SBAS989 April 2019 PCM1840
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Hardware Control
- 7.3.2 Audio Serial Interfaces
- 7.3.3 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) and Clock Generation
- 7.3.4 Input Channel Configurations
- 7.3.5 Reference Voltage
- 7.3.6 Microphone Bias
- 7.3.7
Signal-Chain Processing
- 7.3.7.1 Digital High-Pass Filter
- 7.3.7.2
Configurable Digital Decimation Filters
- 7.3.7.2.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 7.3.7.2.1.1 Sampling Rate: 8 kHz or 7.35 kHz
- 7.3.7.2.1.2 Sampling Rate: 16 kHz or 14.7 kHz
- 7.3.7.2.1.3 Sampling Rate: 24 kHz or 22.05 kHz
- 7.3.7.2.1.4 Sampling Rate: 32 kHz or 29.4 kHz
- 7.3.7.2.1.5 Sampling Rate: 48 kHz or 44.1 kHz
- 7.3.7.2.1.6 Sampling Rate: 96 kHz or 88.2 kHz
- 7.3.7.2.1.7 Sampling Rate: 192 kHz or 176.4 kHz
- 7.3.7.2.2 Low-Latency Filters
- 7.3.7.2.1
Linear Phase Filters
- 7.3.8 Dynamic Range Enhancer (DRE)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.2.1 Time Division Multiplexed Audio (TDM) Interface
In TDM mode, also known as DSP mode, the rising edge of FSYNC starts the data transfer with the slot 0 data first. Immediately after the slot 0 data transmission, the remaining slot data are transmitted in order. FSYNC and each data bit (except the MSB of slot 0 when TX_OFFSET equals 0) is transmitted on the rising edge of BCLK. Figure 14 to Figure 17 illustrate the protocol timing for TDM operation with various configurations.
 Figure 14. TDM Mode Protocol Timing (FMT0 = LOW) In Slave Mode
Figure 14. TDM Mode Protocol Timing (FMT0 = LOW) In Slave Mode 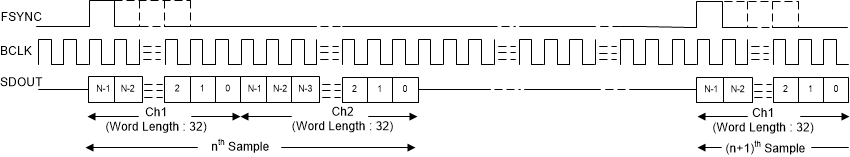 Figure 15. TDM Mode Protocol Timing (FMT0 = HIGH) In Slave Mode
Figure 15. TDM Mode Protocol Timing (FMT0 = HIGH) In Slave Mode  Figure 16. TDM Mode Protocol Timing (FMT0 = LOW) In Master Mode
Figure 16. TDM Mode Protocol Timing (FMT0 = LOW) In Master Mode 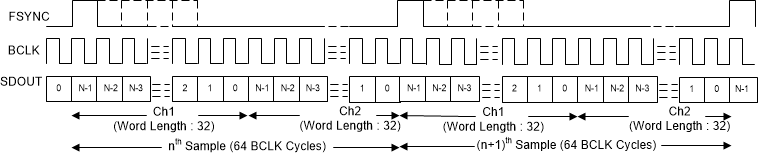 Figure 17. TDM Mode Protocol Timing (FMT0 = HIGH) In Master Mode
Figure 17. TDM Mode Protocol Timing (FMT0 = HIGH) In Master Mode For proper operation of the audio bus in TDM mode, the number of bit clocks per frame must be greater than or equal to the number of active output channels times the 32-bits word length of the output channel data. The device transmits a zero data value on SDOUT for the extra unused bit clock cycles. The device supports FSYNC as a pulse with a 1-cycle-wide bit clock, but also supports multiples as well.