-
ADC to UART SLAAEB1 December 2023 MSPM0G1105 , MSPM0G1106 , MSPM0G1107 , MSPM0G1505 , MSPM0G1506 , MSPM0G1507 , MSPM0G3105 , MSPM0G3105-Q1 , MSPM0G3106 , MSPM0G3106-Q1 , MSPM0G3107 , MSPM0G3107-Q1 , MSPM0G3505 , MSPM0G3505-Q1 , MSPM0G3506 , MSPM0G3506-Q1 , MSPM0G3507 , MSPM0G3507-Q1 , MSPM0L1105 , MSPM0L1106 , MSPM0L1303 , MSPM0L1304 , MSPM0L1305 , MSPM0L1306 , MSPM0L1343 , MSPM0L1344 , MSPM0L1345 , MSPM0L1346
-
ADC to UART
ADC to UART
Description
The ADC to UART subsystem example demonstrates how to use the internal ADC to convert an analog signal into a digital representation and transfer the result through UART. The example configures the MCU to act as an external ADC and send raw ADC data through UART. Optionally the MCU can also preprocess the data then send it through I2C. Download the code for the ADC to UART example.
The following figure shows a block diagram of the system.
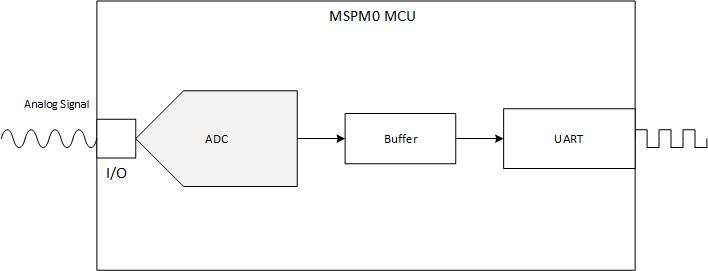 Figure 1-1 Subsystem Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 Subsystem Functional Block DiagramRequired Peripherals
The application requires the internal ADC and 1 instance of UART
| Sub-block Functionality | Peripheral Used | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Analog Signal Capture | ADC | Called ADC12_0_INST in code |
| Sending ADC data | UART | 2 UART transactions are done to send the full ADC data. |
Compatible Devices
Based on the requirements in the table above, the compatible devices are listed below. The corresponding EVM may be used for quick evaluation.
| Compatible Devices | EVM |
|---|---|
| MSPM0Lxxx | LP-MSPM0L1306 |
| MSPM0Gxxx | LP-MSPM0G3507 |
Design Steps
- Determine the configuration for the ADC including reference source, reference value, and sampling rate based on the expected analog input and design requirements.
- Configure the ADC in SysConfig based on requirements in the previous step.
- Configure the UART peripheral in SysConfig, setting the UART to the intended baud rate and other UART options for the intended communication.
- Write Application Code to transfer the ADC data from the memory registers to the UART. See the Software Flowchart for an overview or view the code directly.
Design Considerations
- Max Sampling Speed: The sampling speed of the ADC is based on input signal frequency, analog front end, filters or any other design parameters that affect sampling.
- ADC Reference: Choose the reference to align with the expected max input to utilize the full scale range of the ADC.
- Clock Settings: The clock source determines the total time for sample and conversion time. The clock divider in tandem with the SCOMP setting determine the total sampling time. SysConfig sets the appropriate SCOMP depending on the sampling time setting.
- UART configurations can be adjusted depending on the UART system, such as parity, baud rate, and more.
Software Flowchart
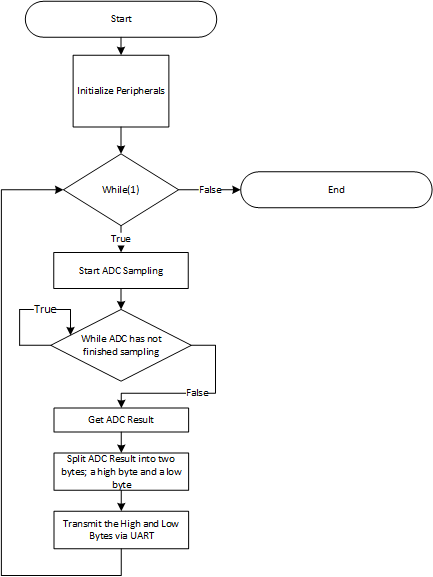
Application Code
The UART peripheral sends data in packets of 8 bits at a time. The ADC module stores the data into a 16-bit register. To transmit the data through the UART peripheral, the ADC data must be split into high and low bytes. The high byte contains the upper 8 bits while the low byte contains the lower 8 bits. Below is the code to split the ADC result and transmit the data through UART.
gADCResult = DL_ADC12_getMemResult(ADC12_0_INST, DL_ADC12_MEM_IDX_0);
uint8_t lowbyte = (uint8_t)(gADCResult & 0xFF);
uint8_t highbyte = (uint8_t)((gADCResult >> 8) & 0xFF);
DL_UART_Main_transmitData(UART_0_INST, highbyte);
DL_UART_Main_transmitData(UART_0_INST, lowbyte);Additional Resources
Revision History
| DATE | REVISION | NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| December 2023 | * | Initial Release |
IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS” AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS.
These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims, damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources.
TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2023, Texas Instruments Incorporated