SBAS444D May 2009 – January 2018 ADS1113 , ADS1114 , ADS1115
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6 Register Map
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.2.1 Shunt Resistor Considerations
- 10.2.2.2 Operational Amplifier Considerations
- 10.2.2.3 ADC Input Common-Mode Considerations
- 10.2.2.4 Resistor (R1, R2, R3, R4) Considerations
- 10.2.2.5 Noise and Input Impedance Considerations
- 10.2.2.6 First-order RC Filter Considerations
- 10.2.2.7 Circuit Implementation
- 10.2.2.8 Results Summary
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
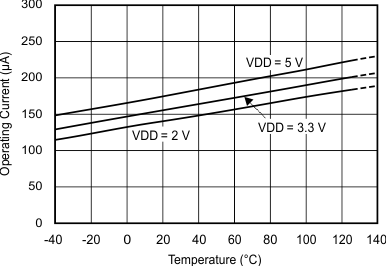
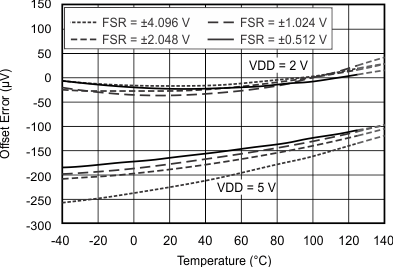
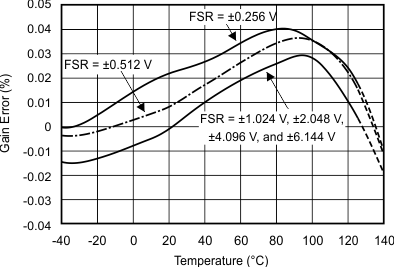
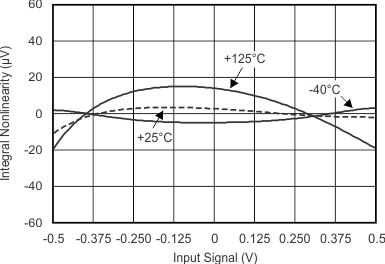
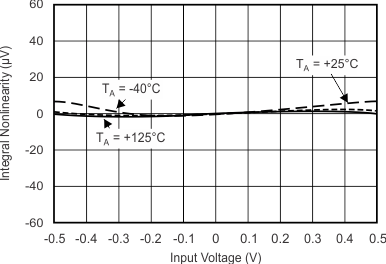
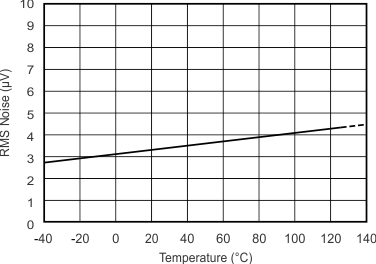
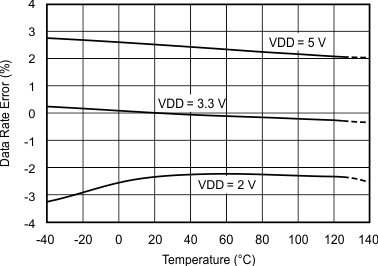
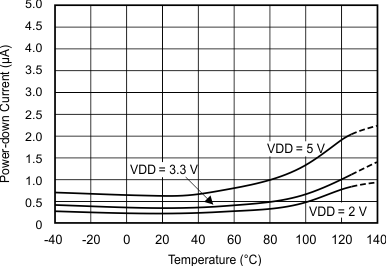
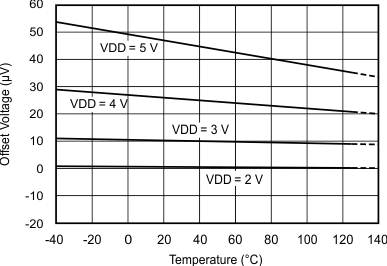
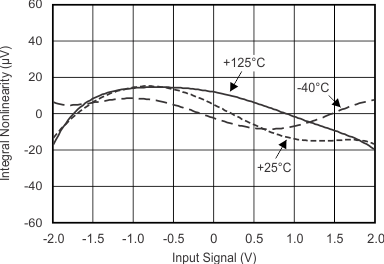
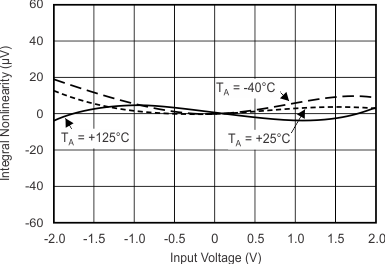
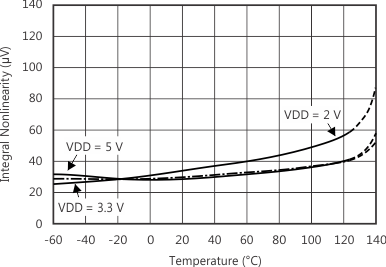
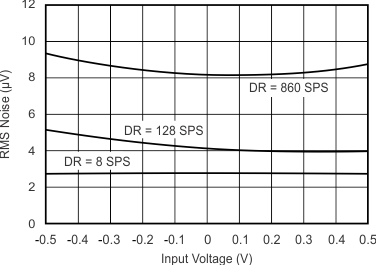
7.7 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VDD = 3.3 V, FSR = ±2.048 V, DR = 8 SPS (unless otherwise noted)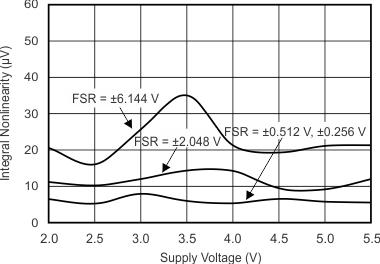
| FSR = ±0.512 V |
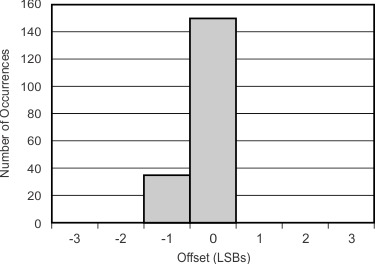
| FSR = ±2.048 V, 185 units |
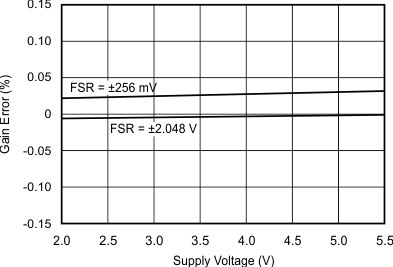
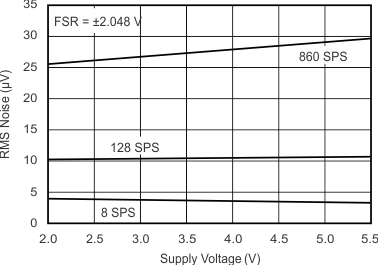
| FSR = ±2.048 V |
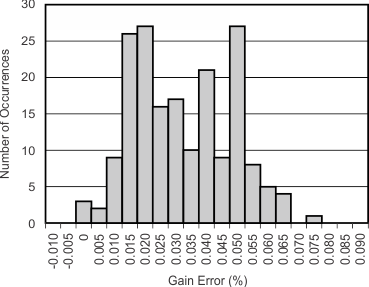
| FSR = ±2.048 V, 185 units |
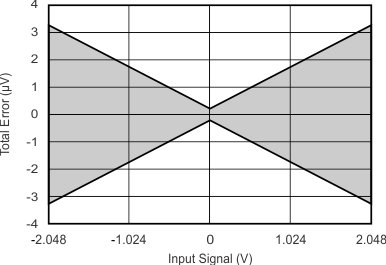
| Differential inputs; includes noise, offset and gain error |
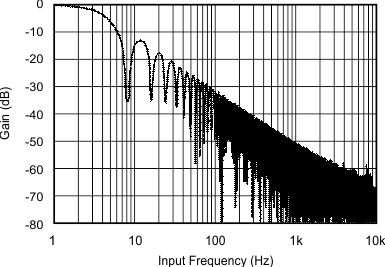
| DR = 8 SPS |