SPRUJG2 December 2024 AM62D-Q1
- 1
- Description
- Get Started
- Features
- 5
- 1Evaluation Module Overview
-
2Hardware
- 2.1 Additional Images
- 2.2 Key Features
- 2.3 Power Requirement
- 2.4 Setup and Configuration
- 2.5 Power ON/OFF Procedures
- 2.6 Interfaces
- 2.7 Power
- 2.8 Clocking
- 2.9 Reset
- 2.10 CPLD Mapping
- 2.11 Audio Expansion Connectors (Headers)
- 2.12 Interrupt
- 2.13 I2C Address Mapping
- 3Hardware Design Files
- 4Compliance Information
- 5Additional Information
2.8 Clocking
The Clock architecture of the AM62D Audio EVM is shown in Figure 2-21.
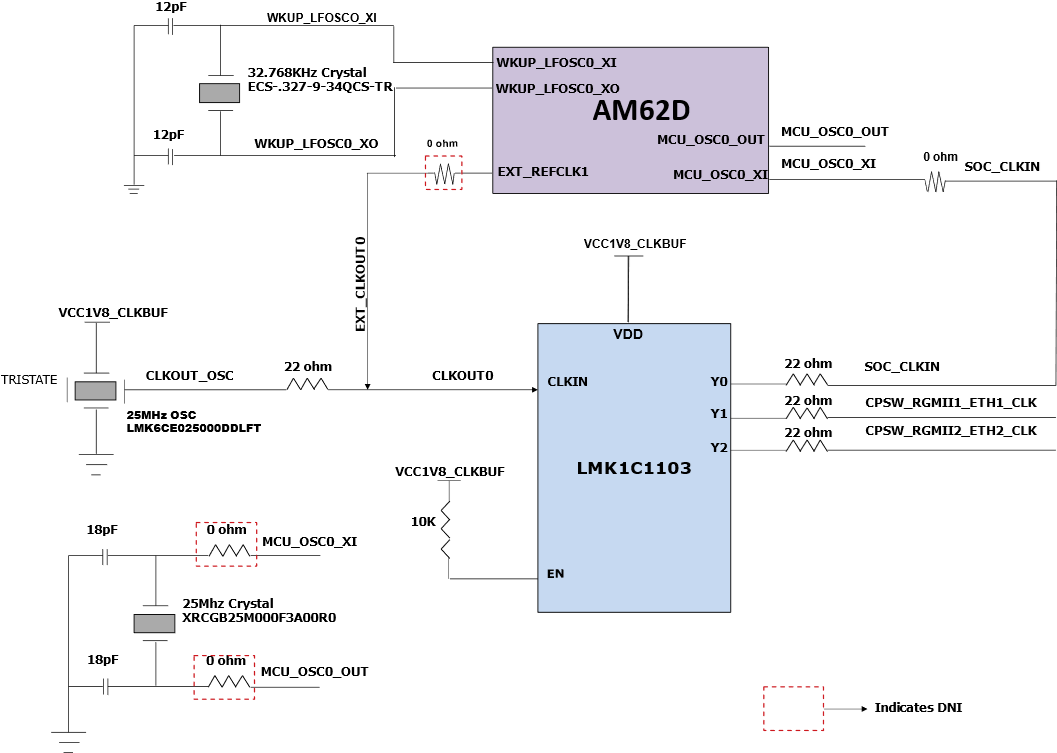 Figure 2-21 Clock Architecture
Figure 2-21 Clock ArchitectureA clock generator of part number LMK1C1103PWR is used to drive the 25MHz clock to the SoC & two Ethernet PHYs. LMK1C1103PWR is a 1:3 LVCMOS clock buffer, which takes the 25MHz crystal/LVCMOS reference input and provides four 25MHz LVCMOS clock outputs. The source for the clock buffer shall be either the CLKOUT0 pin from the SoC or a 25MHz oscillator, the selection of which is made using a set of resistors. By default, an oscillator is used as an input to the clock buffer on the AM62D Audio EVM. Output Y1 and Y2 of the clock buffer are used as reference clock inputs for the two Gigabit Ethernet PHYs.
There is one external crystal (32.768KHz) attached to the AM62D SoC to provide clock to its WKUP domain.
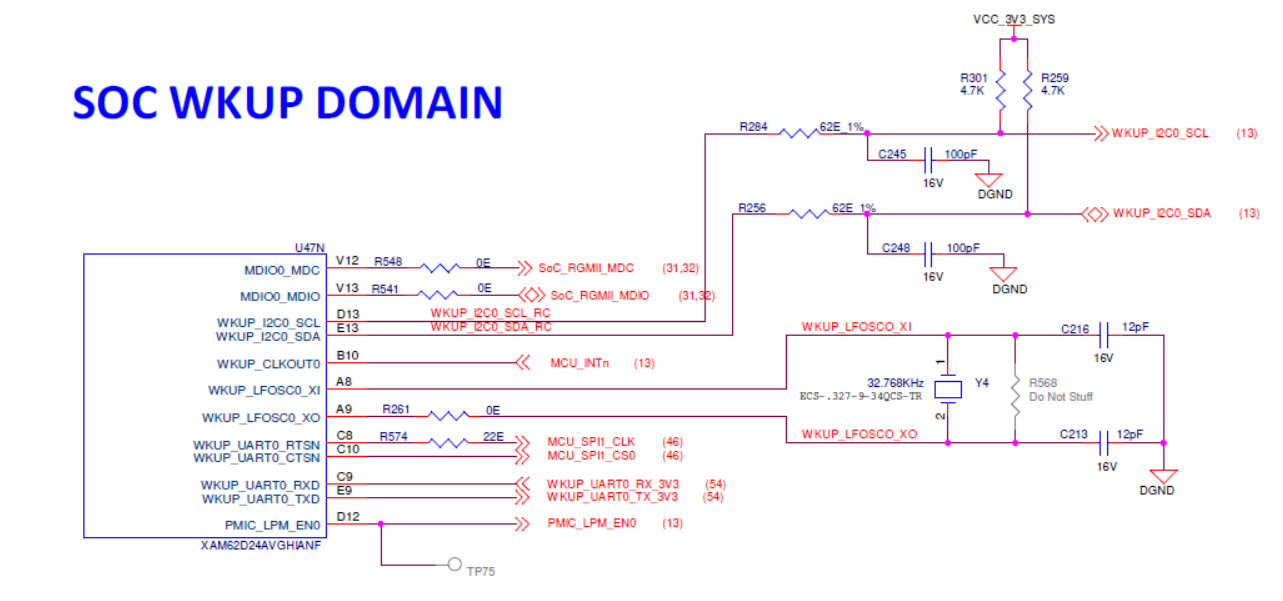 Figure 2-22 SoC WKUP Domain Clock
Figure 2-22 SoC WKUP Domain Clock