SBAS917B August 2019 – May 2021 AMC3301
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Ratings
- 6.6 Insulation Specifications
- 6.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 6.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Timing Diagram
- 6.12 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 6.13 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.3 Analog Output
The AMC3301 offers a differential analog output comprised of the OUTP and OUTN pins. For differential input voltages (VINP – VINN) in the range from –250 mV to +250 mV, the device provides a linear response with a nominal gain of 8.2. For example, for a differential input voltage of 250 mV, the differential output voltage (VOUTP – VOUTN) is 2.05 V. At zero input (INP shorted to INN), both pins output the same common-mode output voltage VCMout, as specified in the Section 6.9 table. For absolute differential input voltages greater than 250 mV but less than 320 mV, the differential output voltage continues to increase in magnitude but with reduced linearity performance. The outputs saturate at a differential output voltage of VCLIPout as shown in Figure 7-2 if the differential input voltage exceeds the VClipping value.
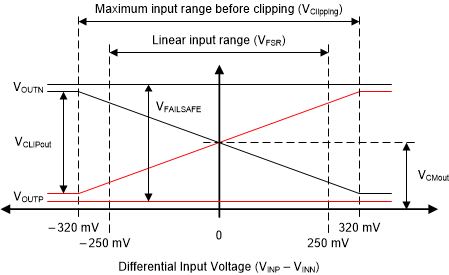 Figure 7-2 Output Behavior of the AMC3301
Figure 7-2 Output Behavior of the AMC3301
The AMC3301 provides a fail-safe output that simplifies diagnostics on system level. Figure 7-2 shows the fail-safe mode, in which the AMC3301 outputs a negative differential output voltage that does not occur under normal operating conditions. The fail-safe output is active in two cases:
- The low-side does not receive data from the high-side (for example, because of a loss of power on the high side).
- The high-side DC/DC output voltage (DCDC_OUT) or the high-side LDO output voltage (HLDO_OUT) drop below their respective undervoltage detection thresholds (brown-out).
Use the maximum VFAILSAFE voltage specified in the Section 6.9 table as a reference value for the fail-safe detection on the system level.