TIDUF84 June 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3System Design Theory
- 4Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 5Design and Documentation Support
- 6About the Author
- 7Recognition
4.5.3.4 Direction Reversal
MCF8315C-Q1 can reverse the direction of fan rotation without applying brake or relying on motor inertia to coast down. This is a useful feature to smoothly change the fan direction as seen in Figure 4-9. The fan is decelerated at a controlled slew rate to prevent voltage spike on 24V rail (using the AVS feature) and upon reaching zero speed is accelerated to set speed in the forward direction.
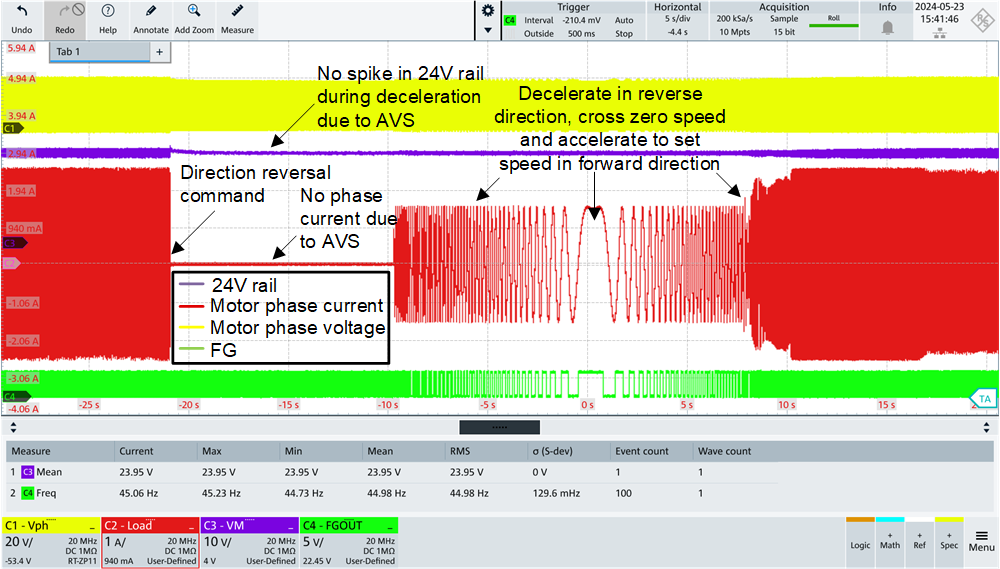 Figure 4-9 Direction Reversal
Figure 4-9 Direction Reversal