TIDT349A January 2024 – December 2024
- 1
- Description
- Features
- Applications
- 1Test Prerequisites
- 2Testing and Results
-
3Waveforms
- 3.1 Charge Mode Start-Up Waveform
- 3.2 OTG Mode Start-Up Waveform
- 3.3 Voltage Transition at OTG Mode
- 3.4 Ripple and Noise at OTG Mode
- 3.5 Load Transients at OTG Mode
- 3.6 Switching Waveform
- 3.7 Overcurrent Protection at OTG Mode
- 3.8 Short-Circuit Protection at OTG Mode
- 3.9 Short-Circuit Protection at Charge Mode
- 4Trademarks
3.1 Charge Mode Start-Up Waveform
Figure 3-1 through Figure 3-4 show the charging waveforms with different input source voltage negotiated on the USB Type-C port. Input source voltage, battery voltage, as well as charge current were captured during the test.
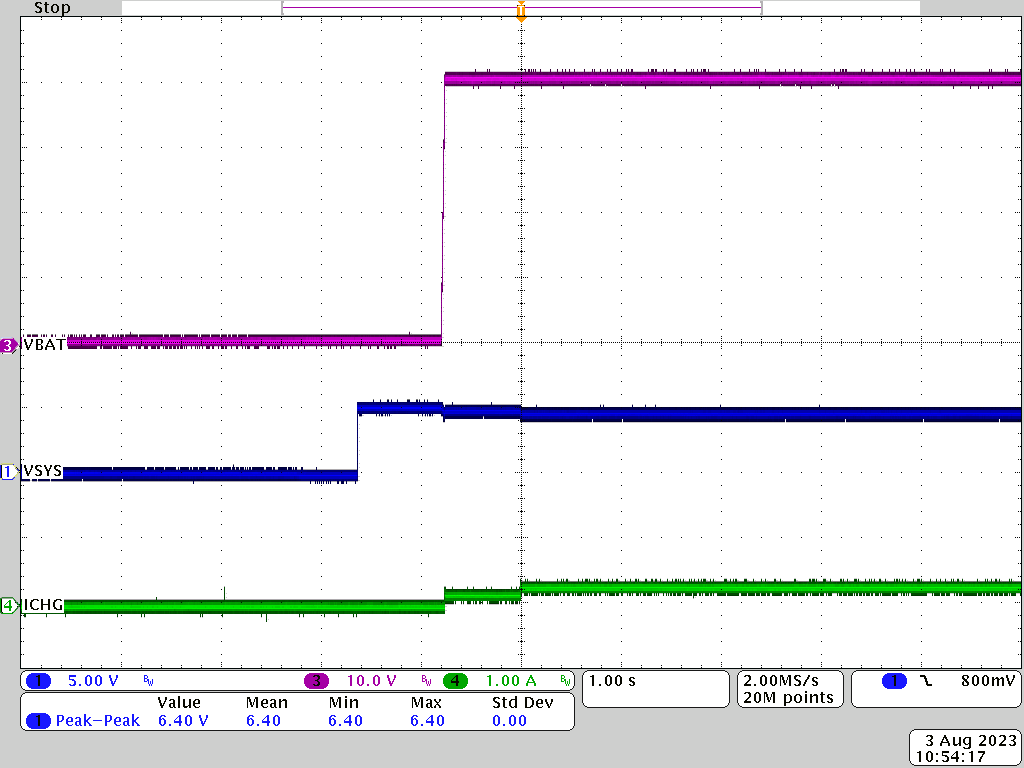 Figure 3-1 5Vsys to 10S BAT = 40V Charge Mode
Figure 3-1 5Vsys to 10S BAT = 40V Charge Mode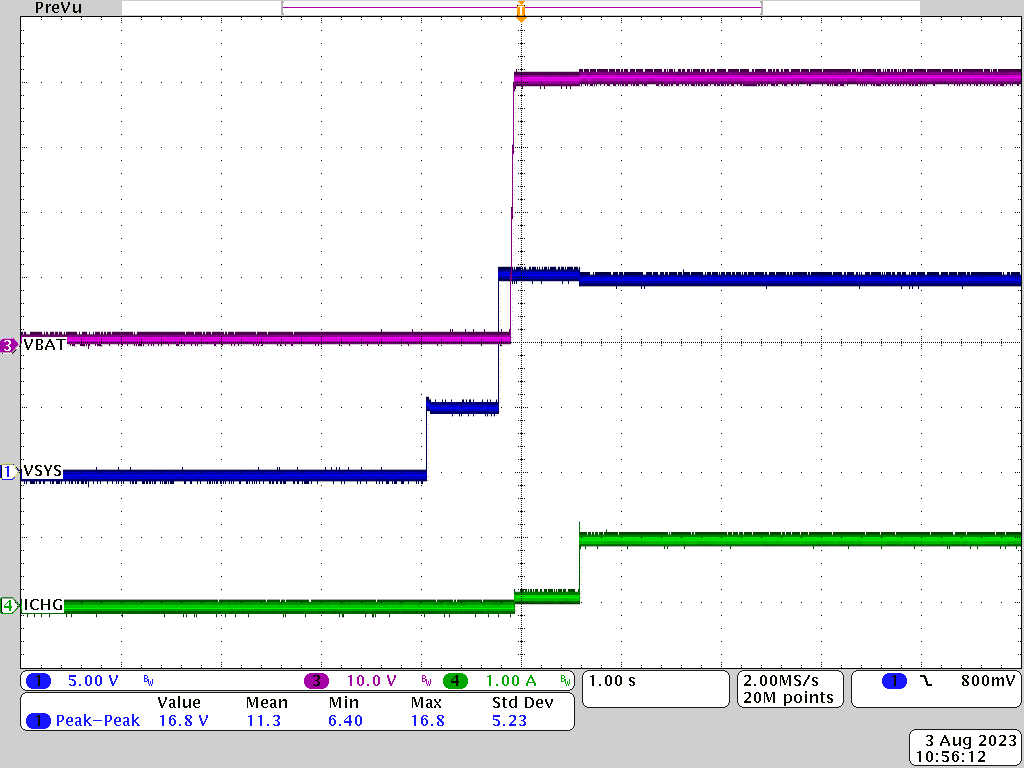 Figure 3-3 15Vsys to 10S BAT = 40V Charge Mode
Figure 3-3 15Vsys to 10S BAT = 40V Charge Mode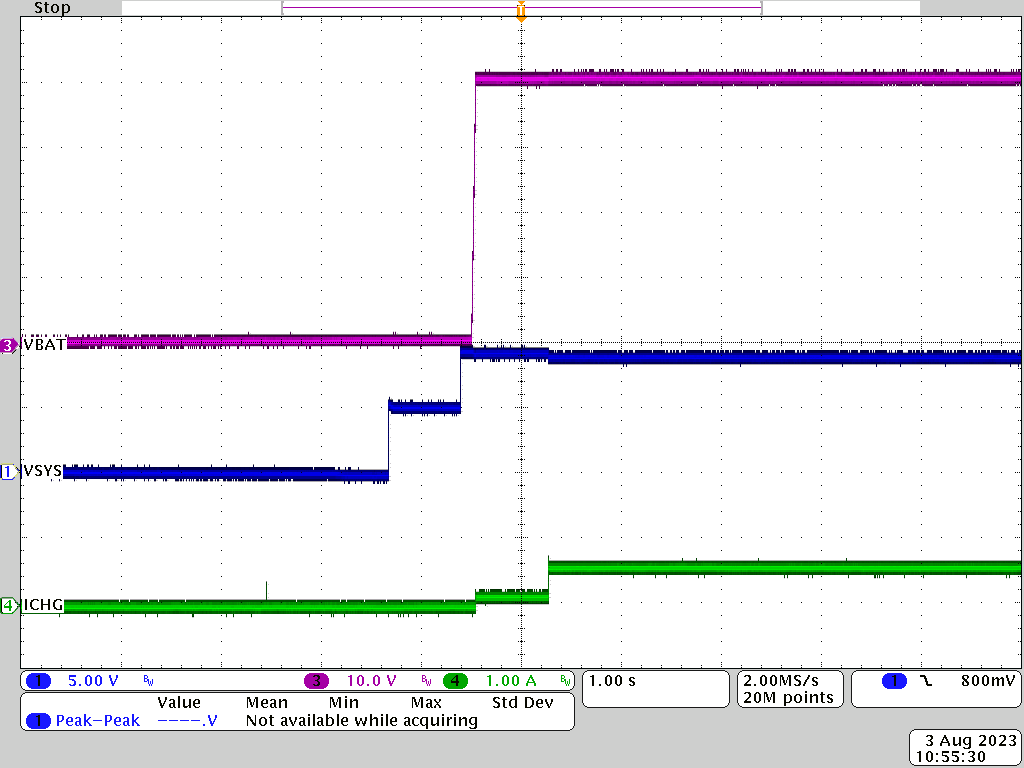 Figure 3-2 9Vsys to 10S BAT = 40V Charge Mode
Figure 3-2 9Vsys to 10S BAT = 40V Charge Mode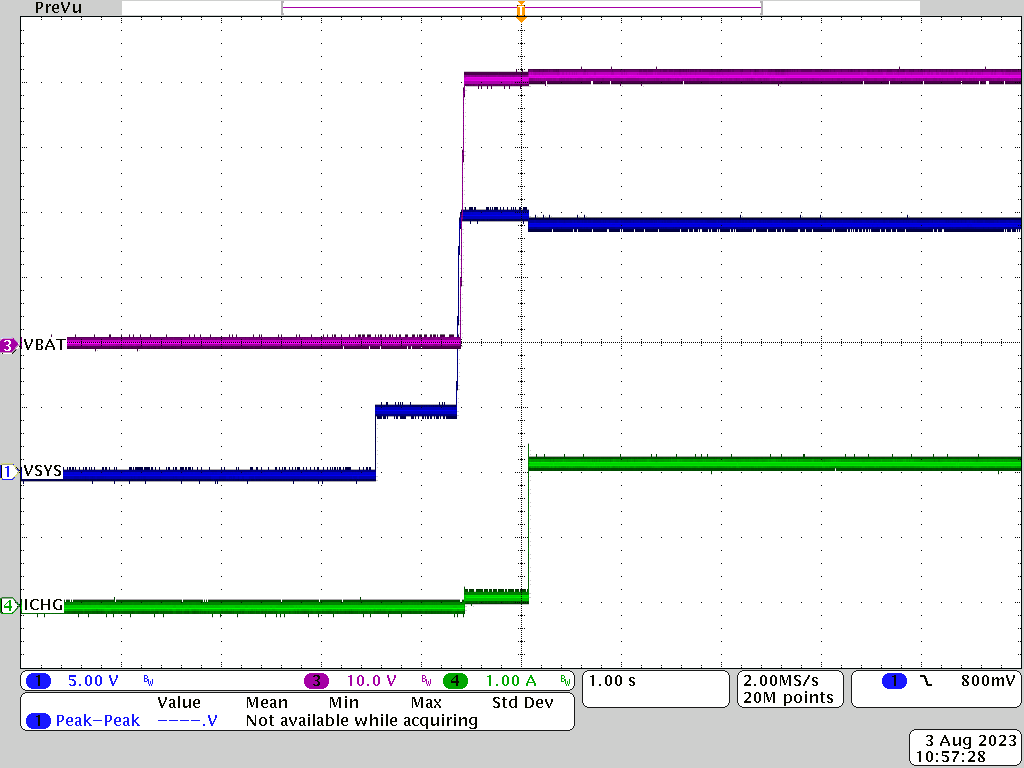 Figure 3-4 20Vsys to 10S BAT = 40V Charge Mode
Figure 3-4 20Vsys to 10S BAT = 40V Charge Mode