-
Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions
Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions
Prajakta Desai
Mark Nadeski
The world of patient care is evolving to the point where the most important features in today’s patient monitors are mobility, ease of use and effortless patient data transfer. Incorporating wireless connectivity into medical devices is driving improvements in these areas and will transform the traditional look and feel of a hospital room.
A traditional hospital room is built around the notion that the patient is primarily stationary in their hospital bed. A patient is hooked up to a patient monitor through cabled sensors that track the patient’s vital signs including blood pressure, electrocardiogram, pulse oximetry, temperature, etc. Most current systems have network connectivity allowing patient monitors to share this information with networked central monitoring stations, providing caregivers the ability to check a patient’s information without having to be physically in the room.
Newer, improved connectivity patient monitors incorporate a wireless protocol, such as 802.11b, enabling the usage of wireless sensors to monitor a patient’s vital signs, providing the patient the ability to easily leave the hospital bed while being continuously monitored without having to be tethered to the patient monitor itself. As an added benefit for facilities where patients are not primarily stationary, a patient’s location can be wirelessly tracked throughout the hospital grounds providing medical staff with knowledge of where patients using this technology are at any given time. Similarly, the patient monitor can wirelessly transmit patient data not only to central monitoring stations, but also to mobile devices that enable monitoring capabilities for medical staff while reducing the expense and limitations of wired network cabling to the patient monitor itself.
Typical use cases for wireless technology in the hospital environment for remote patient monitoring are shown below:

Wireless Hospital Monitoring
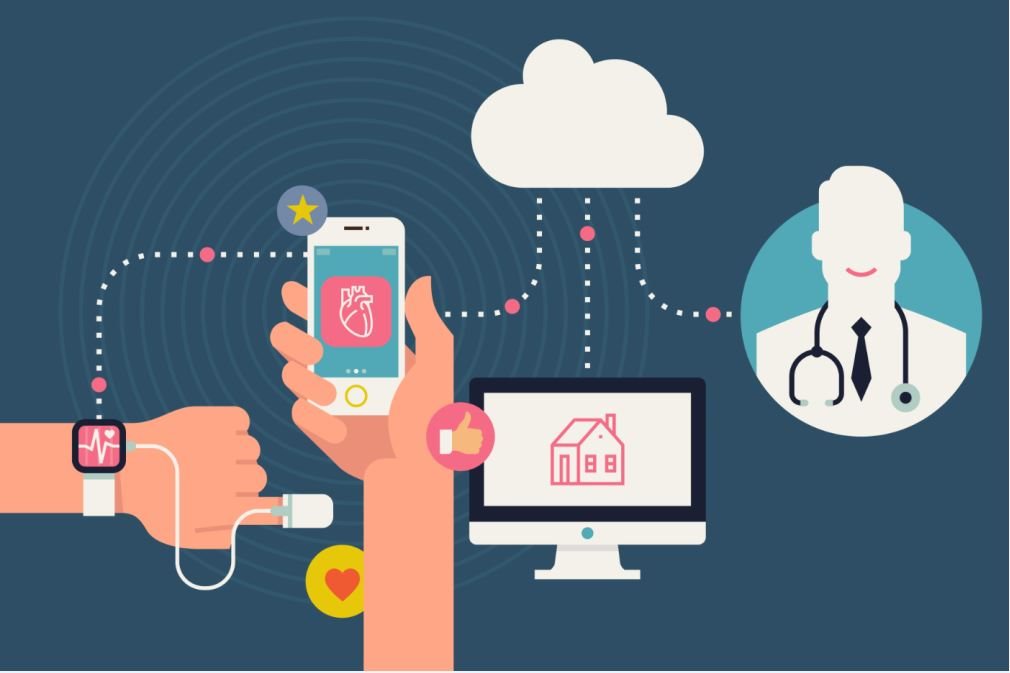
In addition to monitoring inside the hospital environment, the ever-increasing need to minimize healthcare costs is driving healthcare providers to move patient treatment and monitoring outside the hospital. Here, wireless technology can assist customers to enable remote monitoring of people from the comfort of their own home
Customers can evaluate TI’s connectivity solutions and broad, scalable processor portfolio to determine how to address a wide range of needs demanded from the patient monitoring space. For example, our WiLink™ 8 Wi-Fi® + Bluetooth® combo connectivity devices and the Sitara™ processors family can make a great solution for the next generation of patient monitoring equipment.
Below is a generic block diagram illustrating how TI’s WiLink 8 module easily connects to any of the Sitara processors through the SDIO, UART or SPI interfaces, allowing wireless data to be received and accessed by the ARM® Cortex®-A core running a high-level OS (HLOS). Utilizing the integrated display subsystem and graphical acceleration, the Sitara processor provides an enhanced user interface.
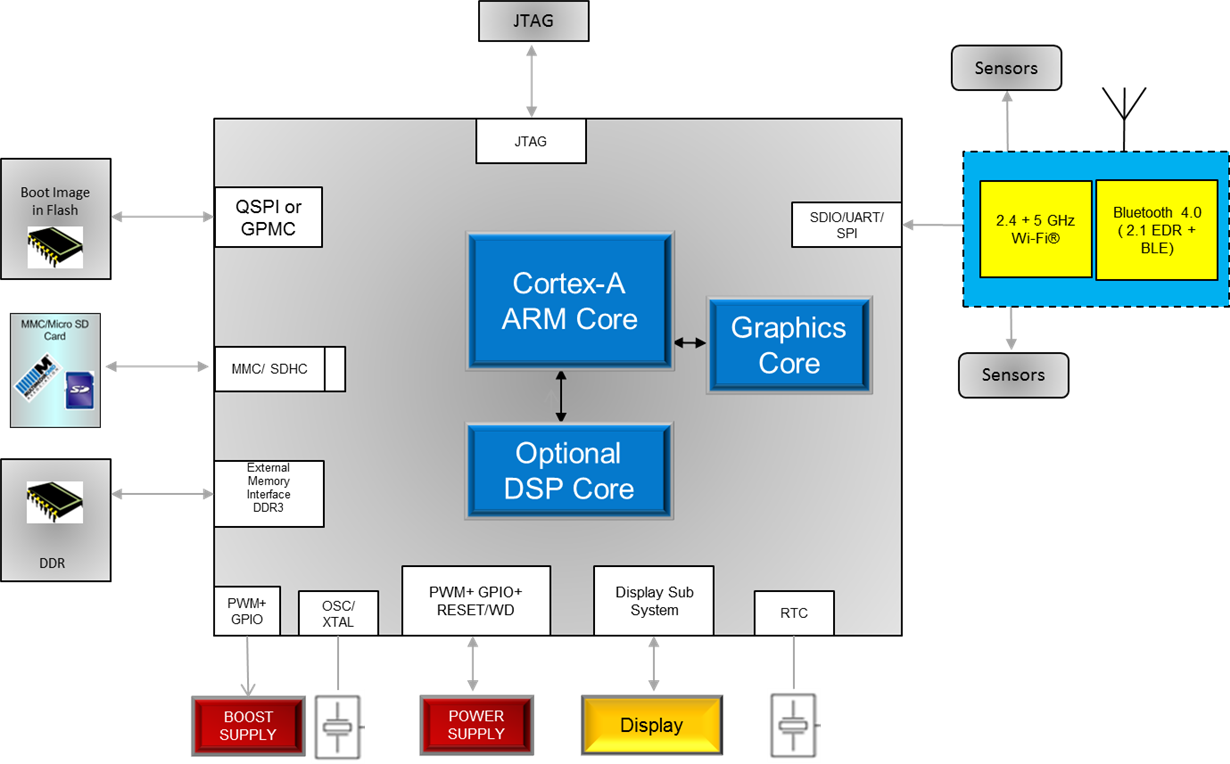
The WiLink 8 modules are a great wireless connectivity choice for customers designing patient monitors developed on Linux®. Why?
- Wi-Fi + Bluetooth coexistence: The ability to switch between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi can extend battery life in portable applications reducing overall system power. This coexistence also reduces the chances of losing a data packet when the increased RF traffic increases the chance of interference.
- High-performance modules: The WiLink 8 modules support advanced features such as MRC for increased range, and MIMO for increased throughput of up to 100 Mbps on dual-antenna modules. This can provide customers a potentially scalable solution for higher-end patient monitors to enable more throughput and reduced latency
- Dual-band support: 5GHz support on the WL1837MOD, enable customers to operate outside the congested 2.4GHz frequency band. This provides the robustness customers need for response times in patient monitoring. 5GHz diversity, which increases overall throughput and reduces latency, also makes it a compelling candidate for customers designing high performance, high end patient monitors.
- Certification: WiLink 8 modules are FCC, CE, IC and TELEC certified* which reduces overall costs and time to market in some instances.
- Pin-to-pin compatible WiLink™8 variants: To accommodate the fast changing requirements for patient monitors, the WiLink 8 portfolio offers pin-to-pin compatible variants that all easily connect to TI’s Sitara family of processors.
TI’s Sitara processors, based on ARM Cortex-A cores, are available for implementing a scalable range of patient monitors. The ARM Cortex-A runs a HLOS and the additional graphics engine provides the graphical user interface for the care giver. An optional DSP can perform real-time analytics for specified patient data. TI provides an online unified software developer kit for all Sitara processors with Processor SDK (software development kit), allowing development to scale across families.
- Sitara AM335x processors: This Cortex-A8-based processor family delivers high DMIPS/dollar to provide cost effective processing for patient monitoring applications.
- Sitara AM437x processors: The Cortex-A9 core provides a boost in performance from the AM335x processor family for greater capability to provide a scalable processing platform for the higher end patient monitors.
- Sitara AM57x processors: Single/dual Cortex-A15 cores combined with single/dual C66x digital signal processor (DSP) cores, 3D graphics and 1080p HD video acceleration, the Sitara AM57x processors are available for designers of the highest end of patient monitors. Capable of running virtualization on the A15 cores, multiple operating systems can be run simultaneously allowing for development in Linux/WinCE/etc for customers while enabling a secondary secure OS as needed. 3D graphics allow detailed visualization in real-time while HD video can be used for high quality playback of videos.
To start developing your monitoring solution with WiLink 8 connectivity modules and Sitara processors, check out the WiLink™ 8 dual-band 2.4 & 5 GHz Wi-Fi + Bluetooth COM8 evaluation module that can be used with the Sitara AM335x processor evaluation module.
This blog entry is not intended for customers designing and manufacturing life-critical medical equipment. To the extent customers’ patient monitoring solutions are life-critical medical equipment, TI’s terms of sale require that customers execute a special contract with TI specifically governing such use. Life-critical medical equipment is medical equipment where failure of such equipment would cause serious bodily injury or death (e.g., life support, pacemakers, defibrillators, heart pumps, neurostimulators, and implantables). Such equipment includes, without limitation, all medical devices identified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as Class III devices and equivalent classifications outside the U.S.
IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS” AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS.
These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims, damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources.
TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2023, Texas Instruments Incorporated