SBAS817D November 2017 – June 2024 ADS8166 , ADS8167 , ADS8168
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
-
7 Register Maps
- 7.1
Interface and Hardware Configuration Registers
- 7.1.1 REG_ACCESS Register (address = 00h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.1.2 PD_CNTL Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.1.3 SDI_CNTL Register (address = 008h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.1.4 SDO_CNTL1 Register (address = 0Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 7.1.5 SDO_CNTL2 Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.1.6 SDO_CNTL3 Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.1.7 SDO_CNTL4 Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.1.8 DATA_CNTL Register (address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.1.9 PARITY_CNTL Register (address = 11h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.2 Device Calibration Registers
- 7.3 Analog Input Configuration Registers
- 7.4
Channel Sequence Configuration Registers Map
- 7.4.1 DEVICE_CFG Register (address = 1Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.2 CHANNEL_ID Register (address = 1Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.3 SEQ_START Register (address = 1Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.4 SEQ_ABORT Register (address = 1Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.5 ON_THE_FLY_CFG Register (address = 2Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.6 AUTO_SEQ_CFG1 Register (address = 80h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.7 AUTO_SEQ_CFG2 Register (address = 82h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.8
Custom Channel Sequencing Mode Registers
- 7.4.8.1 CCS_START_INDEX Register (address = 88h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.8.2 CCS_END_INDEX Register (address = 89h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.8.3 CCS_SEQ_LOOP Register (address = 8Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.8.4 CCS_CHID_INDEX_m Registers (address = 8C, 8E, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 9A, 9C, 9E, A0, A2, A4, A6, A8, and AAh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.4.8.5 REPEAT_INDEX_m Registers (address = 8D, 8F, 91, 93, 95, 97, 99, 9B, 9D, 9F, A1, A3, A5, A7, A9, and ABh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.5
Digital Window Comparator Configuration Registers Map
- 7.5.1 ALERT_CFG Register (address = 2Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.5.2 HI_TRIG_AINx[15:0] Register (address = 4Dh to 30h) [reset = 0000h]
- 7.5.3 LO_TRIG_AINx[15:0] Register (address = 71h to 54h) [reset = 0000h]
- 7.5.4 HYSTERESIS_AINx[7:0] Register (address = 4Fh to 33h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.5.5 ALERT_LO_STATUS Register (address = 78h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.5.6 ALERT_HI_STATUS Register (address = 79h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.5.7 ALERT_STATUS Register (address = 7Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 7.5.8 CURR_ALERT_LO_STATUS Register (address = 7Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 7.5.9 CURR_ALERT_HI_STATUS Register (address = 7Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.5.10 CURR_ALERT_STATUS Register (address = 7Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.1
Interface and Hardware Configuration Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.4.1.2 On-The-Fly Mode
There is a latency of one cycle when switching channels using the register access, just as in manual mode. The newly selected channel data are available two cycles after selecting the desired channel. The ADS816x supports on-the-fly switching of the analog input channels of the multiplexer. Enable this mode by programming the SEQ_MODE[1:0] bits to 01b in the DEVICE_CFG register. When enabled, the analog input channel for the next conversion is determined by the first five bits sent over SDI. The desired analog input channel is selected by setting the MSB to 1 and the following four bits as the channel ID. If the MSB is 0 then the SDI bitstream is decoded as a normal frame on the rising edge of CS. Table 6-3 lists the channel selection commands for this mode.
| SDI BITS [15:11] | SDI BITS [10:0] | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 1 0000 | Don't care | Select analog input 0 |
| 1 0001 | Don't care | Select analog input 1 |
| 1 0010 | Don't care | Select analog input 2 |
| 1 0011 | Don't care | Select analog input 3 |
| 1 0100 | Don't care | Select analog input 4 |
| 1 0101 | Don't care | Select analog input 5 |
| 1 0110 | Don't care | Select analog input 6 |
| 1 0111 | Don't care | Select analog input 7 |
| 1 1000 to 1 1111 | Don't care | Error bit is set; select analog input 0 |
To set the device in on-the-fly mode, configure EN_ON_THE_FLY to 1b in the ON_THE_FLY_CFG register as shown in Figure 6-13 using a 3-byte register access. When in this mode, use the 16-bit data transfer to reduce the required clock speed for operating at full throughput.
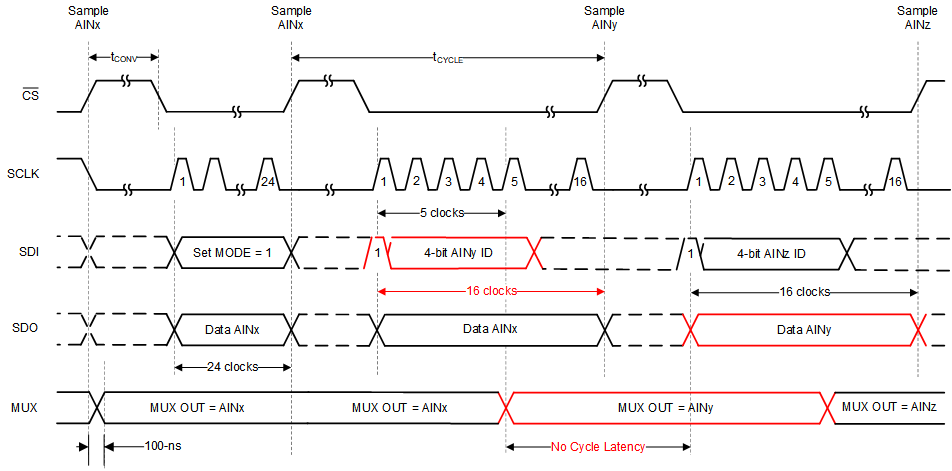 Figure 6-13 On-the-Fly Mode With No MUX
Channel Selection Latency
Figure 6-13 On-the-Fly Mode With No MUX
Channel Selection Latency