TIDT319 December 2022
- Description
- Features
- Applications
- 1Test Prerequisites
- 2Testing and Results
- 3Waveforms for 2 × LM5143A-Q1 in Four Phase Configuration and Interleaved Operation
- A Individual Adjusting of the Rising Edge and Falling Edge With LM5143A
- B Measurements Across the Low-Side FETs to Check at All Four Phases
- C ON Demand – Assembly of Thermal Interface
C ON Demand – Assembly of Thermal Interface
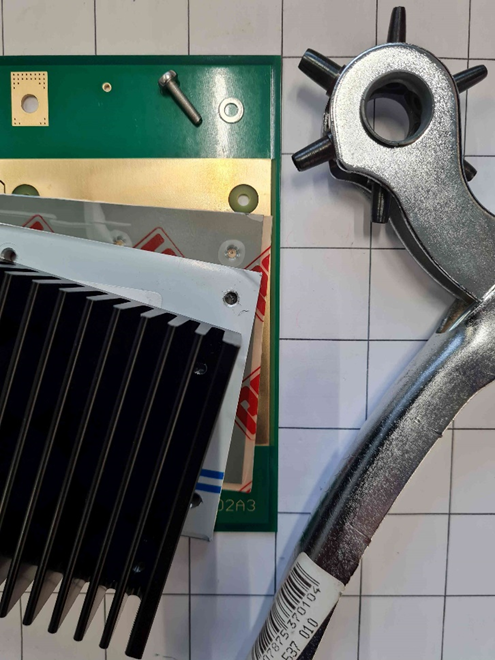 Figure C-1 Stack: PCB
– Thermal Foil – Adapter - Heat Sink
Figure C-1 Stack: PCB
– Thermal Foil – Adapter - Heat Sink |
|
EMI: the adapter and heat sink are floating and provide the shortest connection J3 GND to the screw left of the L2 heat sink. Figure C-2 shows a GND connection.
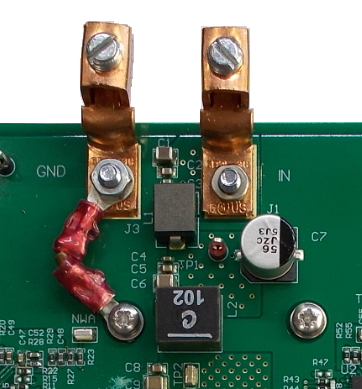 Figure C-2 GND Connection
Figure C-2 GND Connection