SBAA472 May 2021 ADS8353-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a Failure Mode Analysis (FMA) for the pins of the ADS8353-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to Ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance |
Figure 4-1 shows the ADS8353-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the ADS8353-Q1 data sheet.
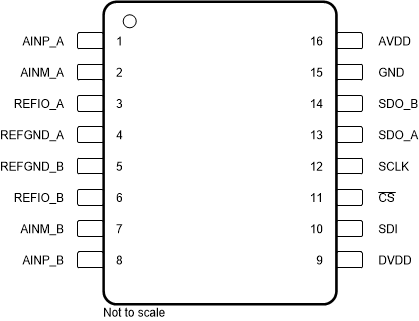 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- AVDD and DVDD use the same supply voltage.
- REFGND_A, REFGND_B and GND use the same GND.
- Short circuit to Power means short to AVDD = DVDD.
- Short circuit to GND means short to REFGND_A = REFGND_B = GND.
-
RC filters on every analog input, AINP_x and AINM_x. Series resistors are sized to limit the input currents into the analog inputs to <10mA in all circumstances, e.g. also in case device is unpowered and input signal is applied.
- Device is the only peripheral on the SPI bus.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| AINP_A | 1 | Single-ended configuration: ADC_A conversion result close to 0 V. | B |
| Pseudo-differential configuration: ADC_A conversion result close to negative full-scale. | B | ||
| AINM_A | 2 | Single-ended configuration: No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| Pseudo-differential configuration: Incorrect ADC_A conversion result. Incorrect voltage on AINM_A. | B | ||
| REFIO_A | 3 | ADC_A conversion result undetermined. ADC_A reference voltage is 0 V (REFGND_A = REFIO_A). | B |
| REFGND_A | 4 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| REFGND_B | 5 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| REFIO_B | 6 | ADC_B conversion result undetermined. ADC_B reference voltage is 0 V (REFGND_B = REFIO_B). | B |
| AINM_B | 7 | Single-ended configuration: Normal operation. | D |
| Pseudo-differential configuration: Incorrect ADC_B conversion result. Incorrect voltage on AINM_B. | B | ||
| AINP_B | 8 | Single-ended configuration: ADC_B conversion result close to 0 V. | B |
| Pseudo-differential configuration: ADC_B conversion result close to negative full-scale. | B | ||
| DVDD | 9 | Digital interface not powered up. No SPI communication with device possible. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all digital pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| SDI | 10 | SDI stuck low. Normal operation in default power-up configuration. Device configuration cannot be changed. | B |
| CS | 11 | CS stuck low. No SPI communication with device possible. Conversions cannot be initiated. | B |
| SCLK | 12 | SCLK stuck low. No SPI communication with device possible. | B |
| SDO_A | 13 |
SDO_A stuck low. ADC_A conversion result or device internal registers cannot be read. Increase in supply current when SDO_A tries to drive high. Device damage plausible if SDO_A drives high for extended period of time. |
A |
| SDO_B | 14 |
32-CLK, dual-SDO mode: SDO_B stuck low. ADC_B conversion results cannot be read. Increase in supply current when SDO_B tries to drive high. Device damage plausible if SDO_B drives high for extended period of time. |
A |
| 32-CLK, single-SDO mode: No effect. Normal operation. | D | ||
| GND | 15 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| AVDD | 16 | Device unpowered. Device not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| AINP_A | 1 | ADC_A conversion result undetermined. | B |
| AINM_A | 2 | ADC_A conversion result undetermined. | B |
| REFIO_A | 3 | ADC_A reference voltage undetermined. ADC_A conversion result undetermined. | B |
| REFGND_A | 4 | Increased gain error for ADC_A. ADC_A reference voltage will connect to ground through internal path in the device. Increased gain error for ADC_A due to reference voltage drop across the internal path in the device. | B |
| REFGND_B | 5 | Increased gain error for ADC_B. ADC_B reference voltage will connect to ground through internal path in the device. Increased gain error for ADC_B due to reference voltage drop across the internal path in the device. | B |
| REFIO_B | 6 | ADC_B reference voltage undetermined. ADC_B conversion result undetermined. | B |
| AINM_B | 7 | ADC_B conversion result undetermined. | B |
| AINP_B | 8 | ADC_B conversion result undetermined. | B |
| DVDD | 9 |
Digital interface not powered up if all external digital pins are held low. No SPI communication with device possible. Digital interface may power up through internal ESD diodes to DVDD if voltages above the device's power-on reset threshold are present on any of the digital pins. |
B |
| SDI | 10 |
State of SDI input undetermined. SPI communication to the device corrupted. Device configuration cannot be changed. Normal operation in default power-up configuration. |
B |
| CS | 11 | State of CS input undetermined. SPI communication corrupted. | B |
| SCLK | 12 | State of SCLK input undetermined. SPI communication corrupted. | B |
| SDO_A | 13 | ADC_A conversion result or device internal registers cannot be read. | B |
| SDO_B | 14 | 32-CLK, dual-SDO mode: ADC_B conversion results cannot be read. | B |
| 32-CLK, single-SDO mode: No effect. Normal operation. | D | ||
| GND | 15 | Device functionality undetermined. Device may connect to ground internally through alternate pin ESD diode and power up. | B |
| AVDD | 16 |
Device functionality undetermined. Device unpowered and not functional if all external analog pins are held low. Device may power up through internal ESD diodes to AVDD if voltages above the device's power-on reset threshold are present on any of the analog pins. |
B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AINP_A | 1 | AINM_A | Differential ADC_A input voltage is 0 V. ADC_A conversion result close to 0 V. | B |
| AINM_A | 2 | REFIO_A | Single-ended configuration: Incorrect voltage on AINM_A. Incorrect ADC_A conversion result. | B |
| Pseudo-differential configuration, VREF range: Incorrect ADC_A conversion result. | B | |||
| Pseudo-differential configuration, 2x VREF range: No effect. Normal operation. | D | |||
| REFIO_A | 3 | REFGND_A | ADC_A reference voltage is 0 V (REFGND_A = REFIO_A). ADC_A conversion result undetermined. | B |
| REFGND_A | 4 | REFGND_B | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| REFGND_B | 5 | REFIO_B | ADC_B reference voltage is 0 V (REFGND_B = REFIO_B). ADC_B conversion result undetermined. | B |
| REFIO_B | 6 | AINM_B | Single-ended configuration: Incorrect voltage on AINM_B. Incorrect ADC_B conversion result. | B |
| Pseudo-differential configuration, VREF range: Incorrect ADC_B conversion result. | B | |||
| Pseudo-differential configuration, 2x VREF range: No effect. Normal operation. | D | |||
| AINM_B | 7 | AINP_B | Differential ADC_B input voltage is 0 V. ADC_B conversion result close to 0 V. | B |
| AINP_B | 8 | - | Not considered. Corner pin. | - |
| DVDD | 9 | SDI | SDI stuck high. Normal operation in default power-up configuration. Device configuration cannot be changed. | B |
| SDI | 10 | CS | SPI communication corrupted. No SPI communication with the device possible. | B |
| CS | 11 | SCLK | SPI communication corrupted. No SPI communication with the device possible. | B |
| SCLK | 12 | SDO_A | SPI communication corrupted. Increase in supply current when SCLK tries to drive high while SDO_A tries to drive low and vice versa. Device damage may be plausible. | A |
| SDO_A | 13 | SDO_B | SPI communication corrupted. Increase in supply current when SDO_B tries to drive high while SDO_A tries to drive low and vice versa. Device damage may be plausible. | A |
| SDO_B | 14 | GND |
32-CLK, dual-SDO mode: SDO_B stuck low. ADC_B conversion results cannot be read. Increase in supply current when SDO_B tries to drive high. Device damage plausible if SDO_B drives high for extended period of time. |
A |
| 32-CLK, single-SDO mode: No effect. Normal operation. | D | |||
| GND | 15 | AVDD | Device unpowered. Device not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| AVDD | 16 | - | Not considered. Corner pin. | - |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| AINP_A | 1 | ADC_A conversion result close to positive full-scale code. | B |
| AINM_A | 2 | Incorrect ADC_A conversion result. Incorrect voltage on AINM_A. | B |
| REFIO_A | 3 | Increased gain error because reference to ADC_A is different from the intended REFIO_A voltage. | B |
| REFGND_A | 4 | Incorrect ADC_A reference voltage. Incorrect ADC_A conversion result. | B |
| REFGND_B | 5 | Incorrect ADC_B reference voltage. Incorrect ADC_B conversion result. | B |
| REFIO_B | 6 | Increased gain error because reference to ADC_B is different from the intended REFIO_B voltage. | B |
| AINM_B | 7 | Incorrect ADC_B conversion result. Incorrect voltage on AINM_B. | B |
| AINP_B | 8 | ADC_B conversion result close to positive full-scale code. | B |
| DVDD | 9 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| SDI | 10 | SDI stuck high. Normal operation in default power-up configuration. Device configuration cannot be changed. | B |
| CS | 11 | CS stuck high. No SPI communication with device possible. Conversions cannot be initiated. | B |
| SCLK | 12 | SCLK stuck high. No SPI communication with device possible. | B |
| SDO_A | 13 |
SDO_A stuck high. ADC_A conversion result or device internal registers cannot be read. Increase in supply current when SDO_A tries to drive low. Device damage plausible if SDO_A drives low for extended period of time. |
A |
| SDO_B | 14 |
32-CLK, dual-SDO mode: SDO_B stuck high. ADC_B conversion results cannot be read. Increase in supply current when SDO_B tries to drive low. Device damage plausible if SDO_B drives low for extended period of time. |
A |
| 32-CLK, single-SDO mode: No effect. Normal operation. | D | ||
| GND | 15 | Device unpowered. Device not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| AVDD | 16 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |