SBAS888B December 2020 – July 2022 ADC3664
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - Power Consumption
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - DC Specifications
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application Information Disclaimer
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.6.1 Detailed Register Description
Figure 8-45 Register 0x00
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | RESET |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-13 Register 0x00 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-1 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 0 | RESET | R/W | 0 | This bit resets all internal registers to the default values and self clears to 0. |
Figure 8-46 Register 0x07
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| OP IF MAPPER | 0 | OP IF EN | OP IF SEL | ||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-14 Register 0x07 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-5 | OP IF MAPPER | R/W | 000 | Output interface mapper. This register contains the proper output interface bit mapping for the different interfaces. The interface bit mapping is internally loaded from e-fuses and also requires a fuse load command to go into effect (0x13, D0). Register 0x07 along with the E-Fuse Load (0x13, D0) needs to be loaded first in the programming sequence since the E-Fuse load resets the SPI writes. After initial reset the default output interface variant is loaded automatically from fuse internally. However when reading back this register reads 000 until a value is written using SPI. 001: 2-wire, 18 and 14-bit 010: 2-wire, 16-bit 011: 1-wire 100: 0.5-wire others: not used |
| 4 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 3 | OP IF EN | R/W | 0 | Enables changing the default output interface mode (D2-D0). |
| 2-0 | OP IF SEL | R/W | 000 | Selection of the output interface mode. OP IF EN (D3) needs to be enabled also. After initial reset the default output interface is loaded automatically from fuse internally. However when reading back this register reads 000 until a value is written using SPI. 011: 2-wire 100: 1-wire 101: 0.5-wire others: not used |
Figure 8-47 Register 0x08
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | PDN CLKBUF | PDN REFAMP | 0 | PDN A | PDN B | PDN GLOBAL |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-15 Register 0x08 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 5 | PDN CLKBUF | R/W | 0 | Powers down sampling clock buffer 0: Clock buffer enabled 1: Clock buffer powered down |
| 4 | PDN REFAMP | R/W | 0 | Powers down internal reference gain amplifier 0: REFAMP enabled 1: REFAMP powered down |
| 3 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 2 | PDN A | R/W | 0 | Powers down ADC channel A 0: ADC channel A enabled 1: ADC channel A powered down |
| 1 | PDN B | R/W | 0 | Powers down ADC channel B 0: ADC channel B enabled 1: ADC channel B powered down |
| 0 | PDN GLOBAL | R/W | 0 | Global power down via SPI 0: Global power disabled 1: Global power down enabled. Power down mask (register 0x0D) determines which internal blocks are powered down. |
Figure 8-48 Register 0x09
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | PDN FCLKOUT | PDN DCLKOUT | PDN DA0 | PDN DA1 | PDN DB0 | PDN DB1 |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-16 Register 0x09 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 5 | PDN FCLKOUT | R/W | 0 | Powers down frame clock (FCLK) LVDS output buffer 0: FCLK output buffer enabled 1: FCLK output buffer powered down |
| 4 | PDN DCLKOUT | R/W | 0 | Powers down DCLK LVDS output buffer 0: DCLK output buffer enabled 1: DCLK output buffer powered down |
| 3 | PDN DA1 | R/W | 0 | Powers down LVDS output buffer for channel A, lane 1. NOT powered down automatically in 1-wire and 1/2-wire mode. 0: DA1 LVDS output buffer enabled 1: DA1 LVDS output buffer powered down |
| 2 | PDN DA0 | R/W | 0 | Powers down LVDS output buffer for channel A, lane 0. 0: DA0 LVDS output buffer enabled 1: DA0 LVDS output buffer powered down |
| 1 | PDN DB1 | R/W | 0 | Powers down LVDS output buffer for channel B, lane 1. NOT powered down automatically in 1-wire and 1/2-wire mode. 0: DB1 LVDS output buffer enabled 1: DB1 LVDS output buffer powered down |
| 0 | PDN DB0 | R/W | 0 | Powers down LVDS output buffer for channel B, lane 0. NOT powered down automatically in 1/2-wire mode. 0: DB0 LVDS output buffer enabled 1: DB0 LVDS output buffer powered down |
Figure 8-49 Register 0x0D (PDN GLOBAL MASK)
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | MASK CLKBUF | MASK REFAMP | MASK BG DIS | 0 |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-17 Register 0x0D Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-4 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 3 | MASK CLKBUF | R/W | 0 | Global power down mask control for sampling clock input buffer. 0: Clock buffer will get powered down when global power down is exercised. 1: Clock buffer will NOT get powered down when global power down is exercised. |
| 2 | MASK REFAMP | R/W | 0 | Global power down mask control for reference amplifier. 0: Reference amplifier will get powered down when global power down is exercised. 1: Reference amplifier will NOT get powered down when global power down is exercised. |
| 1 | MASK BG DIS | R/W | 0 | Global power down mask control for internal 1.2V bandgap voltage reference. Setting this bit reduces power consumption in global power down mode but increases the wake up time. See the power down option overview. 0: Internal 1.2V bandgap voltage reference will NOT get powered down when global power down is exercised. 1: Internal 1.2V bandgap voltage reference will get powered down when global power down is exercised. |
| 0 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
Figure 8-50 Register 0x0E
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| SYNC PIN EN | SPI SYNC | SPI SYNC EN | 0 | REF CTL | REF SEL | SE CLK EN | |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-18 Register 0x0E Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | SYNC PIN EN | R/W | 0 | This bit controls the functionality of the SYNC/PDN pin. 0: SYNC/PDN pin exercises global power down mode when pin is pulled high. 1: SYNC/PDN pin issues the SYNC command when pin is pulled high. |
| 6 | SPI SYNC | R/W | 0 | Toggling this bit issues the SYNC command using the SPI register write. SYNC using SPI must be enabled as well (D5). This bit doesn't self reset to 0. 0: Normal operation 1: SYNC command issued. |
| 5 | SPI SYNC EN | R/W | 0 | This bit enables synchronization using SPI instead of the SYNC/PDN pin. 0: Synchronization using SPI register bit disabled. 1: Synchronization using SPI register bit enabled. |
| 4 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 3 | REF CTL | R/W | 0 | This bit determines if the REFBUF pin controls the voltage reference selection or the SPI register (D2-D1). 0: The REFBUF pin selects the voltage reference option. 1: Voltage reference is selected using SPI (D2-D1) and single ended clock using D0. |
| 2-1 | REF SEL | R/W | 00 | Selects of the voltage reference option. REF CTRL (D3) must be set to 1. 00: Internal reference 01: External voltage reference (1.2V) using internal reference buffer (REFBUF) 10: External voltage reference 11: not used |
| 0 | SE CLK EN | R/W | 0 | Selects single ended clock input and powers down the differential sampling clock input buffer. REF CRTL (D3) must be set to 1. 0: Differential clock input 1: Single ended clock input |
Figure 8-51 Register 0x11
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | SE A | SE B | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-19 Register 0x11 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 5 | SE A | R/W | 0 | This bit enables single ended analog input, channel A. In this mode the SNR is reduced by 3-dB. 0: Differential input 1: Single ended input |
| 4 | SE B | R/W | 0 | This bit enables single ended analog input, channel B. In this mode the SNR is reduced by 3-dB. 0: Differential input 1: Single ended input |
| 3-0 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
Figure 8-52 Register 0x13
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | E-FUSE LD | |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-20 Register 0x13 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-1 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 0 | E-FUSE LD | R/W | 0 | This register bit loads the internal bit mapping for different interfaces. After setting the interface in register 0x07, this E-FUSE LD bit needs to be set to 1 and reset to 0 for loading to go into effect. Register 0x07 along with the E-Fuse Load (0x13, D0) needs to be loaded first in the programming sequence since the E-Fuse load resets the SPI writes. 0: E-FUSE LOAD set 1: E-FUSE LOAD reset |
Figure 8-53 Register 0x14/15/16
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| CUSTOM PAT [7:0] | |||||||
| CUSTOM PAT [15:8] | |||||||
| TEST PAT B | TEST PAT A | CUSTOM PAT [17:16] | |||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-21 Register 0x14/15/16 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | CUSTOM PAT [17:0] | R/W | 00000000 | This register is used for two purposes:
00001: Ramp pattern for 18-bit ADC 00100: Ramp pattern for 16-bit ADC 10000: Ramp pattern for 14-bit ADC |
| 7-5 | TEST PAT B | R/W | 000 | Enables test pattern output mode for channel B (NOTE: The test pattern is set prior to the bit mapper and is based on native resolution of the ADC starting from the MSB). These work in either output format. |
| 000: Normal output mode (test pattern output disabled) 010: Ramp pattern: need to set proper increment using CUSTOM PAT register 011: Constant Pattern using CUSTOM PAT [17:0] in register 0x14/15/16. others: not used | ||||
| 4-2 | TEST PAT A | R/W | 000 | Enables test pattern output mode for channel A (NOTE: The test pattern is set prior to the bit mapper and is based on native resolution of the ADC starting from the MSB). These work in either output format. |
| 000: Normal output mode (test pattern output disabled) 010: Ramp pattern: need to set proper increment using CUSTOM PAT register 011: Constant Pattern using CUSTOM PAT [17:0] in register 0x14/15/16. others: not used |
Figure 8-54 Register 0x19
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| FCLK SRC | 0 | 0 | FCLK DIV | 0 | 0 | 0 | TOG FCLK |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-22 Register 0x19 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | FCLK SRC | R/W | 0 | User has to select if FCLK signal comes from ADC or from DDC block. Here real decimation is treated same as bypass mode 0: FCLK generated from ADC. FCLK SRC set to 0 for DDC bypass, real decimation mode and 1/2-w complex decimation mode. 1: FCLK generated from DDC block. In complex decimation mode only this bit needs to be set for 2-w and 1-w output interface mode but NOT for 1/2-w mode. |
| 6-5 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 4 | FCLK DIV | R/W | 0 | This bit needs to be set to 1 for 2-w output mode in bypass mode only (non decimation). 0: All output interface modes except 2-w bypass mode.. 1: 2-w output interface mode. |
| 3-1 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 0 | TOG FCLK | R/W | 0 | This bit adjusts the FCLK signal appropriately for 1/2-wire mode where FCLK is stretched to cover channel A and channel B. This bit ONLY needs to be set in 1/2-wire mode with complex decimation mode. 0: all other modes. 1: FCLK for 1/2-wire complex decimation mode. |
Table 8-23 Configuration of FCLK SRC and FCLK DIV Register Bits vs Serial Interface
| BYPASS/DECIMATION | SERIAL INTERFACE | FCLK SRC | FCLK DIV | TOG FCLK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decimation Bypass/ Real Decimation | 2-wire | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1-wire | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1/2-wire | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Complex Decimation | 2-wire | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1-wire | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1/2-wire | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Figure 8-55 Register 0x1A
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | LVDS ½ SWING | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-24 Register 0x1A Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 | |
| 6 | LVDS ½ SWING | R/W | 0 | This bit reduces the LVDS output current from 3.5mA to 1.75mA which reduces power consumption. | |
| 5-0 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 | |
Figure 8-56 Register 0x1B
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| MAPPER EN | 20B EN | BIT MAPPER RES | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-25 Register 0x1B Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | MAPPER EN | R/W | 0 | This bit enables changing the resolution of the output (including output serialization factor) in bypass mode only. This bit is not needed for 20-bit resolution output. 0: Output bit mapper disabled. 1: Output bit mapper enabled. |
| 6 | 20B EN | R/W | 0 | This bit enables 20-bit output resolution which can be useful for very high decimation settings so that quantization noise doesn't impact the ADC performance. 0: 20-bit output resolution disabled. 1: 20-bit output resolution enabled. |
| 5-3 | BIT MAPPER RES | R/W | 000 | Sets the output resolution using the bit mapper. MAPPER EN bit (D6) needs to be enabled when operating in bypass mode.. 000: 18 bit 001: 16 bit 010: 14 bit all others, n/a |
| 2-0 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
Table 8-26 Register Settings for Output Bit Mapper vs Operating Mode
| BYPASS/DECIMATION | OUTPUT RESOLUTION | MAPPER EN (D7) | BIT MAPPER RES (D5-D3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decimation Bypass | Resolution Change | 1 | 000: 18-bit 001: 16-bit 010: 14-bit |
| Real Decimation | Resolution Change (default 18-bit) | 0 | |
| Complex Decimation | 0 |
Figure 8-57 Register 0x1E
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | LVDS DATA DEL | LVDS DCLK DEL | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-27 Register 0x1E Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-4 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 3-2 | LVDS DATA DEL | R/W | 00 | These bits adjust the output timing of the SLVDS output data. 00: no delay 01: Data advanced by 50 ps 10: Data delayed by 50 ps 11: Data delayed by 100 ps |
| 1-0 | LVDS DCLK DEL | R/W | 00 | These bits adjust the output timing of the SLVDS DCLK output. 00: no delay 01: DCLK advanced by 50 ps 10: DCLK delayed by 50 ps 11: DCLK delayed by 100 ps |
Figure 8-58 Register 0x20/21/22
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| FCLK PAT [7:0] | |||||||
| FCLK PAT [15:8] | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FCLK PAT [19:16] | |||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-28 Register 0x20/21/22 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | FCLK PAT [19:0] | R/W | 0xFFC00 | These bits can adjust the duty cycle of the FCLK. In decimation bypass mode the FCLK pattern gets adjusted automatically for the different output resolutions. Table 8-29 shows the proper FCLK pattern values for 1-wire and 1/2-wire in real/complex decimation. |
Table 8-29 FCLK Pattern for different resolution based on interface
| DECIMATION | OUTPUT RESOLUTION | 2-WIRE | 1-WIRE | 1/2-WIRE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REAL DECIMATION | 14-bit | Use Default | 0xFE000 | Use Default |
| 16-bit | 0xFF000 | |||
| 18-bit | 0xFF800 | |||
| 20-bit | 0xFFC00 | |||
| COMPLEX DECIMATION | 14-bit | 0xFFFFF | 0xFFFFF | |
| 16-bit | ||||
| 18-bit | ||||
| 20-bit |
Figure 8-59 Register 0x24
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | CH AVG EN | DDC MUX | DIG BYP | DDC EN | 0 | |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-30 Register 0x24 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 5 | CH AVG EN | R/W | 0 | Averages the output of ADC channel A and channel B together. The DDC MUX has to be enabled and set to '11'. The decimation filter needs to be enabled and set to bypass (fullrate output) or decimation and DIG BYP set to 1. 0: Channel averaging feature disabled 1: Output of channel A and channel B are averaged: (A+B)/2. |
| 4-3 | DDC MUX | R/W | 0 | Configures DDC MUX in front of the decimation filter. 00: ADC channel A connected to DDC A; ADC Channel B connected to DDC B 01: ADC channel A connected to DDC A and DDC B. 10: ADC channel B connected to DDC A and DDC B. 11: Output of ADC averaging block (see CH AVG EN) given to DDC A and DDC B. |
| 2 | DIG BYP | R/W | 0 | This bit needs to be set to enable digital features block which includes decimation. 0: Digital feature block bypassed - lowest latency 1: Data path includes digital features |
| 1 | DDC EN | R/W | 0 | Enables internal decimation filter for both channels 0: DDC disabled. 1: DDC enabled. |
| 0 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
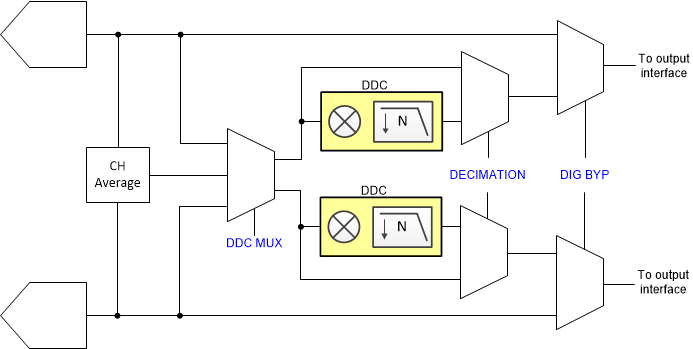 Figure 8-60 Register control for digital features
Figure 8-60 Register control for digital featuresFigure 8-61 Register 0x25
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| DDC MUX EN | DECIMATION | REAL OUT | 0 | 0 | MIX PHASE | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-31 Register 0x25 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | DDC MUX EN | R/W | 0 | Enables the digital mux between ADCs and decimation filters. This bit is required for DDC mux settings in register 0x24 (D4, D3) to go into effect. 0: DDC mux disabled 1: DDC mux enabled |
| 6-4 | DECIMATION | R/W | 000 | Complex decimation setting. This applies to both channels. 000: Bypass mode (no decimation) 001: Decimation by 2 010: Decimation by 4 011: Decimation by 8 100: Decimation by 16 101: Decimation by 32 others: not used |
| 3 | REAL OUT | R/W | 0 | This bit selects real output decimation. This mode applies to both channels. In this mode, the decimation filter is a low pass filter and no complex mixing is performed to reduce power consumption. For maximum power savings the NCO in this case should be set to 0. 0: Complex decimation 1: Real decimation |
| 2-1 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 0 | MIX PHASE | R/W | 0 | This bit used to invert the NCO phase 0: NCO phase as is. 1: NCO phase inverted. |
Figure 8-62 Register 0x26
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| MIX GAIN A | MIX RES A | FS/4 MIX A | MIX GAIN B | MIX RES B | FS/4 MIX B | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-32 Register 0x26 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-6 | MIX GAIN A | R/W | 00 | This bit applies a 0, 3 or 6-dB digital gain to the output of digital mixer to compensate for the mixing loss for channel A. 00: no digital gain added 01: 3-dB digital gain added 10: 6-dB digital gain added 11: not used |
| 5 | MIX RES A | R/W | 0 | Toggling this bit resets the NCO phase of channel A and loads the new NCO frequency. This bit does not self reset. |
| 4 | FS/4 MIX A | R/W | 0 | Enables FS/4 mixing for DDC A (complex decimation only). 0: FS/4 mixing disabled. 1: FS/4 mixing enabled. |
| 3-2 | MIX GAIN B | R/W | 00 | This bit applies a 0, 3 or 6-dB digital gain to the output of digital mixer to compensate for the mixing loss for channel B. 00: no digital gain added 01: 3-dB digital gain added 10: 6-dB digital gain added 11: not used |
| 1 | MIX RES B | R/W | 0 | Toggling this bit resets the NCO phase of channel B and loads the new NCO frequency. This bit does not self reset. |
| 0 | FS/4 MIX B | R/W | 0 | Enables FS/4 mixing for DDC B (complex decimation only). 0: FS/4 mixing disabled. 1: FS/4 mixing enabled. |
Figure 8-63 Register 0x27
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | OP ORDER A | Q-DEL A | FS/4 MIX PH A | 0 | 0 |
| DDC OFFSET A [9:2] | |||||||
| 0 | DDC OFFSET A [16:10] | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-33 Register 0x27 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-5 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 4 | OP ORDER A | R/W | 0 | Swaps the I and Q output order for channel A 0: Output order is I[n], Q[n] 1: Output order is swapped: Q[n], I[n] |
| 3 | Q-DEL A | R/W | 0 | This delays the Q-sample output of channel A by one. 0: Output order is I[n], Q[n] 1: Q-sample is delayed by 1 sample: I[n], Q[n+1], I[n+1], Q[n+2] |
| 2 | FS/4 MIX PH A | R/W | 0 | Inverts the mixer phase for channel A when using FS/4 mixer 0: Mixer phase is non-inverted 1: Mixer phase is inverted |
| 1-0 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
Figure 8-64 Register 0x2A/B/C/D
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| NCO A [7:0] | |||||||
| NCO A [15:8] | |||||||
| NCO A [23:16] | |||||||
| NCO A [31:24] | |||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-34 Register 0x2A/2B/2C/2D Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | NCO A [31:0] | R/W | 0 | Sets the 32 bit NCO value for decimation filter channel A. The NCO value is fNCO× 232/FS In real decimation mode these registers are automatically set to 0. |
Figure 8-65 Register 0x2E
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | OP ORDER B | Q-DEL B | FS/4 MIX PH B | 0 | 0 |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-35 Register 0x2E Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-5 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 4 | OP ORDER B | R/W | 0 | Swaps the I and Q output order for channel B 0: Output order is I[n], Q[n] 1: Output order is swapped: Q[n], I[n] |
| 3 | Q-DEL B | R/W | 0 | This delays the Q-sample output of channel B by one. 0: Output order is I[n], Q[n] 1: Q-sample is delayed by 1 sample: I[n], Q[n+1], I[n+1], Q[n+2] |
| 2 | FS/4 MIX PH B | R/W | 0 | Inverts the mixer phase for channel B when using FS/4 mixer 0: Mixer phase is non-inverted 1: Mixer phase is inverted |
| 1-0 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
Figure 8-66 Register 0x31/32/33/34
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| NCO B [7:0] | |||||||
| NCO B [15:8] | |||||||
| NCO B [23:16] | |||||||
| NCO B [31:24] | |||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-36 Register 0x31/32/33/34 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | NCO B [31:0] | R/W | 0 | Sets the 32 bit NCO value for decimation filter channel B. The NCO value is fNCO× 232/FS In real decimation mode these registers are automatically set to 0. |
Figure 8-67 Register 0x39..0x60
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| OUTPUT BIT MAPPER CHA | |||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-37 Register 0x39..0x60 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | OUTPUT BIT MAPPER CHA | R/W | 0 | These registers are used to reorder the output data bus. See the Section 8.3.5.2 on how to program it. |
Figure 8-68 Register 0x61..0x88
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| OUTPUT BIT MAPPER CHB | |||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-38 Register 0x61..0x88 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-0 | OUTPUT BIT MAPPER CHB | R/W | 0 | These registers are used to reorder the output data bus of channel B. See the Section 8.3.5.2 on how to program it. |
Figure 8-69 Register 0x8F
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FORMAT A | 0 |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-39 Register 0x8F Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 1 | FORMAT A | R/W | 0 | This bit sets the output data format for channel A. Digital bypass register bit (0x24, D2) needs to be enabled as well. 0: 2s complement 1: Offset binary |
| 0 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
Figure 8-70 Register 0x92
| 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FORMAT B | 0 |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
Table 8-40 Register 0x92 Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-2 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |
| 1 | FORMAT B | R/W | 0 | This bit sets the output data format for channel B. Digital bypass register bit (0x24, D2) needs to be enabled as well. 0: 2s complement 1: Offset binary |
| 0 | 0 | R/W | 0 | Must write 0 |