SBAS526D November 2012 – September 2019 ADS1018
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.1.1 Serial Interface Connections
The principle serial interface connections for the ADS1018 are shown in Figure 18.
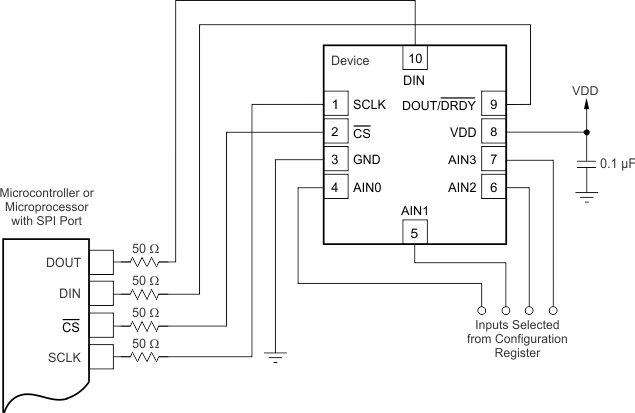 Figure 18. Typical Connections
Figure 18. Typical Connections Most microcontroller SPI peripherals operate with the ADS1018. The interface operates in SPI mode 1 where CPOL = 0 and CPHA = 1, SCLK idles low, and data are launched or changed only on SCLK rising edges; data are latched or read by the master and slave on SCLK falling edges. Details of the SPI communication protocol employed by the ADS1018 can be found in the Timing Requirements: Serial Interface section.
It is a good practice to place 50-Ω resistors in the series path to each of the digital pins to provide some short-circuit protection. Take care to still meet all SPI timing requirements because these additional series resistors along with the bus parasitic capacitances present on the digital signal lines slews the signals.
The fully-differential input of the ADS1018 is ideal for connecting to differential sources (such as thermocouples and thermistors) with a moderately low source impedance. Although the ADS1018 can read fully-differential signals, the device cannot accept negative voltages on either of its inputs because of ESD protection diodes on each pin. When an input exceeds supply or drops below ground, these diodes turn on to prevent any ESD damage to the device.