TIDT280 May 2022
3.2 Output Voltage Ripple
Output voltage ripple is shown in the following figure.
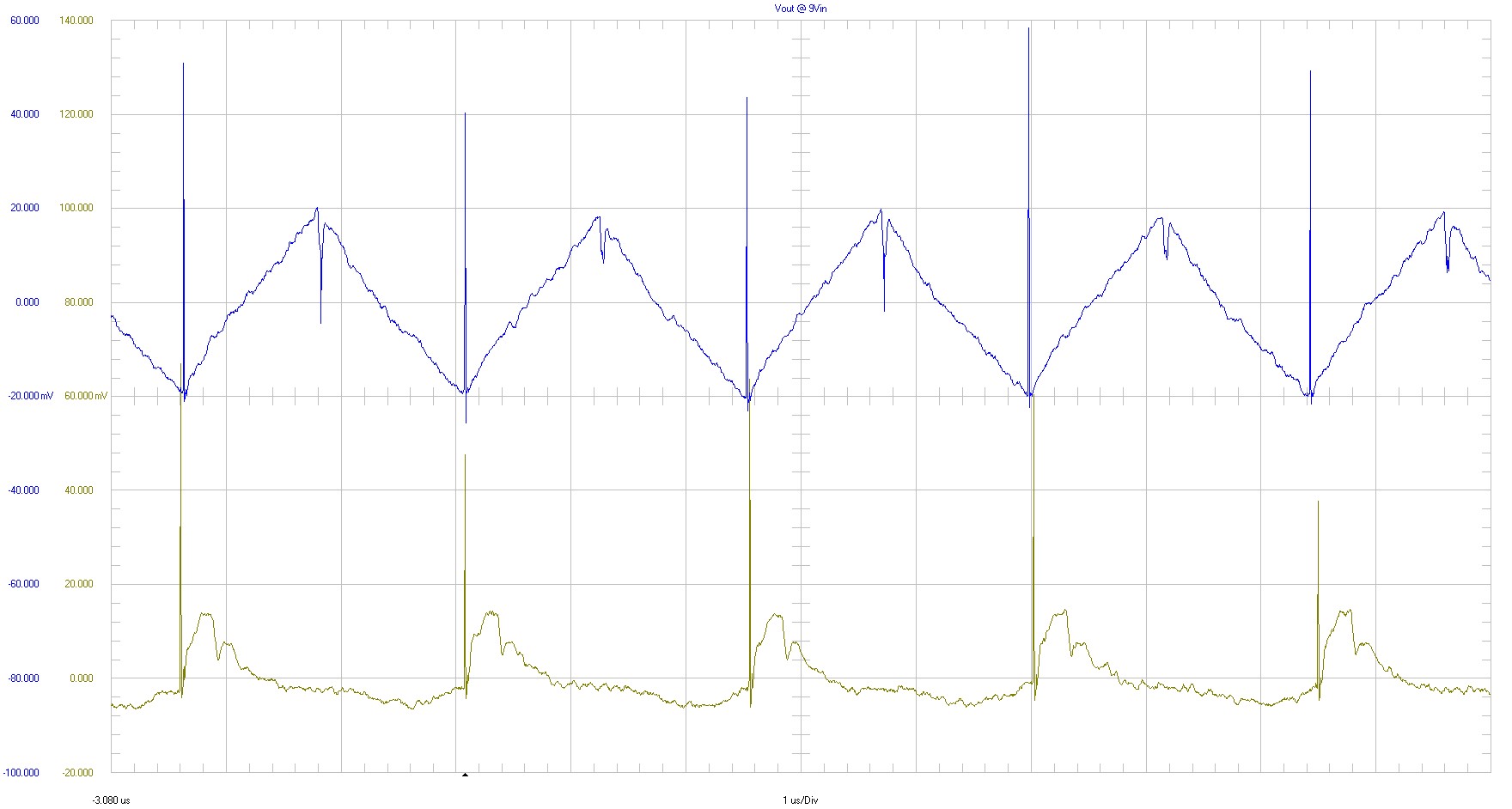
|
Ch1⇒ VOUT at 9 VIN 20 mV /div Ch2 ⇒ VOUT at 56 VIN 20 mV /div AC coupled 20-MHz bandwidth 1 µs/div |
Figure 3-9 Output Voltage Ripple