TIDT388 February 2024
3.4 Start-Up
Figure 3-22 through Figure 3-27 show the start-up waveforms of the converter at various operating conditions.
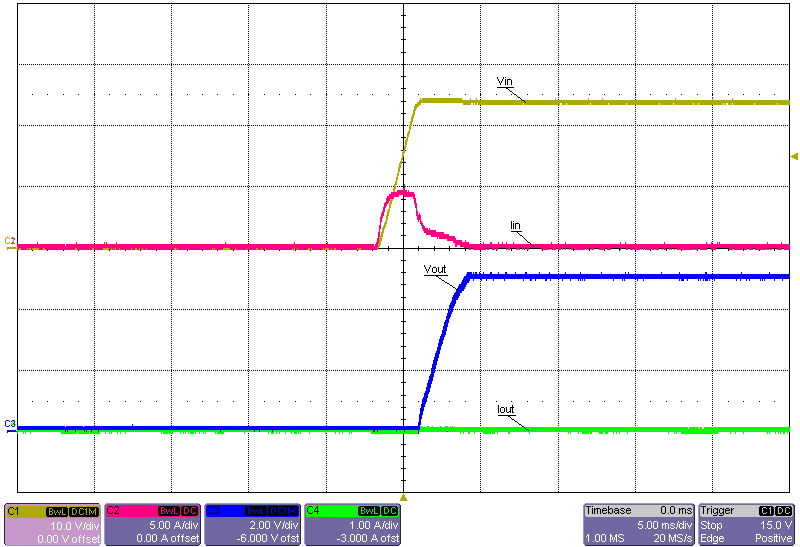 Figure 3-22 Start-Up Into No Load, 24V Input
Figure 3-22 Start-Up Into No Load, 24V Input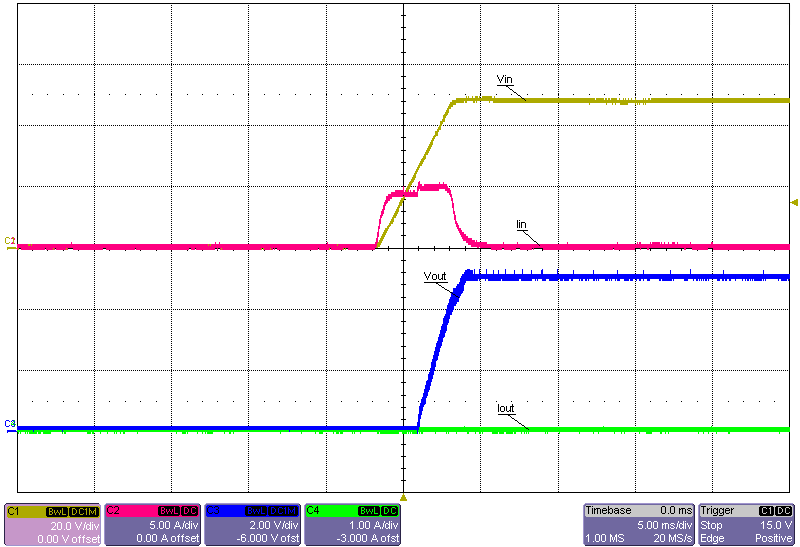 Figure 3-24 Start-Up Into No Load, 48V Input
Figure 3-24 Start-Up Into No Load, 48V Input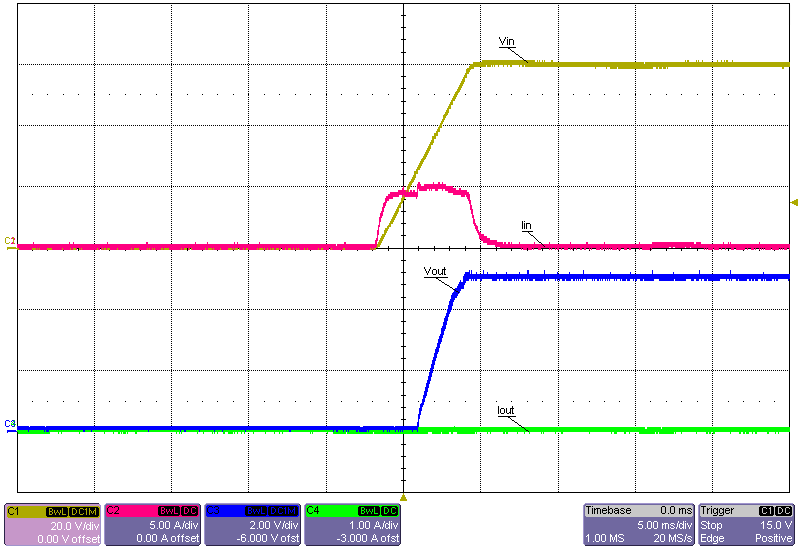 Figure 3-26 Start-Up Into No Load, 60V Input
Figure 3-26 Start-Up Into No Load, 60V Input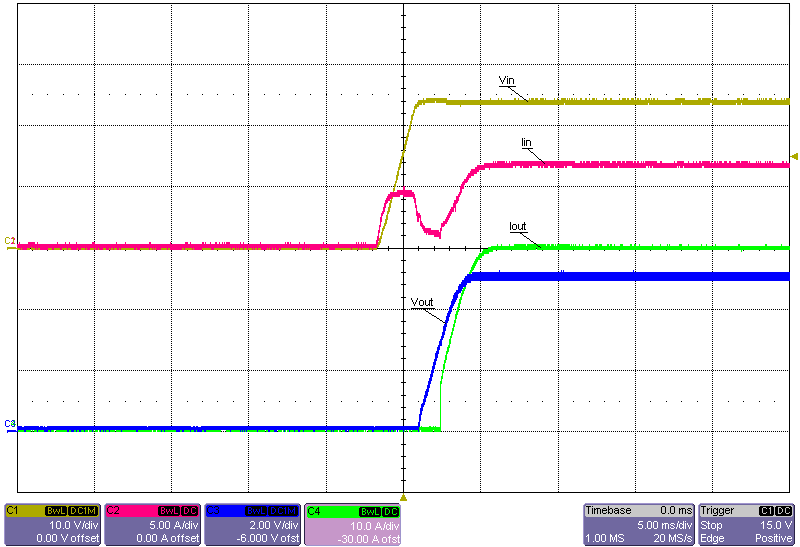 Figure 3-23 Start-Up Into 30A Constant-Resistance Load, 24V Input
Figure 3-23 Start-Up Into 30A Constant-Resistance Load, 24V Input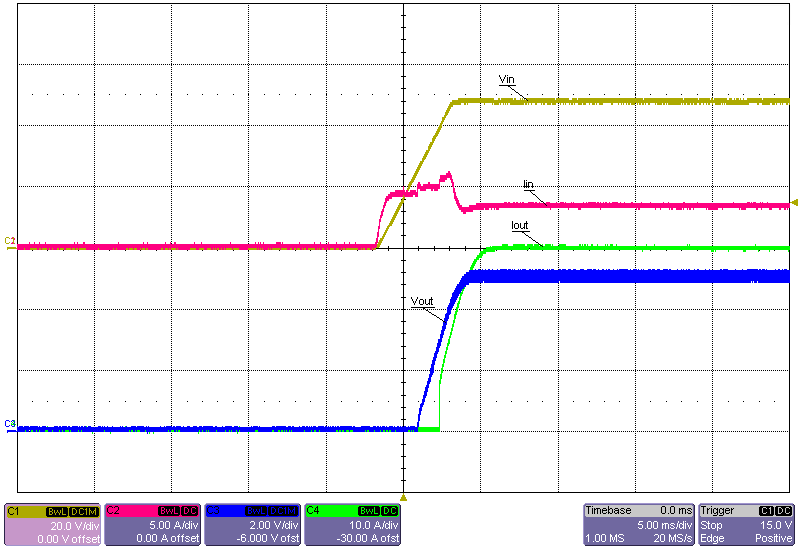 Figure 3-25 Start-Up Into 30A Constant-Resistance Load, 48V Input
Figure 3-25 Start-Up Into 30A Constant-Resistance Load, 48V Input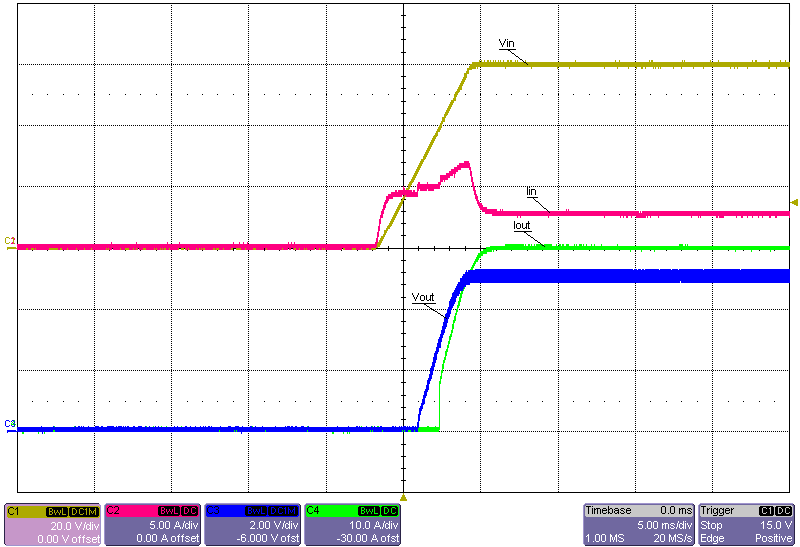 Figure 3-27 Start-Up Into 30A Constant-Resistance Load, 60V Input
Figure 3-27 Start-Up Into 30A Constant-Resistance Load, 60V Input