TIDT280 May 2022
3.5.1 9-V Input Voltage
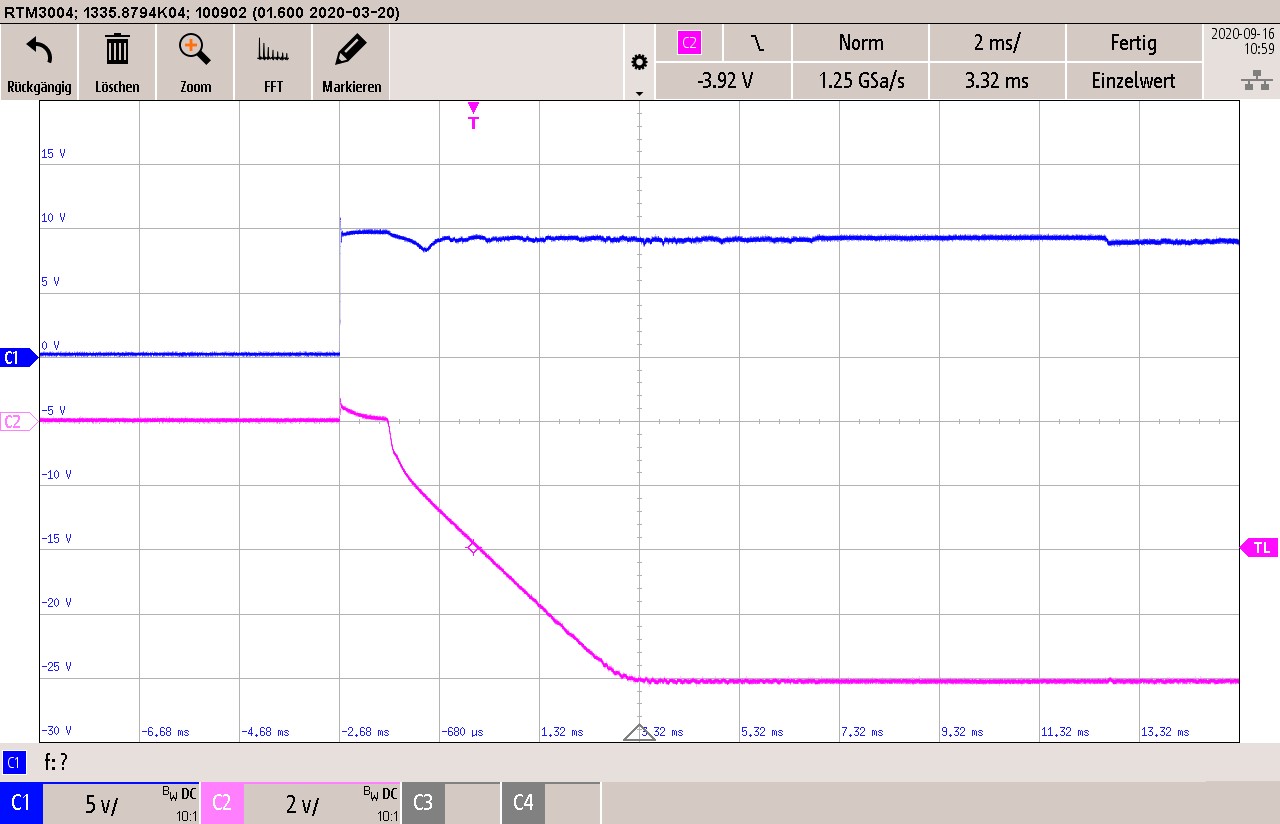
|
C1 Input Voltage C2 Output Voltage 20-MHz bandwidth |
Figure 3-13 Start-Up at 9-V Input
Voltage