 CSTPIU0_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.394 CSTPIU0_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.395 CSTPIU0_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.396 CSTPIU0_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.397 CTF0_CSTFCTLREG Registers
- 14.9.2.398 CTF0_PRIORCTLREG Registers
- 14.9.2.399 CTF0_ITATBDATA0 Registers
- 14.9.2.400 CTF0_ITATBCTR2 Registers
- 14.9.2.401 CTF0_ITATBCTR1 Registers
- 14.9.2.402 CTF0_ITATBCTR0 Registers
- 14.9.2.403 CTF0_INTCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.404 CTF0_CTSET Registers
- 14.9.2.405 CTF0_CTCLR Registers
- 14.9.2.406 CTF0_LAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.407 CTF0_LSREG Registers
- 14.9.2.408 CTF0_AUTHST Registers
- 14.9.2.409 CTF0_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.2.410 CTF0_DEVTYPEID Registers
- 14.9.2.411 CTF0_PERID4 Registers
- 14.9.2.412 CTF0_PERID5 Registers
- 14.9.2.413 CTF0_PERID6 Registers
- 14.9.2.414 CTF0_PERID7 Registers
- 14.9.2.415 CTF0_PERID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.416 CTF0_PERID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.417 CTF0_PERID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.418 CTF0_PERID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.419 CTF0_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.420 CTF0_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.421 CTF0_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.422 CTF0_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.423 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_ENTRY0 Registers
- 14.9.2.424 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_ENTRY1 Registers
- 14.9.2.425 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_ENTRY2 Registers
- 14.9.2.426 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY0 Registers
- 14.9.2.427 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY1 Registers
- 14.9.2.428 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY2 Registers
- 14.9.2.429 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY3 Registers
- 14.9.2.430 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY4 Registers
- 14.9.2.431 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY5 Registers
- 14.9.2.432 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY6 Registers
- 14.9.2.433 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY7 Registers
- 14.9.2.434 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY8 Registers
- 14.9.2.435 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY9 Registers
- 14.9.2.436 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY10 Registers
- 14.9.2.437 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY11 Registers
- 14.9.2.438 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY12 Registers
- 14.9.2.439 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY13 Registers
- 14.9.2.440 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY14 Registers
- 14.9.2.441 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY15 Registers
- 14.9.2.442 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY16 Registers
- 14.9.2.443 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY17 Registers
- 14.9.2.444 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY18 Registers
- 14.9.2.445 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY19 Registers
- 14.9.2.446 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY20 Registers
- 14.9.2.447 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY21 Registers
- 14.9.2.448 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY22 Registers
- 14.9.2.449 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY23 Registers
- 14.9.2.450 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY24 Registers
- 14.9.2.451 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY25 Registers
- 14.9.2.452 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY26 Registers
- 14.9.2.453 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY27 Registers
- 14.9.2.454 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY28 Registers
- 14.9.2.455 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY29 Registers
- 14.9.2.456 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY30 Registers
- 14.9.2.457 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY31 Registers
- 14.9.2.458 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY32 Registers
- 14.9.2.459 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY33 Registers
- 14.9.2.460 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY34 Registers
- 14.9.2.461 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY35 Registers
- 14.9.2.462 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY36 Registers
- 14.9.2.463 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY37 Registers
- 14.9.2.464 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY38 Registers
- 14.9.2.465 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY39 Registers
- 14.9.2.466 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY40 Registers
- 14.9.2.467 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY41 Registers
- 14.9.2.468 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY42 Registers
- 14.9.2.469 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY43 Registers
- 14.9.2.470 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY44 Registers
- 14.9.2.471 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY45 Registers
- 14.9.2.472 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY46 Registers
- 14.9.2.473 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY47 Registers
- 14.9.2.474 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY48 Registers
- 14.9.2.475 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY49 Registers
- 14.9.2.476 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY50 Registers
- 14.9.2.477 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY51 Registers
- 14.9.2.478 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY52 Registers
- 14.9.2.479 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY53 Registers
- 14.9.2.480 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY54 Registers
- 14.9.2.481 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY55 Registers
- 14.9.2.482 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY56 Registers
- 14.9.2.483 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY57 Registers
- 14.9.2.484 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY58 Registers
- 14.9.2.485 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY59 Registers
- 14.9.2.486 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY60 Registers
- 14.9.2.487 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY61 Registers
- 14.9.2.488 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY62 Registers
- 14.9.2.489 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY63 Registers
- 14.9.2.490 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.491 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.492 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.493 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.494 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID4 Registers
- 14.9.2.495 ROM_TABLE_0_1_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.496 ROM_TABLE_0_1_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.497 ROM_TABLE_0_1_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.498 ROM_TABLE_0_1_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.499 CFGAP1_JTAGID_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.500 CFGAP1_USERID_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.501 CFGAP1_VERSION_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.502 CFGAP1_SYSTEMSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.503 CFGAP1_APID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.504 APBAP1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.505 APBAP1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.506 APBAP1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.507 APBAP1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.508 APBAP1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.509 APBAP1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.510 APBAP1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.511 APBAP1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.512 APBAP1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.513 AXIAP1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.514 AXIAP1_TAREGL Registers
- 14.9.2.515 AXIAP1_TAREGH Registers
- 14.9.2.516 AXIAP1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.517 AXIAP1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.518 AXIAP1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.519 AXIAP1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.520 AXIAP1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.521 AXIAP1_MBT_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.522 AXIAP1_ROM_HI_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.523 AXIAP1_CFG_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.524 AXIAP1_ROM_LO_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.525 AXIAP1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.526 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG0 Registers
- 14.9.2.527 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG1 Registers
- 14.9.2.528 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG2 Registers
- 14.9.2.529 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG3 Registers
- 14.9.2.530 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG4 Registers
- 14.9.2.531 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG5 Registers
- 14.9.2.532 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG6 Registers
- 14.9.2.533 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG7 Registers
- 14.9.2.534 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG8 Registers
- 14.9.2.535 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG9 Registers
- 14.9.2.536 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG10 Registers
- 14.9.2.537 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG11 Registers
- 14.9.2.538 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG12 Registers
- 14.9.2.539 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG13 Registers
- 14.9.2.540 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG14 Registers
- 14.9.2.541 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG15 Registers
- 14.9.2.542 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG16 Registers
- 14.9.2.543 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG17 Registers
- 14.9.2.544 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG18 Registers
- 14.9.2.545 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG19 Registers
- 14.9.2.546 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG20 Registers
- 14.9.2.547 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG21 Registers
- 14.9.2.548 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG22 Registers
- 14.9.2.549 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG23 Registers
- 14.9.2.550 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG24 Registers
- 14.9.2.551 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG25 Registers
- 14.9.2.552 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG26 Registers
- 14.9.2.553 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG27 Registers
- 14.9.2.554 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG28 Registers
- 14.9.2.555 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG29 Registers
- 14.9.2.556 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG30 Registers
- 14.9.2.557 PWRAP1_CORE_PRECREG31 Registers
- 14.9.2.558 PWRAP1_SYS_PRECREG Registers
- 14.9.2.559 PWRAP1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.560 PVIEW1_PVIEW_STATE0 Registers
- 14.9.2.561 PVIEW1_PVIEW_CAPABILITY Registers
- 14.9.2.562 PVIEW1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.563 JTAGAP1_CSW Registers
- 14.9.2.564 JTAGAP1_PSEL_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.565 JTAGAP1_PSTA_REG Registers
- 14.9.2.566 JTAGAP1_BYTEFIFO1 Registers
- 14.9.2.567 JTAGAP1_BYTEFIFO2 Registers
- 14.9.2.568 JTAGAP1_BYTEFIFO3 Registers
- 14.9.2.569 JTAGAP1_BYTEFIFO4 Registers
- 14.9.2.570 JTAGAP1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.571 SECAP1_TXDATA Registers
- 14.9.2.572 SECAP1_TXCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.573 SECAP1_RXDATA Registers
- 14.9.2.574 SECAP1_RXCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.575 CORTEX0_CFG1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.576 CORTEX0_CFG1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.577 CORTEX0_CFG1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.578 CORTEX0_CFG1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.579 CORTEX0_CFG1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.580 CORTEX0_CFG1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.581 CORTEX0_CFG1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.582 CORTEX0_CFG1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.583 CORTEX0_CFG1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.584 CORTEX1_CFG1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.585 CORTEX1_CFG1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.586 CORTEX1_CFG1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.587 CORTEX1_CFG1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.588 CORTEX1_CFG1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.589 CORTEX1_CFG1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.590 CORTEX1_CFG1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.591 CORTEX1_CFG1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.592 CORTEX1_CFG1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.593 CORTEX2_CFG1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.594 CORTEX2_CFG1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.595 CORTEX2_CFG1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.596 CORTEX2_CFG1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.597 CORTEX2_CFG1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.598 CORTEX2_CFG1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.599 CORTEX2_CFG1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.600 CORTEX2_CFG1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.601 CORTEX2_CFG1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.602 CORTEX3_CFG1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.603 CORTEX3_CFG1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.604 CORTEX3_CFG1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.605 CORTEX3_CFG1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.606 CORTEX3_CFG1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.607 CORTEX3_CFG1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.608 CORTEX3_CFG1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.609 CORTEX3_CFG1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.610 CORTEX3_CFG1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.611 CORTEX4_CFG1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.612 CORTEX4_CFG1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.613 CORTEX4_CFG1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.614 CORTEX4_CFG1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.615 CORTEX4_CFG1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.616 CORTEX4_CFG1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.617 CORTEX4_CFG1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.618 CORTEX4_CFG1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.619 CORTEX4_CFG1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.620 CORTEX5_CFG1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.621 CORTEX5_CFG1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.622 CORTEX5_CFG1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.623 CORTEX5_CFG1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.624 CORTEX5_CFG1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.625 CORTEX5_CFG1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.626 CORTEX5_CFG1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.627 CORTEX5_CFG1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.628 CORTEX5_CFG1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.629 CORTEX6_CFG1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.630 CORTEX6_CFG1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.631 CORTEX6_CFG1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.632 CORTEX6_CFG1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.633 CORTEX6_CFG1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.634 CORTEX6_CFG1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.635 CORTEX6_CFG1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.636 CORTEX6_CFG1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.637 CORTEX6_CFG1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.638 CORTEX7_CFG1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.639 CORTEX7_CFG1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.640 CORTEX7_CFG1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.641 CORTEX7_CFG1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.642 CORTEX7_CFG1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.643 CORTEX7_CFG1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.644 CORTEX7_CFG1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.645 CORTEX7_CFG1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.646 CORTEX7_CFG1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.647 CORTEX8_CFG1_CSWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.648 CORTEX8_CFG1_TAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.649 CORTEX8_CFG1_DRWREG Registers
- 14.9.2.650 CORTEX8_CFG1_BD0REG Registers
- 14.9.2.651 CORTEX8_CFG1_BD1REG Registers
- 14.9.2.652 CORTEX8_CFG1_BD2REG Registers
- 14.9.2.653 CORTEX8_CFG1_BD3REG Registers
- 14.9.2.654 CORTEX8_CFG1_ROM_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.655 CORTEX8_CFG1_ID_REGISTER Registers
- 14.9.2.656 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY0 Registers
- 14.9.2.657 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY1 Registers
- 14.9.2.658 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY2 Registers
- 14.9.2.659 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY3 Registers
- 14.9.2.660 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY4 Registers
- 14.9.2.661 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY5 Registers
- 14.9.2.662 ROM_TABLE_1_1_COMPUTE_CLUSTER0 Registers
- 14.9.2.663 ROM_TABLE_1_1_COMPUTE_CLUSTER1 Registers
- 14.9.2.664 ROM_TABLE_1_1_COMPUTE_CLUSTER2 Registers
- 14.9.2.665 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL0 Registers
- 14.9.2.666 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL1 Registers
- 14.9.2.667 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL2 Registers
- 14.9.2.668 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL3 Registers
- 14.9.2.669 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL4 Registers
- 14.9.2.670 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL5 Registers
- 14.9.2.671 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL6 Registers
- 14.9.2.672 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL7 Registers
- 14.9.2.673 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL8 Registers
- 14.9.2.674 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL9 Registers
- 14.9.2.675 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL10 Registers
- 14.9.2.676 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL11 Registers
- 14.9.2.677 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP0 Registers
- 14.9.2.678 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP1 Registers
- 14.9.2.679 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP2 Registers
- 14.9.2.680 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP3 Registers
- 14.9.2.681 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP4 Registers
- 14.9.2.682 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP5 Registers
- 14.9.2.683 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP6 Registers
- 14.9.2.684 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP7 Registers
- 14.9.2.685 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP8 Registers
- 14.9.2.686 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP9 Registers
- 14.9.2.687 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP10 Registers
- 14.9.2.688 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP11 Registers
- 14.9.2.689 CSCTI1_CTICONTROL Registers
- 14.9.2.690 CSCTI1_CTIINTACK Registers
- 14.9.2.691 CSCTI1_CTIAPPSET Registers
- 14.9.2.692 CSCTI1_CTIAPPCLEAR Registers
- 14.9.2.693 CSCTI1_CTIAPPPULSE Registers
- 14.9.2.694 CSCTI1_CTIINEN0 Registers
- 14.9.2.695 CSCTI1_CTIINEN1 Registers
- 14.9.2.696 CSCTI1_CTIINEN2 Registers
- 14.9.2.697 CSCTI1_CTIINEN3 Registers
- 14.9.2.698 CSCTI1_CTIINEN4 Registers
- 14.9.2.699 CSCTI1_CTIINEN5 Registers
- 14.9.2.700 CSCTI1_CTIINEN6 Registers
- 14.9.2.701 CSCTI1_CTIINEN7 Registers
- 14.9.2.702 CSCTI1_CTIOUTEN0 Registers
- 14.9.2.703 CSCTI1_CTIOUTEN1 Registers
- 14.9.2.704 CSCTI1_CTIOUTEN2 Registers
- 14.9.2.705 CSCTI1_CTIOUTEN3 Registers
- 14.9.2.706 CSCTI1_CTIOUTEN4 Registers
- 14.9.2.707 CSCTI1_CTIOUTEN5 Registers
- 14.9.2.708 CSCTI1_CTIOUTEN6 Registers
- 14.9.2.709 CSCTI1_CTIOUTEN7 Registers
- 14.9.2.710 CSCTI1_CTITRIGINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.711 CSCTI1_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.712 CSCTI1_CTICHINSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.713 CSCTI1_CTICHOUTSTATUS Registers
- 14.9.2.714 CSCTI1_CTIGATE Registers
- 14.9.2.715 CSCTI1_ASICCTL Registers
- 14.9.2.716 CSCTI1_ITCHINACK Registers
- 14.9.2.717 CSCTI1_ITTRIGINACK Registers
- 14.9.2.718 CSCTI1_ITCHOUT Registers
- 14.9.2.719 CSCTI1_ITTRIGOUT Registers
- 14.9.2.720 CSCTI1_ITCHOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.2.721 CSCTI1_ITTRIGOUTACK Registers
- 14.9.2.722 CSCTI1_ITCHIN Registers
- 14.9.2.723 CSCTI1_ITTRIGIN Registers
- 14.9.2.724 CSCTI1_ITCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.725 CSCTI1_CTSET Registers
- 14.9.2.726 CSCTI1_CTCLR Registers
- 14.9.2.727 CSCTI1_LAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.728 CSCTI1_LSREG Registers
- 14.9.2.729 CSCTI1_AUTHST Registers
- 14.9.2.730 CSCTI1_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.2.731 CSCTI1_DEVTYPEID Registers
- 14.9.2.732 CSCTI1_PERID4 Registers
- 14.9.2.733 CSCTI1_PERID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.734 CSCTI1_PERID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.735 CSCTI1_PERID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.736 CSCTI1_PERID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.737 CSCTI1_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.738 CSCTI1_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.739 CSCTI1_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.740 CSCTI1_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.741 DRM1_PERIPH_ID Registers
- 14.9.2.742 DRM1_VERSION Registers
- 14.9.2.743 DRM1_CAPABILITY Registers
- 14.9.2.744 DRM1_TRACE_CTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.745 DRM1_VBUSM_CTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.746 DRM1_DAP_TIMEOUT Registers
- 14.9.2.747 DRM1_CONFIG Registers
- 14.9.2.748 DRM1_EMUTRIGEN Registers
- 14.9.2.749 DRM1_BINVALLO Registers
- 14.9.2.750 DRM1_BINVALHI Registers
- 14.9.2.751 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG0 Registers
- 14.9.2.752 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG1 Registers
- 14.9.2.753 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG2 Registers
- 14.9.2.754 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG3 Registers
- 14.9.2.755 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG4 Registers
- 14.9.2.756 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG5 Registers
- 14.9.2.757 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG6 Registers
- 14.9.2.758 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG7 Registers
- 14.9.2.759 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG8 Registers
- 14.9.2.760 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG9 Registers
- 14.9.2.761 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG10 Registers
- 14.9.2.762 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG11 Registers
- 14.9.2.763 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG12 Registers
- 14.9.2.764 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG13 Registers
- 14.9.2.765 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG14 Registers
- 14.9.2.766 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG15 Registers
- 14.9.2.767 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG16 Registers
- 14.9.2.768 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG17 Registers
- 14.9.2.769 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG18 Registers
- 14.9.2.770 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG19 Registers
- 14.9.2.771 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG20 Registers
- 14.9.2.772 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG21 Registers
- 14.9.2.773 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG22 Registers
- 14.9.2.774 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG23 Registers
- 14.9.2.775 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG24 Registers
- 14.9.2.776 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG25 Registers
- 14.9.2.777 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG26 Registers
- 14.9.2.778 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG27 Registers
- 14.9.2.779 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG28 Registers
- 14.9.2.780 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG29 Registers
- 14.9.2.781 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG30 Registers
- 14.9.2.782 DRM1_SUSPEND_REG31 Registers
- 14.9.2.783 CSTPIU1_SUPPORTSIZE Registers
- 14.9.2.784 CSTPIU1_CURPORTSIZE Registers
- 14.9.2.785 CSTPIU1_TRIGMODEREG Registers
- 14.9.2.786 CSTPIU1_TRIGCTRREG Registers
- 14.9.2.787 CSTPIU1_TRIGMPYREG Registers
- 14.9.2.788 CSTPIU1_SUPTESTPAT Registers
- 14.9.2.789 CSTPIU1_CURTESTPAT Registers
- 14.9.2.790 CSTPIU1_TESTPATCNT Registers
- 14.9.2.791 CSTPIU1_FORMFLUSHSTAT Registers
- 14.9.2.792 CSTPIU1_FORMFLUSHCTL Registers
- 14.9.2.793 CSTPIU1_FORMSYNCCTR Registers
- 14.9.2.794 CSTPIU1_EXTCTLIN Registers
- 14.9.2.795 CSTPIU1_EXTCTLOUT Registers
- 14.9.2.796 CSTPIU1_ITTRFLINACK Registers
- 14.9.2.797 CSTPIU1_ITTRFLIN Registers
- 14.9.2.798 CSTPIU1_ITATBDATA0 Registers
- 14.9.2.799 CSTPIU1_ITATBCTR2 Registers
- 14.9.2.800 CSTPIU1_ITATBCTR1 Registers
- 14.9.2.801 CSTPIU1_ITATBCTR0 Registers
- 14.9.2.802 CSTPIU1_INTCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.803 CSTPIU1_CTSET Registers
- 14.9.2.804 CSTPIU1_CTCLR Registers
- 14.9.2.805 CSTPIU1_LAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.806 CSTPIU1_LSREG Registers
- 14.9.2.807 CSTPIU1_AUTHST Registers
- 14.9.2.808 CSTPIU1_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.2.809 CSTPIU1_DEVTYPEID Registers
- 14.9.2.810 CSTPIU1_PERID4 Registers
- 14.9.2.811 CSTPIU1_PERID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.812 CSTPIU1_PERID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.813 CSTPIU1_PERID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.814 CSTPIU1_PERID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.815 CSTPIU1_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.816 CSTPIU1_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.817 CSTPIU1_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.818 CSTPIU1_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.819 CTF1_CSTFCTLREG Registers
- 14.9.2.820 CTF1_PRIORCTLREG Registers
- 14.9.2.821 CTF1_ITATBDATA0 Registers
- 14.9.2.822 CTF1_ITATBCTR2 Registers
- 14.9.2.823 CTF1_ITATBCTR1 Registers
- 14.9.2.824 CTF1_ITATBCTR0 Registers
- 14.9.2.825 CTF1_INTCTRL Registers
- 14.9.2.826 CTF1_CTSET Registers
- 14.9.2.827 CTF1_CTCLR Registers
- 14.9.2.828 CTF1_LAREG Registers
- 14.9.2.829 CTF1_LSREG Registers
- 14.9.2.830 CTF1_AUTHST Registers
- 14.9.2.831 CTF1_DEVID Registers
- 14.9.2.832 CTF1_DEVTYPEID Registers
- 14.9.2.833 CTF1_PERID4 Registers
- 14.9.2.834 CTF1_PERID5 Registers
- 14.9.2.835 CTF1_PERID6 Registers
- 14.9.2.836 CTF1_PERID7 Registers
- 14.9.2.837 CTF1_PERID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.838 CTF1_PERID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.839 CTF1_PERID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.840 CTF1_PERID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.841 CTF1_COMPID0 Registers
- 14.9.2.842 CTF1_COMPID1 Registers
- 14.9.2.843 CTF1_COMPID2 Registers
- 14.9.2.844 CTF1_COMPID3 Registers
- 14.9.2.845 Access Table
- 14.9.3 DBGSUSPENDROUTER Registers
- 14.9.4
PBIST Registers
- 14.9.4.1 _PBIST_RF0L Registers
- 14.9.4.2 _PBIST_RF1L Registers
- 14.9.4.3 _PBIST_RF2L Registers
- 14.9.4.4 _PBIST_RF3L Registers
- 14.9.4.5 _PBIST_RF4L Registers
- 14.9.4.6 _PBIST_RF5L Registers
- 14.9.4.7 _PBIST_RF6L Registers
- 14.9.4.8 _PBIST_RF7L Registers
- 14.9.4.9 _PBIST_RF8L Registers
- 14.9.4.10 _PBIST_RF9L Registers
- 14.9.4.11 _PBIST_RF10L Registers
- 14.9.4.12 _PBIST_RF11L Registers
- 14.9.4.13 _PBIST_RF12L Registers
- 14.9.4.14 _PBIST_RF13L Registers
- 14.9.4.15 _PBIST_RF14L Registers
- 14.9.4.16 _PBIST_RF15L Registers
- 14.9.4.17 _PBIST_RF0U Registers
- 14.9.4.18 _PBIST_RF1U Registers
- 14.9.4.19 _PBIST_RF2U Registers
- 14.9.4.20 _PBIST_RF3U Registers
- 14.9.4.21 _PBIST_RF4U Registers
- 14.9.4.22 _PBIST_RF5U Registers
- 14.9.4.23 _PBIST_RF6U Registers
- 14.9.4.24 _PBIST_RF7U Registers
- 14.9.4.25 _PBIST_RF8U Registers
- 14.9.4.26 _PBIST_RF9U Registers
- 14.9.4.27 _PBIST_RF10U Registers
- 14.9.4.28 _PBIST_RF11U Registers
- 14.9.4.29 _PBIST_RF12U Registers
- 14.9.4.30 _PBIST_RF13U Registers
- 14.9.4.31 _PBIST_RF14U Registers
- 14.9.4.32 _PBIST_RF15U Registers
- 14.9.4.33 _PBIST_A0 Registers
- 14.9.4.34 _PBIST_A1 Registers
- 14.9.4.35 _PBIST_A2 Registers
- 14.9.4.36 _PBIST_A3 Registers
- 14.9.4.37 _PBIST_L0 Registers
- 14.9.4.38 _PBIST_L1 Registers
- 14.9.4.39 _PBIST_L2 Registers
- 14.9.4.40 _PBIST_L3 Registers
- 14.9.4.41 _PBIST_D Registers
- 14.9.4.42 _PBIST_E Registers
- 14.9.4.43 _PBIST_CA0 Registers
- 14.9.4.44 _PBIST_CA1 Registers
- 14.9.4.45 _PBIST_CA2 Registers
- 14.9.4.46 _PBIST_CA3 Registers
- 14.9.4.47 _PBIST_CL0 Registers
- 14.9.4.48 _PBIST_CL1 Registers
- 14.9.4.49 _PBIST_CL2 Registers
- 14.9.4.50 _PBIST_CL3 Registers
- 14.9.4.51 _PBIST_I0 Registers
- 14.9.4.52 _PBIST_I1 Registers
- 14.9.4.53 _PBIST_I2 Registers
- 14.9.4.54 _PBIST_I3 Registers
- 14.9.4.55 _PBIST_RAMT Registers
- 14.9.4.56 _PBIST_DLR Registers
- 14.9.4.57 _PBIST_CMS Registers
- 14.9.4.58 _PBIST_STR Registers
- 14.9.4.59 _PBIST_SCR Registers
- 14.9.4.60 _PBIST_CSR Registers
- 14.9.4.61 _PBIST_FDLY Registers
- 14.9.4.62 _PBIST_PACT Registers
- 14.9.4.63 _PBIST_PID Registers
- 14.9.4.64 _PBIST_OVER Registers
- 14.9.4.65 _PBIST_FSRF Registers
- 14.9.4.66 _PBIST_FSRC Registers
- 14.9.4.67 _PBIST_FSRA Registers
- 14.9.4.68 _PBIST_FSRDL0 Registers
- 14.9.4.69 _PBIST_FSRDL1 Registers
- 14.9.4.70 _PBIST_MARGIN_MODE Registers
- 14.9.4.71 _PBIST_WRENZ Registers
- 14.9.4.72 _PBIST_PAGE_PGS Registers
- 14.9.4.73 _PBIST_ROM Registers
- 14.9.4.74 _PBIST_ALGO Registers
- 14.9.4.75 _PBIST_RINFO Registers
- 14.9.4.76 Access Table
- 14.9.1
DEBUGSS Registers
- 14.1
System Interconnect Registers
- 15Revision History
12.1.1.4.2.2 MCASP Receive Clock
The MCASP receive clock generator is built on a very similar to the transmit clock generator (but independent) circuit.
The receive clock configuration is controlled by the following registers:
- MCASP_ACLKRCTL
- MCASP_AHCLKRCTL
In case, the receive bit clock, ACLKR, is generated internally (but asynchronously to XCLK), the MCASP_ACLKRCTL[5] CLKRM bit must be set to 1. Thus, the clock is divided down by a programmable bit clock divider (the MCASP_ACLKRCTL[4-0] CLKRDIV bit field) from the source signal.
If the receive high-frequency controller clock, AHCLKR, is also sourced internally (that is, first scenario described in Section 12.1.1.4.2) and the MCASP_AHCLKRCTL[15] HCLKRM bit must be set to 1. Thus, the clock is divided down by a programmable high-clock divider (the MCASP_AHCLKRCTL[11-0] HCLKRDIV bit field) from the MCASP internal clock source AUXCLK.
The polarity of ACLKR can be controlled in the MCASP_ACLKRCTL[7] CLKRP bit, regardless of ACLKR signal being internally or externally sourced.
In a similar way, the polarity of AHCLKR clock can be controlled in the MCASP_AHCLKRCTL[14] HCLKRP bit, regardless of the AHCLKR signal being internally or externally sourced.
There is an option for the MCASP receiver to be configured to operate synchronously to the ACLKX and AFSX signals. The XCLK output of the Tx Clock generator (see Figure 12-12 and Figure 12-13) becomes source of the receive clock (RCLK output), when the MCASP_ACLKRCTL[6] ASYNC bit in the transmit clock control register is set to '0b0'. For more information, refer to Section 12.1.1.4.2.4.
Figure 12-13 presents the block diagram of the receive clock generator.
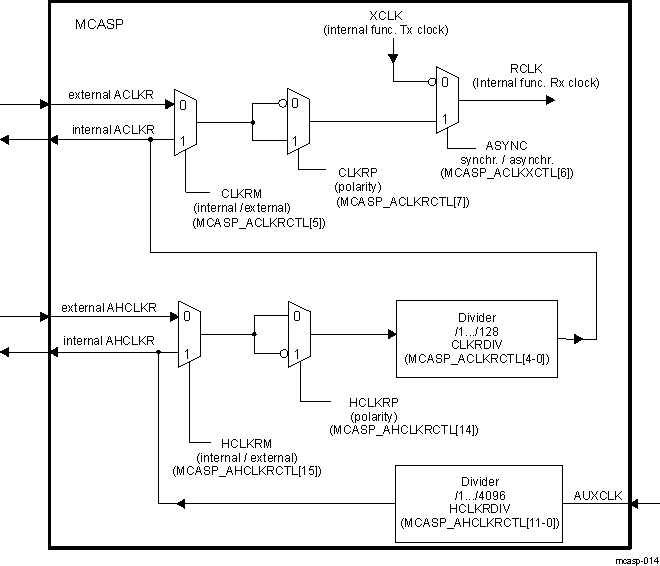 Figure 12-13 Receive
Clock Generator Block Diagram
Figure 12-13 Receive
Clock Generator Block DiagramIn this device:
- ACLKR is mapped on the device ball ACLKR
- internal AHCLKX is mapped on the device balls AUDIO_EXT_REFCLK[0-1]
- external AHCLKR is mapped on Device Configuration MCASPi_AHCLKR from Device Configuration
For more information about MCASP integration, see Section 12.1.1.2, MCASP Environment, and , Module Integration.