TIDT308 October 2022
3.4.3 Overload
The following screen shots (Figure 3-9 and Figure 3-10) show the output voltage during start-up and overload protection, when the converter was loaded at 3.5 A.
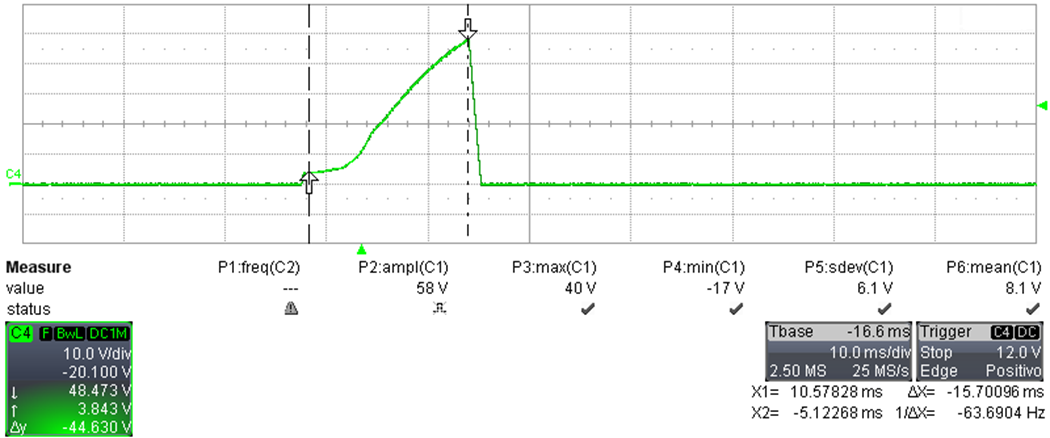 Figure 3-9 Start-Up With Overload Condition (3.5 A), Time Base: 10 ms / div
Figure 3-9 Start-Up With Overload Condition (3.5 A), Time Base: 10 ms / div- Channel C4: Output voltage (10 V /div, 10 ms / div, DC coupling, 20-MHz BWL)
The same condition as in Figure 3-9 with different time base results in Figure 3-10.
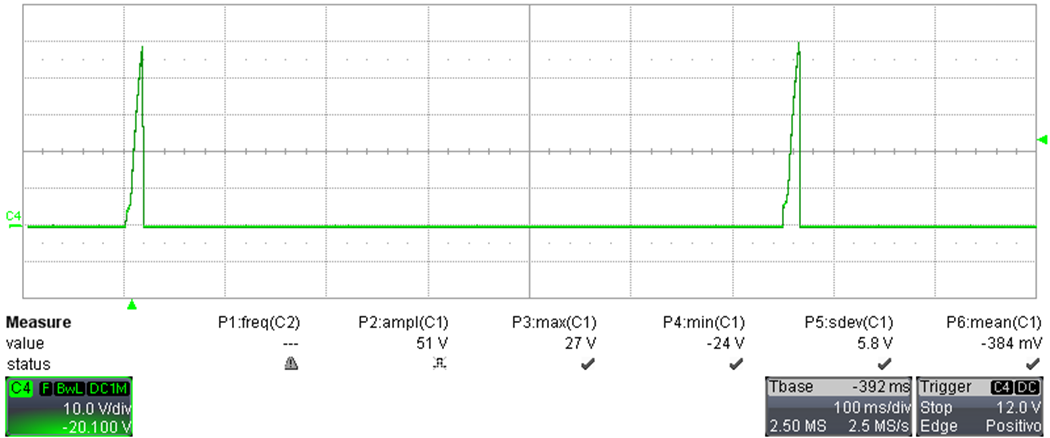 Figure 3-10 Start-Up With Overload Condition (3.5 A), Time Base: 100 ms / div
Figure 3-10 Start-Up With Overload Condition (3.5 A), Time Base: 100 ms / div- Channel C4: Output voltage (10 V / div, 100 ms / div, DC coupling, 20-MHz BWL)