SBAA497B May 2021 – April 2022 PCM3120-Q1 , PCM5120-Q1 , PCM6120-Q1 , TLV320ADC3120 , TLV320ADC5120 , TLV320ADC6120
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Infinite Impulse Response Filters
-
3TLV320ADCx120 and PCMx120-Q1 Digital Biquad Filters
- 3.1 Filter Design Using PurePath Console
- 3.2 How to Generate N0, N1, N2, D1, and D2 Coefficients with a Digital Filter Design Package
- 3.3 Avoid Overflow Conditions
- 3.4 Digital Biquad Filter Allocation to Output Channel
- 3.5 Programmable Coefficient Registers for Digital Biquad Filters 1–6
- 3.6 Programmable Coefficient Registers for Digital Biquad Filters 7–12
- 4How to Program the Digital Biquad Filters on the TLV320ADCx120 and PCMx120-Q1
- 5Typical Audio Applications for Biquad Filtering
- 6Crossover Networks
- 7Voice Boost
- 8Bass Boost
- 9Removing 50 Hz–60 Hz Hum With Notch Filters
- A Digital Filter Design Techniques
- B Related Documentation
- B Revision History
2.1 Digital Biquad Filter
A Digital Biquad Filter is a second-order IIR filter with two poles and two zeros. “Biquad” is an abbreviation of “biquadratic.” Thus, a Digital Biquad Filter is an IIR filter whose transfer function is the ratio of two quadratic functions given by Equation 2 and the corresponding direct form II block diagram shown in Figure 2-1. In this equation, the coefficients are normalized so that a0 = 1 through the division of all the coefficients by a0.
Equation 2. 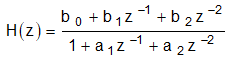
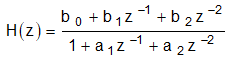
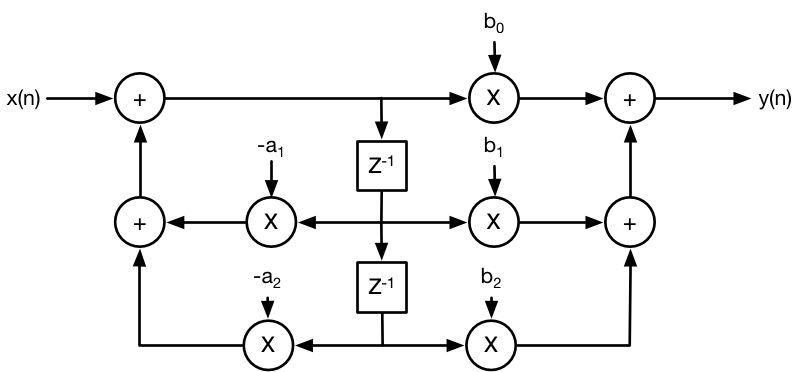 Figure 2-1 Direct Form II Biquad Filter
Figure 2-1 Direct Form II Biquad Filter